How Throttle Body Technology Supports Eco-Driving Systems
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Throttle Body Evolution
The throttle body has undergone significant evolution since its inception, playing a crucial role in the development of eco-driving systems. Initially, throttle bodies were purely mechanical devices, controlled by a cable connected to the accelerator pedal. This simple design, while functional, lacked precision and adaptability, limiting its potential for fuel efficiency optimization.
The introduction of electronic throttle control (ETC) in the 1980s marked a pivotal moment in throttle body technology. ETC replaced the mechanical linkage with sensors and actuators, allowing for more precise control of airflow into the engine. This advancement laid the foundation for integrating throttle bodies into broader engine management systems, a key step towards supporting eco-driving initiatives.
As environmental concerns grew in the 1990s and 2000s, throttle body technology continued to evolve. Manufacturers began incorporating more sophisticated sensors and control algorithms, enabling real-time adjustments based on various driving conditions. This improvement allowed for better fuel economy and reduced emissions, aligning with emerging eco-driving principles.
The advent of drive-by-wire systems in the early 2000s further enhanced the throttle body's role in eco-driving. These systems eliminated the need for a physical connection between the accelerator pedal and the throttle, instead using electronic signals. This innovation provided greater flexibility in programming throttle response, allowing for the implementation of eco-driving modes that prioritize fuel efficiency over performance.
Recent years have seen the integration of throttle bodies with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and artificial intelligence. Modern throttle bodies can now communicate with other vehicle systems, such as transmission control units and adaptive cruise control, to optimize engine performance for specific driving scenarios. This interconnectivity enables more sophisticated eco-driving strategies, such as predictive throttle control based on GPS data and traffic information.
The latest developments in throttle body technology focus on enhancing its responsiveness and efficiency. Variable geometry throttle bodies, which can adjust their shape to optimize airflow under different engine loads, are becoming more common. Additionally, the incorporation of machine learning algorithms allows throttle bodies to adapt to individual driving styles over time, further improving fuel efficiency and supporting personalized eco-driving experiences.
As we look towards the future, throttle body technology continues to evolve in support of eco-driving systems. Research is ongoing into materials that can further reduce weight and improve thermal efficiency. Moreover, the integration of throttle bodies with hybrid and electric powertrains presents new opportunities for optimizing energy use across different propulsion systems, promising even greater advancements in eco-driving capabilities.
The introduction of electronic throttle control (ETC) in the 1980s marked a pivotal moment in throttle body technology. ETC replaced the mechanical linkage with sensors and actuators, allowing for more precise control of airflow into the engine. This advancement laid the foundation for integrating throttle bodies into broader engine management systems, a key step towards supporting eco-driving initiatives.
As environmental concerns grew in the 1990s and 2000s, throttle body technology continued to evolve. Manufacturers began incorporating more sophisticated sensors and control algorithms, enabling real-time adjustments based on various driving conditions. This improvement allowed for better fuel economy and reduced emissions, aligning with emerging eco-driving principles.
The advent of drive-by-wire systems in the early 2000s further enhanced the throttle body's role in eco-driving. These systems eliminated the need for a physical connection between the accelerator pedal and the throttle, instead using electronic signals. This innovation provided greater flexibility in programming throttle response, allowing for the implementation of eco-driving modes that prioritize fuel efficiency over performance.
Recent years have seen the integration of throttle bodies with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and artificial intelligence. Modern throttle bodies can now communicate with other vehicle systems, such as transmission control units and adaptive cruise control, to optimize engine performance for specific driving scenarios. This interconnectivity enables more sophisticated eco-driving strategies, such as predictive throttle control based on GPS data and traffic information.
The latest developments in throttle body technology focus on enhancing its responsiveness and efficiency. Variable geometry throttle bodies, which can adjust their shape to optimize airflow under different engine loads, are becoming more common. Additionally, the incorporation of machine learning algorithms allows throttle bodies to adapt to individual driving styles over time, further improving fuel efficiency and supporting personalized eco-driving experiences.
As we look towards the future, throttle body technology continues to evolve in support of eco-driving systems. Research is ongoing into materials that can further reduce weight and improve thermal efficiency. Moreover, the integration of throttle bodies with hybrid and electric powertrains presents new opportunities for optimizing energy use across different propulsion systems, promising even greater advancements in eco-driving capabilities.
Eco-Driving Market Trends
The eco-driving market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and the push for more sustainable transportation solutions. This trend is expected to continue, with the global eco-driving market projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of over 15% through 2025. The adoption of eco-driving systems is particularly strong in regions with stringent emissions regulations, such as Europe and parts of Asia.
