Steering Wheel Applications: Revolutionizing Personal Transport
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Steering Wheel Tech Evolution and Objectives
The steering wheel has been a fundamental component of personal transport since the inception of automobiles. Its evolution has been closely tied to the advancement of vehicle technology and the changing demands of drivers. Initially, steering wheels were simple mechanical devices designed for basic directional control. However, as automotive technology progressed, steering wheels began to incorporate more sophisticated features and functionalities.
The primary objective of steering wheel technology has always been to provide precise and responsive control over a vehicle's direction. Over time, this objective has expanded to include enhancing driver comfort, improving safety, and integrating advanced vehicle systems. The evolution of steering wheel technology can be traced through several key phases, each marked by significant innovations and improvements.
In the early stages, the focus was on refining the mechanical linkage between the steering wheel and the vehicle's wheels. This led to the development of power steering systems, which reduced the physical effort required to steer, especially at low speeds. The next major leap came with the introduction of electronic power steering (EPS), which replaced hydraulic systems with electric motors, offering more precise control and improved fuel efficiency.
As vehicle electronics became more sophisticated, steering wheels began to incorporate various controls and interfaces. This integration aimed to allow drivers to access multiple vehicle functions without taking their hands off the wheel, enhancing both convenience and safety. Buttons for audio control, cruise control, and phone connectivity became common features on steering wheels.
The advent of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) has further revolutionized steering wheel technology. Features such as lane-keeping assist and adaptive cruise control have led to the development of steering wheels that can provide haptic feedback to the driver, alerting them to potential hazards or the need for intervention.
Looking towards the future, the objectives of steering wheel technology are evolving in response to the emergence of autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles. While maintaining the core function of vehicle control, steering wheels are being reimagined to accommodate new roles in human-machine interaction. Concepts such as retractable steering wheels for autonomous modes and biometric sensors for driver monitoring are being explored.
The ultimate goal of steering wheel technology in personal transport is to create an intuitive, safe, and adaptable interface between the driver and the vehicle. This involves balancing traditional control functions with the integration of advanced technologies, all while preparing for a future where the role of the driver may fundamentally change. As personal transport continues to evolve, steering wheel technology will play a crucial role in shaping the driving experience and bridging the gap between conventional and autonomous vehicles.
The primary objective of steering wheel technology has always been to provide precise and responsive control over a vehicle's direction. Over time, this objective has expanded to include enhancing driver comfort, improving safety, and integrating advanced vehicle systems. The evolution of steering wheel technology can be traced through several key phases, each marked by significant innovations and improvements.
In the early stages, the focus was on refining the mechanical linkage between the steering wheel and the vehicle's wheels. This led to the development of power steering systems, which reduced the physical effort required to steer, especially at low speeds. The next major leap came with the introduction of electronic power steering (EPS), which replaced hydraulic systems with electric motors, offering more precise control and improved fuel efficiency.
As vehicle electronics became more sophisticated, steering wheels began to incorporate various controls and interfaces. This integration aimed to allow drivers to access multiple vehicle functions without taking their hands off the wheel, enhancing both convenience and safety. Buttons for audio control, cruise control, and phone connectivity became common features on steering wheels.
The advent of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) has further revolutionized steering wheel technology. Features such as lane-keeping assist and adaptive cruise control have led to the development of steering wheels that can provide haptic feedback to the driver, alerting them to potential hazards or the need for intervention.
Looking towards the future, the objectives of steering wheel technology are evolving in response to the emergence of autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles. While maintaining the core function of vehicle control, steering wheels are being reimagined to accommodate new roles in human-machine interaction. Concepts such as retractable steering wheels for autonomous modes and biometric sensors for driver monitoring are being explored.
The ultimate goal of steering wheel technology in personal transport is to create an intuitive, safe, and adaptable interface between the driver and the vehicle. This involves balancing traditional control functions with the integration of advanced technologies, all while preparing for a future where the role of the driver may fundamentally change. As personal transport continues to evolve, steering wheel technology will play a crucial role in shaping the driving experience and bridging the gap between conventional and autonomous vehicles.
