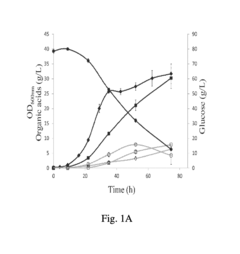
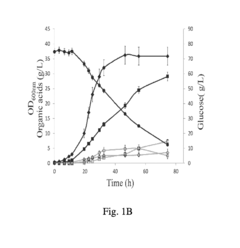
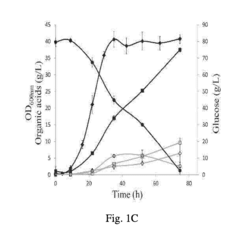
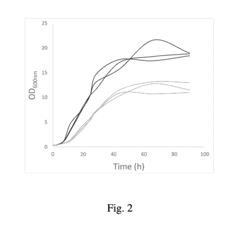
Propionic Acid in Biochemical Reaction Studies: Advancements
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Research Background and Objectives
Propionic acid has been a subject of significant interest in biochemical reaction studies for several decades. This organic compound, with its unique chemical properties and biological relevance, has played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of various metabolic processes and industrial applications. The research background of propionic acid spans across multiple disciplines, including microbiology, biochemistry, and industrial biotechnology.
Initially, propionic acid gained attention due to its natural occurrence in dairy products and its role in the fermentation process. Early studies focused on isolating and characterizing the microorganisms responsible for propionic acid production, particularly Propionibacterium species. This laid the foundation for further investigations into the biochemical pathways involved in propionic acid metabolism.
As research progressed, the significance of propionic acid in human and animal physiology became increasingly apparent. Scientists discovered its involvement in various metabolic processes, including energy production, lipid metabolism, and gut health. This led to a surge in studies exploring the potential health benefits and therapeutic applications of propionic acid and its derivatives.
In recent years, the focus of propionic acid research has shifted towards its potential as a platform chemical for sustainable production of various industrial compounds. The growing demand for eco-friendly alternatives to petrochemical-based products has driven efforts to develop efficient biological production methods for propionic acid. This has resulted in advancements in metabolic engineering and fermentation technologies aimed at optimizing propionic acid yields from renewable resources.
The objectives of current propionic acid research are multifaceted and ambitious. One primary goal is to enhance the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biological propionic acid production to compete with traditional petrochemical routes. This involves developing robust microbial strains capable of high-yield propionic acid synthesis from various feedstocks, including agricultural waste and industrial by-products.
Another key objective is to expand the application scope of propionic acid in biochemical reactions. Researchers are exploring its potential as a building block for the synthesis of high-value chemicals, polymers, and pharmaceuticals. This includes investigating novel catalytic processes and reaction conditions to facilitate the conversion of propionic acid into desired products.
Furthermore, there is a growing interest in elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying propionic acid's biological effects. Scientists aim to gain deeper insights into its role in cellular signaling, gene regulation, and metabolic homeostasis. This knowledge could pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies targeting various metabolic disorders and inflammatory conditions.
Initially, propionic acid gained attention due to its natural occurrence in dairy products and its role in the fermentation process. Early studies focused on isolating and characterizing the microorganisms responsible for propionic acid production, particularly Propionibacterium species. This laid the foundation for further investigations into the biochemical pathways involved in propionic acid metabolism.
As research progressed, the significance of propionic acid in human and animal physiology became increasingly apparent. Scientists discovered its involvement in various metabolic processes, including energy production, lipid metabolism, and gut health. This led to a surge in studies exploring the potential health benefits and therapeutic applications of propionic acid and its derivatives.
In recent years, the focus of propionic acid research has shifted towards its potential as a platform chemical for sustainable production of various industrial compounds. The growing demand for eco-friendly alternatives to petrochemical-based products has driven efforts to develop efficient biological production methods for propionic acid. This has resulted in advancements in metabolic engineering and fermentation technologies aimed at optimizing propionic acid yields from renewable resources.
The objectives of current propionic acid research are multifaceted and ambitious. One primary goal is to enhance the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biological propionic acid production to compete with traditional petrochemical routes. This involves developing robust microbial strains capable of high-yield propionic acid synthesis from various feedstocks, including agricultural waste and industrial by-products.
Another key objective is to expand the application scope of propionic acid in biochemical reactions. Researchers are exploring its potential as a building block for the synthesis of high-value chemicals, polymers, and pharmaceuticals. This includes investigating novel catalytic processes and reaction conditions to facilitate the conversion of propionic acid into desired products.