One of the key factors fueling this market growth is the integration of advanced technologies, including throttle body systems, into eco-driving solutions. These technologies are enabling more precise control over vehicle performance, leading to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. As a result, automotive manufacturers are increasingly incorporating eco-driving features into their vehicle lineups, from entry-level models to high-end luxury vehicles.
The commercial vehicle sector is emerging as a significant driver of eco-driving market growth. Fleet operators are recognizing the potential for substantial fuel cost savings and reduced environmental impact through the implementation of eco-driving systems. This has led to a surge in demand for aftermarket eco-driving solutions that can be retrofitted to existing commercial vehicles.
Consumer awareness and acceptance of eco-driving technologies are also on the rise. As more drivers become conscious of their environmental footprint, there is a growing willingness to adopt driving habits and technologies that promote fuel efficiency. This shift in consumer behavior is creating new opportunities for eco-driving system manufacturers and software developers.
Government initiatives and regulations are playing a crucial role in shaping the eco-driving market landscape. Many countries are implementing stricter fuel efficiency standards and offering incentives for the adoption of eco-friendly vehicles and technologies. These policies are not only driving market growth but also encouraging innovation in eco-driving solutions.
The integration of eco-driving systems with connected car technologies and smart city infrastructure is opening up new avenues for market expansion. Real-time traffic data, predictive analytics, and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication are enhancing the capabilities of eco-driving systems, making them more effective and appealing to both individual consumers and fleet operators.
As the market continues to evolve, there is an increasing focus on developing more sophisticated eco-driving systems that can adapt to different driving conditions and user preferences. This includes the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to optimize vehicle performance and provide personalized eco-driving recommendations to drivers.
One of the key factors fueling this market growth is the integration of advanced technologies, including throttle body systems, into eco-driving solutions. These technologies are enabling more precise control over vehicle performance, leading to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. As a result, automotive manufacturers are increasingly incorporating eco-driving features into their vehicle lineups, from entry-level models to high-end luxury vehicles.
The commercial vehicle sector is emerging as a significant driver of eco-driving market growth. Fleet operators are recognizing the potential for substantial fuel cost savings and reduced environmental impact through the implementation of eco-driving systems. This has led to a surge in demand for aftermarket eco-driving solutions that can be retrofitted to existing commercial vehicles.
Consumer awareness and acceptance of eco-driving technologies are also on the rise. As more drivers become conscious of their environmental footprint, there is a growing willingness to adopt driving habits and technologies that promote fuel efficiency. This shift in consumer behavior is creating new opportunities for eco-driving system manufacturers and software developers.
Government initiatives and regulations are playing a crucial role in shaping the eco-driving market landscape. Many countries are implementing stricter fuel efficiency standards and offering incentives for the adoption of eco-friendly vehicles and technologies. These policies are not only driving market growth but also encouraging innovation in eco-driving solutions.
The integration of eco-driving systems with connected car technologies and smart city infrastructure is opening up new avenues for market expansion. Real-time traffic data, predictive analytics, and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication are enhancing the capabilities of eco-driving systems, making them more effective and appealing to both individual consumers and fleet operators.
As the market continues to evolve, there is an increasing focus on developing more sophisticated eco-driving systems that can adapt to different driving conditions and user preferences. This includes the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to optimize vehicle performance and provide personalized eco-driving recommendations to drivers.
Throttle Tech Challenges
The throttle body, a critical component in modern vehicle engines, faces several challenges in supporting eco-driving systems. One of the primary issues is achieving precise control over air intake. Traditional mechanical throttle bodies often struggle to provide the level of accuracy required for optimal fuel efficiency and emissions reduction. This imprecision can lead to suboptimal air-fuel ratios, resulting in increased fuel consumption and higher emissions.
Another significant challenge is the integration of throttle body technology with advanced engine management systems. As vehicles become more sophisticated, the throttle body must seamlessly communicate with various sensors and control units to optimize engine performance in real-time. This integration is crucial for implementing effective eco-driving strategies but requires complex software algorithms and robust hardware interfaces.
The durability and reliability of throttle bodies in diverse operating conditions also present ongoing challenges. Eco-driving systems demand consistent performance across a wide range of temperatures, altitudes, and driving scenarios. Ensuring that throttle bodies maintain their precision and responsiveness over the vehicle's lifetime is essential for long-term eco-driving benefits.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of advanced throttle body technologies poses a challenge for widespread adoption in eco-driving systems. While electronic throttle bodies offer superior control and integration capabilities, their higher production costs can be a barrier, especially for entry-level and mid-range vehicle segments where price sensitivity is high.