Market Demand Analysis for Smart Steering Wheels
The market demand for smart steering wheels is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing integration of advanced technologies in personal transportation. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, the steering wheel is evolving from a simple control device to a sophisticated interface that enhances driver experience, safety, and vehicle functionality.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards more intelligent and interactive vehicle interiors, with the steering wheel becoming a focal point for innovation. The demand for smart steering wheels is particularly strong in premium and luxury vehicle segments, where early adopters are willing to pay a premium for cutting-edge features. However, as technology costs decrease, this demand is expected to trickle down to mid-range and entry-level vehicles.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the increasing focus on driver safety. Smart steering wheels equipped with biometric sensors can monitor driver alertness, detect signs of fatigue or distraction, and provide timely warnings. This aligns with the growing emphasis on reducing accidents caused by human error, which accounts for a significant percentage of road incidents.
The push for more intuitive and less distracting in-vehicle controls is another factor fueling demand. Smart steering wheels with integrated touch-sensitive surfaces and haptic feedback allow drivers to control various vehicle functions without taking their hands off the wheel or eyes off the road. This seamless integration of controls is particularly appealing in an era where distracted driving is a major concern.
Furthermore, the trend towards vehicle personalization is boosting the appeal of smart steering wheels. These advanced interfaces can recognize different drivers and automatically adjust vehicle settings, from seat position to climate control preferences, enhancing the overall driving experience.
The market is also being influenced by the broader trend of connectivity in vehicles. Smart steering wheels that can interface with smartphones, display notifications, and facilitate voice commands are becoming increasingly desirable as consumers seek seamless integration between their digital lives and their vehicles.
As autonomous driving technology advances, the role of the steering wheel is expected to evolve further. There is growing interest in steering wheels that can retract or transform when the vehicle is in autonomous mode, creating more versatile interior spaces. This anticipation of future autonomous capabilities is driving research and development in adaptive steering wheel designs.
The aftermarket sector for smart steering wheels is also showing promise, with retrofit solutions gaining traction among owners of older vehicles looking to upgrade their driving experience without purchasing a new car. This segment is expected to contribute significantly to market growth in the coming years.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards more intelligent and interactive vehicle interiors, with the steering wheel becoming a focal point for innovation. The demand for smart steering wheels is particularly strong in premium and luxury vehicle segments, where early adopters are willing to pay a premium for cutting-edge features. However, as technology costs decrease, this demand is expected to trickle down to mid-range and entry-level vehicles.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the increasing focus on driver safety. Smart steering wheels equipped with biometric sensors can monitor driver alertness, detect signs of fatigue or distraction, and provide timely warnings. This aligns with the growing emphasis on reducing accidents caused by human error, which accounts for a significant percentage of road incidents.
The push for more intuitive and less distracting in-vehicle controls is another factor fueling demand. Smart steering wheels with integrated touch-sensitive surfaces and haptic feedback allow drivers to control various vehicle functions without taking their hands off the wheel or eyes off the road. This seamless integration of controls is particularly appealing in an era where distracted driving is a major concern.
Furthermore, the trend towards vehicle personalization is boosting the appeal of smart steering wheels. These advanced interfaces can recognize different drivers and automatically adjust vehicle settings, from seat position to climate control preferences, enhancing the overall driving experience.
The market is also being influenced by the broader trend of connectivity in vehicles. Smart steering wheels that can interface with smartphones, display notifications, and facilitate voice commands are becoming increasingly desirable as consumers seek seamless integration between their digital lives and their vehicles.
As autonomous driving technology advances, the role of the steering wheel is expected to evolve further. There is growing interest in steering wheels that can retract or transform when the vehicle is in autonomous mode, creating more versatile interior spaces. This anticipation of future autonomous capabilities is driving research and development in adaptive steering wheel designs.
