Longitudinal wave tactics in advanced manufacturing process simulation
AUG 13, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Longitudinal Wave Simulation Background
Longitudinal wave simulation has emerged as a critical component in advanced manufacturing process simulation, offering unprecedented insights into material behavior and process dynamics. This technology has its roots in the broader field of wave mechanics, which has been studied extensively since the early 20th century. The application of longitudinal wave simulation to manufacturing processes, however, is a more recent development, driven by the increasing demand for high-precision and complex manufacturing techniques.
The evolution of longitudinal wave simulation in manufacturing can be traced back to the 1980s when computational power began to allow for more sophisticated modeling of material properties and wave propagation. Initially, these simulations were limited to simple, idealized scenarios due to computational constraints. As computing capabilities advanced, so did the complexity and accuracy of longitudinal wave simulations, enabling more realistic representations of manufacturing processes.
In the context of advanced manufacturing, longitudinal waves play a crucial role in various processes, including ultrasonic welding, non-destructive testing, and additive manufacturing. These waves, characterized by oscillations parallel to the direction of wave propagation, can provide valuable information about material properties, defect detection, and process optimization. The ability to accurately simulate these waves has become increasingly important as manufacturers strive for higher quality, efficiency, and innovation in their processes.
The current state of longitudinal wave simulation in advanced manufacturing is marked by a convergence of multiple disciplines, including materials science, physics, and computer science. Modern simulation techniques incorporate advanced numerical methods, such as finite element analysis and spectral methods, to model wave propagation in complex geometries and heterogeneous materials. These simulations often integrate with other modeling techniques, such as heat transfer and fluid dynamics, to provide a comprehensive view of the manufacturing process.
As the field progresses, researchers and industry professionals are focusing on several key objectives. These include improving the accuracy and speed of simulations, developing more sophisticated models for complex materials and processes, and integrating real-time simulation capabilities into manufacturing systems. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on leveraging machine learning and artificial intelligence to enhance the predictive power of longitudinal wave simulations and to automate the optimization of manufacturing processes based on simulation results.
The evolution of longitudinal wave simulation in manufacturing can be traced back to the 1980s when computational power began to allow for more sophisticated modeling of material properties and wave propagation. Initially, these simulations were limited to simple, idealized scenarios due to computational constraints. As computing capabilities advanced, so did the complexity and accuracy of longitudinal wave simulations, enabling more realistic representations of manufacturing processes.
In the context of advanced manufacturing, longitudinal waves play a crucial role in various processes, including ultrasonic welding, non-destructive testing, and additive manufacturing. These waves, characterized by oscillations parallel to the direction of wave propagation, can provide valuable information about material properties, defect detection, and process optimization. The ability to accurately simulate these waves has become increasingly important as manufacturers strive for higher quality, efficiency, and innovation in their processes.
The current state of longitudinal wave simulation in advanced manufacturing is marked by a convergence of multiple disciplines, including materials science, physics, and computer science. Modern simulation techniques incorporate advanced numerical methods, such as finite element analysis and spectral methods, to model wave propagation in complex geometries and heterogeneous materials. These simulations often integrate with other modeling techniques, such as heat transfer and fluid dynamics, to provide a comprehensive view of the manufacturing process.
As the field progresses, researchers and industry professionals are focusing on several key objectives. These include improving the accuracy and speed of simulations, developing more sophisticated models for complex materials and processes, and integrating real-time simulation capabilities into manufacturing systems. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on leveraging machine learning and artificial intelligence to enhance the predictive power of longitudinal wave simulations and to automate the optimization of manufacturing processes based on simulation results.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for longitudinal wave tactics in advanced manufacturing process simulation has been steadily growing in recent years. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing complexity of manufacturing processes and the need for more accurate and efficient simulation tools. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics are particularly interested in these advanced simulation techniques to optimize their production processes and reduce costs.
The global market for advanced manufacturing simulation software is expected to reach significant value in the coming years, with longitudinal wave tactics playing a crucial role in this expansion. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies and the increasing focus on digital twins in manufacturing. Longitudinal wave tactics offer unique advantages in simulating complex material behaviors and wave propagation phenomena, making them invaluable for industries dealing with high-precision manufacturing and quality control.
In the automotive sector, there is a growing demand for longitudinal wave simulation in areas such as crash testing, noise and vibration analysis, and structural integrity assessments. These simulations help manufacturers design safer, more efficient vehicles while reducing the need for costly physical prototypes. Similarly, in the aerospace industry, longitudinal wave tactics are essential for simulating the behavior of aircraft structures under various stress conditions, including turbulence and impact scenarios.
