Propionic Acid Development for Leather Preservation Solutions
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Leather Preservation Background
Propionic acid has emerged as a promising solution for leather preservation, addressing the growing need for sustainable and effective methods in the leather industry. The development of propionic acid-based preservation techniques stems from the industry's long-standing challenges with traditional preservation methods, which often involve harmful chemicals and environmental concerns.
Historically, leather preservation has relied on salt curing and the use of biocides, particularly chromium compounds. However, these methods have faced increasing scrutiny due to their environmental impact and potential health risks. The leather industry's shift towards more sustainable practices has driven the exploration of alternative preservation techniques, with propionic acid gaining significant attention in recent years.
Propionic acid, a naturally occurring carboxylic acid, offers several advantages as a leather preservative. Its antimicrobial properties effectively inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi, which are primary causes of leather degradation. Moreover, propionic acid is biodegradable and less toxic compared to traditional preservatives, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals.
The development of propionic acid for leather preservation has been influenced by advancements in biotechnology and green chemistry. Researchers have focused on optimizing formulations that maximize the preservative efficacy of propionic acid while minimizing its potential drawbacks, such as odor and corrosiveness. This has led to the creation of innovative blends and delivery systems that enhance the overall performance of propionic acid-based solutions.
The leather industry's adoption of propionic acid preservation techniques has been gradual but steady. Early applications focused on short-term preservation during transportation and storage. As research progressed, the scope expanded to include long-term preservation and integration into various stages of leather processing. This evolution has been driven by a combination of regulatory pressures, consumer demand for eco-friendly products, and the industry's own sustainability initiatives.
Recent technological advancements have further improved the efficacy of propionic acid in leather preservation. These include the development of controlled-release formulations, which provide prolonged protection, and the integration of propionic acid with other natural preservatives to create synergistic effects. Additionally, nanotechnology has been explored to enhance the penetration and distribution of propionic acid within leather fibers, potentially improving its preservative action.
The ongoing research in propionic acid leather preservation reflects the industry's commitment to innovation and sustainability. As environmental regulations become more stringent and consumer awareness grows, the demand for eco-friendly preservation solutions is expected to increase. This trend positions propionic acid as a key player in the future of leather preservation, driving continued investment in research and development to further optimize its application and expand its potential in the leather industry.
Historically, leather preservation has relied on salt curing and the use of biocides, particularly chromium compounds. However, these methods have faced increasing scrutiny due to their environmental impact and potential health risks. The leather industry's shift towards more sustainable practices has driven the exploration of alternative preservation techniques, with propionic acid gaining significant attention in recent years.
Propionic acid, a naturally occurring carboxylic acid, offers several advantages as a leather preservative. Its antimicrobial properties effectively inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi, which are primary causes of leather degradation. Moreover, propionic acid is biodegradable and less toxic compared to traditional preservatives, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals.
The development of propionic acid for leather preservation has been influenced by advancements in biotechnology and green chemistry. Researchers have focused on optimizing formulations that maximize the preservative efficacy of propionic acid while minimizing its potential drawbacks, such as odor and corrosiveness. This has led to the creation of innovative blends and delivery systems that enhance the overall performance of propionic acid-based solutions.
The leather industry's adoption of propionic acid preservation techniques has been gradual but steady. Early applications focused on short-term preservation during transportation and storage. As research progressed, the scope expanded to include long-term preservation and integration into various stages of leather processing. This evolution has been driven by a combination of regulatory pressures, consumer demand for eco-friendly products, and the industry's own sustainability initiatives.
Recent technological advancements have further improved the efficacy of propionic acid in leather preservation. These include the development of controlled-release formulations, which provide prolonged protection, and the integration of propionic acid with other natural preservatives to create synergistic effects. Additionally, nanotechnology has been explored to enhance the penetration and distribution of propionic acid within leather fibers, potentially improving its preservative action.
The ongoing research in propionic acid leather preservation reflects the industry's commitment to innovation and sustainability. As environmental regulations become more stringent and consumer awareness grows, the demand for eco-friendly preservation solutions is expected to increase. This trend positions propionic acid as a key player in the future of leather preservation, driving continued investment in research and development to further optimize its application and expand its potential in the leather industry.
Market Analysis for Leather Preservation Solutions
The global leather industry has been experiencing steady growth, with an increasing demand for high-quality leather products across various sectors. The market for leather preservation solutions, particularly those utilizing propionic acid, is poised for significant expansion due to the rising awareness of sustainable practices and the need for effective preservation methods.