Furthermore, there is a growing interest in elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying propionic acid's biological effects. Scientists aim to gain deeper insights into its role in cellular signaling, gene regulation, and metabolic homeostasis. This knowledge could pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies targeting various metabolic disorders and inflammatory conditions.
Market Analysis for Propionic Acid in Biochemistry
The market for propionic acid in biochemistry has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications in various industries. As a key component in biochemical reaction studies, propionic acid has garnered significant attention from researchers and industry professionals alike. The global market for propionic acid is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.5% over the next five years, with the biochemistry sector contributing substantially to this growth.
In the field of biochemistry, propionic acid plays a crucial role in numerous applications, including metabolic studies, enzyme kinetics, and cellular energy production research. The increasing focus on understanding metabolic disorders and developing novel therapeutic approaches has led to a surge in demand for propionic acid in biochemical research laboratories. Additionally, the growing interest in biofuels and sustainable chemical production has further boosted the market for propionic acid as a potential platform chemical.
The pharmaceutical industry represents a significant market segment for propionic acid in biochemistry. Its use in drug development, particularly in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical intermediates, has been a key driver of market growth. The rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the subsequent increase in drug discovery efforts have positively impacted the demand for propionic acid in biochemical applications.
Another emerging market for propionic acid in biochemistry is the food and beverage industry. As a natural preservative and flavoring agent, propionic acid has found extensive use in food products. The growing consumer preference for clean-label and natural ingredients has further propelled the demand for propionic acid in this sector. Moreover, its application in animal feed additives as a mold inhibitor has opened up new avenues for market expansion.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the propionic acid market, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in research and development activities. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, primarily due to the presence of established pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
However, the market faces challenges such as volatility in raw material prices and stringent regulations regarding chemical usage. Despite these obstacles, the increasing adoption of bio-based propionic acid and the development of novel production methods are expected to create lucrative opportunities for market growth in the coming years.
In the field of biochemistry, propionic acid plays a crucial role in numerous applications, including metabolic studies, enzyme kinetics, and cellular energy production research. The increasing focus on understanding metabolic disorders and developing novel therapeutic approaches has led to a surge in demand for propionic acid in biochemical research laboratories. Additionally, the growing interest in biofuels and sustainable chemical production has further boosted the market for propionic acid as a potential platform chemical.
The pharmaceutical industry represents a significant market segment for propionic acid in biochemistry. Its use in drug development, particularly in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical intermediates, has been a key driver of market growth. The rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the subsequent increase in drug discovery efforts have positively impacted the demand for propionic acid in biochemical applications.
Another emerging market for propionic acid in biochemistry is the food and beverage industry. As a natural preservative and flavoring agent, propionic acid has found extensive use in food products. The growing consumer preference for clean-label and natural ingredients has further propelled the demand for propionic acid in this sector. Moreover, its application in animal feed additives as a mold inhibitor has opened up new avenues for market expansion.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the propionic acid market, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in research and development activities. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, primarily due to the presence of established pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
However, the market faces challenges such as volatility in raw material prices and stringent regulations regarding chemical usage. Despite these obstacles, the increasing adoption of bio-based propionic acid and the development of novel production methods are expected to create lucrative opportunities for market growth in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Propionic Acid Studies
Despite significant advancements in propionic acid studies within biochemical reactions, researchers continue to face several challenges that hinder further progress in this field. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of metabolic pathways involving propionic acid. The intricate network of reactions and regulatory mechanisms makes it difficult to isolate and study the specific roles of propionic acid in various biochemical processes.
Another challenge lies in the accurate measurement and quantification of propionic acid in biological samples. Current analytical techniques often struggle with sensitivity and specificity, especially when dealing with complex matrices found in cellular environments. This limitation hampers the ability to track propionic acid dynamics in real-time during biochemical reactions, leading to potential gaps in understanding its precise functions and interactions.
The stability and reactivity of propionic acid under different physiological conditions pose additional challenges. Researchers must carefully control experimental parameters to ensure that observed effects are genuinely attributable to propionic acid rather than its derivatives or breakdown products. This requirement for stringent control often complicates experimental design and interpretation of results.
Furthermore, the dual nature of propionic acid as both a metabolite and a potential signaling molecule creates difficulties in distinguishing its primary roles in various biochemical pathways. Elucidating the mechanisms by which propionic acid influences cellular processes, such as gene expression or enzyme activity, remains a complex task that requires sophisticated experimental approaches.
