How Heptane Improves Yield in Extractive Distillation Processes
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Heptane in Extraction
Heptane plays a crucial role in enhancing the yield of extractive distillation processes, particularly in the separation of close-boiling mixtures. This aliphatic hydrocarbon acts as an effective entrainer, altering the relative volatility of the components to be separated, thereby facilitating more efficient separation.
In extractive distillation, heptane is introduced as a third component to the binary mixture, typically at the top of the distillation column. Its presence modifies the vapor-liquid equilibrium of the system, increasing the difference in volatility between the key components. This effect is particularly pronounced in the separation of azeotropic mixtures, where traditional distillation methods are ineffective.
The molecular structure of heptane, with its seven-carbon chain, provides ideal characteristics for extraction. Its non-polar nature allows it to interact selectively with certain components in the mixture, often preferentially associating with the less polar component. This selective interaction changes the activity coefficients of the mixture components, leading to improved separation efficiency.
One of the primary advantages of using heptane in extractive distillation is its relatively low boiling point (98.4°C at atmospheric pressure). This property ensures that heptane can be easily recovered and recycled in the process, contributing to the overall economic viability of the separation technique. Additionally, heptane's low viscosity and surface tension facilitate good mass transfer rates, which are essential for efficient separation.
The effectiveness of heptane as an entrainer is particularly evident in the petrochemical industry, where it is used to separate close-boiling hydrocarbons. For instance, in the production of high-purity cyclohexane, heptane is employed to break the azeotrope formed between cyclohexane and benzene. The addition of heptane increases the relative volatility of cyclohexane, allowing for its separation with higher purity and yield.
Furthermore, heptane's use extends to the pharmaceutical industry, where it aids in the purification of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its selective solvent properties make it valuable in liquid-liquid extraction processes, complementing its role in extractive distillation. This versatility enhances the overall efficiency of separation processes across various industrial applications.
In extractive distillation, heptane is introduced as a third component to the binary mixture, typically at the top of the distillation column. Its presence modifies the vapor-liquid equilibrium of the system, increasing the difference in volatility between the key components. This effect is particularly pronounced in the separation of azeotropic mixtures, where traditional distillation methods are ineffective.
The molecular structure of heptane, with its seven-carbon chain, provides ideal characteristics for extraction. Its non-polar nature allows it to interact selectively with certain components in the mixture, often preferentially associating with the less polar component. This selective interaction changes the activity coefficients of the mixture components, leading to improved separation efficiency.
One of the primary advantages of using heptane in extractive distillation is its relatively low boiling point (98.4°C at atmospheric pressure). This property ensures that heptane can be easily recovered and recycled in the process, contributing to the overall economic viability of the separation technique. Additionally, heptane's low viscosity and surface tension facilitate good mass transfer rates, which are essential for efficient separation.
The effectiveness of heptane as an entrainer is particularly evident in the petrochemical industry, where it is used to separate close-boiling hydrocarbons. For instance, in the production of high-purity cyclohexane, heptane is employed to break the azeotrope formed between cyclohexane and benzene. The addition of heptane increases the relative volatility of cyclohexane, allowing for its separation with higher purity and yield.
Furthermore, heptane's use extends to the pharmaceutical industry, where it aids in the purification of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its selective solvent properties make it valuable in liquid-liquid extraction processes, complementing its role in extractive distillation. This versatility enhances the overall efficiency of separation processes across various industrial applications.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for heptane in extractive distillation processes has been steadily increasing due to its effectiveness in improving yield and efficiency. Extractive distillation is a crucial separation technique in various industries, including petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and fine chemicals. The global market for extractive distillation equipment and processes is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by the need for more efficient and cost-effective separation methods.
Heptane, as an entrainer in extractive distillation, has gained considerable attention due to its ability to enhance the relative volatility of close-boiling mixtures. This property makes it particularly valuable in separating azeotropic mixtures, which are common challenges in industrial processes. The demand for heptane in this application is closely tied to the growth of industries that rely on high-purity chemical separations.
