How telecommunication advances support PHEV expansion
AUG 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Telecom-PHEV Integration Background and Objectives
The integration of telecommunications and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) represents a significant technological convergence that has been evolving over the past decade. This fusion aims to enhance the efficiency, safety, and user experience of PHEVs while simultaneously supporting the expansion of electric vehicle infrastructure. The primary objective of this integration is to leverage advanced telecommunication technologies to overcome the challenges associated with PHEV adoption and to accelerate the transition towards sustainable transportation.
Historically, the development of PHEVs has been driven by the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. However, the widespread adoption of these vehicles has been hindered by factors such as limited range, long charging times, and inadequate charging infrastructure. The incorporation of telecommunication technologies into PHEVs seeks to address these limitations by enabling smart charging, real-time vehicle monitoring, and improved energy management.
The technological evolution in this field has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, basic telematics systems were introduced to provide vehicle location and diagnostic information. This was followed by the integration of cellular networks, allowing for remote vehicle access and control. More recently, the advent of 5G technology has opened up new possibilities for high-speed, low-latency communication between vehicles, charging stations, and the power grid.
Current trends in telecom-PHEV integration focus on developing Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication systems, which enable PHEVs to interact with their surroundings, including other vehicles, infrastructure, and the power grid. This technology aims to optimize energy consumption, enhance traffic management, and improve overall road safety. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on cybersecurity to protect these connected vehicles from potential threats.
The expected outcomes of this technological integration are multifaceted. From an environmental perspective, it is anticipated that improved energy management and charging optimization will lead to reduced emissions and more efficient use of renewable energy sources. For consumers, the integration promises enhanced convenience through features such as predictive maintenance, personalized charging schedules, and seamless integration with smart home systems.
Looking ahead, the telecom-PHEV integration is poised to play a crucial role in the development of smart cities and sustainable transportation networks. As telecommunication technologies continue to advance, they are expected to further support PHEV expansion by addressing current limitations and unlocking new capabilities, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and connected future of mobility.
Historically, the development of PHEVs has been driven by the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. However, the widespread adoption of these vehicles has been hindered by factors such as limited range, long charging times, and inadequate charging infrastructure. The incorporation of telecommunication technologies into PHEVs seeks to address these limitations by enabling smart charging, real-time vehicle monitoring, and improved energy management.
The technological evolution in this field has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, basic telematics systems were introduced to provide vehicle location and diagnostic information. This was followed by the integration of cellular networks, allowing for remote vehicle access and control. More recently, the advent of 5G technology has opened up new possibilities for high-speed, low-latency communication between vehicles, charging stations, and the power grid.
Current trends in telecom-PHEV integration focus on developing Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication systems, which enable PHEVs to interact with their surroundings, including other vehicles, infrastructure, and the power grid. This technology aims to optimize energy consumption, enhance traffic management, and improve overall road safety. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on cybersecurity to protect these connected vehicles from potential threats.
The expected outcomes of this technological integration are multifaceted. From an environmental perspective, it is anticipated that improved energy management and charging optimization will lead to reduced emissions and more efficient use of renewable energy sources. For consumers, the integration promises enhanced convenience through features such as predictive maintenance, personalized charging schedules, and seamless integration with smart home systems.
Looking ahead, the telecom-PHEV integration is poised to play a crucial role in the development of smart cities and sustainable transportation networks. As telecommunication technologies continue to advance, they are expected to further support PHEV expansion by addressing current limitations and unlocking new capabilities, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and connected future of mobility.
PHEV Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) has been steadily increasing, driven by a combination of environmental concerns, government incentives, and advancements in telecommunication technologies. As consumers become more environmentally conscious and seek to reduce their carbon footprint, PHEVs offer an attractive solution that bridges the gap between traditional internal combustion engines and fully electric vehicles.
The global PHEV market has shown significant growth potential, with sales volumes rising year over year. This trend is expected to continue as more countries implement stricter emissions regulations and set targets for electric vehicle adoption. Major automotive markets such as China, Europe, and North America have seen particularly strong demand for PHEVs, with these regions accounting for the majority of global sales.