The aftermarket sector for smart steering wheels is also showing promise, with retrofit solutions gaining traction among owners of older vehicles looking to upgrade their driving experience without purchasing a new car. This segment is expected to contribute significantly to market growth in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Steering Wheel Technology
Despite significant advancements in steering wheel technology, several challenges persist in the development and implementation of innovative steering wheel applications for personal transport. One of the primary obstacles is the integration of multiple functionalities without compromising safety or driver distraction. As steering wheels evolve to incorporate more features, such as touch-sensitive controls and haptic feedback, designers must carefully balance functionality with ergonomics and user-friendliness.
Another significant challenge lies in the standardization of steering wheel interfaces across different vehicle models and manufacturers. The lack of a unified approach to steering wheel design and functionality can lead to confusion for drivers when switching between vehicles, potentially impacting safety and user experience. This issue is further complicated by the rapid pace of technological advancement, which can result in fragmented development efforts and incompatible systems.
The increasing complexity of steering wheel systems also presents challenges in terms of reliability and maintenance. As more electronic components and sensors are integrated into steering wheels, the potential for malfunctions or failures increases. This not only raises concerns about vehicle safety but also impacts the long-term cost of ownership and maintenance for consumers.
Cybersecurity is another critical challenge facing steering wheel technology. With the integration of advanced features and connectivity options, steering wheels are becoming more vulnerable to potential cyber attacks. Ensuring the security of these systems is paramount, as any breach could have severe consequences for vehicle control and passenger safety.
Furthermore, the transition towards autonomous vehicles poses unique challenges for steering wheel design. As vehicles become more automated, the role of the steering wheel is evolving, and designers must consider how to create interfaces that can seamlessly transition between manual and autonomous driving modes. This includes developing intuitive handover mechanisms and clear communication systems between the vehicle and the driver.
Regulatory compliance and safety standards also present ongoing challenges for steering wheel technology. As new features are introduced, manufacturers must navigate complex regulatory landscapes to ensure their innovations meet stringent safety requirements across different regions and jurisdictions. This can sometimes slow down the pace of innovation and market introduction of new steering wheel applications.
Lastly, the cost of implementing advanced steering wheel technologies remains a significant hurdle, particularly for mass-market vehicles. Balancing the desire for innovative features with the need to maintain affordable vehicle prices requires careful consideration and often involves trade-offs in functionality or quality.
Another significant challenge lies in the standardization of steering wheel interfaces across different vehicle models and manufacturers. The lack of a unified approach to steering wheel design and functionality can lead to confusion for drivers when switching between vehicles, potentially impacting safety and user experience. This issue is further complicated by the rapid pace of technological advancement, which can result in fragmented development efforts and incompatible systems.
The increasing complexity of steering wheel systems also presents challenges in terms of reliability and maintenance. As more electronic components and sensors are integrated into steering wheels, the potential for malfunctions or failures increases. This not only raises concerns about vehicle safety but also impacts the long-term cost of ownership and maintenance for consumers.
Cybersecurity is another critical challenge facing steering wheel technology. With the integration of advanced features and connectivity options, steering wheels are becoming more vulnerable to potential cyber attacks. Ensuring the security of these systems is paramount, as any breach could have severe consequences for vehicle control and passenger safety.
Furthermore, the transition towards autonomous vehicles poses unique challenges for steering wheel design. As vehicles become more automated, the role of the steering wheel is evolving, and designers must consider how to create interfaces that can seamlessly transition between manual and autonomous driving modes. This includes developing intuitive handover mechanisms and clear communication systems between the vehicle and the driver.
Regulatory compliance and safety standards also present ongoing challenges for steering wheel technology. As new features are introduced, manufacturers must navigate complex regulatory landscapes to ensure their innovations meet stringent safety requirements across different regions and jurisdictions. This can sometimes slow down the pace of innovation and market introduction of new steering wheel applications.