The leather preservation market is primarily driven by the growing leather goods industry, which includes footwear, garments, accessories, and automotive upholstery. As consumer preferences shift towards durable and eco-friendly products, there is a heightened focus on preserving leather quality while minimizing environmental impact. This trend has created a substantial opportunity for innovative preservation solutions, especially those based on propionic acid.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the leather preservation market, with countries like China and India being major producers and consumers of leather goods. The region's rapid industrialization and increasing disposable income have fueled the demand for leather products, consequently boosting the need for effective preservation techniques. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by their established leather industries and stringent quality standards.
The automotive sector represents a significant market for leather preservation solutions, as luxury car manufacturers increasingly use high-quality leather interiors. The footwear industry also contributes substantially to the market growth, with sports and fashion footwear segments showing particular promise for leather preservation applications.
Environmental regulations and consumer awareness have led to a shift towards more sustainable preservation methods. Propionic acid-based solutions are gaining traction due to their effectiveness in preventing mold growth and bacterial contamination while being relatively eco-friendly compared to traditional preservation chemicals.
Market analysis indicates that small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the leather industry are increasingly adopting advanced preservation techniques to improve product quality and compete with larger manufacturers. This trend is expected to drive the demand for cost-effective and efficient preservation solutions, creating opportunities for propionic acid-based products.
The leather preservation market is also influenced by technological advancements in tanning and finishing processes. As these processes evolve, there is a growing need for compatible preservation methods that can maintain leather quality throughout the production chain and extend the product's lifespan.
In conclusion, the market for leather preservation solutions, particularly those utilizing propionic acid, shows promising growth potential. The industry's focus on sustainability, quality enhancement, and regulatory compliance positions propionic acid-based preservation methods as a key player in the evolving leather market landscape.
The leather preservation market is primarily driven by the growing leather goods industry, which includes footwear, garments, accessories, and automotive upholstery. As consumer preferences shift towards durable and eco-friendly products, there is a heightened focus on preserving leather quality while minimizing environmental impact. This trend has created a substantial opportunity for innovative preservation solutions, especially those based on propionic acid.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the leather preservation market, with countries like China and India being major producers and consumers of leather goods. The region's rapid industrialization and increasing disposable income have fueled the demand for leather products, consequently boosting the need for effective preservation techniques. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by their established leather industries and stringent quality standards.
The automotive sector represents a significant market for leather preservation solutions, as luxury car manufacturers increasingly use high-quality leather interiors. The footwear industry also contributes substantially to the market growth, with sports and fashion footwear segments showing particular promise for leather preservation applications.
Environmental regulations and consumer awareness have led to a shift towards more sustainable preservation methods. Propionic acid-based solutions are gaining traction due to their effectiveness in preventing mold growth and bacterial contamination while being relatively eco-friendly compared to traditional preservation chemicals.
Market analysis indicates that small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the leather industry are increasingly adopting advanced preservation techniques to improve product quality and compete with larger manufacturers. This trend is expected to drive the demand for cost-effective and efficient preservation solutions, creating opportunities for propionic acid-based products.
The leather preservation market is also influenced by technological advancements in tanning and finishing processes. As these processes evolve, there is a growing need for compatible preservation methods that can maintain leather quality throughout the production chain and extend the product's lifespan.
In conclusion, the market for leather preservation solutions, particularly those utilizing propionic acid, shows promising growth potential. The industry's focus on sustainability, quality enhancement, and regulatory compliance positions propionic acid-based preservation methods as a key player in the evolving leather market landscape.
Current Challenges in Leather Preservation
The leather industry faces significant challenges in preserving raw hides and finished leather products. Traditional preservation methods often rely on environmentally harmful chemicals, raising concerns about sustainability and regulatory compliance. Salt-based curing, while effective, contributes to soil and water pollution, prompting a search for more eco-friendly alternatives.
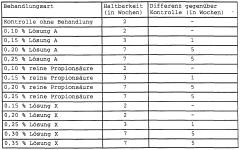
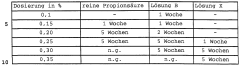
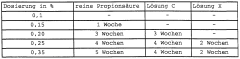
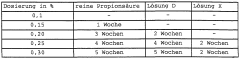
One of the primary challenges is finding a preservation solution that effectively inhibits microbial growth without compromising leather quality. Bacterial and fungal contamination can lead to putrefaction, discoloration, and structural damage, resulting in substantial economic losses. The ideal preservative must provide broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity while maintaining the leather's natural properties.
Another critical issue is the need for long-term preservation during storage and transportation. As global supply chains extend, raw hides and leather products may spend extended periods in varying environmental conditions. Preservatives must offer prolonged protection against degradation, ensuring that the leather remains in optimal condition from production to end-use.
