Exploring the Use of Electromagnetic Waves in Cybersecurity
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
EM Waves in Cybersecurity: Background and Objectives
Electromagnetic waves have been a cornerstone of modern communication and technology for over a century. In recent years, their potential applications in cybersecurity have garnered significant attention from researchers and industry professionals alike. This exploration into the use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity represents a convergence of physics, information technology, and security principles, offering novel approaches to protect digital assets and communications.
The field of cybersecurity has traditionally relied on software-based solutions and cryptographic techniques to safeguard information. However, as cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, there is a growing need for innovative security measures that can provide additional layers of protection. Electromagnetic waves, with their unique properties and behavior, present an intriguing avenue for enhancing cybersecurity measures.
The primary objective of this technological exploration is to investigate how electromagnetic waves can be harnessed to improve various aspects of cybersecurity. This includes developing new methods for secure communication, enhancing data encryption, detecting and preventing unauthorized access, and creating more robust authentication systems. By leveraging the physical properties of electromagnetic waves, researchers aim to create security solutions that are inherently more difficult to compromise than traditional software-based approaches.
One of the key areas of focus is the use of electromagnetic waves for secure communication channels. By manipulating the properties of these waves, such as frequency, amplitude, and phase, it may be possible to create communication systems that are highly resistant to interception and eavesdropping. This could lead to the development of next-generation secure communication protocols for both civilian and military applications.
Another promising direction is the exploration of electromagnetic fingerprinting for device authentication. Every electronic device emits a unique electromagnetic signature, which could potentially be used as a form of hardware-level identification. This approach could significantly enhance the security of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
The use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity also extends to the realm of side-channel attacks and their prevention. By studying the electromagnetic emissions from computing devices, researchers can develop better methods to protect against these subtle but potentially devastating security vulnerabilities. This includes techniques for shielding sensitive equipment and designing hardware that minimizes unintended electromagnetic leakage.
As this field of study progresses, it is expected to yield new insights into the fundamental relationships between electromagnetic phenomena and information security. This could potentially lead to the development of entirely new paradigms in cybersecurity, moving beyond the limitations of current software-centric approaches. The ultimate goal is to create a more resilient and secure digital ecosystem that can withstand the evolving threats of the modern cyber landscape.
The field of cybersecurity has traditionally relied on software-based solutions and cryptographic techniques to safeguard information. However, as cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, there is a growing need for innovative security measures that can provide additional layers of protection. Electromagnetic waves, with their unique properties and behavior, present an intriguing avenue for enhancing cybersecurity measures.
The primary objective of this technological exploration is to investigate how electromagnetic waves can be harnessed to improve various aspects of cybersecurity. This includes developing new methods for secure communication, enhancing data encryption, detecting and preventing unauthorized access, and creating more robust authentication systems. By leveraging the physical properties of electromagnetic waves, researchers aim to create security solutions that are inherently more difficult to compromise than traditional software-based approaches.
One of the key areas of focus is the use of electromagnetic waves for secure communication channels. By manipulating the properties of these waves, such as frequency, amplitude, and phase, it may be possible to create communication systems that are highly resistant to interception and eavesdropping. This could lead to the development of next-generation secure communication protocols for both civilian and military applications.
Another promising direction is the exploration of electromagnetic fingerprinting for device authentication. Every electronic device emits a unique electromagnetic signature, which could potentially be used as a form of hardware-level identification. This approach could significantly enhance the security of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
The use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity also extends to the realm of side-channel attacks and their prevention. By studying the electromagnetic emissions from computing devices, researchers can develop better methods to protect against these subtle but potentially devastating security vulnerabilities. This includes techniques for shielding sensitive equipment and designing hardware that minimizes unintended electromagnetic leakage.
As this field of study progresses, it is expected to yield new insights into the fundamental relationships between electromagnetic phenomena and information security. This could potentially lead to the development of entirely new paradigms in cybersecurity, moving beyond the limitations of current software-centric approaches. The ultimate goal is to create a more resilient and secure digital ecosystem that can withstand the evolving threats of the modern cyber landscape.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity solutions has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing complexity and frequency of cyber threats. As traditional security measures become less effective against sophisticated attacks, organizations are seeking innovative approaches to protect their digital assets and infrastructure.
