How Steering Wheel Design Contributes to Sustainability?
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sustainable Steering Wheel Design Evolution
The evolution of sustainable steering wheel design has been a journey marked by innovation and environmental consciousness. In the early stages, steering wheels were primarily designed for functionality, with little consideration for sustainability. However, as environmental concerns grew, the automotive industry began to shift its focus towards more eco-friendly practices.
The 1990s saw the first significant steps towards sustainable steering wheel design. Manufacturers started experimenting with recycled materials, particularly in non-critical components of the steering wheel. This period also witnessed the introduction of bio-based materials, albeit in limited quantities, as alternatives to traditional petroleum-based plastics.
The turn of the millennium brought about a more concerted effort to integrate sustainability into steering wheel design. Automakers began to explore the use of natural fibers, such as hemp and flax, in steering wheel cores. These materials offered the dual benefits of being renewable and reducing the overall weight of the component, thus contributing to improved fuel efficiency.
By the mid-2000s, the concept of lifecycle assessment gained prominence in steering wheel design. Manufacturers started considering the environmental impact of steering wheels from production to disposal. This holistic approach led to the development of steering wheels with improved recyclability and reduced carbon footprint during manufacturing processes.
The 2010s marked a significant leap in sustainable steering wheel design. Advanced biomaterials, such as mycelium-based composites and algae-derived polymers, began to emerge as viable alternatives to traditional materials. These innovations not only reduced reliance on fossil fuels but also offered enhanced biodegradability at the end of the product's life cycle.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards creating fully circular steering wheel designs. This approach aims to eliminate waste and maximize resource efficiency by ensuring that materials used in steering wheels can be fully recycled or biodegraded. Manufacturers are now exploring modular designs that allow for easy disassembly and material recovery.
The latest trend in sustainable steering wheel design involves the integration of smart materials and technologies. Self-healing surfaces, energy-harvesting capabilities, and the use of sensors made from eco-friendly materials are being developed to extend the lifespan of steering wheels and reduce the need for replacements.
As we look to the future, the evolution of sustainable steering wheel design is likely to continue its trajectory towards greater environmental responsibility. The integration of advanced materials science, circular economy principles, and smart technologies promises to deliver steering wheels that not only meet the functional and safety requirements but also contribute significantly to the overall sustainability of vehicles.
The 1990s saw the first significant steps towards sustainable steering wheel design. Manufacturers started experimenting with recycled materials, particularly in non-critical components of the steering wheel. This period also witnessed the introduction of bio-based materials, albeit in limited quantities, as alternatives to traditional petroleum-based plastics.
The turn of the millennium brought about a more concerted effort to integrate sustainability into steering wheel design. Automakers began to explore the use of natural fibers, such as hemp and flax, in steering wheel cores. These materials offered the dual benefits of being renewable and reducing the overall weight of the component, thus contributing to improved fuel efficiency.
By the mid-2000s, the concept of lifecycle assessment gained prominence in steering wheel design. Manufacturers started considering the environmental impact of steering wheels from production to disposal. This holistic approach led to the development of steering wheels with improved recyclability and reduced carbon footprint during manufacturing processes.
The 2010s marked a significant leap in sustainable steering wheel design. Advanced biomaterials, such as mycelium-based composites and algae-derived polymers, began to emerge as viable alternatives to traditional materials. These innovations not only reduced reliance on fossil fuels but also offered enhanced biodegradability at the end of the product's life cycle.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards creating fully circular steering wheel designs. This approach aims to eliminate waste and maximize resource efficiency by ensuring that materials used in steering wheels can be fully recycled or biodegraded. Manufacturers are now exploring modular designs that allow for easy disassembly and material recovery.
The latest trend in sustainable steering wheel design involves the integration of smart materials and technologies. Self-healing surfaces, energy-harvesting capabilities, and the use of sensors made from eco-friendly materials are being developed to extend the lifespan of steering wheels and reduce the need for replacements.
As we look to the future, the evolution of sustainable steering wheel design is likely to continue its trajectory towards greater environmental responsibility. The integration of advanced materials science, circular economy principles, and smart technologies promises to deliver steering wheels that not only meet the functional and safety requirements but also contribute significantly to the overall sustainability of vehicles.