Telecommunication advances play a crucial role in supporting the expansion of the PHEV market. The integration of advanced connectivity features in PHEVs has become a key selling point for consumers. These features include real-time navigation systems that can locate charging stations, remote vehicle monitoring and control through smartphone apps, and over-the-air software updates that can improve vehicle performance and efficiency.
The demand for PHEVs is also driven by the growing infrastructure of smart grids and charging networks. Telecommunication technologies enable seamless communication between vehicles, charging stations, and power grids, allowing for efficient energy management and optimized charging schedules. This integration helps alleviate range anxiety and makes PHEVs more practical for everyday use.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards vehicles with advanced connectivity features, and PHEVs are well-positioned to meet these expectations. The ability to access real-time vehicle data, such as battery status, charging progress, and energy consumption, enhances the overall ownership experience and contributes to increased market demand.
Furthermore, the rise of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, facilitated by telecommunication advances, is creating new opportunities for PHEV owners. This technology allows PHEVs to not only draw power from the grid but also feed excess energy back, potentially generating revenue for owners and supporting grid stability. As awareness of these capabilities grows, it is likely to further stimulate market demand for PHEVs.
The corporate and fleet markets also represent a significant growth area for PHEVs. Businesses are increasingly adopting PHEVs to meet sustainability goals and reduce operating costs. Telecommunication technologies enable fleet managers to monitor vehicle performance, optimize routes, and manage charging schedules efficiently, making PHEVs an attractive option for commercial applications.
The global PHEV market has shown significant growth potential, with sales volumes rising year over year. This trend is expected to continue as more countries implement stricter emissions regulations and set targets for electric vehicle adoption. Major automotive markets such as China, Europe, and North America have seen particularly strong demand for PHEVs, with these regions accounting for the majority of global sales.
Telecommunication advances play a crucial role in supporting the expansion of the PHEV market. The integration of advanced connectivity features in PHEVs has become a key selling point for consumers. These features include real-time navigation systems that can locate charging stations, remote vehicle monitoring and control through smartphone apps, and over-the-air software updates that can improve vehicle performance and efficiency.
The demand for PHEVs is also driven by the growing infrastructure of smart grids and charging networks. Telecommunication technologies enable seamless communication between vehicles, charging stations, and power grids, allowing for efficient energy management and optimized charging schedules. This integration helps alleviate range anxiety and makes PHEVs more practical for everyday use.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards vehicles with advanced connectivity features, and PHEVs are well-positioned to meet these expectations. The ability to access real-time vehicle data, such as battery status, charging progress, and energy consumption, enhances the overall ownership experience and contributes to increased market demand.
Furthermore, the rise of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, facilitated by telecommunication advances, is creating new opportunities for PHEV owners. This technology allows PHEVs to not only draw power from the grid but also feed excess energy back, potentially generating revenue for owners and supporting grid stability. As awareness of these capabilities grows, it is likely to further stimulate market demand for PHEVs.
The corporate and fleet markets also represent a significant growth area for PHEVs. Businesses are increasingly adopting PHEVs to meet sustainability goals and reduce operating costs. Telecommunication technologies enable fleet managers to monitor vehicle performance, optimize routes, and manage charging schedules efficiently, making PHEVs an attractive option for commercial applications.
Telecom Challenges in PHEV Support
The expansion of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) presents significant challenges for telecommunication systems. As PHEVs become more prevalent, the demand for robust and reliable communication networks increases exponentially. These vehicles rely heavily on real-time data exchange for optimal performance, energy management, and user experience.
One of the primary challenges is the need for seamless connectivity across vast geographical areas. PHEVs require constant communication with charging stations, energy grids, and traffic management systems. This necessitates a comprehensive network infrastructure that can provide uninterrupted coverage, even in remote or rural areas where traditional cellular networks may be limited.
Data security and privacy pose another critical challenge. PHEVs generate and transmit sensitive information, including location data, charging patterns, and personal user preferences. Ensuring the protection of this data from cyber threats and unauthorized access is paramount. Telecommunication systems must implement robust encryption protocols and secure data transmission methods to safeguard user information and maintain trust in the PHEV ecosystem.