The global cybersecurity market is experiencing robust growth, with a particular focus on advanced technologies like electromagnetic wave-based solutions. This segment is expected to see significant expansion due to its potential to address emerging security challenges. The increasing adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, 5G networks, and cloud computing has created new vulnerabilities that conventional cybersecurity measures struggle to address effectively.
Electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity offers unique advantages in detecting and preventing unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. These solutions can provide real-time monitoring of electromagnetic emissions from electronic devices, enabling the identification of potential security risks before they escalate. This proactive approach aligns with the growing demand for preventive security measures in various industries.
The financial sector, in particular, has shown strong interest in electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity. Banks and financial institutions are increasingly concerned about the security of their digital transactions and sensitive customer data. The ability of electromagnetic wave solutions to detect and prevent sophisticated attacks, such as side-channel attacks on cryptographic systems, makes them highly attractive to this sector.
Government and defense organizations are also significant drivers of market demand for electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity. These entities require advanced security measures to protect critical infrastructure and sensitive information from state-sponsored cyber attacks and espionage attempts. The non-invasive nature of electromagnetic wave detection makes it an appealing option for securing high-security facilities and communication systems.
The healthcare industry is another sector showing growing interest in this technology. With the increasing digitization of medical records and the use of connected medical devices, healthcare providers are seeking robust security solutions to protect patient data and ensure the integrity of medical equipment. Electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity offers the potential to safeguard sensitive medical information and prevent tampering with life-critical devices.
As organizations across various sectors become more aware of the potential benefits of electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity, the market is expected to see continued growth. However, challenges such as the need for specialized expertise and potential regulatory hurdles may impact adoption rates. Despite these challenges, the unique capabilities of electromagnetic wave-based solutions in addressing evolving cyber threats position them as a promising and in-demand technology in the cybersecurity landscape.
The global cybersecurity market is experiencing robust growth, with a particular focus on advanced technologies like electromagnetic wave-based solutions. This segment is expected to see significant expansion due to its potential to address emerging security challenges. The increasing adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, 5G networks, and cloud computing has created new vulnerabilities that conventional cybersecurity measures struggle to address effectively.
Electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity offers unique advantages in detecting and preventing unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. These solutions can provide real-time monitoring of electromagnetic emissions from electronic devices, enabling the identification of potential security risks before they escalate. This proactive approach aligns with the growing demand for preventive security measures in various industries.
The financial sector, in particular, has shown strong interest in electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity. Banks and financial institutions are increasingly concerned about the security of their digital transactions and sensitive customer data. The ability of electromagnetic wave solutions to detect and prevent sophisticated attacks, such as side-channel attacks on cryptographic systems, makes them highly attractive to this sector.
Government and defense organizations are also significant drivers of market demand for electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity. These entities require advanced security measures to protect critical infrastructure and sensitive information from state-sponsored cyber attacks and espionage attempts. The non-invasive nature of electromagnetic wave detection makes it an appealing option for securing high-security facilities and communication systems.
The healthcare industry is another sector showing growing interest in this technology. With the increasing digitization of medical records and the use of connected medical devices, healthcare providers are seeking robust security solutions to protect patient data and ensure the integrity of medical equipment. Electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity offers the potential to safeguard sensitive medical information and prevent tampering with life-critical devices.
As organizations across various sectors become more aware of the potential benefits of electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity, the market is expected to see continued growth. However, challenges such as the need for specialized expertise and potential regulatory hurdles may impact adoption rates. Despite these challenges, the unique capabilities of electromagnetic wave-based solutions in addressing evolving cyber threats position them as a promising and in-demand technology in the cybersecurity landscape.
Current Challenges
The use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity presents several significant challenges that researchers and practitioners must address. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent vulnerability of wireless communication systems to interception and interference. As electromagnetic waves propagate through space, they can be easily intercepted by unauthorized parties, potentially compromising sensitive information.
