Propionic Acid: From Research to Market Applications
JUL 3, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Overview
Propionic acid, a three-carbon carboxylic acid, has emerged as a versatile compound with significant industrial applications. This short-chain fatty acid occurs naturally in various foods and is produced by certain bacteria in the human gut. Its chemical formula, C3H6O2, reflects its simple structure, which belies its complex and varied uses across multiple sectors.
In the realm of food preservation, propionic acid and its salts have long been recognized for their antimicrobial properties. These compounds effectively inhibit the growth of mold and certain bacteria, extending the shelf life of baked goods, cheese, and other food products. This application has made propionic acid an indispensable ingredient in the food industry, contributing to food safety and reducing waste.
Beyond food preservation, propionic acid plays a crucial role in the production of cellulose acetate propionate, a polymer used in various applications including eyeglass frames, tool handles, and packaging materials. Its ability to act as a precursor in polymer synthesis underscores its importance in the plastics and materials science industries.
In agriculture, propionic acid finds use as a preservative for animal feed, particularly in silage production. By preventing the growth of harmful microorganisms, it helps maintain the nutritional quality of animal feed over extended periods, supporting efficient livestock management and production.
The pharmaceutical industry also benefits from propionic acid's properties. It serves as a starting material for the synthesis of various drugs and as a preservative in some pharmaceutical formulations. Its role in drug development highlights the compound's versatility and importance in medical advancements.
Recent research has explored propionic acid's potential in biofuel production. As a fermentation product of certain bacteria, it represents a promising intermediate in the conversion of biomass to value-added chemicals and fuels, aligning with global efforts towards sustainable energy solutions.
The global market for propionic acid has seen steady growth, driven by increasing demand across its various applications. Major producers have invested in expanding production capacities to meet this growing demand, reflecting the compound's economic significance and market potential.
As research continues to uncover new applications and production methods for propionic acid, its importance in industry and daily life is likely to expand further. From its humble origins as a natural preservative to its role in cutting-edge materials and sustainable technologies, propionic acid exemplifies the journey of a simple chemical compound to a versatile industrial staple.
In the realm of food preservation, propionic acid and its salts have long been recognized for their antimicrobial properties. These compounds effectively inhibit the growth of mold and certain bacteria, extending the shelf life of baked goods, cheese, and other food products. This application has made propionic acid an indispensable ingredient in the food industry, contributing to food safety and reducing waste.
Beyond food preservation, propionic acid plays a crucial role in the production of cellulose acetate propionate, a polymer used in various applications including eyeglass frames, tool handles, and packaging materials. Its ability to act as a precursor in polymer synthesis underscores its importance in the plastics and materials science industries.
In agriculture, propionic acid finds use as a preservative for animal feed, particularly in silage production. By preventing the growth of harmful microorganisms, it helps maintain the nutritional quality of animal feed over extended periods, supporting efficient livestock management and production.
The pharmaceutical industry also benefits from propionic acid's properties. It serves as a starting material for the synthesis of various drugs and as a preservative in some pharmaceutical formulations. Its role in drug development highlights the compound's versatility and importance in medical advancements.
Recent research has explored propionic acid's potential in biofuel production. As a fermentation product of certain bacteria, it represents a promising intermediate in the conversion of biomass to value-added chemicals and fuels, aligning with global efforts towards sustainable energy solutions.
The global market for propionic acid has seen steady growth, driven by increasing demand across its various applications. Major producers have invested in expanding production capacities to meet this growing demand, reflecting the compound's economic significance and market potential.
As research continues to uncover new applications and production methods for propionic acid, its importance in industry and daily life is likely to expand further. From its humble origins as a natural preservative to its role in cutting-edge materials and sustainable technologies, propionic acid exemplifies the journey of a simple chemical compound to a versatile industrial staple.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for propionic acid has been steadily increasing due to its versatile applications across various industries. In the food and beverage sector, propionic acid serves as a crucial preservative, extending the shelf life of baked goods, dairy products, and processed foods. This application has seen significant growth, driven by the rising consumer demand for convenience foods and the need for longer-lasting products in global supply chains.