In the petrochemical industry, the use of heptane in extractive distillation has shown promising results in improving the separation of aromatics from aliphatic hydrocarbons. This application is particularly important in the production of high-purity benzene, toluene, and xylenes (BTX). As the demand for these aromatic compounds continues to rise, driven by their use in plastics, fibers, and other consumer products, the market for heptane-based extractive distillation processes is expected to expand.
The pharmaceutical industry is another key driver of demand for improved extractive distillation processes. As drug manufacturing becomes increasingly complex, the need for efficient purification methods grows. Heptane's role in enhancing the separation of pharmaceutical intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) is becoming more critical, especially in the production of high-value, low-volume compounds.
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals are also influencing market demand. As industries face pressure to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste, the improved yield offered by heptane in extractive distillation becomes more attractive. This aligns with the global trend towards greener and more sustainable chemical processes, potentially expanding the market for heptane-based solutions.
The market for heptane in extractive distillation is not limited to specific regions but is global in nature. However, regions with strong petrochemical and pharmaceutical industries, such as North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, are expected to be the primary drivers of demand. Emerging economies with growing industrial sectors are also likely to contribute significantly to market growth as they adopt more advanced separation technologies.
Heptane, as an entrainer in extractive distillation, has gained considerable attention due to its ability to enhance the relative volatility of close-boiling mixtures. This property makes it particularly valuable in separating azeotropic mixtures, which are common challenges in industrial processes. The demand for heptane in this application is closely tied to the growth of industries that rely on high-purity chemical separations.
In the petrochemical industry, the use of heptane in extractive distillation has shown promising results in improving the separation of aromatics from aliphatic hydrocarbons. This application is particularly important in the production of high-purity benzene, toluene, and xylenes (BTX). As the demand for these aromatic compounds continues to rise, driven by their use in plastics, fibers, and other consumer products, the market for heptane-based extractive distillation processes is expected to expand.
The pharmaceutical industry is another key driver of demand for improved extractive distillation processes. As drug manufacturing becomes increasingly complex, the need for efficient purification methods grows. Heptane's role in enhancing the separation of pharmaceutical intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) is becoming more critical, especially in the production of high-value, low-volume compounds.
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals are also influencing market demand. As industries face pressure to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste, the improved yield offered by heptane in extractive distillation becomes more attractive. This aligns with the global trend towards greener and more sustainable chemical processes, potentially expanding the market for heptane-based solutions.
The market for heptane in extractive distillation is not limited to specific regions but is global in nature. However, regions with strong petrochemical and pharmaceutical industries, such as North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, are expected to be the primary drivers of demand. Emerging economies with growing industrial sectors are also likely to contribute significantly to market growth as they adopt more advanced separation technologies.
Technical Challenges
The extractive distillation process using heptane as an entrainer faces several technical challenges that need to be addressed to optimize yield and efficiency. One of the primary obstacles is the precise control of the heptane-to-feed ratio. Fluctuations in this ratio can significantly impact the separation efficiency and product purity. Maintaining a consistent ratio requires advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring capabilities, which may not be readily available in all industrial settings.
Another challenge lies in the energy consumption associated with the process. The addition of heptane as an entrainer increases the overall liquid load in the distillation column, necessitating higher energy input for heating and cooling. This increased energy demand can lead to higher operational costs and reduced sustainability, particularly in large-scale industrial applications. Developing energy-efficient heat integration strategies and exploring alternative heat sources are crucial areas for improvement.
The recovery and recycling of heptane present additional technical hurdles. Efficient separation of heptane from the product streams is essential to maintain process economics and minimize environmental impact. However, achieving high recovery rates while maintaining product purity can be challenging, often requiring additional separation steps or specialized equipment. This complexity can increase capital costs and operational complexity.
Material compatibility is another significant concern in heptane-based extractive distillation. Heptane's chemical properties may lead to corrosion or degradation of certain materials commonly used in distillation equipment. This necessitates careful selection of construction materials and regular maintenance to prevent equipment failure and ensure long-term reliability. The use of specialized corrosion-resistant materials may increase initial investment costs.
Furthermore, the potential for heptane emissions and their environmental impact pose regulatory and safety challenges. Stringent emission control measures and robust safety protocols are necessary to comply with environmental regulations and ensure worker safety. This may require the implementation of advanced vapor recovery systems and leak detection technologies, adding to the overall process complexity and cost.