Market Demand for Eco-Friendly Automotive Components
The automotive industry is experiencing a significant shift towards sustainability, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations. This trend has created a growing market demand for eco-friendly automotive components, including steering wheels. Consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious, seeking vehicles that align with their values and contribute to reducing carbon footprints.
The market for eco-friendly automotive components is expanding rapidly, with a particular focus on interior elements such as steering wheels. This demand is fueled by several factors, including government regulations promoting sustainable manufacturing practices, consumer preferences for green products, and automakers' commitments to sustainability goals.
Steering wheels, being a crucial interface between driver and vehicle, present a unique opportunity for incorporating sustainable materials and design principles. The market is seeing increased interest in steering wheels made from recycled or bio-based materials, as well as those designed for longevity and easy recyclability at the end of their lifecycle.
Major automotive manufacturers are responding to this demand by investing in research and development of sustainable steering wheel designs. These efforts include exploring alternative materials such as recycled plastics, natural fibers, and bio-composites to replace traditional petroleum-based materials. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on reducing the overall environmental impact of steering wheel production processes.
The market is also witnessing a rise in demand for steering wheels that incorporate advanced technologies while maintaining a focus on sustainability. This includes the integration of touch-sensitive controls and displays that can potentially reduce the need for additional plastic components in the vehicle interior.
Consumer surveys indicate a willingness to pay a premium for vehicles with eco-friendly components, including steering wheels. This trend is particularly strong among younger demographics and in markets with high environmental awareness. As a result, automakers are increasingly viewing sustainable steering wheel designs as a competitive advantage and a means to differentiate their products in a crowded market.
The aftermarket sector is also experiencing growth in demand for eco-friendly steering wheel options, as consumers seek to upgrade their existing vehicles with more sustainable components. This presents opportunities for both established manufacturers and innovative startups to enter the market with retrofit solutions.
As the automotive industry continues its transition towards electrification, the demand for sustainable components is expected to accelerate further. Electric vehicle manufacturers, in particular, are placing a strong emphasis on overall vehicle sustainability, creating additional market pull for eco-friendly steering wheel designs.
The market for eco-friendly automotive components is expanding rapidly, with a particular focus on interior elements such as steering wheels. This demand is fueled by several factors, including government regulations promoting sustainable manufacturing practices, consumer preferences for green products, and automakers' commitments to sustainability goals.
Steering wheels, being a crucial interface between driver and vehicle, present a unique opportunity for incorporating sustainable materials and design principles. The market is seeing increased interest in steering wheels made from recycled or bio-based materials, as well as those designed for longevity and easy recyclability at the end of their lifecycle.
Major automotive manufacturers are responding to this demand by investing in research and development of sustainable steering wheel designs. These efforts include exploring alternative materials such as recycled plastics, natural fibers, and bio-composites to replace traditional petroleum-based materials. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on reducing the overall environmental impact of steering wheel production processes.
The market is also witnessing a rise in demand for steering wheels that incorporate advanced technologies while maintaining a focus on sustainability. This includes the integration of touch-sensitive controls and displays that can potentially reduce the need for additional plastic components in the vehicle interior.
Consumer surveys indicate a willingness to pay a premium for vehicles with eco-friendly components, including steering wheels. This trend is particularly strong among younger demographics and in markets with high environmental awareness. As a result, automakers are increasingly viewing sustainable steering wheel designs as a competitive advantage and a means to differentiate their products in a crowded market.
The aftermarket sector is also experiencing growth in demand for eco-friendly steering wheel options, as consumers seek to upgrade their existing vehicles with more sustainable components. This presents opportunities for both established manufacturers and innovative startups to enter the market with retrofit solutions.
As the automotive industry continues its transition towards electrification, the demand for sustainable components is expected to accelerate further. Electric vehicle manufacturers, in particular, are placing a strong emphasis on overall vehicle sustainability, creating additional market pull for eco-friendly steering wheel designs.
Current Challenges in Sustainable Steering Wheel Production
The production of sustainable steering wheels faces several significant challenges in the current automotive industry. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of material selection. Traditional steering wheels often incorporate materials that are not environmentally friendly, such as petroleum-based plastics and synthetic leathers. Finding suitable eco-friendly alternatives that meet the stringent safety and durability requirements of steering wheels is a considerable challenge.