The animal feed industry represents another major market for propionic acid. As a feed preservative, it prevents mold growth and bacterial contamination, ensuring the quality and safety of livestock feed. With the expanding global population and increasing meat consumption, the demand for animal feed additives, including propionic acid, is projected to grow substantially in the coming years.
In the pharmaceutical sector, propionic acid finds applications in the production of various medications and as a precursor for vitamin E synthesis. The growing healthcare industry and increasing focus on preventive medicine contribute to the rising demand for propionic acid in this sector.
The chemical industry utilizes propionic acid as an intermediate in the production of cellulose acetate propionate, herbicides, and other specialty chemicals. The expanding chemical manufacturing sector, particularly in emerging economies, is expected to drive further demand for propionic acid.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth in propionic acid demand, attributed to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and changing dietary habits. North America and Europe remain significant markets, with established food and pharmaceutical industries driving consistent demand.
Environmental concerns and sustainability trends are influencing market dynamics. The potential of bio-based propionic acid production methods is gaining attention, as they align with the growing preference for eco-friendly and renewable products. This shift could open new market opportunities and reshape the competitive landscape in the coming years.
The global propionic acid market is characterized by moderate fragmentation, with several key players dominating the industry. Market consolidation through mergers and acquisitions is a notable trend, as companies seek to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
Pricing volatility remains a challenge in the propionic acid market, primarily due to fluctuations in raw material costs. However, the overall market outlook remains positive, driven by the expanding applications and growing demand across multiple industries.
The animal feed industry represents another major market for propionic acid. As a feed preservative, it prevents mold growth and bacterial contamination, ensuring the quality and safety of livestock feed. With the expanding global population and increasing meat consumption, the demand for animal feed additives, including propionic acid, is projected to grow substantially in the coming years.
In the pharmaceutical sector, propionic acid finds applications in the production of various medications and as a precursor for vitamin E synthesis. The growing healthcare industry and increasing focus on preventive medicine contribute to the rising demand for propionic acid in this sector.
The chemical industry utilizes propionic acid as an intermediate in the production of cellulose acetate propionate, herbicides, and other specialty chemicals. The expanding chemical manufacturing sector, particularly in emerging economies, is expected to drive further demand for propionic acid.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth in propionic acid demand, attributed to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and changing dietary habits. North America and Europe remain significant markets, with established food and pharmaceutical industries driving consistent demand.
Environmental concerns and sustainability trends are influencing market dynamics. The potential of bio-based propionic acid production methods is gaining attention, as they align with the growing preference for eco-friendly and renewable products. This shift could open new market opportunities and reshape the competitive landscape in the coming years.
The global propionic acid market is characterized by moderate fragmentation, with several key players dominating the industry. Market consolidation through mergers and acquisitions is a notable trend, as companies seek to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
Pricing volatility remains a challenge in the propionic acid market, primarily due to fluctuations in raw material costs. However, the overall market outlook remains positive, driven by the expanding applications and growing demand across multiple industries.
Technical Challenges
Propionic acid production and application face several technical challenges that require innovative solutions. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost of production, particularly when using traditional petrochemical methods. The current production processes often involve energy-intensive steps and expensive catalysts, making it difficult to achieve cost-effective large-scale production.
Another significant challenge is the low yield and productivity of biological production methods. While microbial fermentation offers a more sustainable approach, the efficiency of propionic acid-producing microorganisms needs improvement. Researchers are working on metabolic engineering and strain optimization to enhance the production rates and titers, but achieving industrial-scale production levels remains a hurdle.
The purification and separation of propionic acid from fermentation broths present additional technical difficulties. The acid's high solubility in water and its similar properties to other organic acids in the fermentation mixture make it challenging to isolate efficiently. Current separation techniques, such as distillation or liquid-liquid extraction, are often energy-intensive and not always economically viable for large-scale operations.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges in propionic acid production. Traditional petrochemical routes generate significant amounts of waste and greenhouse gas emissions. While bio-based production methods offer a greener alternative, they still face issues related to feedstock sustainability and competition with food crops.