Miniaturization and weight reduction of throttle bodies without compromising functionality is another area of concern. As automotive manufacturers strive to reduce overall vehicle weight to improve fuel efficiency, every component, including the throttle body, is scrutinized for potential size and weight optimization.
Lastly, the throttle body's role in managing engine start-stop systems, a common feature in eco-driving vehicles, presents unique challenges. Rapid and smooth engagement of the throttle during frequent engine restarts is crucial for driver comfort and fuel savings but requires sophisticated control mechanisms and durable components.
Addressing these challenges is vital for the continued evolution of throttle body technology in support of eco-driving systems. Innovations in materials science, control algorithms, and manufacturing processes will be key to overcoming these hurdles and enhancing the throttle body's contribution to sustainable transportation.
Another significant challenge is the integration of throttle body technology with advanced engine management systems. As vehicles become more sophisticated, the throttle body must seamlessly communicate with various sensors and control units to optimize engine performance in real-time. This integration is crucial for implementing effective eco-driving strategies but requires complex software algorithms and robust hardware interfaces.
The durability and reliability of throttle bodies in diverse operating conditions also present ongoing challenges. Eco-driving systems demand consistent performance across a wide range of temperatures, altitudes, and driving scenarios. Ensuring that throttle bodies maintain their precision and responsiveness over the vehicle's lifetime is essential for long-term eco-driving benefits.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of advanced throttle body technologies poses a challenge for widespread adoption in eco-driving systems. While electronic throttle bodies offer superior control and integration capabilities, their higher production costs can be a barrier, especially for entry-level and mid-range vehicle segments where price sensitivity is high.
Miniaturization and weight reduction of throttle bodies without compromising functionality is another area of concern. As automotive manufacturers strive to reduce overall vehicle weight to improve fuel efficiency, every component, including the throttle body, is scrutinized for potential size and weight optimization.
Lastly, the throttle body's role in managing engine start-stop systems, a common feature in eco-driving vehicles, presents unique challenges. Rapid and smooth engagement of the throttle during frequent engine restarts is crucial for driver comfort and fuel savings but requires sophisticated control mechanisms and durable components.
Addressing these challenges is vital for the continued evolution of throttle body technology in support of eco-driving systems. Innovations in materials science, control algorithms, and manufacturing processes will be key to overcoming these hurdles and enhancing the throttle body's contribution to sustainable transportation.
Current Throttle Solutions
01 Throttle body design optimization
Improving the design of throttle bodies to enhance fuel efficiency. This includes optimizing the shape and size of the throttle bore, improving airflow characteristics, and reducing turbulence. These design improvements can lead to better fuel atomization and more precise control of the air-fuel mixture, resulting in improved fuel efficiency.- Throttle body design optimization: Improving the design of throttle bodies to enhance fuel efficiency. This includes optimizing the shape and size of the throttle bore, improving airflow characteristics, and reducing turbulence. These design improvements can lead to better fuel atomization and more precise control of air-fuel mixture, resulting in improved fuel efficiency.
- Electronic throttle control systems: Implementing advanced electronic throttle control systems to improve fuel efficiency. These systems use sensors and actuators to precisely control throttle position based on various engine parameters. By optimizing throttle response and reducing unnecessary fuel consumption during idle and partial throttle conditions, these systems can significantly enhance overall fuel efficiency.
- Throttle body heating and cooling: Incorporating heating and cooling mechanisms in throttle bodies to maintain optimal operating temperatures. This can prevent issues such as icing and ensure consistent performance across various environmental conditions. By maintaining ideal operating temperatures, these systems can contribute to improved fuel efficiency and engine performance.
- Integration with fuel injection systems: Enhancing the integration between throttle bodies and fuel injection systems to optimize fuel delivery. This includes improving the coordination between throttle position and fuel injection timing, as well as implementing adaptive strategies based on real-time engine data. Such integration can lead to more precise fuel metering and improved overall fuel efficiency.
- Throttle body materials and manufacturing: Utilizing advanced materials and manufacturing techniques to produce lighter and more efficient throttle bodies. This includes the use of lightweight alloys, composite materials, and precision manufacturing processes to reduce weight, improve durability, and enhance overall performance. These improvements can contribute to better fuel efficiency by reducing engine load and improving throttle response.