Lastly, the cost of implementing advanced steering wheel technologies remains a significant hurdle, particularly for mass-market vehicles. Balancing the desire for innovative features with the need to maintain affordable vehicle prices requires careful consideration and often involves trade-offs in functionality or quality.
Existing Smart Steering Wheel Solutions
01 Steering wheel design and ergonomics
Innovations in steering wheel design focus on improving ergonomics and driver comfort. This includes optimizing the shape, size, and grip of the steering wheel to reduce fatigue during long drives and enhance control. Advanced materials and manufacturing techniques are employed to create steering wheels that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.- Steering wheel design and ergonomics: Innovations in steering wheel design focus on improving ergonomics and driver comfort. This includes optimizing the shape, size, and grip of the steering wheel to reduce fatigue during long drives and enhance control. Advanced materials and manufacturing techniques are employed to create steering wheels that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
- Integration of controls and displays: Modern steering wheels incorporate various controls and displays to enhance driver convenience and safety. These may include buttons for audio control, cruise control, and phone operations, as well as small screens or heads-up displays for providing important vehicle information without requiring the driver to look away from the road.
- Steering wheel heating and cooling systems: To improve comfort in various weather conditions, steering wheels are being equipped with heating and cooling systems. These systems can quickly adjust the temperature of the steering wheel surface, providing a more pleasant driving experience in extreme hot or cold environments.
- Advanced safety features in steering wheels: Steering wheels are being designed with advanced safety features to protect drivers in the event of a collision. This includes the integration of airbags directly into the steering wheel, as well as energy-absorbing materials and structures to reduce the risk of injury during impacts.
- Adjustable and customizable steering wheels: Innovations in steering wheel technology allow for greater adjustability and customization. This includes steering wheels that can change shape or size to accommodate different drivers, as well as those that can be easily removed or replaced for racing or specialized applications. Some designs also incorporate memory functions to recall preferred settings for multiple drivers.
02 Integration of controls and displays
Modern steering wheels incorporate various controls and displays to enhance driver convenience and safety. These may include buttons for audio control, cruise control, and voice commands, as well as small screens or heads-up displays for providing important vehicle information without requiring the driver to look away from the road.Expand Specific Solutions03 Steering wheel heating and cooling systems
To improve comfort in various weather conditions, steering wheels are being equipped with heating and cooling systems. These systems can quickly adjust the temperature of the steering wheel surface, providing a more pleasant driving experience in extreme hot or cold environments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advanced safety features in steering wheels
Steering wheels are being developed with advanced safety features such as airbag integration, impact-absorbing materials, and sensors for detecting driver grip and alertness. These innovations aim to reduce injuries in the event of a collision and improve overall vehicle safety.Expand Specific Solutions05 Adjustable and customizable steering wheels
Steering wheels with adjustable features are being developed to cater to individual driver preferences. These may include telescoping and tilting mechanisms, as well as customizable grip materials and button layouts. Some designs even allow for quick removal and replacement of the steering wheel for improved vehicle security or racing applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Steering Wheel Tech Industry
The steering wheel applications market for personal transport is in a dynamic growth phase, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for smart, connected vehicles. The market size is expanding rapidly, with major automotive players like BMW, Ford, BYD, Hyundai, and Tesla investing heavily in innovative steering technologies. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring traditional automakers, tech giants, and specialized suppliers. While established companies like ThyssenKrupp and JTEKT have a strong foothold, emerging players such as Polestar and LG Electronics are disrupting the market with cutting-edge solutions. The technology maturity varies, ranging from advanced driver assistance systems to fully autonomous steering, with companies at different stages of development and implementation.