The development of suitable model systems for studying propionic acid in biochemical reactions presents another significant challenge. While in vitro studies provide valuable insights, they often fail to capture the full complexity of in vivo environments. Conversely, in vivo studies face limitations in terms of controllability and the ability to isolate specific effects of propionic acid.
Lastly, the potential cross-talk between propionic acid and other short-chain fatty acids in biochemical reactions adds another layer of complexity to research efforts. Disentangling the individual contributions of these closely related compounds requires advanced analytical and experimental techniques that are still being developed and refined.
Addressing these challenges will be crucial for advancing our understanding of propionic acid's role in biochemical reactions and unlocking its full potential in various applications, from metabolic engineering to therapeutic interventions.
Another challenge lies in the accurate measurement and quantification of propionic acid in biological samples. Current analytical techniques often struggle with sensitivity and specificity, especially when dealing with complex matrices found in cellular environments. This limitation hampers the ability to track propionic acid dynamics in real-time during biochemical reactions, leading to potential gaps in understanding its precise functions and interactions.
The stability and reactivity of propionic acid under different physiological conditions pose additional challenges. Researchers must carefully control experimental parameters to ensure that observed effects are genuinely attributable to propionic acid rather than its derivatives or breakdown products. This requirement for stringent control often complicates experimental design and interpretation of results.
Furthermore, the dual nature of propionic acid as both a metabolite and a potential signaling molecule creates difficulties in distinguishing its primary roles in various biochemical pathways. Elucidating the mechanisms by which propionic acid influences cellular processes, such as gene expression or enzyme activity, remains a complex task that requires sophisticated experimental approaches.
The development of suitable model systems for studying propionic acid in biochemical reactions presents another significant challenge. While in vitro studies provide valuable insights, they often fail to capture the full complexity of in vivo environments. Conversely, in vivo studies face limitations in terms of controllability and the ability to isolate specific effects of propionic acid.
Lastly, the potential cross-talk between propionic acid and other short-chain fatty acids in biochemical reactions adds another layer of complexity to research efforts. Disentangling the individual contributions of these closely related compounds requires advanced analytical and experimental techniques that are still being developed and refined.
Addressing these challenges will be crucial for advancing our understanding of propionic acid's role in biochemical reactions and unlocking its full potential in various applications, from metabolic engineering to therapeutic interventions.
Current Methodologies in Propionic Acid Studies
01 Production methods of propionic acid
Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries: Propionic acid finds applications in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. It is used as a precursor in the synthesis of certain drugs and as a pH adjuster in various formulations. In cosmetics, it may be used as a preservative or in the production of other cosmetic ingredients.
- Industrial applications of propionic acid: Propionic acid has diverse industrial applications beyond food and pharmaceuticals. It is used in the production of plastics, herbicides, and as a chemical intermediate in various manufacturing processes. Its properties make it valuable in industries such as agriculture, textiles, and rubber production.
- Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling: The handling and use of propionic acid require specific safety measures due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Proper storage, transportation, and disposal methods are essential to ensure worker safety and environmental protection. Regulations and guidelines exist for the safe handling of propionic acid in various industries.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations
Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the formulation of various medications, including topical treatments and oral drugs, due to their antimicrobial properties and ability to enhance drug absorption.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental applications of propionic acid
Propionic acid is utilized in environmental applications, such as wastewater treatment and soil remediation. It can be used to control pH levels, reduce odors, and inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms in various environmental settings.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial uses of propionic acid
Propionic acid has diverse industrial applications, including its use as a chemical intermediate in the production of plastics, solvents, and other chemicals. It is also employed in the manufacturing of herbicides, textile dyes, and as a corrosion inhibitor in various industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Propionic Acid Research
The propionic acid market in biochemical reaction studies is experiencing significant advancements, driven by growing applications in various industries. The market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand for sustainable and bio-based chemicals. Key players like Arkema, BASF, and Dow are investing heavily in research and development to improve production processes and expand applications. The market size is expected to grow steadily, fueled by rising demand in pharmaceuticals, food preservation, and agriculture. Technological advancements by companies such as LG Chem and Novomer are enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of propionic acid production, indicating a moderate to high level of technological maturity in the field.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has made significant advancements in propionic acid production and its application in biochemical reaction studies. They have developed a novel catalytic process for propionic acid synthesis from ethylene and carbon monoxide, achieving higher yields and selectivity compared to traditional methods[1]. The company has also explored the use of propionic acid as a key intermediate in the production of bio-based polymers and chemicals. Their research focuses on optimizing fermentation processes using propionibacteria strains, which can convert renewable feedstocks into propionic acid with improved efficiency[3]. Additionally, Sinopec has investigated the role of propionic acid in enhancing the stability and shelf-life of various biochemical products, particularly in the food and pharmaceutical industries[5].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, integrated supply chain, and extensive R&D resources. Weaknesses: Dependence on petrochemical feedstocks and potential environmental concerns associated with traditional production methods.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has made substantial progress in propionic acid research for biochemical applications. They have developed a proprietary fermentation process using genetically engineered microorganisms to produce propionic acid from renewable resources[2]. This bio-based approach offers a more sustainable alternative to traditional petrochemical routes. BASF has also focused on the application of propionic acid in animal nutrition, developing feed additives that improve gut health and reduce the need for antibiotics in livestock[4]. Furthermore, the company has explored the use of propionic acid derivatives in biodegradable polymers, contributing to the circular economy. Their research extends to the use of propionic acid as a building block for specialty chemicals, including preservatives and solvents with enhanced performance characteristics[6].