The sheer volume of data generated by PHEVs presents a significant bandwidth challenge. Each vehicle continuously transmits and receives data related to battery status, charging availability, route optimization, and vehicle diagnostics. As the number of PHEVs on the road increases, telecommunication networks must be capable of handling this surge in data traffic without compromising speed or reliability.
Latency is another crucial factor in supporting PHEV expansion. Many PHEV functions, such as real-time energy management and dynamic route planning, require near-instantaneous data processing and transmission. Telecommunication systems must minimize latency to ensure these time-sensitive operations function effectively, enhancing vehicle performance and user satisfaction.
Interoperability between different communication protocols and standards presents an ongoing challenge. PHEVs may utilize various communication technologies, including cellular networks, Wi-Fi, and dedicated short-range communications (DSRC). Ensuring seamless integration and compatibility between these diverse systems is essential for creating a cohesive and efficient PHEV ecosystem.
The need for scalability is another significant telecommunication challenge. As PHEV adoption rates increase, the infrastructure must be capable of accommodating a growing number of connected vehicles without degradation in service quality. This requires forward-thinking network design and the ability to rapidly deploy additional capacity as demand grows.
Lastly, the integration of PHEVs with smart grid systems introduces complex telecommunication challenges. Effective vehicle-to-grid (V2G) communication is crucial for managing energy flow, optimizing charging schedules, and balancing load on the electrical grid. Telecommunication systems must facilitate this bidirectional communication while ensuring reliability and minimizing latency.
One of the primary challenges is the need for seamless connectivity across vast geographical areas. PHEVs require constant communication with charging stations, energy grids, and traffic management systems. This necessitates a comprehensive network infrastructure that can provide uninterrupted coverage, even in remote or rural areas where traditional cellular networks may be limited.
Data security and privacy pose another critical challenge. PHEVs generate and transmit sensitive information, including location data, charging patterns, and personal user preferences. Ensuring the protection of this data from cyber threats and unauthorized access is paramount. Telecommunication systems must implement robust encryption protocols and secure data transmission methods to safeguard user information and maintain trust in the PHEV ecosystem.
The sheer volume of data generated by PHEVs presents a significant bandwidth challenge. Each vehicle continuously transmits and receives data related to battery status, charging availability, route optimization, and vehicle diagnostics. As the number of PHEVs on the road increases, telecommunication networks must be capable of handling this surge in data traffic without compromising speed or reliability.
Latency is another crucial factor in supporting PHEV expansion. Many PHEV functions, such as real-time energy management and dynamic route planning, require near-instantaneous data processing and transmission. Telecommunication systems must minimize latency to ensure these time-sensitive operations function effectively, enhancing vehicle performance and user satisfaction.
Interoperability between different communication protocols and standards presents an ongoing challenge. PHEVs may utilize various communication technologies, including cellular networks, Wi-Fi, and dedicated short-range communications (DSRC). Ensuring seamless integration and compatibility between these diverse systems is essential for creating a cohesive and efficient PHEV ecosystem.
The need for scalability is another significant telecommunication challenge. As PHEV adoption rates increase, the infrastructure must be capable of accommodating a growing number of connected vehicles without degradation in service quality. This requires forward-thinking network design and the ability to rapidly deploy additional capacity as demand grows.
Lastly, the integration of PHEVs with smart grid systems introduces complex telecommunication challenges. Effective vehicle-to-grid (V2G) communication is crucial for managing energy flow, optimizing charging schedules, and balancing load on the electrical grid. Telecommunication systems must facilitate this bidirectional communication while ensuring reliability and minimizing latency.
Current Telecom Solutions for PHEVs
01 Network optimization and management
Advancements in telecommunication networks focus on optimizing performance, managing resources efficiently, and improving overall network functionality. This includes techniques for load balancing, traffic management, and enhancing network capacity to handle increasing data demands.- Network infrastructure improvements: Advancements in telecommunication network infrastructure, including the development of more efficient routing protocols, improved bandwidth allocation, and enhanced network management systems. These improvements lead to faster and more reliable communication services, supporting the growing demand for data-intensive applications and services.
