How to Optimize Carbonyl Detection in Complex Mixtures?
JUL 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carbonyl Detection Background and Objectives
Carbonyl compounds play a crucial role in various fields, including atmospheric chemistry, food science, and pharmaceutical research. The detection and quantification of these compounds in complex mixtures have been a longstanding challenge for researchers and industry professionals. Over the past few decades, significant advancements have been made in analytical techniques and methodologies to address this issue.
The evolution of carbonyl detection methods can be traced back to traditional wet chemical techniques, such as the use of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH) derivatization. These methods, while effective, often lacked the sensitivity and specificity required for analyzing complex environmental and biological samples. As technology progressed, more sophisticated approaches emerged, including gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with various detection systems.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in the development of novel sensing technologies, such as fluorescence-based probes and electrochemical sensors, which offer improved selectivity and sensitivity for carbonyl detection. These advancements have been driven by the growing demand for rapid, on-site analysis in environmental monitoring, food quality control, and medical diagnostics.
The primary objective of optimizing carbonyl detection in complex mixtures is to overcome the limitations of existing methods and develop more robust, sensitive, and selective analytical techniques. This involves addressing several key challenges, including matrix interference, low analyte concentrations, and the presence of structurally similar compounds that may lead to false positives or negatives.
Researchers aim to enhance the specificity of detection methods to distinguish between different carbonyl species, particularly in samples containing a wide range of organic compounds. Additionally, there is a focus on improving the detection limits to enable the quantification of trace-level carbonyls, which is crucial for applications such as air quality monitoring and early disease diagnosis.
Another important goal is to develop rapid and cost-effective screening methods that can be deployed in field settings or integrated into automated analytical systems. This would facilitate real-time monitoring and high-throughput analysis, addressing the growing need for efficient quality control processes in various industries.
As the field continues to evolve, there is an increasing emphasis on developing multi-analyte detection platforms capable of simultaneously identifying and quantifying multiple carbonyl compounds in a single analysis. This approach not only improves efficiency but also provides a more comprehensive understanding of the sample composition, which is particularly valuable in complex environmental and biological systems.
The evolution of carbonyl detection methods can be traced back to traditional wet chemical techniques, such as the use of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH) derivatization. These methods, while effective, often lacked the sensitivity and specificity required for analyzing complex environmental and biological samples. As technology progressed, more sophisticated approaches emerged, including gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with various detection systems.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in the development of novel sensing technologies, such as fluorescence-based probes and electrochemical sensors, which offer improved selectivity and sensitivity for carbonyl detection. These advancements have been driven by the growing demand for rapid, on-site analysis in environmental monitoring, food quality control, and medical diagnostics.
The primary objective of optimizing carbonyl detection in complex mixtures is to overcome the limitations of existing methods and develop more robust, sensitive, and selective analytical techniques. This involves addressing several key challenges, including matrix interference, low analyte concentrations, and the presence of structurally similar compounds that may lead to false positives or negatives.
Researchers aim to enhance the specificity of detection methods to distinguish between different carbonyl species, particularly in samples containing a wide range of organic compounds. Additionally, there is a focus on improving the detection limits to enable the quantification of trace-level carbonyls, which is crucial for applications such as air quality monitoring and early disease diagnosis.
Another important goal is to develop rapid and cost-effective screening methods that can be deployed in field settings or integrated into automated analytical systems. This would facilitate real-time monitoring and high-throughput analysis, addressing the growing need for efficient quality control processes in various industries.
As the field continues to evolve, there is an increasing emphasis on developing multi-analyte detection platforms capable of simultaneously identifying and quantifying multiple carbonyl compounds in a single analysis. This approach not only improves efficiency but also provides a more comprehensive understanding of the sample composition, which is particularly valuable in complex environmental and biological systems.
Market Demand Analysis for Carbonyl Detection
The market demand for carbonyl detection in complex mixtures has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by growing concerns over product quality, safety regulations, and environmental monitoring. In the food and beverage sector, carbonyl compounds play a crucial role in flavor and aroma profiles, making their detection essential for quality control and product development. The global food testing market, which includes carbonyl detection, is projected to reach $29 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2%.
The pharmaceutical industry also presents a significant market for carbonyl detection, particularly in drug development and manufacturing processes. Carbonyl impurities can affect drug stability and efficacy, necessitating robust detection methods. The pharmaceutical analytical testing outsourcing market, which encompasses carbonyl detection services, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.4% from 2021 to 2028.
Environmental monitoring represents another key area driving demand for carbonyl detection. With increasing awareness of air quality issues and stricter regulations on emissions, there is a growing need for accurate and sensitive carbonyl detection methods in atmospheric and industrial settings. The global environmental testing market, including air quality monitoring, is forecasted to reach $14.3 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 6.9%.