The electronics industry is another significant driver of market demand for longitudinal wave simulation. As electronic devices become increasingly compact and complex, manufacturers require advanced simulation tools to predict and optimize the performance of components under various conditions. Longitudinal wave tactics are particularly useful in simulating thermal management, signal integrity, and electromagnetic interference in electronic systems.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices is creating new opportunities for longitudinal wave simulation. These techniques can help optimize material usage, reduce waste, and improve energy efficiency in manufacturing processes. As companies strive to meet stringent environmental regulations and consumer demands for eco-friendly products, the demand for advanced simulation tools incorporating longitudinal wave tactics is expected to rise.
The market for longitudinal wave tactics in manufacturing simulation is also benefiting from advancements in computing power and artificial intelligence. These technological improvements are enabling more complex and accurate simulations, further driving adoption across various industries. As a result, software vendors and research institutions are investing heavily in developing more sophisticated longitudinal wave simulation tools to meet the evolving needs of the manufacturing sector.
The global market for advanced manufacturing simulation software is expected to reach significant value in the coming years, with longitudinal wave tactics playing a crucial role in this expansion. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies and the increasing focus on digital twins in manufacturing. Longitudinal wave tactics offer unique advantages in simulating complex material behaviors and wave propagation phenomena, making them invaluable for industries dealing with high-precision manufacturing and quality control.
In the automotive sector, there is a growing demand for longitudinal wave simulation in areas such as crash testing, noise and vibration analysis, and structural integrity assessments. These simulations help manufacturers design safer, more efficient vehicles while reducing the need for costly physical prototypes. Similarly, in the aerospace industry, longitudinal wave tactics are essential for simulating the behavior of aircraft structures under various stress conditions, including turbulence and impact scenarios.
The electronics industry is another significant driver of market demand for longitudinal wave simulation. As electronic devices become increasingly compact and complex, manufacturers require advanced simulation tools to predict and optimize the performance of components under various conditions. Longitudinal wave tactics are particularly useful in simulating thermal management, signal integrity, and electromagnetic interference in electronic systems.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices is creating new opportunities for longitudinal wave simulation. These techniques can help optimize material usage, reduce waste, and improve energy efficiency in manufacturing processes. As companies strive to meet stringent environmental regulations and consumer demands for eco-friendly products, the demand for advanced simulation tools incorporating longitudinal wave tactics is expected to rise.
The market for longitudinal wave tactics in manufacturing simulation is also benefiting from advancements in computing power and artificial intelligence. These technological improvements are enabling more complex and accurate simulations, further driving adoption across various industries. As a result, software vendors and research institutions are investing heavily in developing more sophisticated longitudinal wave simulation tools to meet the evolving needs of the manufacturing sector.
Current Challenges in Manufacturing Simulation
Manufacturing simulation has become an indispensable tool in modern industrial processes, yet it faces several significant challenges in accurately representing complex manufacturing systems. One of the primary obstacles is the difficulty in simulating the propagation of longitudinal waves through materials during advanced manufacturing processes. This challenge arises from the multiscale nature of wave propagation, which spans from atomic-level interactions to macroscopic material behavior.
The current simulation models often struggle to capture the full spectrum of wave phenomena, particularly in heterogeneous materials or complex geometries commonly encountered in advanced manufacturing. The computational demands for high-fidelity simulations that incorporate longitudinal wave effects are substantial, often exceeding the capabilities of standard industrial computing resources. This limitation forces many manufacturers to rely on simplified models that may not fully capture the nuances of wave-material interactions.
Another significant challenge lies in the integration of real-time data from manufacturing processes into simulation models. The dynamic nature of longitudinal wave propagation requires continuous updating of simulation parameters, which is difficult to achieve with current sensor technologies and data processing capabilities. This gap between real-world observations and simulation outputs can lead to discrepancies in predicting material behavior and process outcomes.
The validation of simulation results against experimental data presents another hurdle. The complexity of longitudinal wave behavior in advanced manufacturing processes makes it challenging to design experiments that can accurately measure and isolate wave effects. This validation gap undermines confidence in simulation outcomes and hinders the widespread adoption of wave-based simulation techniques in industrial settings.
Furthermore, the interdisciplinary nature of advanced manufacturing simulation poses challenges in terms of expertise and collaboration. Effective simulation of longitudinal wave tactics requires knowledge spanning materials science, wave physics, numerical methods, and manufacturing processes. Many organizations struggle to assemble teams with the diverse skill sets necessary to develop and implement these sophisticated simulation tools.
