How to Optimize Propionic Acid for Future Manufacturing Demands?
Propionic Acid Evolution and Objectives
Propionic acid has been a key component in various industries for decades, with its applications ranging from food preservation to polymer production. The evolution of propionic acid manufacturing has been driven by increasing demand and the need for more efficient production methods. Initially produced through petrochemical processes, the industry has gradually shifted towards more sustainable bio-based production techniques.
The primary objective in optimizing propionic acid for future manufacturing demands is to develop more cost-effective and environmentally friendly production methods. This involves improving fermentation processes, enhancing microbial strains, and exploring novel catalytic pathways. Additionally, there is a focus on increasing production yields and purity while reducing energy consumption and waste generation.
One of the key trends in propionic acid evolution is the shift towards renewable feedstocks. As sustainability becomes a critical factor in industrial processes, manufacturers are exploring the use of biomass-derived raw materials to replace traditional petroleum-based feedstocks. This transition aligns with global efforts to reduce carbon footprints and promote circular economy principles.
Another significant aspect of propionic acid's evolution is the development of advanced fermentation technologies. Researchers are working on optimizing microbial strains and fermentation conditions to enhance productivity and selectivity. This includes the use of genetic engineering techniques to create more efficient producer organisms and the implementation of continuous fermentation processes to improve overall production efficiency.
The optimization of downstream processing is also a crucial objective in propionic acid manufacturing. This involves developing more effective separation and purification techniques to obtain high-purity propionic acid while minimizing energy consumption and waste generation. Advanced membrane technologies and innovative extraction methods are being explored to achieve these goals.
As the demand for propionic acid continues to grow in various sectors, including food, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture, there is a pressing need to scale up production capabilities. This necessitates the development of larger, more efficient reactors and the implementation of process intensification strategies to maximize output while minimizing resource utilization.
In conclusion, the evolution and objectives of propionic acid optimization for future manufacturing demands are centered around sustainability, efficiency, and scalability. By addressing these key areas, the industry aims to meet the growing global demand for propionic acid while adhering to stringent environmental and economic standards.
Market Analysis for Propionic Acid
The global propionic acid market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The market size was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $2.1 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of around 5.2% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising consumption of propionic acid in food preservatives, animal feed, and pharmaceuticals.
The food and beverage industry remains the largest consumer of propionic acid, accounting for over 40% of the total market share. The increasing demand for packaged and processed foods, coupled with growing concerns about food safety and shelf life extension, is driving the use of propionic acid as a preservative. Additionally, the animal feed sector is witnessing significant growth in propionic acid consumption, particularly in developing regions where livestock production is expanding rapidly.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for propionic acid, collectively accounting for more than 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable income, and changing dietary habits in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by the presence of several key players, including BASF SE, Dow Inc., Eastman Chemical Company, and Perstorp Holding AB. These companies are focusing on expanding their production capacities and developing innovative applications to maintain their competitive edge in the market.
Despite the positive outlook, the propionic acid market faces challenges such as volatile raw material prices and stringent environmental regulations. The fluctuating prices of propylene, the primary raw material for propionic acid production, can significantly impact profit margins. Moreover, increasing environmental concerns and regulations regarding chemical manufacturing processes may pose challenges to market growth.
To address future manufacturing demands, the industry is exploring sustainable production methods and alternative feedstocks. Bio-based propionic acid production using renewable resources is gaining traction, with several companies investing in research and development to commercialize these processes. Additionally, there is a growing focus on developing high-purity grades of propionic acid to cater to specialized applications in pharmaceuticals and personal care products.
Technical Challenges in Propionic Acid Production
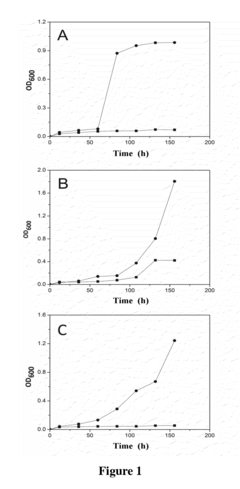
The production of propionic acid faces several significant technical challenges that need to be addressed to meet future manufacturing demands. One of the primary issues is the low yield and productivity of current fermentation processes. Traditional methods using Propionibacterium strains often result in limited product concentrations, typically below 50 g/L, which is insufficient for large-scale industrial applications.