Another major hurdle is the energy-intensive manufacturing process. The production of steering wheels typically involves multiple stages, including molding, trimming, and assembly, each consuming substantial amounts of energy. Transitioning to more sustainable production methods while maintaining efficiency and quality standards presents a significant technical challenge for manufacturers.
The integration of advanced technologies into steering wheels, such as heating elements and touch-sensitive controls, further complicates sustainable production efforts. These features often require the use of rare earth metals and complex electronic components, which can be difficult to source sustainably and pose end-of-life recycling challenges.
Recycling and end-of-life management of steering wheels also present substantial difficulties. The composite nature of modern steering wheels, combining various materials and embedded electronics, makes them challenging to disassemble and recycle effectively. Developing efficient recycling processes that can separate and recover different materials without compromising their quality is an ongoing challenge.
Cost considerations pose another significant barrier to sustainable steering wheel production. Eco-friendly materials and sustainable manufacturing processes often come with higher costs, which can be challenging to justify in the competitive automotive market. Balancing sustainability goals with economic viability remains a key challenge for manufacturers.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized sustainability metrics and certification processes specific to steering wheel production makes it difficult for manufacturers to benchmark their efforts and communicate their sustainability achievements to consumers. This absence of clear industry standards can hinder the widespread adoption of sustainable practices in steering wheel design and production.
Lastly, the global supply chain for steering wheel components presents challenges in ensuring sustainability throughout the entire production process. Tracing the origin of materials and ensuring ethical and sustainable practices at every stage of the supply chain is a complex task that requires significant resources and collaboration across multiple stakeholders.
Another major hurdle is the energy-intensive manufacturing process. The production of steering wheels typically involves multiple stages, including molding, trimming, and assembly, each consuming substantial amounts of energy. Transitioning to more sustainable production methods while maintaining efficiency and quality standards presents a significant technical challenge for manufacturers.
The integration of advanced technologies into steering wheels, such as heating elements and touch-sensitive controls, further complicates sustainable production efforts. These features often require the use of rare earth metals and complex electronic components, which can be difficult to source sustainably and pose end-of-life recycling challenges.
Recycling and end-of-life management of steering wheels also present substantial difficulties. The composite nature of modern steering wheels, combining various materials and embedded electronics, makes them challenging to disassemble and recycle effectively. Developing efficient recycling processes that can separate and recover different materials without compromising their quality is an ongoing challenge.
Cost considerations pose another significant barrier to sustainable steering wheel production. Eco-friendly materials and sustainable manufacturing processes often come with higher costs, which can be challenging to justify in the competitive automotive market. Balancing sustainability goals with economic viability remains a key challenge for manufacturers.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized sustainability metrics and certification processes specific to steering wheel production makes it difficult for manufacturers to benchmark their efforts and communicate their sustainability achievements to consumers. This absence of clear industry standards can hinder the widespread adoption of sustainable practices in steering wheel design and production.
Lastly, the global supply chain for steering wheel components presents challenges in ensuring sustainability throughout the entire production process. Tracing the origin of materials and ensuring ethical and sustainable practices at every stage of the supply chain is a complex task that requires significant resources and collaboration across multiple stakeholders.
Existing Eco-Friendly Steering Wheel Solutions
01 Sustainable materials for steering wheel construction
Incorporating eco-friendly and recyclable materials in steering wheel manufacturing to reduce environmental impact. This includes using bio-based plastics, recycled materials, and sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based components.- Sustainable materials for steering wheel construction: Incorporating eco-friendly and recyclable materials in steering wheel manufacturing to reduce environmental impact. This includes using bio-based plastics, recycled materials, and sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based components.
- Energy-efficient steering systems: Developing steering systems that optimize energy consumption and reduce overall vehicle fuel consumption. This involves implementing advanced power steering technologies, regenerative systems, and lightweight designs to improve efficiency.
- Durability and longevity improvements: Enhancing the durability and lifespan of steering wheel components to reduce the need for replacements and minimize waste. This includes developing wear-resistant materials, improved coatings, and modular designs for easy repair and maintenance.
- Integration of sustainable technologies: Incorporating sustainable technologies into steering wheel design, such as energy harvesting systems, solar-powered components, or biodegradable electronics. These innovations aim to reduce the overall environmental footprint of the steering system.