The leather industry also grapples with the challenge of developing preservation methods that are compatible with diverse leather types and tanning processes. Different animal hides and finishing techniques require tailored preservation approaches, complicating the development of universal solutions.
Regulatory pressures and consumer demands for sustainable and non-toxic products further complicate preservation efforts. Many traditional preservatives face scrutiny due to their potential environmental and health impacts. The industry must navigate a complex landscape of regulations, balancing efficacy with safety and environmental responsibility.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant hurdle in adopting new preservation technologies. While innovative solutions may offer improved performance and sustainability, they often come with higher implementation costs. Manufacturers must weigh the long-term benefits against short-term economic considerations.
Lastly, the integration of new preservation methods into existing production processes poses technical and logistical challenges. Adopting novel technologies may require significant modifications to equipment and workflows, necessitating substantial investments in infrastructure and training.
As the leather industry seeks to address these multifaceted challenges, the development of propionic acid-based preservation solutions emerges as a promising avenue. This approach offers the potential to overcome many of the current obstacles, providing an effective, sustainable, and economically viable alternative to traditional preservation methods.
One of the primary challenges is finding a preservation solution that effectively inhibits microbial growth without compromising leather quality. Bacterial and fungal contamination can lead to putrefaction, discoloration, and structural damage, resulting in substantial economic losses. The ideal preservative must provide broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity while maintaining the leather's natural properties.
Another critical issue is the need for long-term preservation during storage and transportation. As global supply chains extend, raw hides and leather products may spend extended periods in varying environmental conditions. Preservatives must offer prolonged protection against degradation, ensuring that the leather remains in optimal condition from production to end-use.
The leather industry also grapples with the challenge of developing preservation methods that are compatible with diverse leather types and tanning processes. Different animal hides and finishing techniques require tailored preservation approaches, complicating the development of universal solutions.
Regulatory pressures and consumer demands for sustainable and non-toxic products further complicate preservation efforts. Many traditional preservatives face scrutiny due to their potential environmental and health impacts. The industry must navigate a complex landscape of regulations, balancing efficacy with safety and environmental responsibility.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant hurdle in adopting new preservation technologies. While innovative solutions may offer improved performance and sustainability, they often come with higher implementation costs. Manufacturers must weigh the long-term benefits against short-term economic considerations.
Lastly, the integration of new preservation methods into existing production processes poses technical and logistical challenges. Adopting novel technologies may require significant modifications to equipment and workflows, necessitating substantial investments in infrastructure and training.
As the leather industry seeks to address these multifaceted challenges, the development of propionic acid-based preservation solutions emerges as a promising avenue. This approach offers the potential to overcome many of the current obstacles, providing an effective, sustainable, and economically viable alternative to traditional preservation methods.
Existing Propionic Acid-based Solutions
01 Production methods of propionic acid
Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods for producing propionic acid are described, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis routes, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of propionic acid production for industrial applications.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective against molds and bacteria, extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in bakery goods and dairy products.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations: Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in pharmaceutical formulations. They are used as excipients, pH adjusters, and in some cases, as active pharmaceutical ingredients for various therapeutic purposes.
- Industrial applications of propionic acid: Propionic acid has diverse industrial applications beyond food and pharmaceuticals. It is used in the production of plastics, herbicides, and as a chemical intermediate in various manufacturing processes. The acid's properties make it valuable in multiple industries.
- Purification and analysis methods for propionic acid: Various techniques for purifying and analyzing propionic acid are described. These include distillation methods, chromatographic techniques, and spectroscopic analysis. These methods are crucial for ensuring the quality and purity of propionic acid for different applications.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries
Propionic acid finds applications in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. It is used as a precursor in the synthesis of various drugs and as a pH adjuster in cosmetic formulations. Its antimicrobial properties also make it useful in certain topical medications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and industrial applications of propionic acid
Propionic acid has various environmental and industrial applications, including its use as a chemical intermediate in the production of plastics, herbicides, and other industrial chemicals. It is also employed in wastewater treatment and as a solvent in certain industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Purification and analysis methods for propionic acid
Various techniques are used for the purification and analysis of propionic acid, including distillation, crystallization, and chromatographic methods. These processes are crucial for ensuring the quality and purity of propionic acid for different applications, as well as for monitoring its production and use in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Propionic Acid Production
The development of propionic acid for leather preservation solutions is in a mature stage, with a well-established market and significant industry players. The global leather chemicals market, which includes preservation solutions, is projected to reach $8.4 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand for leather products. Key players in this field include BASF Corp., Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, and Buckman Laboratories International, Inc., who have extensive experience in chemical manufacturing and leather industry applications. These companies, along with emerging players like Sichuan Dowell Science & Technology, Inc. and Shanghai Goldlion Chemicals Co. Ltd., are continuously innovating to improve the efficacy and sustainability of leather preservation solutions, indicating a high level of technological maturity in this sector.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a novel propionic acid-based leather preservation solution called Preventol® P. This solution utilizes a synergistic blend of propionic acid and other organic acids to provide effective antimicrobial protection for raw hides and leather. The formulation is designed to penetrate deeply into the leather structure, ensuring long-lasting preservation against a wide spectrum of microorganisms. BASF's approach focuses on optimizing the pH level and concentration of propionic acid to maximize its efficacy while minimizing potential negative impacts on leather quality[1][3]. The company has also invested in research to improve the stability and shelf-life of their propionic acid formulations, resulting in products that maintain their effectiveness over extended periods[2].