02 Electronic throttle control systems
Implementing advanced electronic throttle control systems to improve fuel efficiency. These systems use sensors and actuators to precisely control the throttle position based on various engine parameters. This allows for more accurate fuel metering and better response to changing driving conditions, leading to improved fuel economy.Expand Specific Solutions03 Throttle body heating and cooling
Incorporating heating and cooling mechanisms in throttle bodies to optimize fuel efficiency. These systems help maintain optimal operating temperatures, prevent icing, and ensure consistent performance across various environmental conditions. By maintaining ideal temperatures, fuel vaporization and mixing are improved, leading to better combustion efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration with fuel injection systems
Enhancing the integration between throttle bodies and fuel injection systems to improve fuel efficiency. This involves coordinating throttle position with fuel injection timing and quantity, as well as optimizing the placement of fuel injectors relative to the throttle body. Such integration allows for more precise control of the air-fuel mixture, resulting in improved combustion efficiency and fuel economy.Expand Specific Solutions05 Adaptive throttle control algorithms
Developing and implementing adaptive throttle control algorithms to optimize fuel efficiency. These algorithms use machine learning and real-time data analysis to continuously adjust throttle behavior based on driving conditions, engine load, and other factors. By dynamically optimizing throttle response, these systems can significantly improve fuel economy across various driving scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The throttle body technology market supporting eco-driving systems is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles. The global market size is expanding rapidly, with major automotive manufacturers and suppliers investing heavily in research and development. The technology's maturity varies, with established players like Toyota, GM, and Ford leading in innovation and implementation. Emerging companies such as Geely and BYD are also making significant strides, particularly in electric vehicle applications. Tier 1 suppliers like Bosch and Continental are developing advanced throttle body systems, while specialized firms like K&N Engineering focus on performance-oriented solutions. The competitive landscape is dynamic, with collaborations between OEMs, suppliers, and research institutions driving technological advancements.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM has developed an advanced throttle body technology that integrates with their eco-driving systems. Their solution uses a smart electronic throttle control (ETC) system that precisely regulates airflow into the engine based on real-time driving conditions and eco-driving parameters[1]. The system incorporates machine learning algorithms to adapt to individual driving styles and optimize fuel efficiency. GM's throttle body technology also features a fast-response actuator that can make micro-adjustments up to 1000 times per second, allowing for seamless integration with start-stop systems and hybrid powertrains[3]. This technology is coupled with GM's ecoTEC engine management system, which uses predictive analytics to further enhance fuel economy and reduce emissions[5].
Strengths: Precise control, adaptive learning, seamless integration with hybrid systems. Weaknesses: Complexity may lead to higher maintenance costs, potential over-reliance on electronic systems.
Ford Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Ford's throttle body technology for eco-driving systems focuses on their patented EcoBoost engine architecture. The throttle body in EcoBoost engines is designed with a twin-independent variable camshaft timing (Ti-VCT) system that works in conjunction with direct fuel injection and turbocharging[2]. This allows for dynamic adjustment of the air-fuel mixture, optimizing combustion efficiency across various driving conditions. Ford's throttle bodies also incorporate a low-friction design and advanced coatings to reduce parasitic losses. The company has recently introduced a predictive throttle control system that uses GPS and topographical data to anticipate upcoming road conditions and adjust throttle response accordingly, further enhancing fuel efficiency[4]. Ford's eco-driving system also includes a smart gauge with EcoGuide, providing real-time feedback to drivers on their eco-driving performance[6].
Strengths: Integrated approach with turbocharging and direct injection, predictive control using GPS data. Weaknesses: Potential for increased complexity in engine design, higher initial cost for advanced features.
Throttle Innovations
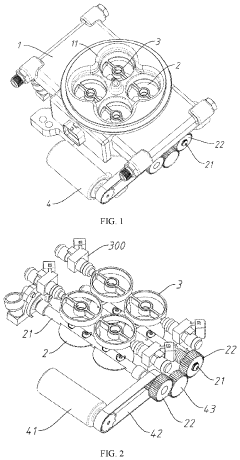
Throttle body with an actuator for autodrive
PatentInactiveUS5269273A
Innovation
- A throttle body with an integrated autodrive actuator, featuring an arm, arm spring, accelerator lever, electromagnetic clutch, and engaging mechanisms, eliminating the need for a relay mechanism and cables, thereby improving control accuracy and assembly efficiency.