- End-of-life considerations and recycling: Designing steering wheels with end-of-life considerations in mind, focusing on easy disassembly, material separation, and recyclability. This approach aims to minimize waste and promote circular economy principles in the automotive industry.
02 Energy-efficient steering systems
Developing steering systems that optimize energy consumption and reduce overall vehicle fuel consumption. This involves implementing advanced power steering technologies, regenerative systems, and lightweight designs to improve efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Durability and longevity improvements
Enhancing the lifespan of steering wheel components to reduce waste and the need for frequent replacements. This includes developing wear-resistant materials, improved coatings, and modular designs for easy repair and maintenance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of sustainable technologies
Incorporating sustainable technologies into steering wheels, such as energy harvesting systems, solar-powered features, or biodegradable electronics. These innovations aim to reduce the overall environmental footprint of the vehicle.Expand Specific Solutions05 End-of-life recycling and disposal solutions
Developing strategies for efficient recycling and environmentally friendly disposal of steering wheel components at the end of their lifecycle. This includes designing for disassembly, implementing take-back programs, and exploring upcycling opportunities.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Automotive Design
The steering wheel design industry is in a mature phase, with established players focusing on sustainability innovations. The market size is significant, driven by global automotive production and increasing demand for eco-friendly solutions. Technological maturity varies, with companies like Autoliv Development AB, ZF Automotive Safety Germany GmbH, and Hyundai Motor Co., Ltd. leading in advanced sustainable designs. These firms are investing in lightweight materials, recycled components, and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Emerging players such as Joyson Safety Systems and Toyoda Gosei Co., Ltd. are also contributing to the competitive landscape, pushing for more sustainable steering wheel solutions across the automotive sector.
Autoliv Development AB
Technical Solution: Autoliv has developed a sustainable steering wheel design that incorporates recycled and bio-based materials. Their approach focuses on reducing the carbon footprint of steering wheel production while maintaining safety standards. The company has introduced a steering wheel made with 30% recycled content and 5% bio-based materials[1]. This design also incorporates weight reduction techniques, resulting in a 10% lighter steering wheel compared to traditional models[2]. Autoliv's sustainable steering wheel features a core made from recycled carbon fiber, which not only reduces waste but also enhances the wheel's strength-to-weight ratio[3]. The company has also implemented a closed-loop recycling process for steering wheel components, further contributing to sustainability efforts in the automotive industry.
Strengths: Significant reduction in carbon footprint, use of recycled and bio-based materials, weight reduction. Weaknesses: Potential higher initial production costs, limited availability of recycled materials at scale.
Hyundai Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hyundai has developed an innovative steering wheel design that contributes to sustainability through material selection and manufacturing processes. The company has introduced a steering wheel made from bio-composite materials, including corn-based bioplastics and natural wood fibers[4]. This eco-friendly design reduces the use of petroleum-based plastics by up to 25% compared to conventional steering wheels[5]. Hyundai's sustainable steering wheel also incorporates a modular design that allows for easier disassembly and recycling at the end of the vehicle's life. The company has implemented a low-energy production process for these steering wheels, reducing energy consumption by 15% during manufacturing[6]. Additionally, Hyundai has developed a special coating for the steering wheel that is free from harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs), improving indoor air quality and reducing environmental impact.
Strengths: Use of bio-composite materials, modular design for easier recycling, reduced energy consumption in production. Weaknesses: Potential durability concerns with bio-based materials, higher production costs initially.
Innovative Materials for Sustainable Steering Wheels
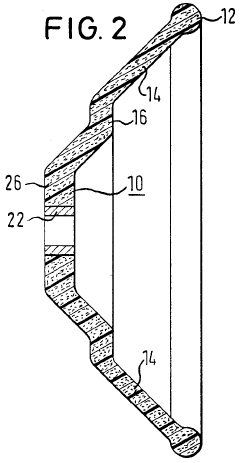
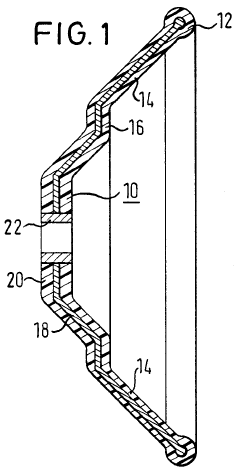
Steering wheel for motor vehicles
PatentWO2000044604A1
Innovation
- A steering wheel design utilizing a fiber-reinforced plastic hub and rim, where the spokes and rim are molded continuously as a single self-supporting body, eliminating the need for a metallic skeleton, with reinforcing fibers arranged predominantly parallel to the surface for enhanced strength and internal random distribution for energy dissipation.