Another major challenge lies in the development of robust encryption methods that can effectively secure data transmitted via electromagnetic waves. While traditional encryption techniques have been adapted for wireless communications, the increasing computational power of adversaries necessitates continuous innovation in this area.
The issue of signal jamming and interference poses a substantial threat to the reliability and security of electromagnetic wave-based systems. Malicious actors can disrupt communications by flooding the frequency spectrum with noise or targeted interference, potentially rendering critical systems inoperable.
Furthermore, the growing prevalence of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. Many IoT devices rely on electromagnetic waves for communication but often lack robust security measures, making them vulnerable entry points for network breaches.
The detection and prevention of electromagnetic side-channel attacks represent another significant challenge. These attacks exploit unintentional electromagnetic emissions from electronic devices to extract sensitive information, such as encryption keys or confidential data.
Ensuring the integrity and authenticity of data transmitted via electromagnetic waves remains a persistent challenge. Man-in-the-middle attacks and spoofing techniques can compromise the trustworthiness of wireless communications, necessitating advanced authentication mechanisms.
The rapid evolution of quantum computing technology poses a looming threat to current encryption methods used in electromagnetic wave-based communications. Quantum computers have the potential to break many of the cryptographic algorithms currently in use, requiring the development of quantum-resistant encryption techniques.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding electromagnetic spectrum usage presents challenges for cybersecurity implementations. Balancing the need for secure communications with compliance to international and national regulations on spectrum allocation and usage requires careful consideration and adaptation of security protocols.
Another major challenge lies in the development of robust encryption methods that can effectively secure data transmitted via electromagnetic waves. While traditional encryption techniques have been adapted for wireless communications, the increasing computational power of adversaries necessitates continuous innovation in this area.
The issue of signal jamming and interference poses a substantial threat to the reliability and security of electromagnetic wave-based systems. Malicious actors can disrupt communications by flooding the frequency spectrum with noise or targeted interference, potentially rendering critical systems inoperable.
Furthermore, the growing prevalence of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. Many IoT devices rely on electromagnetic waves for communication but often lack robust security measures, making them vulnerable entry points for network breaches.
The detection and prevention of electromagnetic side-channel attacks represent another significant challenge. These attacks exploit unintentional electromagnetic emissions from electronic devices to extract sensitive information, such as encryption keys or confidential data.
Ensuring the integrity and authenticity of data transmitted via electromagnetic waves remains a persistent challenge. Man-in-the-middle attacks and spoofing techniques can compromise the trustworthiness of wireless communications, necessitating advanced authentication mechanisms.
The rapid evolution of quantum computing technology poses a looming threat to current encryption methods used in electromagnetic wave-based communications. Quantum computers have the potential to break many of the cryptographic algorithms currently in use, requiring the development of quantum-resistant encryption techniques.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding electromagnetic spectrum usage presents challenges for cybersecurity implementations. Balancing the need for secure communications with compliance to international and national regulations on spectrum allocation and usage requires careful consideration and adaptation of security protocols.
Existing EM Wave Solutions
01 Electromagnetic wave detection and measurement
Various devices and methods for detecting and measuring electromagnetic waves are described. These include sensors, antennas, and other specialized equipment designed to capture and analyze electromagnetic signals across different frequencies and intensities.- Electromagnetic wave detection and measurement: Various devices and methods for detecting and measuring electromagnetic waves are described. These include sensors, antennas, and specialized equipment designed to capture and analyze electromagnetic signals across different frequencies and intensities.
- Electromagnetic wave shielding and protection: Technologies for shielding and protecting against electromagnetic waves are presented. These include materials and structures designed to block or absorb electromagnetic radiation, protecting sensitive equipment or living organisms from potential harmful effects.
- Electromagnetic wave communication systems: Advancements in communication systems utilizing electromagnetic waves are discussed. These include improvements in wireless communication technologies, signal processing techniques, and novel methods for transmitting and receiving electromagnetic signals.
- Electromagnetic wave energy harvesting: Innovations in harvesting energy from electromagnetic waves are explored. These include devices and methods for capturing and converting ambient electromagnetic radiation into usable electrical energy, potentially providing power for various applications.