- Mobile communication technologies: Evolution of mobile communication technologies, encompassing advancements in cellular networks, smartphone capabilities, and wireless protocols. This includes the development of 4G and 5G networks, improved handover mechanisms, and enhanced mobile data services, enabling seamless connectivity and higher data transfer rates for mobile users.
- Voice over IP (VoIP) and unified communications: Integration of voice, video, and data communications over IP networks, leading to the development of VoIP technologies and unified communication platforms. These advancements enable more flexible and cost-effective communication solutions for businesses and individuals, including features like video conferencing and instant messaging.
- Security and encryption in telecommunications: Enhancements in telecommunication security, including advanced encryption methods, secure authentication protocols, and improved network protection mechanisms. These developments aim to safeguard communication channels against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats, ensuring the privacy and integrity of transmitted information.
- User interface and experience improvements: Advancements in telecommunication device interfaces and user experience, including the development of more intuitive and accessible communication applications, improved voice recognition systems, and enhanced visual displays. These improvements make telecommunication technologies more user-friendly and accessible to a wider range of users.
02 Voice over IP (VoIP) technology
VoIP technology has revolutionized telecommunications by enabling voice communication over internet protocols. Innovations in this area include improved call quality, integration with existing telephony systems, and enhanced features for both personal and business communications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Mobile communication advancements
Developments in mobile communication technologies have led to improved connectivity, faster data speeds, and enhanced user experiences. This includes advancements in cellular networks, smartphone capabilities, and seamless integration of various communication services on mobile devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Security and privacy enhancements
Telecommunication advances have focused on improving security measures and protecting user privacy. This includes encryption techniques, secure authentication methods, and protocols to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches in communication networks.Expand Specific Solutions05 User interface and experience improvements
Advancements in telecommunication user interfaces have led to more intuitive and user-friendly communication experiences. This includes innovations in graphical user interfaces, voice recognition technologies, and seamless integration of various communication channels for enhanced user convenience.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Telecom-PHEV Ecosystem
The telecommunication advances supporting PHEV expansion are in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological maturity. The industry is experiencing rapid development as major players like Hyundai Motor, Toyota Motor, and Tesla invest heavily in PHEV technology. The market is characterized by intense competition among established automakers and new entrants, driving innovation in areas such as battery technology, charging infrastructure, and vehicle-to-grid communication. Companies like Huawei Technologies and Qualcomm are contributing to advancements in connectivity and data transmission, crucial for PHEV integration with smart grids. As the technology matures, we're seeing increased collaboration between automotive, telecom, and energy sectors to create more efficient and connected PHEV ecosystems.
Nokia Technologies Oy
Technical Solution: Nokia has developed a comprehensive telecommunication solution for PHEV expansion, leveraging its expertise in 5G and IoT technologies. Their approach includes a dedicated network slice for PHEV communications, ensuring prioritized and secure connectivity. Nokia's IMPACT IoT platform enables seamless integration of PHEVs with smart city infrastructure, facilitating efficient energy management and charging optimization[2]. The company has also introduced advanced location services that enhance navigation and charging station discovery for PHEV users, improving the overall driving experience[4].
Strengths: Extensive experience in telecommunications, strong 5G capabilities, and robust IoT platform. Weaknesses: Limited direct experience in automotive sector, potential need for partnerships with car manufacturers.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei has developed advanced 5G technologies specifically tailored for PHEV applications. Their solution includes high-speed, low-latency 5G networks that enable real-time communication between vehicles and charging infrastructure. Huawei's 5G V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) technology allows PHEVs to communicate with smart grids, optimizing charging schedules and improving overall energy efficiency[1]. The company has also introduced AI-powered network slicing, which prioritizes critical PHEV communications, ensuring reliable connectivity for essential functions like remote diagnostics and over-the-air updates[3].
Strengths: Strong 5G infrastructure, advanced V2X technology, and AI integration. Weaknesses: Potential geopolitical challenges in some markets, and reliance on partnerships for automotive integration.