The petrochemical industry is another significant contributor to the demand for carbonyl detection. Carbonyl compounds are important intermediates and by-products in many petrochemical processes, and their detection is crucial for process optimization and quality control. The global petrochemicals market size was valued at $452.9 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2021 to 2028, indicating a parallel increase in demand for carbonyl detection technologies.
Emerging applications in the field of metabolomics and biomarker discovery are also fueling the demand for advanced carbonyl detection methods. As researchers explore the role of carbonyl compounds in various diseases and biological processes, there is an increasing need for sensitive and specific detection techniques in complex biological matrices.
The market trend indicates a shift towards more sensitive, selective, and high-throughput detection methods capable of analyzing complex mixtures. There is a growing demand for technologies that can provide real-time or near-real-time analysis, especially in industrial process control and environmental monitoring applications. Additionally, there is an increasing focus on developing portable and field-deployable carbonyl detection systems to meet the needs of on-site testing and remote monitoring scenarios.
The pharmaceutical industry also presents a significant market for carbonyl detection, particularly in drug development and manufacturing processes. Carbonyl impurities can affect drug stability and efficacy, necessitating robust detection methods. The pharmaceutical analytical testing outsourcing market, which encompasses carbonyl detection services, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.4% from 2021 to 2028.
Environmental monitoring represents another key area driving demand for carbonyl detection. With increasing awareness of air quality issues and stricter regulations on emissions, there is a growing need for accurate and sensitive carbonyl detection methods in atmospheric and industrial settings. The global environmental testing market, including air quality monitoring, is forecasted to reach $14.3 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 6.9%.
The petrochemical industry is another significant contributor to the demand for carbonyl detection. Carbonyl compounds are important intermediates and by-products in many petrochemical processes, and their detection is crucial for process optimization and quality control. The global petrochemicals market size was valued at $452.9 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2021 to 2028, indicating a parallel increase in demand for carbonyl detection technologies.
Emerging applications in the field of metabolomics and biomarker discovery are also fueling the demand for advanced carbonyl detection methods. As researchers explore the role of carbonyl compounds in various diseases and biological processes, there is an increasing need for sensitive and specific detection techniques in complex biological matrices.
The market trend indicates a shift towards more sensitive, selective, and high-throughput detection methods capable of analyzing complex mixtures. There is a growing demand for technologies that can provide real-time or near-real-time analysis, especially in industrial process control and environmental monitoring applications. Additionally, there is an increasing focus on developing portable and field-deployable carbonyl detection systems to meet the needs of on-site testing and remote monitoring scenarios.
Current Challenges in Complex Mixture Analysis
The analysis of complex mixtures presents numerous challenges in the field of analytical chemistry, particularly when it comes to the detection and quantification of carbonyl compounds. One of the primary difficulties lies in the vast diversity of chemical species present in these mixtures, which can range from simple organic molecules to complex biomolecules. This heterogeneity often leads to signal interference and matrix effects, making it challenging to accurately identify and measure specific carbonyl compounds of interest.
Another significant challenge is the varying concentrations of different components within the mixture. Carbonyl compounds may be present in trace amounts, while other compounds exist in much higher concentrations. This disparity can result in masking effects, where the signals of low-abundance carbonyls are overwhelmed by those of more abundant species. Consequently, traditional analytical techniques may struggle to detect and quantify these trace-level carbonyls accurately.
The reactivity of carbonyl compounds further complicates their analysis in complex mixtures. These compounds can undergo various chemical transformations, such as condensation reactions or oxidation, during sample preparation or analysis. Such reactions can alter the original composition of the mixture, leading to inaccurate results and misinterpretation of data. Additionally, some carbonyl compounds are volatile, making their retention and analysis challenging, especially in complex matrices.
The presence of isomers and structurally similar compounds in complex mixtures poses another significant challenge. Many analytical techniques struggle to differentiate between closely related carbonyl species, leading to potential misidentification or overestimation of certain compounds. This issue is particularly pronounced in biological samples or environmental matrices, where numerous structurally similar molecules coexist.
Sample preparation and extraction methods also present challenges in complex mixture analysis. The diverse nature of the components often requires compromises in extraction efficiency, as no single method can optimally extract all compounds of interest. This can lead to selective loss or enrichment of certain carbonyl species, potentially skewing the analytical results.
Furthermore, the stability of carbonyl compounds during storage and analysis is a critical concern. Many of these compounds are susceptible to degradation or transformation over time, especially when exposed to light, heat, or certain chemical environments. This instability can lead to underestimation of carbonyl content or the formation of artifacts that complicate the analysis.