Lastly, the rapid evolution of manufacturing technologies outpaces the development of corresponding simulation capabilities. As new manufacturing processes emerge, such as additive manufacturing or advanced joining techniques, existing simulation frameworks often lag behind in their ability to accurately model the associated longitudinal wave phenomena. This gap between innovation in manufacturing processes and simulation capabilities creates a bottleneck in the development and optimization of new production methods.
The current simulation models often struggle to capture the full spectrum of wave phenomena, particularly in heterogeneous materials or complex geometries commonly encountered in advanced manufacturing. The computational demands for high-fidelity simulations that incorporate longitudinal wave effects are substantial, often exceeding the capabilities of standard industrial computing resources. This limitation forces many manufacturers to rely on simplified models that may not fully capture the nuances of wave-material interactions.
Another significant challenge lies in the integration of real-time data from manufacturing processes into simulation models. The dynamic nature of longitudinal wave propagation requires continuous updating of simulation parameters, which is difficult to achieve with current sensor technologies and data processing capabilities. This gap between real-world observations and simulation outputs can lead to discrepancies in predicting material behavior and process outcomes.
The validation of simulation results against experimental data presents another hurdle. The complexity of longitudinal wave behavior in advanced manufacturing processes makes it challenging to design experiments that can accurately measure and isolate wave effects. This validation gap undermines confidence in simulation outcomes and hinders the widespread adoption of wave-based simulation techniques in industrial settings.
Furthermore, the interdisciplinary nature of advanced manufacturing simulation poses challenges in terms of expertise and collaboration. Effective simulation of longitudinal wave tactics requires knowledge spanning materials science, wave physics, numerical methods, and manufacturing processes. Many organizations struggle to assemble teams with the diverse skill sets necessary to develop and implement these sophisticated simulation tools.
Lastly, the rapid evolution of manufacturing technologies outpaces the development of corresponding simulation capabilities. As new manufacturing processes emerge, such as additive manufacturing or advanced joining techniques, existing simulation frameworks often lag behind in their ability to accurately model the associated longitudinal wave phenomena. This gap between innovation in manufacturing processes and simulation capabilities creates a bottleneck in the development and optimization of new production methods.
Existing Longitudinal Wave Solutions
01 Acoustic wave propagation techniques
This category focuses on methods and systems for generating, controlling, and analyzing longitudinal acoustic waves. It includes techniques for wave propagation in various mediums, signal processing algorithms, and applications in fields such as medical imaging, non-destructive testing, and underwater communication.- Acoustic wave propagation techniques: This category focuses on methods and systems for generating, controlling, and analyzing longitudinal acoustic waves. It includes techniques for wave propagation in various mediums, signal processing algorithms, and applications in fields such as medical imaging, non-destructive testing, and underwater communication.
- Ultrasonic devices and transducers: This point covers the design and development of ultrasonic devices and transducers specifically for generating and detecting longitudinal waves. It includes innovations in transducer materials, array configurations, and signal generation techniques to improve the efficiency and accuracy of longitudinal wave applications.
- Longitudinal wave-based imaging systems: This category encompasses imaging systems that utilize longitudinal waves for various applications. It includes advancements in medical ultrasound, industrial non-destructive testing, and underwater sonar systems. The focus is on improving image resolution, penetration depth, and real-time processing capabilities.
- Signal processing for longitudinal waves: This point covers advanced signal processing techniques specifically designed for longitudinal wave applications. It includes methods for noise reduction, echo cancellation, Doppler processing, and beamforming algorithms to enhance the quality and interpretability of longitudinal wave signals in various environments.
- Longitudinal wave-based communication systems: This category focuses on the development of communication systems that utilize longitudinal waves for data transmission. It includes underwater acoustic communication, through-wall communication, and other challenging environments where traditional electromagnetic waves are ineffective. The emphasis is on improving data rates, reducing latency, and enhancing reliability in these systems.