Core Telecom Innovations for PHEVs
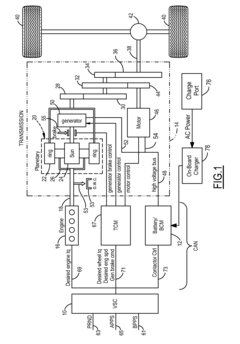
System and method for charging electric vehicle from another electric vehicle
PatentPendingCN116945956A
Innovation
- A real-time server (RTS) is used to wirelessly communicate with multiple communication devices. The RTS transmits charging requests, power distribution proposals, suggested locations on the map, charging parameters and payment information to the associated PEVs to achieve charging service coordination between PEVs. , and update the geographical location of each PEV.
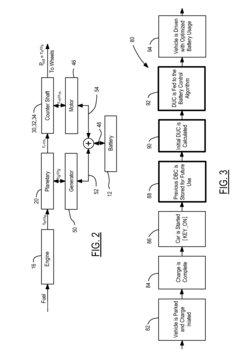
Adaptive Initial Estimation and Dynamic Determination and Update of Distance Until Charge of a Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle
PatentActiveUS20110184600A1
Innovation
- A method and system that dynamically control battery usage based on the estimated or user-provided 'distance until charge' (DUC) value, utilizing historical data and real-time information from navigation systems to optimize battery depletion and charging strategies.
Smart Grid Integration for PHEVs
The integration of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) with smart grid technology represents a significant advancement in the synergy between transportation and energy systems. Smart grids, characterized by their ability to intelligently manage electricity distribution, offer numerous benefits for PHEV adoption and operation. These advanced grid systems utilize two-way communication between utilities and consumers, enabling real-time monitoring and control of energy flow.
For PHEVs, smart grid integration provides several key advantages. Firstly, it allows for optimized charging schedules, enabling vehicles to charge during off-peak hours when electricity demand and costs are lower. This not only reduces the strain on the grid but also minimizes charging expenses for PHEV owners. Additionally, smart grids can facilitate vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, where PHEVs can serve as mobile energy storage units, feeding electricity back into the grid during peak demand periods.
The implementation of smart charging infrastructure is crucial for effective PHEV integration. This includes the deployment of smart charging stations that can communicate with both the grid and vehicles, adjusting charging rates based on grid conditions and user preferences. Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) plays a vital role in this ecosystem, providing detailed energy consumption data and enabling dynamic pricing models.
Telecommunication advancements are fundamental to the successful integration of PHEVs with smart grids. High-speed, low-latency communication networks are essential for real-time data exchange between vehicles, charging stations, and grid operators. Technologies such as 5G and beyond are particularly promising, offering the bandwidth and responsiveness required for sophisticated grid management and V2G applications.
Moreover, smart grid integration supports the broader adoption of PHEVs by addressing range anxiety and charging convenience concerns. Through intelligent energy management and predictive analytics, smart grids can help optimize the distribution of charging stations and predict energy demand patterns, ensuring that the infrastructure can support growing PHEV populations.
As the integration of PHEVs and smart grids progresses, it paves the way for more sustainable and efficient transportation systems. This symbiotic relationship not only enhances the value proposition of PHEVs but also contributes to the overall stability and resilience of the electrical grid, marking a significant step towards a more interconnected and environmentally friendly energy ecosystem.
For PHEVs, smart grid integration provides several key advantages. Firstly, it allows for optimized charging schedules, enabling vehicles to charge during off-peak hours when electricity demand and costs are lower. This not only reduces the strain on the grid but also minimizes charging expenses for PHEV owners. Additionally, smart grids can facilitate vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, where PHEVs can serve as mobile energy storage units, feeding electricity back into the grid during peak demand periods.
The implementation of smart charging infrastructure is crucial for effective PHEV integration. This includes the deployment of smart charging stations that can communicate with both the grid and vehicles, adjusting charging rates based on grid conditions and user preferences. Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) plays a vital role in this ecosystem, providing detailed energy consumption data and enabling dynamic pricing models.
Telecommunication advancements are fundamental to the successful integration of PHEVs with smart grids. High-speed, low-latency communication networks are essential for real-time data exchange between vehicles, charging stations, and grid operators. Technologies such as 5G and beyond are particularly promising, offering the bandwidth and responsiveness required for sophisticated grid management and V2G applications.