Electronic throttle body with improved structure
PatentActiveUS11674458B1
Innovation
- An electronic throttle body with vertically oriented airflow channels, linked butterfly valves connected through rotating shafts and a servo driving apparatus for precise control, and a fuel atomizing ring with downward-facing atomizing holes to ensure efficient fuel-air mixing and reduce filter pollution.
Emissions Regulations
Emissions regulations have played a crucial role in shaping the development and implementation of throttle body technology in eco-driving systems. These regulations, established by governmental bodies worldwide, aim to reduce harmful emissions from vehicles and improve overall air quality. The stringent nature of these regulations has driven automotive manufacturers to innovate and adopt advanced technologies to meet increasingly strict standards.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets and enforces emissions standards for vehicles. The Clean Air Act, first enacted in 1970 and subsequently amended, provides the legal framework for these regulations. Similarly, the European Union has implemented Euro emissions standards, which have progressively tightened since their introduction in 1992. These regulations have significantly influenced the design and functionality of throttle bodies in modern vehicles.
Throttle body technology has evolved to support eco-driving systems by enabling more precise control over engine air intake. This enhanced control allows for optimized fuel consumption and reduced emissions. Advanced electronic throttle control systems, also known as drive-by-wire systems, have replaced traditional mechanical linkages. These systems use sensors and actuators to adjust throttle position based on various parameters, including driver input, engine load, and environmental conditions.
The integration of throttle body technology with eco-driving systems has led to the development of intelligent throttle control algorithms. These algorithms analyze real-time data from multiple vehicle sensors to determine the most efficient throttle position for any given driving scenario. By optimizing air-fuel mixture and combustion efficiency, these systems contribute significantly to reducing emissions and improving fuel economy.
Emissions regulations have also driven the adoption of idle stop-start systems, which rely on precise throttle control for seamless engine restarts. These systems automatically shut off the engine when the vehicle is stationary and restart it when the driver is ready to move, reducing unnecessary idling and associated emissions. The throttle body plays a critical role in ensuring smooth engine restarts and maintaining optimal air-fuel ratios during these transitions.
Furthermore, the push for lower emissions has led to the development of advanced throttle body designs that incorporate features such as integrated air temperature sensors and improved airflow characteristics. These enhancements contribute to more accurate engine management and emissions control across a wide range of operating conditions.
As emissions regulations continue to evolve, throttle body technology is expected to play an increasingly important role in eco-driving systems. Future developments may include further integration with hybrid and electric powertrains, as well as advanced predictive algorithms that anticipate driving conditions to optimize throttle control and emissions reduction strategies.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets and enforces emissions standards for vehicles. The Clean Air Act, first enacted in 1970 and subsequently amended, provides the legal framework for these regulations. Similarly, the European Union has implemented Euro emissions standards, which have progressively tightened since their introduction in 1992. These regulations have significantly influenced the design and functionality of throttle bodies in modern vehicles.
Throttle body technology has evolved to support eco-driving systems by enabling more precise control over engine air intake. This enhanced control allows for optimized fuel consumption and reduced emissions. Advanced electronic throttle control systems, also known as drive-by-wire systems, have replaced traditional mechanical linkages. These systems use sensors and actuators to adjust throttle position based on various parameters, including driver input, engine load, and environmental conditions.
The integration of throttle body technology with eco-driving systems has led to the development of intelligent throttle control algorithms. These algorithms analyze real-time data from multiple vehicle sensors to determine the most efficient throttle position for any given driving scenario. By optimizing air-fuel mixture and combustion efficiency, these systems contribute significantly to reducing emissions and improving fuel economy.
Emissions regulations have also driven the adoption of idle stop-start systems, which rely on precise throttle control for seamless engine restarts. These systems automatically shut off the engine when the vehicle is stationary and restart it when the driver is ready to move, reducing unnecessary idling and associated emissions. The throttle body plays a critical role in ensuring smooth engine restarts and maintaining optimal air-fuel ratios during these transitions.
Furthermore, the push for lower emissions has led to the development of advanced throttle body designs that incorporate features such as integrated air temperature sensors and improved airflow characteristics. These enhancements contribute to more accurate engine management and emissions control across a wide range of operating conditions.
As emissions regulations continue to evolve, throttle body technology is expected to play an increasingly important role in eco-driving systems. Future developments may include further integration with hybrid and electric powertrains, as well as advanced predictive algorithms that anticipate driving conditions to optimize throttle control and emissions reduction strategies.