02 Ultrasonic devices and transducers
This point covers the design and development of ultrasonic devices and transducers specifically for generating and detecting longitudinal waves. It includes innovations in transducer materials, array configurations, and signal generation techniques to improve the efficiency and accuracy of longitudinal wave applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Longitudinal wave-based imaging systems
This category encompasses imaging systems that utilize longitudinal waves for various applications. It includes advancements in medical ultrasound, industrial non-destructive testing, and seismic imaging techniques. The focus is on improving image resolution, penetration depth, and real-time processing capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions04 Signal processing for longitudinal waves
This point covers advanced signal processing techniques specifically designed for longitudinal wave applications. It includes methods for noise reduction, signal enhancement, feature extraction, and pattern recognition in longitudinal wave data. These techniques aim to improve the accuracy and reliability of wave-based measurements and analyses.Expand Specific Solutions05 Longitudinal wave-based communication systems
This category focuses on the development of communication systems that utilize longitudinal waves for data transmission. It includes techniques for modulation, encoding, and multiplexing of longitudinal wave signals, as well as methods for overcoming challenges in wave propagation through various mediums, particularly in underwater and subterranean environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Simulation Software
The longitudinal wave tactics in advanced manufacturing process simulation market is in its growth stage, with increasing adoption across industries. The market size is expanding as more companies recognize the value of simulation in optimizing manufacturing processes. Technologically, the field is rapidly evolving, with key players like Southwest Research Institute, IBM, and Siemens AG driving innovation. These companies are developing sophisticated simulation tools that incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning. While established firms lead in market share, emerging players like Deep R&D Ltd. are introducing novel approaches, intensifying competition and accelerating technological advancement in this domain.
Southwest Research Institute
Technical Solution: Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has developed advanced simulation techniques for longitudinal wave tactics in manufacturing processes. Their approach utilizes high-fidelity computational models to simulate wave propagation in complex materials and structures. SwRI's method incorporates multi-physics simulations that account for material nonlinearities, temperature effects, and dynamic loading conditions[1]. The institute has also implemented machine learning algorithms to optimize simulation parameters and reduce computational time[3]. Their simulation platform integrates with digital twin technology, allowing real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance in manufacturing environments[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive multi-physics modeling, integration with digital twin technology, and machine learning optimization. Weaknesses: May require significant computational resources and specialized expertise for implementation.