The stability and storage of propionic acid products can be problematic due to its corrosive nature. This necessitates the use of specialized handling and storage equipment, which can increase overall production costs. Additionally, the development of more stable formulations for various applications, particularly in the food industry, remains an ongoing challenge.
In terms of market applications, expanding the use of propionic acid beyond its traditional sectors requires overcoming technical barriers. For instance, in the development of biodegradable plastics, researchers must address issues related to material properties, such as mechanical strength and thermal stability, to make propionic acid-based polymers competitive with conventional plastics.
Regulatory compliance and safety considerations also present challenges, especially when introducing propionic acid into new application areas. Meeting stringent quality standards and ensuring the safety of propionic acid derivatives in various products, particularly those intended for human consumption or contact, requires extensive testing and validation processes.
Another significant challenge is the low yield and productivity of biological production methods. While microbial fermentation offers a more sustainable approach, the efficiency of propionic acid-producing microorganisms needs improvement. Researchers are working on metabolic engineering and strain optimization to enhance the production rates and titers, but achieving industrial-scale production levels remains a hurdle.
The purification and separation of propionic acid from fermentation broths present additional technical difficulties. The acid's high solubility in water and its similar properties to other organic acids in the fermentation mixture make it challenging to isolate efficiently. Current separation techniques, such as distillation or liquid-liquid extraction, are often energy-intensive and not always economically viable for large-scale operations.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges in propionic acid production. Traditional petrochemical routes generate significant amounts of waste and greenhouse gas emissions. While bio-based production methods offer a greener alternative, they still face issues related to feedstock sustainability and competition with food crops.
The stability and storage of propionic acid products can be problematic due to its corrosive nature. This necessitates the use of specialized handling and storage equipment, which can increase overall production costs. Additionally, the development of more stable formulations for various applications, particularly in the food industry, remains an ongoing challenge.
In terms of market applications, expanding the use of propionic acid beyond its traditional sectors requires overcoming technical barriers. For instance, in the development of biodegradable plastics, researchers must address issues related to material properties, such as mechanical strength and thermal stability, to make propionic acid-based polymers competitive with conventional plastics.
Regulatory compliance and safety considerations also present challenges, especially when introducing propionic acid into new application areas. Meeting stringent quality standards and ensuring the safety of propionic acid derivatives in various products, particularly those intended for human consumption or contact, requires extensive testing and validation processes.
Current Production Methods
01 Production methods of propionic acid
Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid is widely used as a food preservative due to its antimicrobial properties. It is effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical industry: Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the synthesis of various drugs, as intermediates in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients, and in some cases, as therapeutic agents themselves.
- Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling: The handling and storage of propionic acid require specific safety measures due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Proper containment, neutralization techniques, and waste management strategies are essential for safe and environmentally responsible use of propionic acid in industrial settings.
- Purification and quality control of propionic acid: Various purification techniques and quality control measures are employed to ensure the production of high-purity propionic acid. These may include distillation, crystallization, and advanced analytical methods to monitor and maintain the desired quality standards for different industrial applications.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations
Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the formulation of various medications, including topical treatments and oral drugs. The acid's properties make it useful as an excipient or active ingredient in certain pharmaceutical preparations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial applications of propionic acid
Propionic acid has diverse industrial applications beyond food and pharmaceuticals. It is used in the production of plastics, herbicides, and as a chemical intermediate in various manufacturing processes. The acid's versatility makes it valuable in multiple industrial sectors.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling
The handling and use of propionic acid require specific safety measures and environmental considerations. This includes proper storage, transportation, and disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination and ensure worker safety. Regulations and guidelines are in place to manage these aspects of propionic acid use in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The propionic acid market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The global market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate expected to be in the mid-single digits. Technologically, propionic acid production is relatively mature, with established processes in place. However, ongoing research and development efforts by key players such as BASF, Eastman Chemical, and Dow Chemical are focused on improving production efficiency and exploring new applications. Companies like Arkema and LG Chem are also actively involved in the market, contributing to its competitive landscape. Academic institutions, including the University of Queensland and Nanjing Tech University, are collaborating with industry partners to advance research in this field, potentially leading to innovative applications and production methods.