- Electromagnetic wave applications in medical field: The use of electromagnetic waves in medical applications is presented. This includes diagnostic tools, therapeutic devices, and imaging technologies that utilize electromagnetic radiation for various medical purposes, such as disease detection and treatment.
02 Electromagnetic wave shielding and protection
Technologies for shielding and protecting against electromagnetic waves are presented. These involve materials and structures designed to block, absorb, or redirect electromagnetic radiation, often used in electronic devices, buildings, or protective gear.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electromagnetic wave communication systems
Advancements in communication systems utilizing electromagnetic waves are discussed. These include improvements in wireless transmission, reception, and processing of electromagnetic signals for various applications such as mobile networks, satellite communications, and IoT devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electromagnetic wave energy harvesting
Innovations in harnessing energy from electromagnetic waves are explored. These technologies aim to capture and convert ambient electromagnetic radiation into usable electrical energy, potentially providing power for low-energy devices or supplementing existing power sources.Expand Specific Solutions05 Electromagnetic wave applications in medical field
The use of electromagnetic waves in medical applications is examined. This includes diagnostic imaging techniques, therapeutic treatments, and monitoring devices that utilize various forms of electromagnetic radiation to improve healthcare outcomes and patient care.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The exploration of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity is in its early stages, with the market showing significant growth potential. The technology's maturity varies across applications, with some areas more developed than others. Key players like Sony Group Corp., NEC Corp., and Siemens Corp. are investing in research and development to leverage electromagnetic waves for enhanced security measures. The Boeing Co. and BAE Systems are also exploring applications in defense-related cybersecurity. Universities such as MIT and the University of Tokyo are contributing to fundamental research, while companies like Bastille Networks are developing specialized solutions. As the field evolves, collaboration between academia and industry is likely to accelerate innovation and market expansion.
Siemens Corp.
Technical Solution: Siemens has developed advanced electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) solutions for cybersecurity in industrial control systems and critical infrastructure. Their approach involves using electromagnetic shielding and filtering techniques to protect sensitive electronic equipment from both intentional electromagnetic interference (IEMI) and unintentional electromagnetic disturbances[4]. Siemens' technology includes specialized EMC cabinets and enclosures that can block high-intensity electromagnetic pulses, protecting vital systems from potential cyber-attacks that exploit electromagnetic vulnerabilities[5]. Additionally, they have implemented electromagnetic sensors and monitoring systems in their industrial control products to detect and mitigate electromagnetic-based cyber threats in real-time[6].
Strengths: Comprehensive protection against electromagnetic-based attacks, integration with existing industrial control systems. Weaknesses: May be costly to implement across large-scale infrastructure, requires ongoing maintenance and updates to keep pace with evolving threats.
Nokia Technologies Oy
Technical Solution: Nokia has been exploring the use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity through their research into 5G and beyond technologies. They have developed a concept called "Physical Layer Security" that leverages the properties of electromagnetic waves to enhance the security of wireless communications[7]. This approach uses the unique characteristics of the wireless channel, such as multipath fading and spatial diversity, to create secure communication links that are inherently resistant to eavesdropping and interception[8]. Nokia's technology includes advanced beamforming techniques that can focus electromagnetic energy towards intended receivers while minimizing signal leakage to potential attackers[9]. They are also investigating quantum key distribution over free-space optical links, which uses the quantum properties of photons to create unbreakable encryption keys[10].
Strengths: Cutting-edge approach to wireless security, potential for integration with existing and future cellular networks. Weaknesses: Still in research phase for some technologies, may require significant changes to existing infrastructure for full implementation.