Schlumberger Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Schlumberger has pioneered the application of longitudinal wave tactics in advanced manufacturing process simulation, particularly for the oil and gas industry. Their approach combines high-frequency ultrasonic imaging with sophisticated numerical modeling to simulate material behavior under extreme conditions. Schlumberger's technology utilizes adaptive mesh refinement techniques to accurately capture wave propagation in heterogeneous media[2]. The company has also developed proprietary algorithms for real-time inversion of wave data, enabling rapid characterization of material properties during manufacturing processes[4]. Their simulation platform incorporates machine learning for predictive maintenance and process optimization[6].
Strengths: Industry-specific expertise, real-time data inversion capabilities, and integration with predictive maintenance systems. Weaknesses: Solutions may be tailored primarily to oil and gas applications, potentially limiting broader manufacturing applicability.
Core Innovations in Wave Modeling
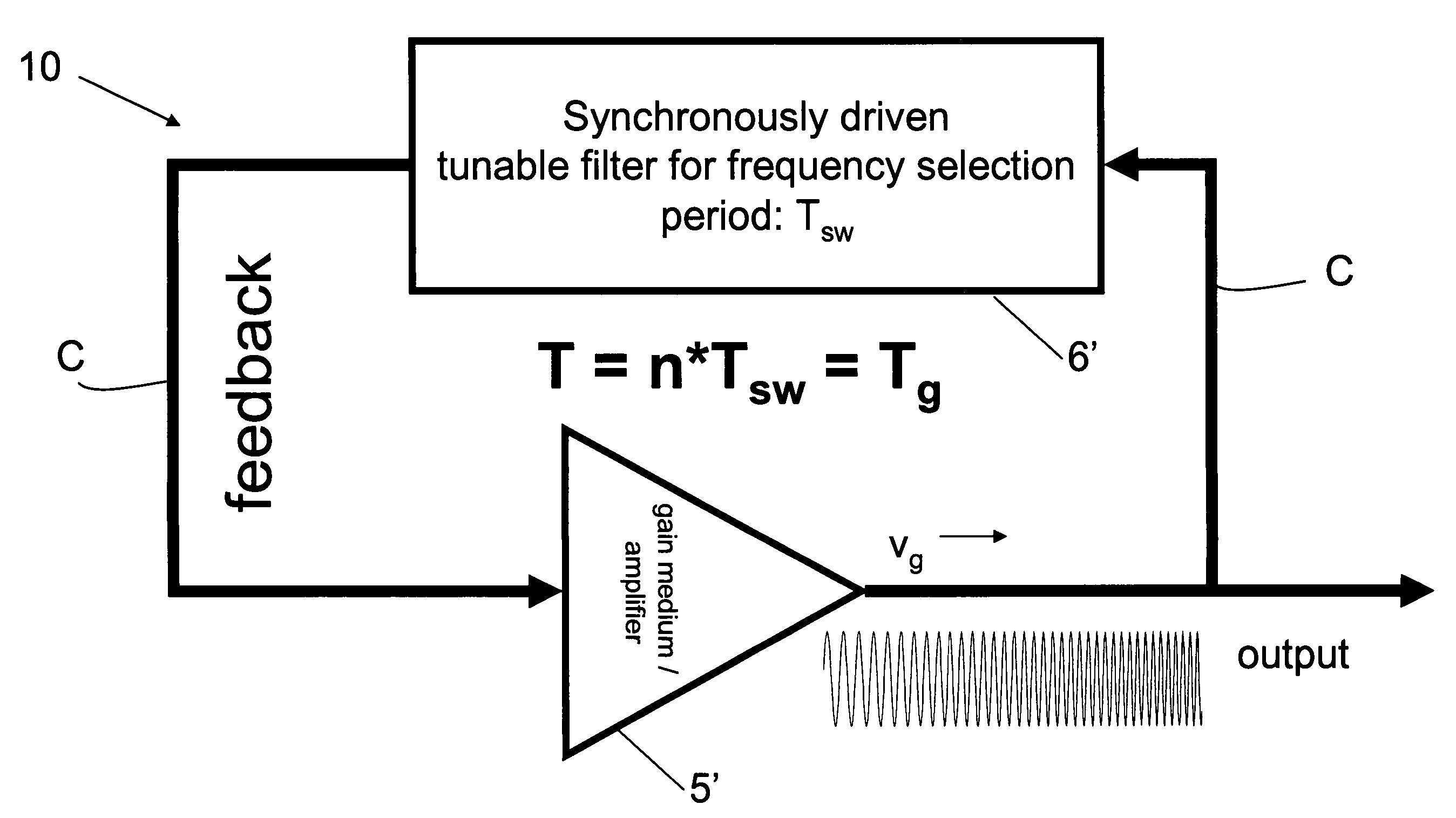
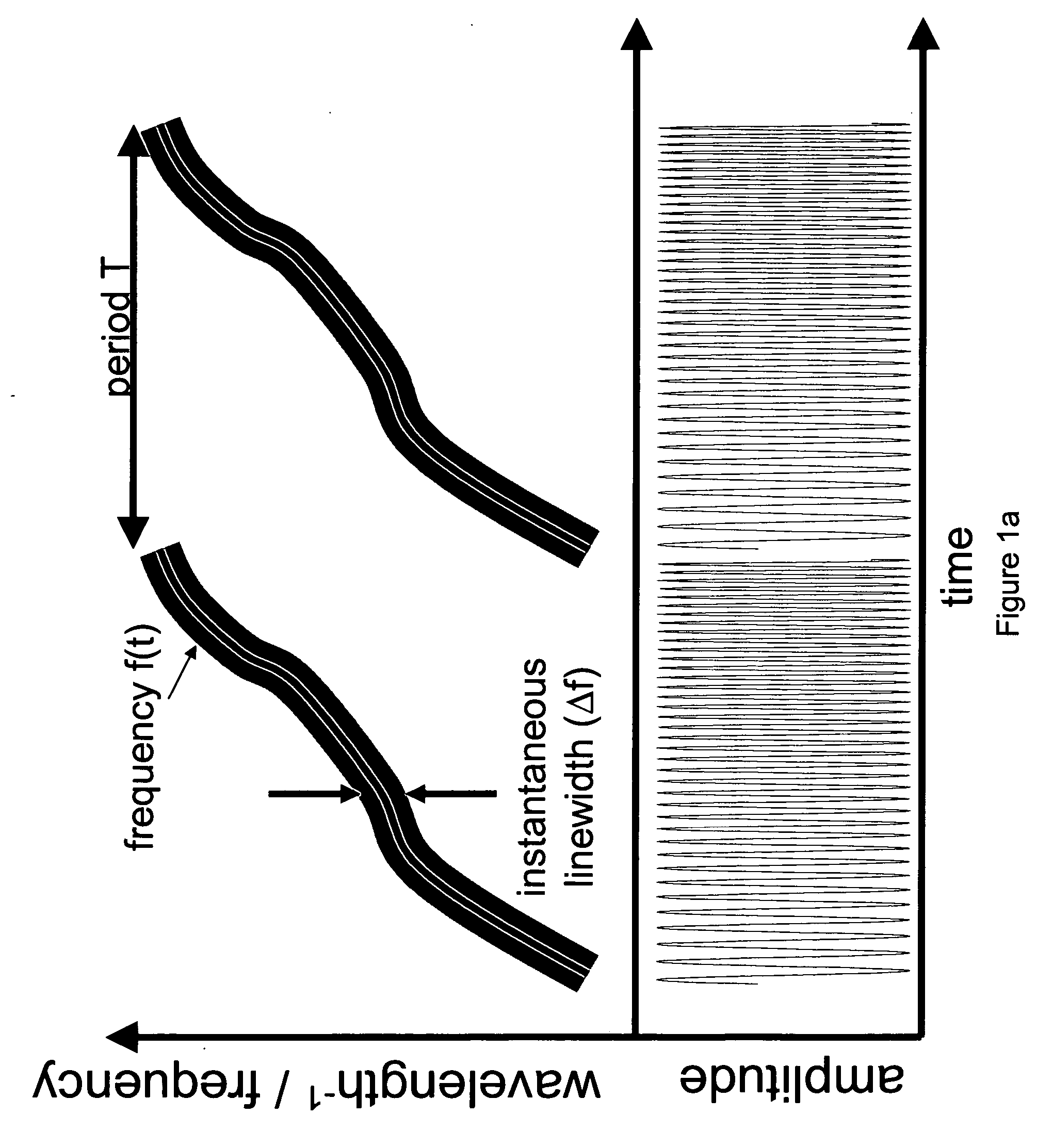
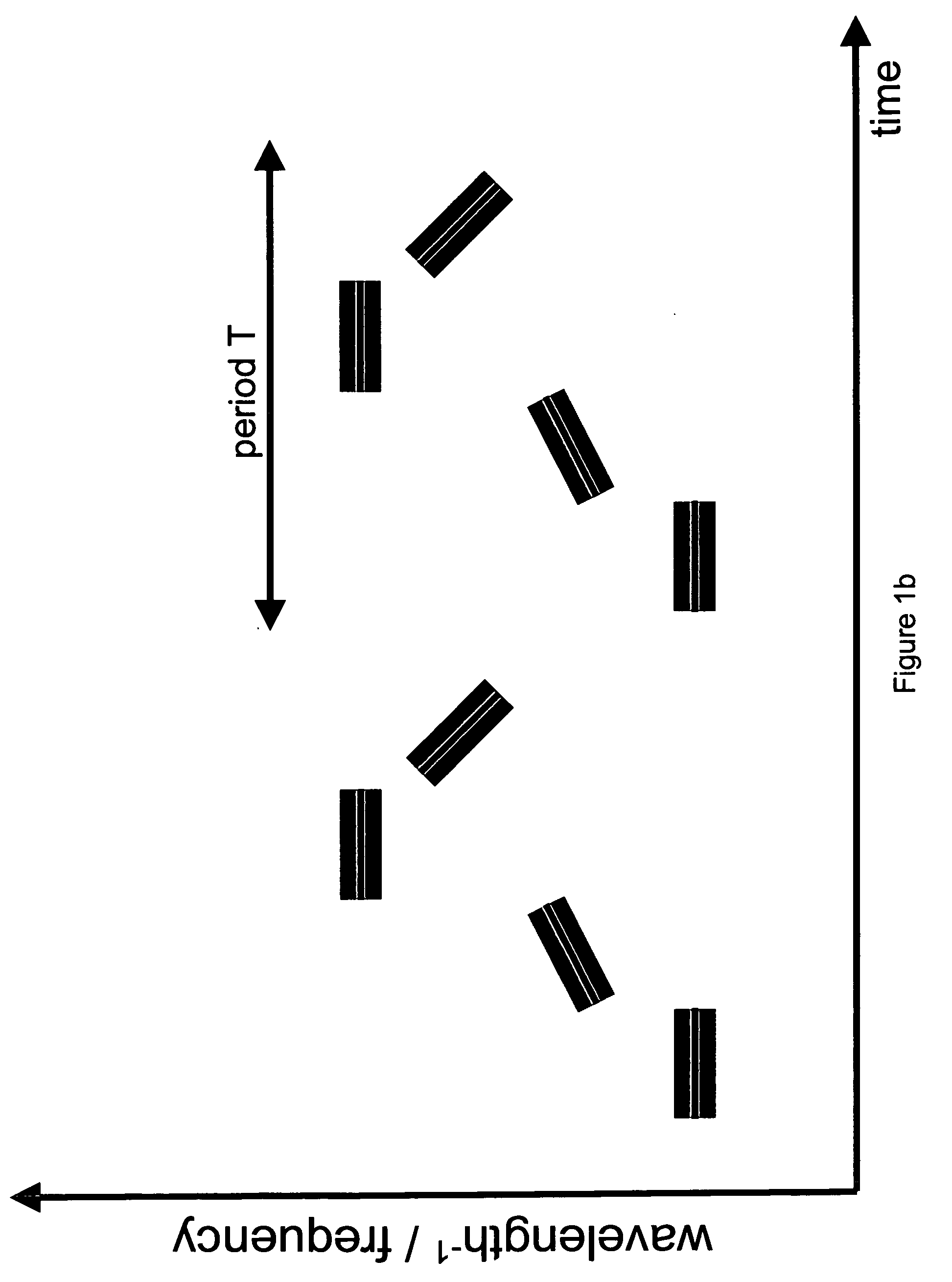
Mode locking methods and apparatus
PatentActiveUS20060187537A1
Innovation
- A wave generator system utilizing a gain element, a time-varying tunable wavelength selective filter, and a feedback element to produce frequency swept waveforms and chirped pulses, with the roundtrip time synchronized with the filter's tuning period, enabling enhanced power delivery and spectral utilization.