Lastly, the need for high-throughput analysis in many applications adds another layer of complexity. Developing methods that can rapidly and accurately detect and quantify multiple carbonyl compounds in complex mixtures, while maintaining sensitivity and specificity, remains a significant challenge in the field.
Another significant challenge is the varying concentrations of different components within the mixture. Carbonyl compounds may be present in trace amounts, while other compounds exist in much higher concentrations. This disparity can result in masking effects, where the signals of low-abundance carbonyls are overwhelmed by those of more abundant species. Consequently, traditional analytical techniques may struggle to detect and quantify these trace-level carbonyls accurately.
The reactivity of carbonyl compounds further complicates their analysis in complex mixtures. These compounds can undergo various chemical transformations, such as condensation reactions or oxidation, during sample preparation or analysis. Such reactions can alter the original composition of the mixture, leading to inaccurate results and misinterpretation of data. Additionally, some carbonyl compounds are volatile, making their retention and analysis challenging, especially in complex matrices.
The presence of isomers and structurally similar compounds in complex mixtures poses another significant challenge. Many analytical techniques struggle to differentiate between closely related carbonyl species, leading to potential misidentification or overestimation of certain compounds. This issue is particularly pronounced in biological samples or environmental matrices, where numerous structurally similar molecules coexist.
Sample preparation and extraction methods also present challenges in complex mixture analysis. The diverse nature of the components often requires compromises in extraction efficiency, as no single method can optimally extract all compounds of interest. This can lead to selective loss or enrichment of certain carbonyl species, potentially skewing the analytical results.
Furthermore, the stability of carbonyl compounds during storage and analysis is a critical concern. Many of these compounds are susceptible to degradation or transformation over time, especially when exposed to light, heat, or certain chemical environments. This instability can lead to underestimation of carbonyl content or the formation of artifacts that complicate the analysis.
Lastly, the need for high-throughput analysis in many applications adds another layer of complexity. Developing methods that can rapidly and accurately detect and quantify multiple carbonyl compounds in complex mixtures, while maintaining sensitivity and specificity, remains a significant challenge in the field.
Existing Methods for Carbonyl Detection
01 Optimization of carbonyl detection methods
Various techniques are employed to enhance the sensitivity and accuracy of carbonyl detection. These may include improvements in sample preparation, use of advanced analytical instruments, and development of novel detection reagents. Optimization strategies focus on reducing interference, increasing signal-to-noise ratio, and improving detection limits for carbonyl compounds in different matrices.- Optimization of carbonyl detection methods: Various techniques are employed to enhance the sensitivity and accuracy of carbonyl detection. These may include improvements in sample preparation, use of advanced analytical instruments, and development of novel detection reagents. Optimization strategies focus on reducing interference, increasing signal-to-noise ratio, and improving overall detection limits.
- Advanced spectroscopic techniques for carbonyl detection: Spectroscopic methods such as infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are utilized for carbonyl detection. These techniques offer high sensitivity and specificity, allowing for the identification and quantification of carbonyl compounds in complex matrices. Optimization involves refining spectral analysis algorithms and enhancing instrument performance.
- Electrochemical sensors for carbonyl detection: Development of electrochemical sensors for carbonyl detection focuses on improving electrode materials, surface modifications, and signal transduction mechanisms. These sensors offer advantages such as rapid response, miniaturization potential, and in-situ monitoring capabilities. Optimization efforts aim to enhance selectivity, stability, and reproducibility of the sensors.
- Derivatization techniques for carbonyl detection: Chemical derivatization methods are employed to enhance the detectability of carbonyl compounds. This involves the use of specific reagents that react with carbonyl groups to form easily detectable derivatives. Optimization focuses on improving reaction kinetics, yield, and stability of the derivatives, as well as developing novel derivatizing agents for increased sensitivity and selectivity.
- Data analysis and processing for carbonyl detection: Advanced data analysis and processing techniques are crucial for optimizing carbonyl detection. This includes the development of sophisticated algorithms for signal processing, peak identification, and quantification. Machine learning and artificial intelligence approaches are also being explored to improve data interpretation and reduce false positives in complex samples.