Arkema France SA
Technical Solution: Arkema has developed a proprietary process for propionic acid production based on the carbonylation of ethylene. This technology offers improved atom economy and reduced waste compared to traditional oxidation methods. The company has also invested in green chemistry initiatives, exploring the use of bio-based feedstocks and catalytic systems that operate under milder conditions [2]. Arkema's process incorporates advanced separation and purification techniques, ensuring high-quality propionic acid suitable for demanding applications such as pharmaceutical intermediates and specialty chemicals [5].
Strengths: Efficient carbonylation process, focus on green chemistry, and high-quality product. Weaknesses: Potential reliance on ethylene availability and price fluctuations in the petrochemical market.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has pioneered a novel approach to propionic acid production using a combination of fermentation and chemical synthesis. This hybrid process utilizes renewable resources as feedstock for the initial fermentation step, followed by catalytic upgrading to produce high-purity propionic acid [4]. The company has also developed specialized catalysts that enable direct synthesis of propionic acid derivatives, expanding the range of potential applications. Evonik's technology incorporates advanced process intensification techniques, such as reactive distillation, to improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption [6].
Strengths: Innovative hybrid process, utilization of renewable resources, and direct synthesis of derivatives. Weaknesses: Complexity of the hybrid process and potential challenges in scaling up the technology.
Key Patents and Research
Improved propionibacterium strains for the production of propionic acid
PatentWO2017055932A2
Innovation
- Genome shuffling between selected Propionibacterium strains, such as P. acidipropionici ATCC 4875 and P. acidipropionici ATCC 55737, to generate novel strains with enhanced growth rates and propionic acid production, utilizing genetic material exchange to create strains with improved metabolic pathways and regulatory mechanisms.
Method for production of propionic acid from inulins
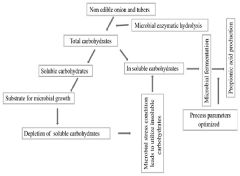
PatentPendingIN202141042851A
Innovation
- A single-step process optimizing enzymatic hydrolysis of inulin from onion waste and non-edible tubers to convert insoluble carbohydrates into fermentable sugars, followed by microbial fermentation to produce propionic acid, addressing issues like bi-product formation and downstream processing through optimized microbial growth conditions and stress parameters.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding propionic acid plays a crucial role in its research, production, and market applications. As a widely used chemical in various industries, propionic acid is subject to comprehensive regulations to ensure safety, quality, and environmental protection.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates propionic acid as a food additive. It is classified as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) when used as a preservative in food products. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also oversees its production and use under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), focusing on potential environmental impacts and worker safety.
The European Union has established stringent regulations for propionic acid through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) program. Manufacturers and importers must register propionic acid with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide detailed safety information. The EU also sets specific limits for its use in food products through the Food Additives Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory frameworks. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) oversees the use of propionic acid in food and pharmaceutical applications. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates its use through the Food Sanitation Act.
Globally, the transportation of propionic acid is governed by international agreements such as the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code and the International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations. These regulations ensure safe handling and transport of the chemical across borders.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US, mandate specific handling procedures and exposure limits for workers in facilities producing or using propionic acid. Similar regulations exist in other countries to protect worker health and safety.
As research continues to expand the applications of propionic acid, regulatory bodies are likely to adapt their frameworks to address new uses and potential risks. This dynamic regulatory landscape requires companies involved in propionic acid research, production, and application to stay informed and compliant with evolving standards across different regions and industries.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates propionic acid as a food additive. It is classified as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) when used as a preservative in food products. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also oversees its production and use under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), focusing on potential environmental impacts and worker safety.
The European Union has established stringent regulations for propionic acid through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) program. Manufacturers and importers must register propionic acid with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide detailed safety information. The EU also sets specific limits for its use in food products through the Food Additives Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory frameworks. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) oversees the use of propionic acid in food and pharmaceutical applications. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates its use through the Food Sanitation Act.