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG
Technical Solution: BMW has made significant advancements in steering wheel applications for personal transport. The company has developed a multi-function steering wheel that incorporates touch-sensitive controls and haptic feedback, allowing drivers to manage various vehicle functions without taking their hands off the wheel[1]. BMW's latest steering wheels feature integrated LED displays that provide real-time information and alerts directly in the driver's line of sight[2]. The company has also implemented variable-ratio steering systems that adjust the steering response based on vehicle speed and driving mode, enhancing both comfort and sportiness[3]. In terms of autonomous driving, BMW has developed a retractable steering wheel concept for future self-driving vehicles, which can be tucked away when not in use, transforming the cabin space[4]. Additionally, BMW has introduced gesture control technology that works in conjunction with the steering wheel, allowing drivers to perform certain functions with simple hand movements[5].
Strengths: Advanced integration of technology and ergonomics; Adaptable steering systems for various driving conditions. Weaknesses: Complexity of systems may lead to higher maintenance costs; Potential for information overload with multiple integrated displays and controls.
Ford Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Ford has made significant strides in steering wheel applications for personal transport. The company has developed an adaptive steering technology that changes the ratio between the driver's steering input and how much the front wheels turn[1]. This system uses an electric motor and gearing unit to add to or subtract from the driver's steering inputs, requiring less steering input for low-speed maneuvers and providing more precise steering at high speeds[2]. Ford has also integrated advanced driver-assist technologies into its steering systems, including Lane-Keeping Aid and Adaptive Cruise Control with Stop-and-Go and Lane Centering[3]. The company's latest steering wheels incorporate capacitive touch sensors that can detect the driver's hands, enhancing the effectiveness of driver alert systems[4]. Ford has also experimented with shape-shifting steering wheel designs for future autonomous vehicles, which can transform into a tablet-like device when self-driving mode is engaged[5].
Strengths: Adaptive steering technology improves maneuverability and comfort; Integration of advanced driver-assist features. Weaknesses: Complexity of systems may increase maintenance costs; Potential for over-reliance on electronic assistance.
Core Innovations in Steering Wheel Applications
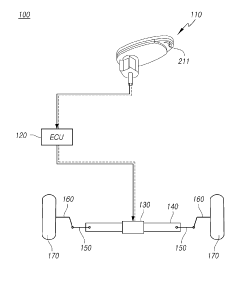
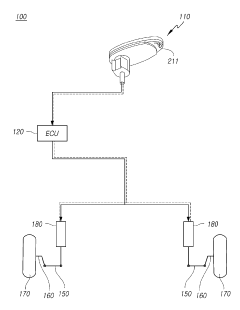
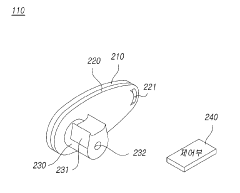
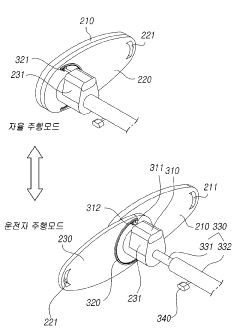
Transforming steering wheel and steering apparatus including the same and driving method thereof
PatentActiveKR1020190111233A
Innovation
- A deformable steering wheel design with grip members that can unfold or fold around a coupling shaft member, controlled by an electronic unit, allowing the steering wheel to adapt to different driving modes and providing a wider space in autonomous driving and easier steering in manual modes.
Personal transport vehicle
PatentActiveUS20200385081A9
Innovation
- A two-wheeled personal transport vehicle with a low center of gravity and large contact patch tires that can self-balance without a stand, incorporating a steering assembly and propulsion device within the wheels for a compact and efficient design, allowing for easy disassembly and transport.
Safety Regulations for Smart Steering Systems
As smart steering systems continue to evolve and become more prevalent in personal transport, the need for comprehensive safety regulations has become paramount. These regulations aim to ensure that advanced steering technologies enhance road safety rather than compromise it. Regulatory bodies worldwide are working to establish guidelines that address the unique challenges posed by intelligent steering systems.
One of the primary focuses of safety regulations is the reliability and robustness of smart steering systems. Manufacturers are required to demonstrate that their systems can operate consistently under various conditions, including adverse weather, electromagnetic interference, and potential software glitches. Rigorous testing protocols are being developed to simulate real-world scenarios and assess the system's response to unexpected events or failures.