02 Advanced spectroscopic techniques for carbonyl detection
Spectroscopic methods such as infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and fluorescence spectroscopy are utilized for carbonyl detection. These techniques offer high sensitivity and specificity for identifying carbonyl groups in various compounds. Optimization of these methods involves improving spectral resolution, enhancing signal processing algorithms, and developing specialized probes or markers for carbonyl groups.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrochemical sensors for carbonyl detection
Electrochemical sensors are developed for rapid and sensitive detection of carbonyl compounds. These sensors often incorporate nanomaterials or modified electrodes to enhance selectivity and sensitivity. Optimization efforts focus on improving electrode materials, enhancing electron transfer kinetics, and developing novel sensing mechanisms for specific carbonyl compounds.Expand Specific Solutions04 Chromatographic methods for carbonyl separation and detection
Chromatographic techniques, such as gas chromatography and liquid chromatography, are optimized for efficient separation and detection of carbonyl compounds. Improvements include development of specialized stationary phases, optimization of mobile phase compositions, and integration with mass spectrometry for enhanced detection and identification of carbonyl species in complex mixtures.Expand Specific Solutions05 Derivatization strategies for carbonyl detection
Chemical derivatization methods are employed to enhance the detectability of carbonyl compounds. These strategies involve the use of specific reagents that react with carbonyl groups to form easily detectable derivatives. Optimization focuses on developing more selective and efficient derivatizing agents, improving reaction conditions, and enhancing the stability and detectability of the resulting derivatives.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Analytical Chemistry Industry
The optimization of carbonyl detection in complex mixtures is a rapidly evolving field with significant market potential. The industry is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for accurate and sensitive detection methods across various sectors. The global market for analytical instruments, including carbonyl detection technologies, is projected to reach substantial figures in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like LG Chem, BASF, and ExxonMobil Chemical Patents leading innovation. Research institutions such as CNRS, Helmholtz Zentrum München, and Fudan University are contributing to fundamental advancements. The technology's maturity varies, with established methods being refined and novel approaches emerging, indicating a dynamic and competitive landscape.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc. has developed a sophisticated approach to optimize carbonyl detection in complex mixtures, particularly focusing on petroleum and petrochemical products. Their method combines advanced sample preparation techniques with high-resolution analytical instrumentation. ExxonMobil employs a novel microfluidic device for on-line sample preparation and derivatization of carbonyl compounds, significantly reducing analysis time and improving reproducibility[1]. This is coupled with multidimensional gas chromatography (MDGC) for enhanced separation of complex hydrocarbon mixtures, effectively resolving co-elution issues common in petroleum samples[2]. The company has also developed proprietary chemiluminescent nitrogen detectors (CLND) optimized for carbonyl compound detection, offering high sensitivity and selectivity[3]. ExxonMobil's approach incorporates Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR-MS) for ultra-high resolution analysis and accurate mass determination of carbonyl compounds in complex matrices[4]. Additionally, they have implemented advanced data processing algorithms and machine learning techniques for automated peak identification and quantification, enabling rapid analysis of large datasets from complex refinery and petrochemical streams[5].
Strengths: Highly specialized for petroleum and petrochemical applications, advanced separation and detection techniques, automated data processing. Weaknesses: May be overly specialized for general laboratory use, potentially high implementation costs.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed a multi-faceted approach to optimize carbonyl detection in complex mixtures, leveraging their expertise in chemical analysis and industrial processes. Their method combines advanced sample preparation techniques with state-of-the-art analytical instrumentation. BASF employs a novel solid-phase microextraction (SPME) technique optimized for carbonyl compounds, which allows for efficient extraction and pre-concentration of analytes from complex matrices[1]. This is coupled with comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC×GC) for enhanced separation of complex mixtures, significantly reducing co-elution issues[2]. The company has also developed proprietary derivatization reagents that selectively react with carbonyl compounds, improving their detectability and stability during analysis[3]. BASF's approach incorporates high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HR-TOF-MS) for accurate mass determination and structural elucidation of carbonyl compounds[4]. Additionally, they have implemented machine learning algorithms for automated peak identification and quantification, enhancing the speed and accuracy of data analysis in complex mixture scenarios[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining advanced sample preparation, separation, and detection techniques. Excellent for industrial-scale applications. Weaknesses: May require significant investment in equipment and expertise, potentially less suitable for smaller-scale or routine analyses.