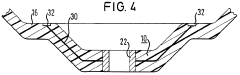
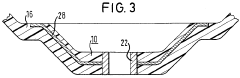
Steering wheel and method for manufacturing a steering wheel
PatentWO2007079933A1
Innovation
- A steering wheel design featuring a dimensionally stable base body with a separate, mechanically attached plastic extension that complements the grip area's contour, allowing for easy assembly and disassembly, and a method using snap connections and recesses for secure attachment, enabling the use of different materials and simplifying the assembly process.
Life Cycle Assessment of Steering Wheel Materials
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of steering wheel materials is a crucial aspect of evaluating the sustainability of automotive components. This comprehensive analysis examines the environmental impacts associated with the entire life cycle of steering wheel materials, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
The primary materials used in steering wheel construction typically include metals (such as aluminum or magnesium alloys), plastics (like polyurethane or ABS), and leather or synthetic leather coverings. Each of these materials has its own unique environmental footprint throughout its life cycle.
In the raw material extraction phase, the environmental impact varies significantly among different materials. Metal extraction, for instance, often involves energy-intensive mining operations and can lead to habitat disruption. Plastic production relies heavily on fossil fuel resources, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Leather production, if used, raises concerns about land use for cattle farming and the environmental effects of tanning processes.
The manufacturing stage of steering wheels involves various processes such as molding, casting, and assembly. These processes consume energy and may produce emissions and waste. The choice of manufacturing techniques and the efficiency of production lines play a significant role in determining the overall environmental impact at this stage.
During the use phase, the weight of the steering wheel becomes a critical factor. Lighter materials can contribute to overall vehicle weight reduction, leading to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions over the vehicle's lifetime. However, durability and longevity of the materials must also be considered to ensure that the environmental benefits are not offset by the need for frequent replacements.
End-of-life considerations are increasingly important in the automotive industry. The recyclability and recoverability of steering wheel materials significantly influence their overall environmental impact. Metals are generally highly recyclable, while certain plastics and composite materials may pose challenges in recycling processes.
Innovative materials and designs are emerging to address sustainability concerns. Bio-based plastics, recycled materials, and advanced composites are being explored as alternatives to traditional materials. These innovations aim to reduce the carbon footprint and improve the overall sustainability profile of steering wheels.
Conducting a thorough LCA helps manufacturers make informed decisions about material selection and design strategies. It allows for the identification of hotspots in the life cycle where environmental impacts are most significant, enabling targeted improvements. Furthermore, LCA results can guide the development of more sustainable manufacturing processes and end-of-life management strategies for steering wheels.
The primary materials used in steering wheel construction typically include metals (such as aluminum or magnesium alloys), plastics (like polyurethane or ABS), and leather or synthetic leather coverings. Each of these materials has its own unique environmental footprint throughout its life cycle.
In the raw material extraction phase, the environmental impact varies significantly among different materials. Metal extraction, for instance, often involves energy-intensive mining operations and can lead to habitat disruption. Plastic production relies heavily on fossil fuel resources, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Leather production, if used, raises concerns about land use for cattle farming and the environmental effects of tanning processes.
The manufacturing stage of steering wheels involves various processes such as molding, casting, and assembly. These processes consume energy and may produce emissions and waste. The choice of manufacturing techniques and the efficiency of production lines play a significant role in determining the overall environmental impact at this stage.
During the use phase, the weight of the steering wheel becomes a critical factor. Lighter materials can contribute to overall vehicle weight reduction, leading to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions over the vehicle's lifetime. However, durability and longevity of the materials must also be considered to ensure that the environmental benefits are not offset by the need for frequent replacements.
End-of-life considerations are increasingly important in the automotive industry. The recyclability and recoverability of steering wheel materials significantly influence their overall environmental impact. Metals are generally highly recyclable, while certain plastics and composite materials may pose challenges in recycling processes.