Optimizing the column design and internals for heptane-based extractive distillation is also a significant technical challenge. The presence of heptane alters the vapor-liquid equilibrium and fluid dynamics within the column, potentially affecting tray efficiency and mass transfer rates. Developing innovative column designs and packing materials that can enhance separation efficiency while accommodating the unique properties of heptane-containing mixtures is an ongoing area of research and development.
Lastly, the scalability of heptane-based extractive distillation processes from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. Factors such as heat and mass transfer limitations, fluid distribution, and residence time distributions can behave differently at larger scales, potentially impacting the overall process performance and yield. Addressing these scale-up issues requires extensive pilot-scale testing and sophisticated process modeling techniques to accurately predict and optimize industrial-scale operations.
Another challenge lies in the energy consumption associated with the process. The addition of heptane as an entrainer increases the overall liquid load in the distillation column, necessitating higher energy input for heating and cooling. This increased energy demand can lead to higher operational costs and reduced sustainability, particularly in large-scale industrial applications. Developing energy-efficient heat integration strategies and exploring alternative heat sources are crucial areas for improvement.
The recovery and recycling of heptane present additional technical hurdles. Efficient separation of heptane from the product streams is essential to maintain process economics and minimize environmental impact. However, achieving high recovery rates while maintaining product purity can be challenging, often requiring additional separation steps or specialized equipment. This complexity can increase capital costs and operational complexity.
Material compatibility is another significant concern in heptane-based extractive distillation. Heptane's chemical properties may lead to corrosion or degradation of certain materials commonly used in distillation equipment. This necessitates careful selection of construction materials and regular maintenance to prevent equipment failure and ensure long-term reliability. The use of specialized corrosion-resistant materials may increase initial investment costs.
Furthermore, the potential for heptane emissions and their environmental impact pose regulatory and safety challenges. Stringent emission control measures and robust safety protocols are necessary to comply with environmental regulations and ensure worker safety. This may require the implementation of advanced vapor recovery systems and leak detection technologies, adding to the overall process complexity and cost.
Optimizing the column design and internals for heptane-based extractive distillation is also a significant technical challenge. The presence of heptane alters the vapor-liquid equilibrium and fluid dynamics within the column, potentially affecting tray efficiency and mass transfer rates. Developing innovative column designs and packing materials that can enhance separation efficiency while accommodating the unique properties of heptane-containing mixtures is an ongoing area of research and development.
Lastly, the scalability of heptane-based extractive distillation processes from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. Factors such as heat and mass transfer limitations, fluid distribution, and residence time distributions can behave differently at larger scales, potentially impacting the overall process performance and yield. Addressing these scale-up issues requires extensive pilot-scale testing and sophisticated process modeling techniques to accurately predict and optimize industrial-scale operations.
Current Solutions
01 Catalytic processes for heptane production
Various catalytic processes are employed to enhance heptane yield. These methods often involve the use of specific catalysts and reaction conditions to optimize the conversion of precursor molecules into heptane. The processes may include hydrocracking, isomerization, or reforming of hydrocarbon feedstocks.- Catalytic processes for heptane production: Various catalytic processes are employed to enhance heptane yield. These methods often involve the use of specific catalysts and reaction conditions to promote the formation of heptane from different feedstocks. The processes may include hydrocracking, isomerization, or reforming reactions to optimize heptane production.
- Separation and purification techniques: Efficient separation and purification methods are crucial for improving heptane yield. These techniques may involve distillation, extraction, or adsorption processes to isolate heptane from complex mixtures. Advanced separation technologies can significantly enhance the purity and overall yield of heptane in industrial production.
- Feedstock optimization for heptane production: The choice and preparation of feedstock play a vital role in maximizing heptane yield. Various hydrocarbon sources, including naphtha, natural gas condensates, or specific petroleum fractions, can be optimized to increase heptane production. Pretreatment methods and feedstock blending strategies may be employed to enhance the overall yield.