Innovative Approaches in Carbonyl Analysis
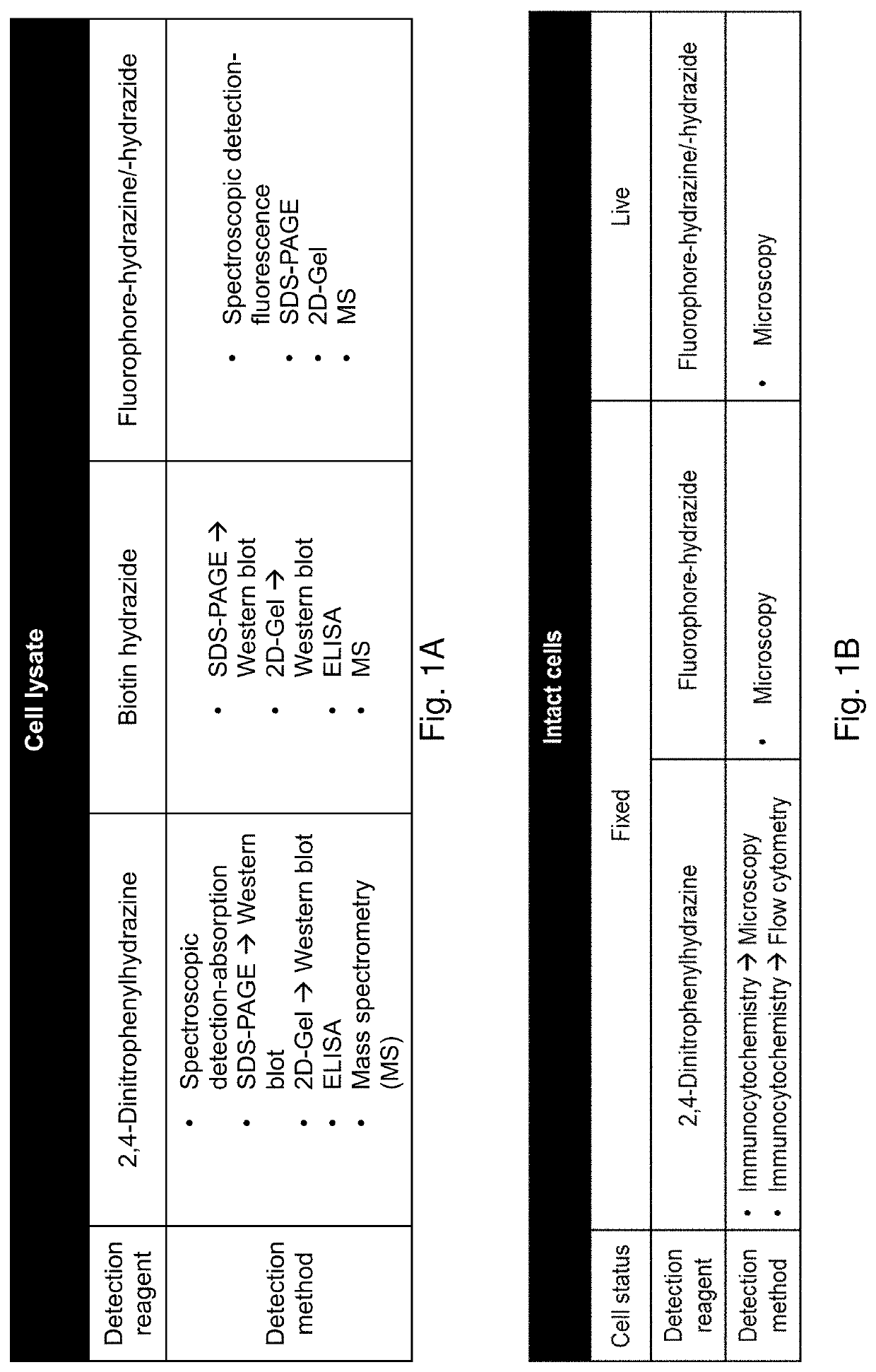
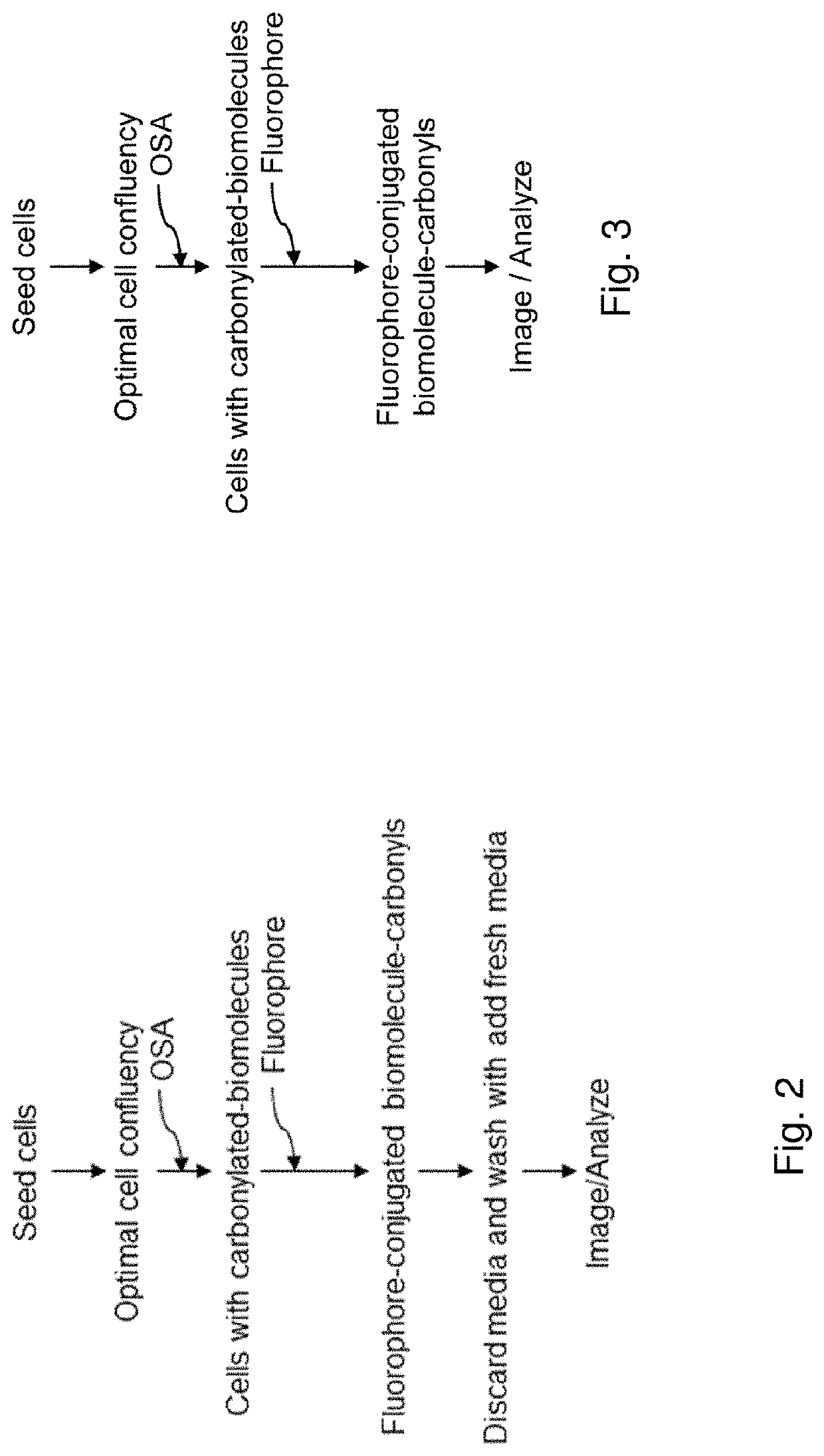
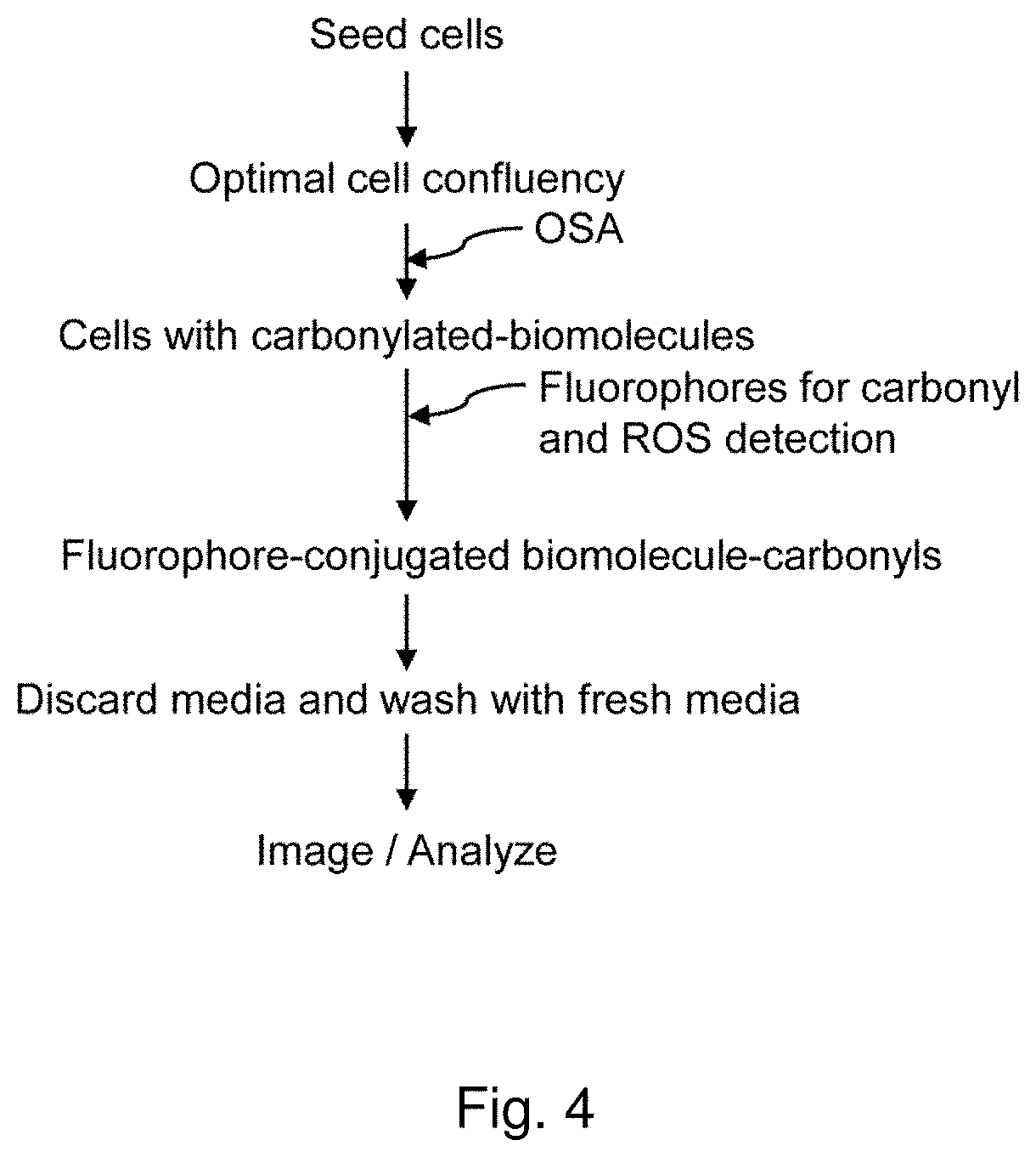
Methods and compositions for detection and visualization of oxidative stress-induced carbonylation in cells
PatentPendingUS20210356472A1
Innovation
- Development of a hydrazine-functionalized fluorophore, 7-hydrazinyl-4-methylcoumarin (coumarin hydrazine, CH), and its derivative, 4-trifluoromethyl-7-hydrazinyl-2H-chromen-2-one (TFCH), which allows for direct and rapid in-situ detection of carbonylated biomolecules by forming hydrazones, enabling visualization and quantification of oxidative stress-induced carbonylation in live cells without the need for extensive purification or secondary reagents.
Nucleic acid detection using type iii crispr complex
PatentWO2023004391A2
Innovation
- The use of an engineered type III CRISPR complex to capture and concentrate target nucleic acids, activating ancillary nucleases that generate detectable signals without prior amplification, utilizing cyclic oligonucleotides and specific nucleases like Canl and NucC to enhance detection sensitivity.
Regulatory Considerations for Analytical Methods
The optimization of carbonyl detection in complex mixtures is subject to various regulatory considerations that must be carefully addressed when developing and implementing analytical methods. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA), and International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) have established guidelines and requirements for analytical method validation and quality control in pharmaceutical and food industries.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is method validation, which ensures the reliability and reproducibility of the analytical technique. Validation parameters typically include accuracy, precision, specificity, linearity, range, and robustness. For carbonyl detection in complex mixtures, special attention must be given to matrix effects and potential interferences, as these can significantly impact the method's performance and compliance with regulatory standards.
Regulatory agencies also emphasize the importance of using standardized protocols and reference materials. In the case of carbonyl detection, certified reference materials for various carbonyl compounds should be used to demonstrate the method's accuracy and traceability. Additionally, participation in proficiency testing programs may be required to ensure ongoing compliance and comparability of results across different laboratories.
Data integrity and documentation are critical aspects of regulatory compliance. Analytical methods for carbonyl detection must be supported by comprehensive documentation, including standard operating procedures (SOPs), method validation reports, and ongoing quality control records. Electronic data systems used in the analysis should comply with 21 CFR Part 11 or similar regulations regarding electronic records and signatures.
Method transfer and comparability studies are often necessary when implementing a new or optimized method for carbonyl detection. Regulatory bodies may require demonstration of equivalence between the new method and previously validated techniques, especially if the method is intended to replace an existing compendial method.
Stability-indicating properties of the analytical method are particularly important for carbonyl detection, as these compounds can be products of degradation in various matrices. Regulatory guidelines often require that methods can effectively separate and quantify carbonyl compounds from potential degradation products and impurities.
Lastly, the choice of equipment and reagents used in the analytical method must comply with regulatory standards. This includes the use of appropriately calibrated and maintained instruments, as well as the selection of high-quality, traceable reagents and standards. Regular system suitability tests and instrument qualification procedures should be implemented to ensure ongoing compliance with regulatory requirements.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is method validation, which ensures the reliability and reproducibility of the analytical technique. Validation parameters typically include accuracy, precision, specificity, linearity, range, and robustness. For carbonyl detection in complex mixtures, special attention must be given to matrix effects and potential interferences, as these can significantly impact the method's performance and compliance with regulatory standards.