Another critical aspect of safety regulations is the human-machine interface. As steering systems become more automated, clear guidelines are needed to ensure that drivers remain engaged and capable of taking control when necessary. Regulations are being formulated to standardize warning systems, control transitions, and driver monitoring technologies. These measures aim to prevent over-reliance on automated features and maintain driver awareness.
Data security and privacy are also significant concerns addressed by safety regulations. Smart steering systems often collect and process large amounts of data, including vehicle location, driver behavior, and environmental conditions. Regulations are being put in place to protect this sensitive information from unauthorized access or misuse, ensuring that personal data is handled responsibly and securely.
Interoperability and standardization form another crucial component of safety regulations. As different manufacturers develop proprietary smart steering technologies, there is a need for common protocols and interfaces to ensure seamless integration with other vehicle systems and infrastructure. Regulatory bodies are working towards establishing industry-wide standards that promote compatibility and facilitate the widespread adoption of smart steering technologies.
Emergency override capabilities are a key focus area for safety regulators. Guidelines are being developed to ensure that smart steering systems include fail-safe mechanisms that allow drivers to override automated functions in critical situations. These regulations aim to maintain a balance between the benefits of automation and the need for human control in unpredictable scenarios.
As the technology continues to advance, safety regulations for smart steering systems are expected to evolve. Regulatory bodies are adopting a proactive approach, collaborating with industry experts, researchers, and manufacturers to anticipate potential risks and develop appropriate safeguards. This ongoing process aims to create a regulatory framework that fosters innovation while prioritizing the safety of all road users.
One of the primary focuses of safety regulations is the reliability and robustness of smart steering systems. Manufacturers are required to demonstrate that their systems can operate consistently under various conditions, including adverse weather, electromagnetic interference, and potential software glitches. Rigorous testing protocols are being developed to simulate real-world scenarios and assess the system's response to unexpected events or failures.
Another critical aspect of safety regulations is the human-machine interface. As steering systems become more automated, clear guidelines are needed to ensure that drivers remain engaged and capable of taking control when necessary. Regulations are being formulated to standardize warning systems, control transitions, and driver monitoring technologies. These measures aim to prevent over-reliance on automated features and maintain driver awareness.
Data security and privacy are also significant concerns addressed by safety regulations. Smart steering systems often collect and process large amounts of data, including vehicle location, driver behavior, and environmental conditions. Regulations are being put in place to protect this sensitive information from unauthorized access or misuse, ensuring that personal data is handled responsibly and securely.
Interoperability and standardization form another crucial component of safety regulations. As different manufacturers develop proprietary smart steering technologies, there is a need for common protocols and interfaces to ensure seamless integration with other vehicle systems and infrastructure. Regulatory bodies are working towards establishing industry-wide standards that promote compatibility and facilitate the widespread adoption of smart steering technologies.
Emergency override capabilities are a key focus area for safety regulators. Guidelines are being developed to ensure that smart steering systems include fail-safe mechanisms that allow drivers to override automated functions in critical situations. These regulations aim to maintain a balance between the benefits of automation and the need for human control in unpredictable scenarios.
As the technology continues to advance, safety regulations for smart steering systems are expected to evolve. Regulatory bodies are adopting a proactive approach, collaborating with industry experts, researchers, and manufacturers to anticipate potential risks and develop appropriate safeguards. This ongoing process aims to create a regulatory framework that fosters innovation while prioritizing the safety of all road users.
Human-Machine Interface in Steering Wheel Design
The human-machine interface (HMI) in steering wheel design has become a critical focal point in the evolution of personal transport. As vehicles become increasingly sophisticated and connected, the steering wheel has transformed from a simple control mechanism into a multifunctional hub for driver interaction and vehicle management.