Innovative materials and designs are emerging to address sustainability concerns. Bio-based plastics, recycled materials, and advanced composites are being explored as alternatives to traditional materials. These innovations aim to reduce the carbon footprint and improve the overall sustainability profile of steering wheels.
Conducting a thorough LCA helps manufacturers make informed decisions about material selection and design strategies. It allows for the identification of hotspots in the life cycle where environmental impacts are most significant, enabling targeted improvements. Furthermore, LCA results can guide the development of more sustainable manufacturing processes and end-of-life management strategies for steering wheels.
Regulatory Framework for Automotive Sustainability
The regulatory framework for automotive sustainability plays a crucial role in shaping the design and development of steering wheels, as well as other vehicle components. Governments and international organizations have established various regulations and standards to promote sustainability in the automotive industry, including those that directly impact steering wheel design.
One of the key aspects of this regulatory framework is the emphasis on reducing the environmental impact of vehicles throughout their lifecycle. This includes regulations on material selection, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life recycling. For steering wheels, this translates into requirements for using sustainable materials, such as recycled plastics or bio-based composites, and designing for easy disassembly and recyclability.
Energy efficiency and emissions reduction are also central to automotive sustainability regulations. While steering wheels do not directly contribute to a vehicle's fuel consumption or emissions, their design can indirectly impact these factors. For instance, regulations promoting lightweight vehicle components to improve fuel efficiency have led to the development of lighter steering wheel materials and structures.
Safety regulations, which are integral to automotive sustainability, also influence steering wheel design. These include requirements for impact absorption, airbag integration, and ergonomic considerations. Sustainable steering wheel designs must balance these safety requirements with environmental considerations, often leading to innovative solutions that meet both criteria.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the use of hazardous substances in automotive components. Steering wheel manufacturers must comply with regulations such as the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives. These regulations limit the use of certain chemicals and materials in steering wheels and other vehicle parts, promoting safer and more environmentally friendly designs.
As the automotive industry moves towards electrification and autonomous driving, new regulations are emerging that will further impact steering wheel design. These include standards for integrating advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and human-machine interfaces into steering wheels, as well as requirements for adaptable or removable steering systems in autonomous vehicles.
Compliance with these regulations often drives innovation in steering wheel design, encouraging manufacturers to develop new materials, manufacturing techniques, and design approaches that meet both sustainability and performance requirements. This regulatory framework, therefore, serves as a catalyst for continuous improvement in steering wheel sustainability, pushing the industry towards more environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices.
One of the key aspects of this regulatory framework is the emphasis on reducing the environmental impact of vehicles throughout their lifecycle. This includes regulations on material selection, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life recycling. For steering wheels, this translates into requirements for using sustainable materials, such as recycled plastics or bio-based composites, and designing for easy disassembly and recyclability.
Energy efficiency and emissions reduction are also central to automotive sustainability regulations. While steering wheels do not directly contribute to a vehicle's fuel consumption or emissions, their design can indirectly impact these factors. For instance, regulations promoting lightweight vehicle components to improve fuel efficiency have led to the development of lighter steering wheel materials and structures.
Safety regulations, which are integral to automotive sustainability, also influence steering wheel design. These include requirements for impact absorption, airbag integration, and ergonomic considerations. Sustainable steering wheel designs must balance these safety requirements with environmental considerations, often leading to innovative solutions that meet both criteria.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the use of hazardous substances in automotive components. Steering wheel manufacturers must comply with regulations such as the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives. These regulations limit the use of certain chemicals and materials in steering wheels and other vehicle parts, promoting safer and more environmentally friendly designs.
As the automotive industry moves towards electrification and autonomous driving, new regulations are emerging that will further impact steering wheel design. These include standards for integrating advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and human-machine interfaces into steering wheels, as well as requirements for adaptable or removable steering systems in autonomous vehicles.
Compliance with these regulations often drives innovation in steering wheel design, encouraging manufacturers to develop new materials, manufacturing techniques, and design approaches that meet both sustainability and performance requirements. This regulatory framework, therefore, serves as a catalyst for continuous improvement in steering wheel sustainability, pushing the industry towards more environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!