Globally, the transportation of propionic acid is governed by international agreements such as the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code and the International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations. These regulations ensure safe handling and transport of the chemical across borders.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US, mandate specific handling procedures and exposure limits for workers in facilities producing or using propionic acid. Similar regulations exist in other countries to protect worker health and safety.
As research continues to expand the applications of propionic acid, regulatory bodies are likely to adapt their frameworks to address new uses and potential risks. This dynamic regulatory landscape requires companies involved in propionic acid research, production, and application to stay informed and compliant with evolving standards across different regions and industries.
Environmental Impact
Propionic acid production and its market applications have significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The manufacturing process of propionic acid traditionally relies on petrochemical feedstocks, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. However, recent advancements in biotechnology have opened up more sustainable production routes using renewable resources, such as biomass fermentation.
The shift towards bio-based propionic acid production offers several environmental benefits. It reduces dependency on fossil fuels, lowers carbon footprint, and promotes circular economy principles by utilizing agricultural waste streams. Additionally, fermentation processes generally require less energy input compared to petrochemical synthesis, further reducing the overall environmental impact.
In terms of market applications, propionic acid's use as a food preservative helps extend shelf life and reduce food waste, indirectly contributing to environmental conservation. Its application in animal feed as a mold inhibitor also improves feed efficiency, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of livestock production.
However, the environmental impact of propionic acid is not uniformly positive. Its production, regardless of the method, still requires energy and resources. The disposal of by-products and waste from manufacturing processes needs careful management to prevent soil and water contamination. Moreover, the increased demand for bio-based production could potentially lead to land-use changes if not managed sustainably.
The use of propionic acid in various industries also raises concerns about its potential release into the environment. While it is biodegradable and does not persist in ecosystems, high concentrations can temporarily affect aquatic life and soil microorganisms. Proper handling, storage, and disposal protocols are crucial to mitigate these risks.
As the market for propionic acid expands, lifecycle assessments become increasingly important to quantify its environmental impact comprehensively. These assessments consider factors such as raw material sourcing, production processes, transportation, use phase, and end-of-life disposal. Such holistic evaluations help identify areas for improvement and guide the development of more environmentally friendly practices throughout the propionic acid value chain.
In conclusion, while propionic acid offers environmental benefits through its applications and potential for sustainable production, its overall environmental impact remains complex. Continued research and innovation are necessary to optimize production processes, enhance resource efficiency, and minimize negative environmental effects as the industry evolves from research to widespread market applications.
The shift towards bio-based propionic acid production offers several environmental benefits. It reduces dependency on fossil fuels, lowers carbon footprint, and promotes circular economy principles by utilizing agricultural waste streams. Additionally, fermentation processes generally require less energy input compared to petrochemical synthesis, further reducing the overall environmental impact.
In terms of market applications, propionic acid's use as a food preservative helps extend shelf life and reduce food waste, indirectly contributing to environmental conservation. Its application in animal feed as a mold inhibitor also improves feed efficiency, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of livestock production.
However, the environmental impact of propionic acid is not uniformly positive. Its production, regardless of the method, still requires energy and resources. The disposal of by-products and waste from manufacturing processes needs careful management to prevent soil and water contamination. Moreover, the increased demand for bio-based production could potentially lead to land-use changes if not managed sustainably.
The use of propionic acid in various industries also raises concerns about its potential release into the environment. While it is biodegradable and does not persist in ecosystems, high concentrations can temporarily affect aquatic life and soil microorganisms. Proper handling, storage, and disposal protocols are crucial to mitigate these risks.
As the market for propionic acid expands, lifecycle assessments become increasingly important to quantify its environmental impact comprehensively. These assessments consider factors such as raw material sourcing, production processes, transportation, use phase, and end-of-life disposal. Such holistic evaluations help identify areas for improvement and guide the development of more environmentally friendly practices throughout the propionic acid value chain.
In conclusion, while propionic acid offers environmental benefits through its applications and potential for sustainable production, its overall environmental impact remains complex. Continued research and innovation are necessary to optimize production processes, enhance resource efficiency, and minimize negative environmental effects as the industry evolves from research to widespread market applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!