Strengths: Broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, deep penetration into leather, long-lasting protection. Weaknesses: Potential for odor issues, may require careful handling due to acidity.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed a propionic acid-based leather preservation system called Loctite® Purmelt. This innovative solution combines propionic acid with other preservatives in a polymer matrix, creating a controlled-release mechanism for prolonged antimicrobial activity. The Purmelt technology allows for a more uniform distribution of propionic acid throughout the leather, reducing the risk of localized over-concentration and potential damage. Henkel's approach also incorporates environmentally friendly additives to enhance the overall sustainability profile of their preservation solution[4]. The company has conducted extensive testing to optimize the release rate of propionic acid, ensuring effective preservation while minimizing the total amount of chemicals used[5].
Strengths: Controlled-release mechanism, uniform distribution, improved sustainability profile. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial cost, may require specialized application equipment.
Innovations in Propionic Acid Synthesis
Propionic acid, ammonia, propanediol and water solutions and the use thereof
PatentInactiveEP1222862A2
Innovation
- A solution comprising 78.0 to 93.0% propionic acid, 0.5 to 5.0% ammonia, 1.0 to 6.0% propanediol, and up to 10.0% water, with optional additional C1-C8 carboxylic acids and surfactants, which reduces water content and enhances biocidal and biostatic effects while minimizing corrosiveness and odor.
Propionic acid, ammonia, propanediol and water solutions and the use thereof
PatentWO1998042205A1
Innovation
- A solution comprising 78.0 - 93.0% propionic acid, 0.5 - 5.0% ammonia, 1.0 - 6.0% propanediol, and 0.1 - 10.0% water, with optional auxiliaries like surfactants and other carboxylic acids, which reduces water content and enhances biocidal and biostatic effects while minimizing corrosive and odor issues.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact of propionic acid development for leather preservation solutions is a critical consideration in the industry's sustainability efforts. Propionic acid, while effective in preserving leather, poses potential risks to the environment if not properly managed throughout its lifecycle.
In the production phase, the synthesis of propionic acid typically involves petrochemical processes that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. However, recent advancements in bio-based production methods using renewable resources have shown promise in reducing the carbon footprint associated with propionic acid manufacturing.
During the application of propionic acid in leather preservation, there are concerns regarding its potential release into the environment. Improper handling or disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, affecting local ecosystems. The acidic nature of the compound may alter soil pH levels and impact microbial communities if released in significant quantities.
Wastewater from leather processing facilities using propionic acid requires careful treatment to prevent environmental pollution. Advanced treatment technologies, such as activated carbon adsorption and biological degradation, have been developed to effectively remove propionic acid from wastewater streams before discharge.
The persistence of propionic acid in the environment is relatively low, as it is biodegradable under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. This characteristic reduces the long-term environmental impact compared to some alternative preservation chemicals. However, the rate of biodegradation can vary depending on environmental conditions, necessitating proper management practices.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of propionic acid in leather preservation have focused on developing more sustainable application methods. These include optimizing dosage rates to minimize excess use, implementing closed-loop systems to reduce waste, and exploring encapsulation technologies to control release rates.
The potential for bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms is considered low for propionic acid, which is advantageous from an ecological perspective. However, acute toxicity to aquatic life can occur at high concentrations, emphasizing the importance of proper handling and disposal practices in leather processing facilities.
As the leather industry continues to prioritize sustainability, ongoing research is exploring green chemistry approaches to further reduce the environmental footprint of propionic acid-based preservation solutions. This includes investigating synergistic combinations with natural preservatives and developing bio-based derivatives with enhanced environmental profiles.
In the production phase, the synthesis of propionic acid typically involves petrochemical processes that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. However, recent advancements in bio-based production methods using renewable resources have shown promise in reducing the carbon footprint associated with propionic acid manufacturing.