Moreover, smart grid integration supports the broader adoption of PHEVs by addressing range anxiety and charging convenience concerns. Through intelligent energy management and predictive analytics, smart grids can help optimize the distribution of charging stations and predict energy demand patterns, ensuring that the infrastructure can support growing PHEV populations.
As the integration of PHEVs and smart grids progresses, it paves the way for more sustainable and efficient transportation systems. This symbiotic relationship not only enhances the value proposition of PHEVs but also contributes to the overall stability and resilience of the electrical grid, marking a significant step towards a more interconnected and environmentally friendly energy ecosystem.
Cybersecurity in Telecom-PHEV Systems
As telecommunication technologies advance and support the expansion of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), the importance of cybersecurity in these interconnected systems becomes paramount. The integration of telecom and PHEV systems creates a complex network that requires robust security measures to protect against potential cyber threats.
One of the primary concerns in telecom-PHEV systems is the protection of sensitive data transmitted between vehicles and charging infrastructure. This includes personal information, payment details, and vehicle diagnostics. Encryption protocols and secure communication channels are essential to safeguard this data from unauthorized access or interception.
Another critical aspect of cybersecurity in these systems is the prevention of unauthorized access to vehicle control systems. As PHEVs become more connected, the risk of remote hacking increases. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms and access controls is crucial to prevent malicious actors from gaining control over vehicle functions or manipulating charging processes.
The charging infrastructure itself presents a potential target for cyberattacks. Securing the communication between charging stations and the power grid is vital to prevent disruptions in energy distribution or unauthorized energy consumption. This requires the implementation of secure protocols and regular security audits of the charging network.
As PHEVs rely increasingly on over-the-air updates for software and firmware, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of these updates becomes a key cybersecurity challenge. Robust verification processes and secure update mechanisms are necessary to prevent the installation of malicious code or compromised software versions.
The interconnected nature of telecom-PHEV systems also raises concerns about privacy and data protection. Strict data governance policies and compliance with relevant regulations, such as GDPR, are essential to protect user information and maintain trust in the ecosystem.
To address these cybersecurity challenges, a multi-layered approach is required. This includes implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and establishing incident response plans. Additionally, fostering collaboration between automotive manufacturers, telecom providers, and cybersecurity experts is crucial for developing comprehensive security solutions.
As the PHEV market expands, standardization of cybersecurity protocols across the industry becomes increasingly important. This ensures interoperability and consistent security measures across different vehicle models and charging networks. Industry-wide initiatives and regulatory frameworks play a vital role in establishing and enforcing these standards.
One of the primary concerns in telecom-PHEV systems is the protection of sensitive data transmitted between vehicles and charging infrastructure. This includes personal information, payment details, and vehicle diagnostics. Encryption protocols and secure communication channels are essential to safeguard this data from unauthorized access or interception.
Another critical aspect of cybersecurity in these systems is the prevention of unauthorized access to vehicle control systems. As PHEVs become more connected, the risk of remote hacking increases. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms and access controls is crucial to prevent malicious actors from gaining control over vehicle functions or manipulating charging processes.
The charging infrastructure itself presents a potential target for cyberattacks. Securing the communication between charging stations and the power grid is vital to prevent disruptions in energy distribution or unauthorized energy consumption. This requires the implementation of secure protocols and regular security audits of the charging network.
As PHEVs rely increasingly on over-the-air updates for software and firmware, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of these updates becomes a key cybersecurity challenge. Robust verification processes and secure update mechanisms are necessary to prevent the installation of malicious code or compromised software versions.
The interconnected nature of telecom-PHEV systems also raises concerns about privacy and data protection. Strict data governance policies and compliance with relevant regulations, such as GDPR, are essential to protect user information and maintain trust in the ecosystem.
To address these cybersecurity challenges, a multi-layered approach is required. This includes implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and establishing incident response plans. Additionally, fostering collaboration between automotive manufacturers, telecom providers, and cybersecurity experts is crucial for developing comprehensive security solutions.
As the PHEV market expands, standardization of cybersecurity protocols across the industry becomes increasingly important. This ensures interoperability and consistent security measures across different vehicle models and charging networks. Industry-wide initiatives and regulatory frameworks play a vital role in establishing and enforcing these standards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!