Another major challenge is the high energy consumption associated with downstream processing, particularly in the separation and purification stages. The recovery of propionic acid from fermentation broths is complex due to its high water solubility and low volatility. Conventional distillation methods are energy-intensive and often economically unfeasible, especially when dealing with dilute solutions.
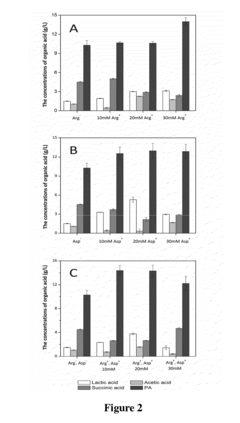
The formation of by-products during fermentation poses an additional hurdle. Acetic acid and succinic acid are common co-products that complicate the purification process and reduce overall yield. Developing strategies to minimize by-product formation or to efficiently separate these compounds from propionic acid is crucial for optimizing production.
Substrate cost and availability present ongoing challenges. While glycerol has emerged as a promising low-cost substrate, its inconsistent supply and quality can affect process stability and economics. Finding alternative, readily available, and cost-effective carbon sources remains a key area of research.
pH control during fermentation is another critical issue. Propionic acid production leads to a decrease in pH, which inhibits microbial growth and productivity. Maintaining an optimal pH without excessive use of neutralizing agents, which can increase production costs and complicate downstream processing, is a delicate balance that needs to be achieved.
Genetic instability of production strains over extended cultivation periods is a concern that affects long-term process reliability. Developing robust strains that maintain high productivity over multiple generations is essential for consistent industrial-scale production.
Lastly, the development of continuous fermentation processes presents both opportunities and challenges. While continuous operations can potentially increase productivity and reduce costs, they require sophisticated process control and face issues such as cell washout and contamination risks. Overcoming these technical hurdles is crucial for realizing the full potential of continuous propionic acid production.
Current Production Methods
01 Fermentation process optimization
Optimization of propionic acid production through fermentation involves improving bacterial strains, adjusting fermentation conditions, and enhancing substrate utilization. This can include modifying temperature, pH, and nutrient composition to maximize yield and productivity.- Fermentation process optimization: Optimization of propionic acid production through fermentation involves improving bacterial strains, adjusting fermentation conditions, and enhancing substrate utilization. This includes optimizing temperature, pH, and nutrient composition to maximize yield and productivity.
- Catalytic synthesis methods: Development of efficient catalytic processes for propionic acid synthesis, focusing on improving catalyst selectivity, activity, and stability. This includes exploring novel catalysts and optimizing reaction conditions to enhance yield and reduce byproduct formation.
- Purification and separation techniques: Advancements in purification and separation methods for propionic acid, including distillation, extraction, and membrane-based processes. These techniques aim to improve product purity, reduce energy consumption, and increase overall process efficiency.
- Process integration and waste reduction: Optimization of propionic acid production through process integration, focusing on reducing waste, improving energy efficiency, and implementing circular economy principles. This includes developing closed-loop systems and utilizing byproducts for other applications.
- Continuous production methods: Development of continuous production processes for propionic acid, aiming to improve productivity, reduce operational costs, and enhance product quality. This includes designing and optimizing continuous reactors and implementing advanced process control strategies.
02 Catalytic synthesis methods
Development of efficient catalytic processes for propionic acid synthesis, focusing on improving selectivity and yield. This may involve the use of novel catalysts, optimizing reaction conditions, and exploring alternative feedstocks to enhance overall process efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Purification and separation techniques
Advancements in purification and separation methods for propionic acid, including distillation, extraction, and membrane-based processes. These techniques aim to increase product purity and reduce energy consumption in the separation process.Expand Specific Solutions04 Process integration and waste reduction
Optimization of propionic acid production through process integration, focusing on reducing waste streams and improving overall resource efficiency. This may include the development of closed-loop systems and the utilization of by-products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Continuous production methods
Development of continuous production processes for propionic acid, aiming to improve productivity and reduce operational costs. This includes the design of specialized reactors and the optimization of process parameters for sustained production.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Producers and Competitors
The propionic acid market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in various industries such as food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. The global market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate expected to be in the high single digits. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with key players like BASF, Eastman Chemical, and Dow Chemical leading innovation efforts. Academic institutions such as The Ohio State University and Nanjing Tech University are contributing to research and development, focusing on optimizing production processes and exploring new applications. The technology's maturity is moderate, with ongoing efforts to improve efficiency and sustainability in manufacturing methods.