- Process control and optimization strategies: Advanced process control and optimization techniques are implemented to improve heptane yield. These may include real-time monitoring systems, predictive modeling, and adaptive control algorithms. By fine-tuning reaction parameters and operating conditions, the overall efficiency and yield of heptane production can be significantly enhanced.
- Novel reactor designs for heptane synthesis: Innovative reactor designs are developed to increase heptane yield. These may include advanced fluidized bed reactors, membrane reactors, or microreactor systems. The novel reactor configurations aim to improve mass and heat transfer, enhance reaction kinetics, and ultimately boost heptane production efficiency.
02 Separation and purification techniques
Efficient separation and purification methods are crucial for improving heptane yield. These techniques may include distillation, extraction, or membrane separation processes. Advanced separation technologies are employed to isolate heptane from complex hydrocarbon mixtures, thereby increasing the overall yield and purity of the product.Expand Specific Solutions03 Feedstock selection and pretreatment
The choice of feedstock and its pretreatment significantly impact heptane yield. Various hydrocarbon sources, such as crude oil fractions or natural gas liquids, can be used. Pretreatment methods may involve desulfurization, denitrogenation, or other purification steps to prepare the feedstock for efficient heptane production.Expand Specific Solutions04 Process optimization and control
Optimizing reaction conditions and implementing advanced control strategies are essential for maximizing heptane yield. This may involve adjusting parameters such as temperature, pressure, and residence time, as well as utilizing sophisticated process control systems to maintain optimal operating conditions throughout the production process.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel reactor designs and configurations
Innovative reactor designs and configurations can enhance heptane yield by improving mass and heat transfer, increasing reaction efficiency, and minimizing unwanted side reactions. These may include advanced fluidized bed reactors, membrane reactors, or multi-stage reactor systems tailored for heptane production.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The extractive distillation process using heptane is in a mature stage of development, with significant market potential in the petrochemical industry. The global market for this technology is substantial, driven by the increasing demand for efficient separation processes. Major players like ExxonMobil, Sinopec, and BP are actively involved in research and implementation, indicating a high level of technological maturity. Academic institutions such as Nanjing Normal University and research organizations like CNRS are contributing to further advancements. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established oil and gas companies and specialized chemical firms like UOP LLC and Novozymes participating in the development and application of this technology.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an advanced extractive distillation process using heptane as an entrainer to improve the separation of close-boiling hydrocarbon mixtures. Their approach involves a two-column system where heptane is introduced in the first column to enhance the relative volatility of the key components. This results in a more efficient separation with lower energy consumption compared to conventional distillation[1]. The process incorporates a heat integration scheme, utilizing the heat from the bottom stream of the second column to partially vaporize the feed to the first column, further improving energy efficiency[3]. Sinopec's method also includes a solvent recovery system that minimizes heptane losses and ensures high-purity product streams[5].
Strengths: Improved separation efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and high product purity. Weaknesses: Potential complexity in process control and initial capital investment for retrofitting existing systems.
UOP LLC
Technical Solution: UOP LLC has pioneered a novel extractive distillation technology utilizing heptane to enhance the separation of close-boiling hydrocarbons, particularly in the production of high-purity aromatics. Their process employs a specially designed extractive distillation column with optimized internals to maximize the contact between the vapor phase and the heptane-rich liquid phase[2]. This configuration allows for a significant increase in relative volatility, enabling sharper separations at lower reflux ratios. UOP's technology also incorporates an advanced control system that dynamically adjusts the heptane-to-feed ratio based on real-time composition analysis, ensuring consistent product quality across varying feed compositions[4]. Additionally, they have developed a proprietary solvent recovery unit that achieves over 99.9% heptane recovery, minimizing makeup requirements and environmental impact[6].
Strengths: High separation efficiency, adaptability to feed variations, and excellent solvent recovery. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial capital costs and the need for specialized operator training.
Heptane Innovations
Heptane from a plant source, for the extraction of natural products
PatentActiveUS11845720B2
Innovation
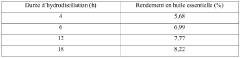
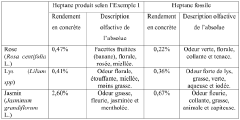
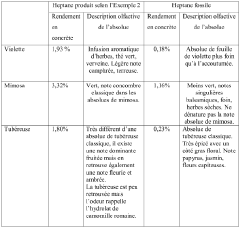
- Heptane is obtained through hydrodistillation or steam distillation of Commiphora wildii resin, which is then purified to produce a high-yield, high-purity n-heptane suitable for use as a solvent in perfumery, cosmetics, and food flavorings, offering unique olfactory characteristics.