Fuel Efficiency Metrics
Fuel efficiency metrics play a crucial role in evaluating the performance of eco-driving systems and throttle body technology. These metrics provide quantitative measures to assess the effectiveness of various fuel-saving strategies and technologies implemented in modern vehicles.
One of the primary fuel efficiency metrics is miles per gallon (MPG) or kilometers per liter (km/L), which indicates the distance a vehicle can travel on a single unit of fuel. This metric is widely used by consumers and manufacturers alike to compare the fuel economy of different vehicles. However, it's important to note that MPG can vary significantly depending on driving conditions, making it necessary to consider both city and highway MPG ratings.
Another key metric is the CO2 emissions per kilometer (g CO2/km), which directly relates to the vehicle's fuel consumption and environmental impact. This metric is particularly relevant in the context of eco-driving systems, as it helps quantify the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions achieved through improved throttle body technology and driving techniques.
Fuel consumption rate, measured in liters per 100 kilometers (L/100km), is another essential metric that provides a more linear representation of fuel efficiency compared to MPG. This metric is especially useful when comparing vehicles with different fuel types or propulsion systems.
Advanced eco-driving systems often incorporate real-time fuel efficiency metrics, such as instantaneous fuel consumption (L/h or gal/h) and average fuel economy over a specific trip or time period. These metrics help drivers make informed decisions about their driving behavior and encourage more efficient throttle control.
Engine-specific fuel consumption (ESFC), typically measured in grams of fuel per kilowatt-hour (g/kWh), is a metric that evaluates the efficiency of the engine itself. This metric is particularly relevant when assessing the impact of throttle body technology on overall vehicle efficiency, as it isolates the engine's performance from other factors that may affect fuel consumption.
The brake specific fuel consumption (BSFC) is another important metric, measured in grams of fuel per brake horsepower-hour (g/bhp-hr). This metric takes into account the power output of the engine and is useful for comparing the efficiency of different engine designs and throttle body configurations.
In the context of eco-driving systems, metrics such as acceleration smoothness and throttle position variability are also considered. These metrics help evaluate how well a driver or automated system manages the throttle to minimize unnecessary fuel consumption during acceleration and deceleration events.
By analyzing these fuel efficiency metrics in conjunction with throttle body technology advancements, researchers and engineers can develop more effective eco-driving systems that optimize fuel consumption and reduce environmental impact across various driving conditions and vehicle types.
One of the primary fuel efficiency metrics is miles per gallon (MPG) or kilometers per liter (km/L), which indicates the distance a vehicle can travel on a single unit of fuel. This metric is widely used by consumers and manufacturers alike to compare the fuel economy of different vehicles. However, it's important to note that MPG can vary significantly depending on driving conditions, making it necessary to consider both city and highway MPG ratings.
Another key metric is the CO2 emissions per kilometer (g CO2/km), which directly relates to the vehicle's fuel consumption and environmental impact. This metric is particularly relevant in the context of eco-driving systems, as it helps quantify the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions achieved through improved throttle body technology and driving techniques.
Fuel consumption rate, measured in liters per 100 kilometers (L/100km), is another essential metric that provides a more linear representation of fuel efficiency compared to MPG. This metric is especially useful when comparing vehicles with different fuel types or propulsion systems.
Advanced eco-driving systems often incorporate real-time fuel efficiency metrics, such as instantaneous fuel consumption (L/h or gal/h) and average fuel economy over a specific trip or time period. These metrics help drivers make informed decisions about their driving behavior and encourage more efficient throttle control.
Engine-specific fuel consumption (ESFC), typically measured in grams of fuel per kilowatt-hour (g/kWh), is a metric that evaluates the efficiency of the engine itself. This metric is particularly relevant when assessing the impact of throttle body technology on overall vehicle efficiency, as it isolates the engine's performance from other factors that may affect fuel consumption.
The brake specific fuel consumption (BSFC) is another important metric, measured in grams of fuel per brake horsepower-hour (g/bhp-hr). This metric takes into account the power output of the engine and is useful for comparing the efficiency of different engine designs and throttle body configurations.
In the context of eco-driving systems, metrics such as acceleration smoothness and throttle position variability are also considered. These metrics help evaluate how well a driver or automated system manages the throttle to minimize unnecessary fuel consumption during acceleration and deceleration events.
By analyzing these fuel efficiency metrics in conjunction with throttle body technology advancements, researchers and engineers can develop more effective eco-driving systems that optimize fuel consumption and reduce environmental impact across various driving conditions and vehicle types.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!