During the application of propionic acid in leather preservation, there are concerns regarding its potential release into the environment. Improper handling or disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, affecting local ecosystems. The acidic nature of the compound may alter soil pH levels and impact microbial communities if released in significant quantities.
Wastewater from leather processing facilities using propionic acid requires careful treatment to prevent environmental pollution. Advanced treatment technologies, such as activated carbon adsorption and biological degradation, have been developed to effectively remove propionic acid from wastewater streams before discharge.
The persistence of propionic acid in the environment is relatively low, as it is biodegradable under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. This characteristic reduces the long-term environmental impact compared to some alternative preservation chemicals. However, the rate of biodegradation can vary depending on environmental conditions, necessitating proper management practices.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of propionic acid in leather preservation have focused on developing more sustainable application methods. These include optimizing dosage rates to minimize excess use, implementing closed-loop systems to reduce waste, and exploring encapsulation technologies to control release rates.
The potential for bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms is considered low for propionic acid, which is advantageous from an ecological perspective. However, acute toxicity to aquatic life can occur at high concentrations, emphasizing the importance of proper handling and disposal practices in leather processing facilities.
As the leather industry continues to prioritize sustainability, ongoing research is exploring green chemistry approaches to further reduce the environmental footprint of propionic acid-based preservation solutions. This includes investigating synergistic combinations with natural preservatives and developing bio-based derivatives with enhanced environmental profiles.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Preservatives
The regulatory framework for chemical preservatives in the leather industry is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the development and use of propionic acid as a preservation solution. Globally, regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, with a focus on environmental protection, worker safety, and consumer health.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation plays a crucial role in governing the use of chemical preservatives. Under REACH, propionic acid must be registered and its safety profile thoroughly evaluated before it can be used in leather preservation. The regulation also mandates that manufacturers and importers provide detailed information on the properties, potential risks, and safe handling procedures of the chemical.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates chemical preservatives under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Propionic acid, when used in leather preservation, must comply with TSCA requirements, including reporting, record-keeping, and testing. The EPA also sets guidelines for the safe use and disposal of chemical preservatives to minimize environmental impact.
In Asia, countries like China and India are rapidly updating their regulatory frameworks to align with international standards. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and India's Chemical (Management and Safety) Rules are examples of evolving regulations that impact the use of propionic acid in leather preservation.
Many countries have implemented specific regulations for the leather industry, addressing the use of preservatives. These regulations often set limits on the concentration of preservatives in finished leather products and specify acceptable preservation methods. For instance, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides guidelines for leather testing and chemical limits, which are widely adopted by regulatory bodies worldwide.
The regulatory landscape also emphasizes the importance of labeling and safety data sheets. Manufacturers using propionic acid in leather preservation must provide comprehensive information on the chemical's properties, potential hazards, and proper handling procedures. This ensures transparency and enables downstream users to implement appropriate safety measures.
As sustainability becomes a global priority, regulations are increasingly focusing on promoting eco-friendly alternatives to traditional chemical preservatives. This trend is driving research and development efforts towards more sustainable preservation solutions, potentially impacting the future use of propionic acid in the leather industry.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation plays a crucial role in governing the use of chemical preservatives. Under REACH, propionic acid must be registered and its safety profile thoroughly evaluated before it can be used in leather preservation. The regulation also mandates that manufacturers and importers provide detailed information on the properties, potential risks, and safe handling procedures of the chemical.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates chemical preservatives under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Propionic acid, when used in leather preservation, must comply with TSCA requirements, including reporting, record-keeping, and testing. The EPA also sets guidelines for the safe use and disposal of chemical preservatives to minimize environmental impact.
In Asia, countries like China and India are rapidly updating their regulatory frameworks to align with international standards. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and India's Chemical (Management and Safety) Rules are examples of evolving regulations that impact the use of propionic acid in leather preservation.
Many countries have implemented specific regulations for the leather industry, addressing the use of preservatives. These regulations often set limits on the concentration of preservatives in finished leather products and specify acceptable preservation methods. For instance, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides guidelines for leather testing and chemical limits, which are widely adopted by regulatory bodies worldwide.
The regulatory landscape also emphasizes the importance of labeling and safety data sheets. Manufacturers using propionic acid in leather preservation must provide comprehensive information on the chemical's properties, potential hazards, and proper handling procedures. This ensures transparency and enables downstream users to implement appropriate safety measures.
As sustainability becomes a global priority, regulations are increasingly focusing on promoting eco-friendly alternatives to traditional chemical preservatives. This trend is driving research and development efforts towards more sustainable preservation solutions, potentially impacting the future use of propionic acid in the leather industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!