Heptane from a plant source, for the extraction of natural products
PatentWO2019149701A1
Innovation
- The extraction of heptane from Commiphora wildii resin using hydrodistillation and steam stripping, followed by physical purification, providing a high-yield, plant-based solvent suitable for perfumery, cosmetics, and food aromatics, with a composition predominantly comprising n-heptane and additional odor compounds.
Process Optimization
Process optimization in extractive distillation using heptane as an entrainer involves a systematic approach to enhance the overall efficiency and yield of the separation process. The addition of heptane as a mass separating agent alters the relative volatility of the components in the mixture, facilitating improved separation and increased product purity.
One key aspect of process optimization is the determination of optimal operating conditions. This includes identifying the ideal feed stage location for both the feed mixture and the entrainer. The feed stage location significantly impacts the separation efficiency and energy consumption of the process. Advanced simulation tools and optimization algorithms are employed to determine the optimal feed stage that maximizes separation while minimizing energy requirements.
Another critical factor in process optimization is the entrainer-to-feed ratio. The amount of heptane introduced into the system directly affects the separation efficiency and product yield. Too little heptane may result in insufficient separation, while excessive amounts can lead to unnecessary energy consumption and increased operational costs. Rigorous optimization techniques, such as response surface methodology or genetic algorithms, are utilized to determine the optimal entrainer-to-feed ratio that maximizes yield and minimizes energy consumption.
Temperature and pressure profiles within the distillation column play a crucial role in the separation process. Optimizing these parameters ensures efficient mass transfer and vapor-liquid equilibrium throughout the column. Advanced control strategies, such as model predictive control or artificial neural networks, can be implemented to maintain optimal temperature and pressure profiles, adapting to process disturbances and variations in feed composition.
Heat integration is another essential aspect of process optimization. By recovering and reusing waste heat from various streams within the process, overall energy consumption can be significantly reduced. Pinch analysis and heat exchanger network design techniques are employed to maximize heat recovery and minimize utility requirements, leading to improved process economics and reduced environmental impact.
The design and selection of column internals, such as trays or packings, also contribute to process optimization. High-efficiency internals can enhance mass transfer and reduce pressure drop, resulting in improved separation performance and reduced energy consumption. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations and pilot-scale testing are often used to optimize the design and arrangement of column internals for specific applications.
Finally, process optimization extends to the broader aspects of plant-wide integration and scheduling. This includes optimizing the production schedule, inventory management, and integration with upstream and downstream processes. Advanced planning and scheduling tools, coupled with real-time optimization algorithms, ensure that the extractive distillation process operates at peak efficiency within the context of the entire production facility.
One key aspect of process optimization is the determination of optimal operating conditions. This includes identifying the ideal feed stage location for both the feed mixture and the entrainer. The feed stage location significantly impacts the separation efficiency and energy consumption of the process. Advanced simulation tools and optimization algorithms are employed to determine the optimal feed stage that maximizes separation while minimizing energy requirements.
Another critical factor in process optimization is the entrainer-to-feed ratio. The amount of heptane introduced into the system directly affects the separation efficiency and product yield. Too little heptane may result in insufficient separation, while excessive amounts can lead to unnecessary energy consumption and increased operational costs. Rigorous optimization techniques, such as response surface methodology or genetic algorithms, are utilized to determine the optimal entrainer-to-feed ratio that maximizes yield and minimizes energy consumption.
Temperature and pressure profiles within the distillation column play a crucial role in the separation process. Optimizing these parameters ensures efficient mass transfer and vapor-liquid equilibrium throughout the column. Advanced control strategies, such as model predictive control or artificial neural networks, can be implemented to maintain optimal temperature and pressure profiles, adapting to process disturbances and variations in feed composition.