Arkema France SA
Novomer, Inc.
Innovative Patents in Propionic Acid Synthesis
- Adding arginine and/or aspartic acid to the culture medium during the cultivation of Propionibacterium acdipropionici to enhance acid tolerance and propionic acid productivity.
- A method involving the dehydration of 3-hydroxypropionic acid to form acrylic acid using a first catalyst, followed by hydrogenation of acrylic acid to propionic acid using a second catalyst, with specific temperature and pressure conditions, and optionally using a polymerization inhibitor to prevent acrylic acid polymerization.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of propionic acid production and optimization is crucial for ensuring sustainable manufacturing practices in the future. As demand for propionic acid continues to grow, it is essential to evaluate and mitigate potential environmental risks associated with its production processes.
One of the primary environmental concerns in propionic acid manufacturing is the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and greenhouse gases. Traditional production methods often rely on petrochemical feedstocks, which contribute to carbon dioxide emissions and air pollution. To address this issue, researchers are exploring bio-based production routes using renewable resources such as biomass or agricultural waste. These alternative methods have shown promising results in reducing the carbon footprint of propionic acid production.
Water consumption and wastewater management are also significant environmental factors to consider. The production process typically requires substantial amounts of water for cooling and separation processes. Implementing water recycling systems and optimizing water usage can help minimize the environmental impact on local water resources. Additionally, proper treatment of wastewater streams is essential to prevent contamination of aquatic ecosystems.
Energy efficiency is another critical aspect of environmental impact assessment. Conventional production methods often involve energy-intensive processes, contributing to increased greenhouse gas emissions. Developing more energy-efficient technologies, such as advanced catalysts and reactor designs, can significantly reduce energy consumption and associated environmental impacts.
Land use and biodiversity considerations are particularly relevant when exploring bio-based production routes. While these methods offer potential environmental benefits, they may require significant land resources for feedstock cultivation. Careful planning and sustainable agricultural practices are necessary to minimize negative impacts on local ecosystems and biodiversity.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies have been conducted to evaluate the overall environmental impact of propionic acid production. These assessments consider factors such as raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, transportation, and end-of-life disposal. Results from LCA studies can guide decision-making processes and help identify areas for improvement in the production chain.
As the demand for propionic acid grows, it is crucial to prioritize the development of cleaner production technologies and sustainable manufacturing practices. This includes exploring green chemistry principles, implementing circular economy concepts, and investing in research and development of novel production methods with reduced environmental footprints. By addressing these environmental concerns, the propionic acid industry can work towards meeting future manufacturing demands while minimizing its impact on the planet.
Regulatory Framework for Propionic Acid
The regulatory framework for propionic acid plays a crucial role in shaping its production, distribution, and use across various industries. As the demand for propionic acid continues to grow, manufacturers must navigate an increasingly complex landscape of regulations to ensure compliance and optimize their operations.
At the global level, organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) provide guidelines for the safe use of propionic acid in food preservation and animal feed. These international standards serve as a foundation for many national regulatory bodies to develop their own specific regulations.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates propionic acid as a food additive under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. The FDA has established specific limits for its use in various food products and requires manufacturers to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in its production. Additionally, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees the environmental impact of propionic acid manufacturing under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA).
The European Union has implemented stringent regulations through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) program. These regulations set strict guidelines for the production, import, and use of propionic acid within the EU market, emphasizing safety assessments and risk management.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory frameworks. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) and Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) oversee the use of propionic acid in food and pharmaceutical applications, respectively.
To optimize propionic acid production for future manufacturing demands, companies must invest in robust compliance systems and stay abreast of evolving regulations. This includes implementing traceability measures, conducting regular safety assessments, and adopting sustainable production practices that align with emerging environmental regulations.
Furthermore, manufacturers should engage in proactive dialogue with regulatory bodies to anticipate future changes and contribute to the development of science-based regulations. Collaboration with industry associations and participation in public consultations can help shape a regulatory environment that balances safety concerns with innovation and economic growth.
As the global regulatory landscape continues to evolve, manufacturers must also consider the impact of trade agreements and international harmonization efforts on propionic acid regulations. Adapting to these changes while maintaining efficiency in production will be key to meeting future manufacturing demands.