Core EM Wave Innovations
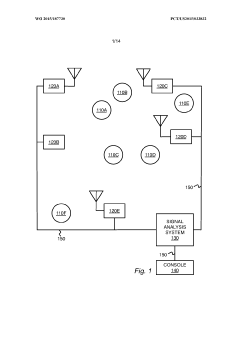
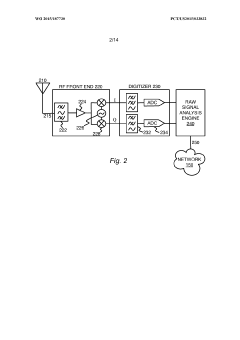
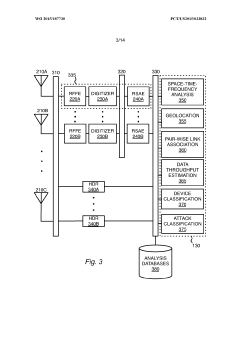
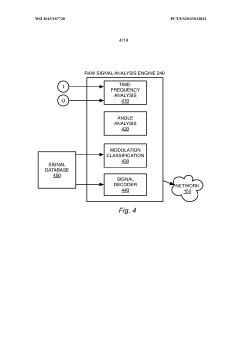
Electromagnetic threat detection and mitigation in the internet of things
PatentWO2015187730A1
Innovation
- A system and method for detecting and mitigating electromagnetic threats using a network of sensors that collect and process radio frequency signals to identify, geolocate, and classify wireless attacks, employing software-defined radio receivers and signal analysis engines to monitor and visualize electromagnetic signatures for security threat detection and mitigation.
Information processing system
PatentWO2009148119A1
Innovation
- The implementation of an information processing system that encrypts image information using pseudo-random numbers, specifically through addition/subtraction encryption methods, to ensure that intercepted electromagnetic waves do not reveal the original display image, thereby preventing information leakage without relying on shielding or jamming techniques.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding the use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity is complex and multifaceted, involving various national and international bodies. At the forefront, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) plays a crucial role in setting global standards for electromagnetic spectrum allocation and usage. Their recommendations often form the basis for national policies, ensuring a degree of international harmonization in the field.
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is the primary regulatory authority for electromagnetic spectrum usage. The FCC's regulations cover a wide range of applications, including those related to cybersecurity. They establish guidelines for power levels, frequency bands, and interference mitigation, which directly impact the development and deployment of electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity solutions.
The European Union, through its European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), has developed a comprehensive set of standards and regulations. These include specific provisions for electromagnetic compatibility and radio spectrum matters, which are critical considerations in cybersecurity applications utilizing electromagnetic waves.
Many countries have their own regulatory bodies that oversee the use of electromagnetic spectrum, often working in conjunction with international standards. For instance, in the UK, Ofcom regulates the electromagnetic spectrum and sets policies that affect cybersecurity applications.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses specific cybersecurity standards that intersect with electromagnetic wave technologies. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the US provides guidelines for securing wireless communications, which include considerations for electromagnetic wave-based security measures.
As the field of electromagnetic wave applications in cybersecurity evolves, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address new challenges. This includes regulations around emerging technologies such as quantum key distribution systems that utilize electromagnetic waves for secure communication.
Privacy concerns are increasingly shaping the regulatory environment. Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU have implications for how electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity solutions can be implemented, particularly in terms of data collection and processing.
The military and defense sectors have their own set of regulations governing the use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity. These often involve stricter controls and classified standards that are not publicly available but significantly influence the development of advanced cybersecurity technologies.
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is the primary regulatory authority for electromagnetic spectrum usage. The FCC's regulations cover a wide range of applications, including those related to cybersecurity. They establish guidelines for power levels, frequency bands, and interference mitigation, which directly impact the development and deployment of electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity solutions.
The European Union, through its European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), has developed a comprehensive set of standards and regulations. These include specific provisions for electromagnetic compatibility and radio spectrum matters, which are critical considerations in cybersecurity applications utilizing electromagnetic waves.
Many countries have their own regulatory bodies that oversee the use of electromagnetic spectrum, often working in conjunction with international standards. For instance, in the UK, Ofcom regulates the electromagnetic spectrum and sets policies that affect cybersecurity applications.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses specific cybersecurity standards that intersect with electromagnetic wave technologies. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the US provides guidelines for securing wireless communications, which include considerations for electromagnetic wave-based security measures.