Modern steering wheel designs incorporate a wide array of sensors and input devices, allowing drivers to control various vehicle functions without removing their hands from the wheel. Touch-sensitive surfaces, haptic feedback systems, and voice recognition technologies are being integrated to create intuitive and responsive interfaces. These advancements aim to minimize driver distraction while maximizing accessibility to essential features.
One of the key trends in steering wheel HMI is the incorporation of customizable displays. These screens, often integrated into the center of the wheel, can provide real-time information on vehicle status, navigation, and infotainment systems. The ability to personalize these displays according to individual preferences enhances the driving experience and improves overall user satisfaction.
Gesture recognition technology is another innovative feature being explored in steering wheel design. By interpreting hand movements and gestures, drivers can control various functions without the need for physical buttons or switches. This technology not only streamlines the interface but also contributes to a cleaner, more ergonomic design.
Safety considerations play a crucial role in steering wheel HMI development. Manufacturers are implementing advanced driver monitoring systems within the steering wheel, using sensors to detect driver fatigue, distraction, or impairment. These systems can provide warnings or even initiate autonomous safety measures when necessary.
The integration of biometric sensors in steering wheels is an emerging trend with significant potential. These sensors can monitor the driver's vital signs, such as heart rate and stress levels, providing valuable data for both safety and health applications. This information can be used to adjust vehicle settings or alert the driver to potential health issues.
As autonomous driving technologies continue to advance, the role of the steering wheel in HMI is evolving. Concepts for retractable or transformable steering wheels are being developed, allowing for seamless transitions between manual and autonomous driving modes. These designs aim to optimize space and functionality in future vehicle interiors.
The challenge for designers and engineers lies in balancing the integration of advanced technologies with the need for simplicity and ease of use. As steering wheels become more complex, ensuring that drivers can interact with these systems safely and efficiently remains paramount. The future of steering wheel HMI will likely see continued innovation in areas such as augmented reality displays, advanced haptics, and AI-driven personalization to create truly intuitive and responsive interfaces.
Modern steering wheel designs incorporate a wide array of sensors and input devices, allowing drivers to control various vehicle functions without removing their hands from the wheel. Touch-sensitive surfaces, haptic feedback systems, and voice recognition technologies are being integrated to create intuitive and responsive interfaces. These advancements aim to minimize driver distraction while maximizing accessibility to essential features.
One of the key trends in steering wheel HMI is the incorporation of customizable displays. These screens, often integrated into the center of the wheel, can provide real-time information on vehicle status, navigation, and infotainment systems. The ability to personalize these displays according to individual preferences enhances the driving experience and improves overall user satisfaction.
Gesture recognition technology is another innovative feature being explored in steering wheel design. By interpreting hand movements and gestures, drivers can control various functions without the need for physical buttons or switches. This technology not only streamlines the interface but also contributes to a cleaner, more ergonomic design.
Safety considerations play a crucial role in steering wheel HMI development. Manufacturers are implementing advanced driver monitoring systems within the steering wheel, using sensors to detect driver fatigue, distraction, or impairment. These systems can provide warnings or even initiate autonomous safety measures when necessary.
The integration of biometric sensors in steering wheels is an emerging trend with significant potential. These sensors can monitor the driver's vital signs, such as heart rate and stress levels, providing valuable data for both safety and health applications. This information can be used to adjust vehicle settings or alert the driver to potential health issues.
As autonomous driving technologies continue to advance, the role of the steering wheel in HMI is evolving. Concepts for retractable or transformable steering wheels are being developed, allowing for seamless transitions between manual and autonomous driving modes. These designs aim to optimize space and functionality in future vehicle interiors.
The challenge for designers and engineers lies in balancing the integration of advanced technologies with the need for simplicity and ease of use. As steering wheels become more complex, ensuring that drivers can interact with these systems safely and efficiently remains paramount. The future of steering wheel HMI will likely see continued innovation in areas such as augmented reality displays, advanced haptics, and AI-driven personalization to create truly intuitive and responsive interfaces.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!