Shear wave velocity determination using multi-pole wave
PatentInactiveUS20050185510A1
Innovation
- A method involving the transmission and reception of multi-pole acoustic waveforms, which do not require isolating or enhancing specific waveform modes, using a mathematical model to determine borehole guided wave velocity, and subsequently the formation shear wave velocity, with simpler and less expensive transmitters and receivers.
High-Performance Computing Integration
The integration of high-performance computing (HPC) into advanced manufacturing process simulation, particularly for longitudinal wave tactics, represents a significant leap forward in computational capabilities. This integration enables the handling of complex, large-scale simulations that were previously infeasible due to computational limitations. HPC systems, with their massive parallel processing power, allow for the simulation of intricate wave propagation phenomena in manufacturing processes with unprecedented accuracy and speed.
In the context of longitudinal wave tactics, HPC integration facilitates the modeling of wave behavior in materials under various manufacturing conditions. This includes simulating the effects of high-frequency vibrations, ultrasonic welding processes, and acoustic emission during material deformation. The ability to process vast amounts of data in parallel allows for the incorporation of multi-physics models that account for thermal, mechanical, and electromagnetic interactions simultaneously.
One of the key advantages of HPC integration is the reduction in simulation time. Complex simulations that once took weeks or months can now be completed in hours or days. This acceleration in computational speed enables manufacturers to iterate designs more rapidly, optimize processes more efficiently, and explore a wider range of parameters. For longitudinal wave simulations, this means the ability to model wave propagation across multiple scales, from microscopic material interactions to macroscopic structural responses.
HPC also enhances the fidelity of simulations by allowing for finer mesh resolutions and more detailed material models. In longitudinal wave simulations, this translates to more accurate predictions of wave attenuation, dispersion, and interaction with material defects or boundaries. The increased resolution can reveal subtle phenomena that may be critical in understanding and optimizing manufacturing processes.
Furthermore, HPC integration enables the use of advanced numerical methods and algorithms that were previously impractical due to computational constraints. These include adaptive mesh refinement techniques, spectral element methods, and machine learning-enhanced simulations. For longitudinal wave tactics, this opens up possibilities for real-time process control and optimization based on predictive modeling.
The scalability of HPC systems also allows for the seamless integration of simulation results with experimental data. This synergy between simulation and experiment is particularly valuable in validating models for longitudinal wave propagation in complex manufacturing scenarios. It facilitates the development of digital twins that can accurately represent and predict the behavior of physical systems under various operating conditions.
In the context of longitudinal wave tactics, HPC integration facilitates the modeling of wave behavior in materials under various manufacturing conditions. This includes simulating the effects of high-frequency vibrations, ultrasonic welding processes, and acoustic emission during material deformation. The ability to process vast amounts of data in parallel allows for the incorporation of multi-physics models that account for thermal, mechanical, and electromagnetic interactions simultaneously.
One of the key advantages of HPC integration is the reduction in simulation time. Complex simulations that once took weeks or months can now be completed in hours or days. This acceleration in computational speed enables manufacturers to iterate designs more rapidly, optimize processes more efficiently, and explore a wider range of parameters. For longitudinal wave simulations, this means the ability to model wave propagation across multiple scales, from microscopic material interactions to macroscopic structural responses.
HPC also enhances the fidelity of simulations by allowing for finer mesh resolutions and more detailed material models. In longitudinal wave simulations, this translates to more accurate predictions of wave attenuation, dispersion, and interaction with material defects or boundaries. The increased resolution can reveal subtle phenomena that may be critical in understanding and optimizing manufacturing processes.