Strengths: Strong expertise in biotechnology and chemical engineering, global market presence, and commitment to sustainability. Weaknesses: Higher production costs associated with bio-based processes and potential regulatory challenges in some markets.
Breakthrough Discoveries in Propionic Acid Biochemistry
Improved propionibacterium strains for the production of propionic acid
PatentWO2017055932A2
Innovation
- Genome shuffling between selected Propionibacterium strains, such as P. acidipropionici ATCC 4875 and P. acidipropionici ATCC 55737, to generate novel strains with enhanced growth rates and propionic acid production, utilizing genetic material exchange to create strains with improved metabolic pathways and regulatory mechanisms.
Improved propionibacterium strains for the production of propionic acid
PatentInactiveUS20190071697A1
Innovation
- Selecting and combining Propionibacterium strains with high potential for propionic acid production, such as P. acidipropionici ATCC 4875 and P. acidipropionici ATCC 55737, through genome shuffling to create novel strains with improved growth rates and reduced byproduct production, such as P. acidipropionici F3E8, which achieves enhanced propionic acid yields and growth rates.
Environmental Impact of Propionic Acid Production
The production of propionic acid has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The traditional petrochemical-based production methods have been associated with substantial carbon emissions and energy consumption. However, recent advancements in biochemical reaction studies have paved the way for more sustainable production processes.
Fermentation-based production of propionic acid using renewable feedstocks has emerged as a promising alternative. This approach utilizes microorganisms, particularly Propionibacterium species, to convert biomass-derived sugars into propionic acid. The use of agricultural waste and other renewable resources as feedstock significantly reduces the carbon footprint compared to petrochemical routes.
Water consumption and wastewater generation are critical environmental factors in propionic acid production. Biochemical processes generally require less water than traditional chemical synthesis methods. Additionally, the wastewater from fermentation processes contains fewer toxic compounds, making it easier to treat and potentially recyclable within the production system.
Energy efficiency is another area where biochemical reactions offer environmental benefits. Fermentation processes typically operate at lower temperatures and pressures compared to petrochemical synthesis, resulting in reduced energy requirements. Furthermore, the integration of biorefinery concepts allows for the utilization of by-products and waste streams, improving overall resource efficiency.
The environmental impact of propionic acid production extends to land use and biodiversity. While the shift towards bio-based production reduces reliance on fossil resources, it raises concerns about potential competition with food crops for agricultural land. Sustainable feedstock sourcing and the development of processes that can utilize non-food biomass are crucial to mitigate these concerns.
Air quality is also affected by propionic acid production. Traditional methods often involve the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. Biochemical processes, when properly managed, can significantly reduce air emissions, contributing to improved local air quality and reduced health risks for surrounding communities.
Lifecycle assessment studies have shown that bio-based propionic acid production can achieve substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions compared to petrochemical routes. However, the environmental benefits are highly dependent on factors such as feedstock choice, process efficiency, and energy sources used in production.
As research in biochemical reaction studies continues to advance, there is potential for further improvements in the environmental profile of propionic acid production. Developments in metabolic engineering, process intensification, and the use of renewable energy sources in production facilities are expected to enhance the sustainability of this important industrial chemical.