Regulatory agencies also emphasize the importance of using standardized protocols and reference materials. In the case of carbonyl detection, certified reference materials for various carbonyl compounds should be used to demonstrate the method's accuracy and traceability. Additionally, participation in proficiency testing programs may be required to ensure ongoing compliance and comparability of results across different laboratories.
Data integrity and documentation are critical aspects of regulatory compliance. Analytical methods for carbonyl detection must be supported by comprehensive documentation, including standard operating procedures (SOPs), method validation reports, and ongoing quality control records. Electronic data systems used in the analysis should comply with 21 CFR Part 11 or similar regulations regarding electronic records and signatures.
Method transfer and comparability studies are often necessary when implementing a new or optimized method for carbonyl detection. Regulatory bodies may require demonstration of equivalence between the new method and previously validated techniques, especially if the method is intended to replace an existing compendial method.
Stability-indicating properties of the analytical method are particularly important for carbonyl detection, as these compounds can be products of degradation in various matrices. Regulatory guidelines often require that methods can effectively separate and quantify carbonyl compounds from potential degradation products and impurities.
Lastly, the choice of equipment and reagents used in the analytical method must comply with regulatory standards. This includes the use of appropriately calibrated and maintained instruments, as well as the selection of high-quality, traceable reagents and standards. Regular system suitability tests and instrument qualification procedures should be implemented to ensure ongoing compliance with regulatory requirements.
Environmental Impact of Carbonyl Detection Techniques
The environmental impact of carbonyl detection techniques is a critical consideration in the optimization of these methods for complex mixtures. Traditional carbonyl detection methods often involve the use of chemical reagents and solvents that can have significant environmental implications. These substances may contribute to air and water pollution, pose risks to ecosystems, and require careful disposal procedures.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during the detection process. Many carbonyl detection techniques utilize derivatization agents, such as 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH), which can emit VOCs into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, potentially impacting air quality and human health in surrounding areas.
Water pollution is another significant issue associated with carbonyl detection methods. The use of organic solvents and reagents can lead to contamination of water sources if not properly managed. Improper disposal of these chemicals may result in the introduction of harmful substances into aquatic ecosystems, affecting flora and fauna and potentially entering the food chain.
The production and disposal of single-use materials, such as cartridges and filters used in some carbonyl detection techniques, also contribute to environmental concerns. These materials often end up in landfills, adding to the growing problem of solid waste management and potentially leaching harmful chemicals into the soil and groundwater.
Energy consumption is an additional factor to consider when evaluating the environmental impact of carbonyl detection methods. Some techniques require sophisticated instrumentation that consumes significant amounts of electricity, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change if powered by non-renewable energy sources.
To address these environmental challenges, researchers and industry professionals are exploring more sustainable approaches to carbonyl detection. Green chemistry principles are being applied to develop eco-friendly reagents and solvents that minimize environmental impact. Additionally, efforts are being made to reduce the overall chemical consumption in detection processes through the development of more sensitive and efficient analytical methods.
Advancements in instrumentation are also contributing to reduced environmental impact. The development of more energy-efficient equipment and the integration of renewable energy sources in laboratory settings are helping to decrease the carbon footprint associated with carbonyl detection techniques. Furthermore, the implementation of closed-loop systems and improved waste management practices are minimizing the release of harmful substances into the environment.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during the detection process. Many carbonyl detection techniques utilize derivatization agents, such as 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH), which can emit VOCs into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, potentially impacting air quality and human health in surrounding areas.
Water pollution is another significant issue associated with carbonyl detection methods. The use of organic solvents and reagents can lead to contamination of water sources if not properly managed. Improper disposal of these chemicals may result in the introduction of harmful substances into aquatic ecosystems, affecting flora and fauna and potentially entering the food chain.
The production and disposal of single-use materials, such as cartridges and filters used in some carbonyl detection techniques, also contribute to environmental concerns. These materials often end up in landfills, adding to the growing problem of solid waste management and potentially leaching harmful chemicals into the soil and groundwater.
Energy consumption is an additional factor to consider when evaluating the environmental impact of carbonyl detection methods. Some techniques require sophisticated instrumentation that consumes significant amounts of electricity, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change if powered by non-renewable energy sources.
To address these environmental challenges, researchers and industry professionals are exploring more sustainable approaches to carbonyl detection. Green chemistry principles are being applied to develop eco-friendly reagents and solvents that minimize environmental impact. Additionally, efforts are being made to reduce the overall chemical consumption in detection processes through the development of more sensitive and efficient analytical methods.
Advancements in instrumentation are also contributing to reduced environmental impact. The development of more energy-efficient equipment and the integration of renewable energy sources in laboratory settings are helping to decrease the carbon footprint associated with carbonyl detection techniques. Furthermore, the implementation of closed-loop systems and improved waste management practices are minimizing the release of harmful substances into the environment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!