Furthermore, HPC integration enables the use of advanced numerical methods and algorithms that were previously impractical due to computational constraints. These include adaptive mesh refinement techniques, spectral element methods, and machine learning-enhanced simulations. For longitudinal wave tactics, this opens up possibilities for real-time process control and optimization based on predictive modeling.
The scalability of HPC systems also allows for the seamless integration of simulation results with experimental data. This synergy between simulation and experiment is particularly valuable in validating models for longitudinal wave propagation in complex manufacturing scenarios. It facilitates the development of digital twins that can accurately represent and predict the behavior of physical systems under various operating conditions.
Industrial Applications and Case Studies
Longitudinal wave tactics have found significant applications in advanced manufacturing process simulation across various industries. In the automotive sector, these techniques have been employed to optimize the design and production of vehicle components. For instance, leading manufacturers have utilized longitudinal wave simulations to analyze the structural integrity of car bodies during crash tests, resulting in improved safety features and reduced development costs.
The aerospace industry has also benefited from the implementation of longitudinal wave tactics in process simulation. Aircraft manufacturers have applied these methods to simulate the behavior of materials under high-stress conditions, such as those experienced during takeoff and landing. This has led to the development of more durable and lightweight components, enhancing overall aircraft performance and fuel efficiency.
In the field of electronics manufacturing, longitudinal wave simulations have proven invaluable for predicting and mitigating thermal stress in printed circuit boards (PCBs). By accurately modeling the propagation of heat waves through multi-layer PCBs, manufacturers have been able to optimize component placement and improve the reliability of electronic devices.
The oil and gas industry has leveraged longitudinal wave tactics to enhance the efficiency of drilling operations. Simulations of wave propagation through different geological formations have enabled companies to optimize drilling parameters, reducing equipment wear and improving overall extraction rates. This has resulted in significant cost savings and increased productivity in offshore and onshore drilling projects.
In the realm of additive manufacturing, longitudinal wave simulations have been instrumental in improving the quality of 3D-printed parts. By modeling the behavior of materials during the layer-by-layer deposition process, manufacturers have been able to minimize defects and optimize printing parameters for various materials, including metals and polymers.
The medical device industry has also embraced longitudinal wave tactics in process simulation. Manufacturers of implantable devices, such as artificial joints and cardiac stents, have utilized these techniques to predict the long-term performance of their products under physiological conditions. This has led to the development of more durable and biocompatible medical devices, improving patient outcomes and reducing the need for revision surgeries.
These case studies demonstrate the wide-ranging applicability and significant impact of longitudinal wave tactics in advanced manufacturing process simulation across diverse industries. By enabling more accurate predictions of material behavior and process outcomes, these techniques have contributed to improved product quality, reduced development costs, and enhanced manufacturing efficiency in numerous sectors.
The aerospace industry has also benefited from the implementation of longitudinal wave tactics in process simulation. Aircraft manufacturers have applied these methods to simulate the behavior of materials under high-stress conditions, such as those experienced during takeoff and landing. This has led to the development of more durable and lightweight components, enhancing overall aircraft performance and fuel efficiency.
In the field of electronics manufacturing, longitudinal wave simulations have proven invaluable for predicting and mitigating thermal stress in printed circuit boards (PCBs). By accurately modeling the propagation of heat waves through multi-layer PCBs, manufacturers have been able to optimize component placement and improve the reliability of electronic devices.
The oil and gas industry has leveraged longitudinal wave tactics to enhance the efficiency of drilling operations. Simulations of wave propagation through different geological formations have enabled companies to optimize drilling parameters, reducing equipment wear and improving overall extraction rates. This has resulted in significant cost savings and increased productivity in offshore and onshore drilling projects.
In the realm of additive manufacturing, longitudinal wave simulations have been instrumental in improving the quality of 3D-printed parts. By modeling the behavior of materials during the layer-by-layer deposition process, manufacturers have been able to minimize defects and optimize printing parameters for various materials, including metals and polymers.
The medical device industry has also embraced longitudinal wave tactics in process simulation. Manufacturers of implantable devices, such as artificial joints and cardiac stents, have utilized these techniques to predict the long-term performance of their products under physiological conditions. This has led to the development of more durable and biocompatible medical devices, improving patient outcomes and reducing the need for revision surgeries.
These case studies demonstrate the wide-ranging applicability and significant impact of longitudinal wave tactics in advanced manufacturing process simulation across diverse industries. By enabling more accurate predictions of material behavior and process outcomes, these techniques have contributed to improved product quality, reduced development costs, and enhanced manufacturing efficiency in numerous sectors.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!