Heat integration is another essential aspect of process optimization. By recovering and reusing waste heat from various streams within the process, overall energy consumption can be significantly reduced. Pinch analysis and heat exchanger network design techniques are employed to maximize heat recovery and minimize utility requirements, leading to improved process economics and reduced environmental impact.
The design and selection of column internals, such as trays or packings, also contribute to process optimization. High-efficiency internals can enhance mass transfer and reduce pressure drop, resulting in improved separation performance and reduced energy consumption. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations and pilot-scale testing are often used to optimize the design and arrangement of column internals for specific applications.
Finally, process optimization extends to the broader aspects of plant-wide integration and scheduling. This includes optimizing the production schedule, inventory management, and integration with upstream and downstream processes. Advanced planning and scheduling tools, coupled with real-time optimization algorithms, ensure that the extractive distillation process operates at peak efficiency within the context of the entire production facility.
Environmental Impact
The use of heptane in extractive distillation processes, while improving yield, raises significant environmental concerns that must be carefully considered. Heptane, a volatile organic compound (VOC), can contribute to air pollution and potentially harm human health and ecosystems if released into the environment. Its low boiling point and high vapor pressure increase the risk of atmospheric emissions during storage, handling, and processing.
When used in extractive distillation, heptane may be partially lost through evaporation or carried over in product streams. These losses not only reduce process efficiency but also pose environmental risks. Fugitive emissions from equipment leaks, storage tanks, and transfer operations can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, particularly in urban and industrial areas. Moreover, heptane vapors can react with other atmospheric pollutants, forming secondary organic aerosols that impact air quality and climate.
Water contamination is another potential environmental impact. Accidental spills or improper disposal of heptane-containing waste streams can lead to soil and groundwater pollution. Heptane's low water solubility and tendency to form a separate phase make it challenging to remove from water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems and drinking water sources.
The production and transportation of heptane also contribute to its environmental footprint. As a petroleum-derived product, its manufacture involves energy-intensive processes and greenhouse gas emissions. The transportation of heptane to industrial sites further adds to carbon emissions and the risk of accidental releases during transit.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, industries employing heptane in extractive distillation must implement robust emission control systems, such as vapor recovery units and sealed storage tanks. Proper handling procedures, regular equipment maintenance, and leak detection programs are essential to minimize fugitive emissions. Additionally, the development of closed-loop systems and solvent recovery technologies can significantly reduce heptane consumption and environmental release.
Research into more environmentally friendly alternatives to heptane is ongoing. Bio-based solvents and ionic liquids are being explored as potential substitutes that could offer similar yield improvements with reduced environmental impact. However, the full life-cycle assessment of these alternatives must be conducted to ensure they truly represent a more sustainable option.
When used in extractive distillation, heptane may be partially lost through evaporation or carried over in product streams. These losses not only reduce process efficiency but also pose environmental risks. Fugitive emissions from equipment leaks, storage tanks, and transfer operations can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, particularly in urban and industrial areas. Moreover, heptane vapors can react with other atmospheric pollutants, forming secondary organic aerosols that impact air quality and climate.
Water contamination is another potential environmental impact. Accidental spills or improper disposal of heptane-containing waste streams can lead to soil and groundwater pollution. Heptane's low water solubility and tendency to form a separate phase make it challenging to remove from water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems and drinking water sources.
The production and transportation of heptane also contribute to its environmental footprint. As a petroleum-derived product, its manufacture involves energy-intensive processes and greenhouse gas emissions. The transportation of heptane to industrial sites further adds to carbon emissions and the risk of accidental releases during transit.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, industries employing heptane in extractive distillation must implement robust emission control systems, such as vapor recovery units and sealed storage tanks. Proper handling procedures, regular equipment maintenance, and leak detection programs are essential to minimize fugitive emissions. Additionally, the development of closed-loop systems and solvent recovery technologies can significantly reduce heptane consumption and environmental release.
Research into more environmentally friendly alternatives to heptane is ongoing. Bio-based solvents and ionic liquids are being explored as potential substitutes that could offer similar yield improvements with reduced environmental impact. However, the full life-cycle assessment of these alternatives must be conducted to ensure they truly represent a more sustainable option.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!