As the field of electromagnetic wave applications in cybersecurity evolves, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address new challenges. This includes regulations around emerging technologies such as quantum key distribution systems that utilize electromagnetic waves for secure communication.
Privacy concerns are increasingly shaping the regulatory environment. Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU have implications for how electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity solutions can be implemented, particularly in terms of data collection and processing.
The military and defense sectors have their own set of regulations governing the use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity. These often involve stricter controls and classified standards that are not publicly available but significantly influence the development of advanced cybersecurity technologies.
Ethical Implications
The use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity raises significant ethical concerns that must be carefully considered. As this technology advances, it becomes crucial to address the potential impacts on privacy, human rights, and societal norms. One primary ethical issue is the potential for unauthorized surveillance and data interception. Electromagnetic waves can penetrate walls and other physical barriers, potentially enabling the collection of sensitive information without the knowledge or consent of individuals. This capability raises questions about the right to privacy and the boundaries of acceptable security measures.
Another ethical consideration is the potential for electromagnetic waves to be used as a weapon or for malicious purposes. While the technology may enhance cybersecurity defenses, it could also be exploited by bad actors to disrupt critical infrastructure, interfere with communication systems, or cause harm to individuals. The dual-use nature of this technology necessitates careful regulation and oversight to prevent misuse and ensure responsible development and deployment.
The use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity also raises concerns about fairness and equality. Advanced electromagnetic detection and protection systems may be costly, potentially creating a digital divide where only well-resourced organizations and individuals can afford adequate cybersecurity measures. This disparity could exacerbate existing inequalities and leave vulnerable populations more susceptible to cyber threats.
Furthermore, the widespread adoption of electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity measures could lead to an escalation in the technological arms race between security professionals and malicious actors. This constant evolution of attack and defense mechanisms may result in increased societal tension and a perpetual state of technological conflict.
Ethical considerations must also extend to the potential health impacts of prolonged exposure to electromagnetic waves. While current research suggests minimal health risks from low-level electromagnetic fields, the long-term effects of more powerful and focused electromagnetic waves used in cybersecurity applications remain uncertain. Ensuring the safety of individuals exposed to these technologies is paramount.
Addressing these ethical implications requires a multifaceted approach involving policymakers, technologists, ethicists, and civil society organizations. Developing comprehensive guidelines and regulations for the use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity is essential to strike a balance between security needs and ethical considerations. Transparency in the development and deployment of these technologies, along with public education and engagement, will be crucial in building trust and ensuring responsible innovation in this field.
Another ethical consideration is the potential for electromagnetic waves to be used as a weapon or for malicious purposes. While the technology may enhance cybersecurity defenses, it could also be exploited by bad actors to disrupt critical infrastructure, interfere with communication systems, or cause harm to individuals. The dual-use nature of this technology necessitates careful regulation and oversight to prevent misuse and ensure responsible development and deployment.
The use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity also raises concerns about fairness and equality. Advanced electromagnetic detection and protection systems may be costly, potentially creating a digital divide where only well-resourced organizations and individuals can afford adequate cybersecurity measures. This disparity could exacerbate existing inequalities and leave vulnerable populations more susceptible to cyber threats.
Furthermore, the widespread adoption of electromagnetic wave-based cybersecurity measures could lead to an escalation in the technological arms race between security professionals and malicious actors. This constant evolution of attack and defense mechanisms may result in increased societal tension and a perpetual state of technological conflict.
Ethical considerations must also extend to the potential health impacts of prolonged exposure to electromagnetic waves. While current research suggests minimal health risks from low-level electromagnetic fields, the long-term effects of more powerful and focused electromagnetic waves used in cybersecurity applications remain uncertain. Ensuring the safety of individuals exposed to these technologies is paramount.
Addressing these ethical implications requires a multifaceted approach involving policymakers, technologists, ethicists, and civil society organizations. Developing comprehensive guidelines and regulations for the use of electromagnetic waves in cybersecurity is essential to strike a balance between security needs and ethical considerations. Transparency in the development and deployment of these technologies, along with public education and engagement, will be crucial in building trust and ensuring responsible innovation in this field.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!