Fermentation-based production of propionic acid using renewable feedstocks has emerged as a promising alternative. This approach utilizes microorganisms, particularly Propionibacterium species, to convert biomass-derived sugars into propionic acid. The use of agricultural waste and other renewable resources as feedstock significantly reduces the carbon footprint compared to petrochemical routes.
Water consumption and wastewater generation are critical environmental factors in propionic acid production. Biochemical processes generally require less water than traditional chemical synthesis methods. Additionally, the wastewater from fermentation processes contains fewer toxic compounds, making it easier to treat and potentially recyclable within the production system.
Energy efficiency is another area where biochemical reactions offer environmental benefits. Fermentation processes typically operate at lower temperatures and pressures compared to petrochemical synthesis, resulting in reduced energy requirements. Furthermore, the integration of biorefinery concepts allows for the utilization of by-products and waste streams, improving overall resource efficiency.
The environmental impact of propionic acid production extends to land use and biodiversity. While the shift towards bio-based production reduces reliance on fossil resources, it raises concerns about potential competition with food crops for agricultural land. Sustainable feedstock sourcing and the development of processes that can utilize non-food biomass are crucial to mitigate these concerns.
Air quality is also affected by propionic acid production. Traditional methods often involve the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. Biochemical processes, when properly managed, can significantly reduce air emissions, contributing to improved local air quality and reduced health risks for surrounding communities.
Lifecycle assessment studies have shown that bio-based propionic acid production can achieve substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions compared to petrochemical routes. However, the environmental benefits are highly dependent on factors such as feedstock choice, process efficiency, and energy sources used in production.
As research in biochemical reaction studies continues to advance, there is potential for further improvements in the environmental profile of propionic acid production. Developments in metabolic engineering, process intensification, and the use of renewable energy sources in production facilities are expected to enhance the sustainability of this important industrial chemical.
Regulatory Framework for Propionic Acid Use
The regulatory framework for propionic acid use in biochemical reaction studies has evolved significantly in recent years, reflecting the growing importance of this compound in various research and industrial applications. Regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines to ensure the safe handling, storage, and use of propionic acid in laboratory and industrial settings.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) play crucial roles in regulating propionic acid. The EPA has set specific guidelines for the environmental release and disposal of propionic acid, while OSHA has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with its use.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to propionic acid and its derivatives. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers are required to register propionic acid and provide detailed safety information, including its potential environmental and health impacts.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have their own regulatory frameworks for chemical substances, including propionic acid. The Japanese Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and the Korean Chemical Control Act (CCA) mandate the registration and risk assessment of propionic acid before its use in research or industrial applications.
International organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), have also provided guidelines for the use of propionic acid in food preservation and animal feed applications. These guidelines ensure the safe use of propionic acid in the food industry and agricultural sector.
Specific to biochemical reaction studies, regulatory bodies have established protocols for the proper handling and disposal of propionic acid in laboratory settings. These protocols typically include requirements for personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilation systems, and proper waste management procedures.
As research in biochemical reactions involving propionic acid continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve. There is an increasing focus on the development of more environmentally friendly and sustainable processes involving propionic acid, which may lead to new regulations promoting green chemistry principles.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks is essential for researchers and industries working with propionic acid. It ensures not only the safety of personnel and the environment but also facilitates the global acceptance and application of research findings involving propionic acid in biochemical reaction studies.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) play crucial roles in regulating propionic acid. The EPA has set specific guidelines for the environmental release and disposal of propionic acid, while OSHA has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with its use.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to propionic acid and its derivatives. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers are required to register propionic acid and provide detailed safety information, including its potential environmental and health impacts.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have their own regulatory frameworks for chemical substances, including propionic acid. The Japanese Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and the Korean Chemical Control Act (CCA) mandate the registration and risk assessment of propionic acid before its use in research or industrial applications.
International organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), have also provided guidelines for the use of propionic acid in food preservation and animal feed applications. These guidelines ensure the safe use of propionic acid in the food industry and agricultural sector.
Specific to biochemical reaction studies, regulatory bodies have established protocols for the proper handling and disposal of propionic acid in laboratory settings. These protocols typically include requirements for personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilation systems, and proper waste management procedures.
As research in biochemical reactions involving propionic acid continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve. There is an increasing focus on the development of more environmentally friendly and sustainable processes involving propionic acid, which may lead to new regulations promoting green chemistry principles.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks is essential for researchers and industries working with propionic acid. It ensures not only the safety of personnel and the environment but also facilitates the global acceptance and application of research findings involving propionic acid in biochemical reaction studies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!