Propionic Acid in Biotechnology: Current Research Directions
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Biotech Evolution and Objectives
Propionic acid has emerged as a significant player in the biotechnology sector, with its evolution and applications spanning several decades. The journey of propionic acid in biotechnology began in the mid-20th century when researchers first recognized its potential as a metabolic product of certain microorganisms. Since then, the field has witnessed remarkable progress, driven by advancements in microbial fermentation techniques and genetic engineering.
The evolution of propionic acid biotechnology can be traced through several key milestones. In the 1960s and 1970s, scientists focused on isolating and characterizing propionic acid-producing bacteria, primarily from the genus Propionibacterium. This laid the foundation for understanding the metabolic pathways involved in propionic acid production. The 1980s and 1990s saw significant improvements in fermentation processes, with researchers optimizing culture conditions and developing more efficient bioreactors.
The turn of the millennium marked a new era in propionic acid biotechnology with the advent of metabolic engineering and synthetic biology. These cutting-edge techniques allowed scientists to manipulate microbial genomes to enhance propionic acid production. Researchers began to explore alternative substrates, including renewable resources and waste streams, to make the production process more sustainable and cost-effective.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing high-yield strains and improving downstream processing techniques. The integration of advanced analytical tools and bioinformatics has accelerated strain development and process optimization. Moreover, the growing interest in bio-based chemicals has propelled propionic acid to the forefront of industrial biotechnology, with applications expanding beyond traditional uses in food preservation to include bioplastics, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
The current objectives in propionic acid biotechnology are multifaceted and ambitious. Researchers aim to further increase production yields and efficiency, with a particular emphasis on developing robust microbial strains capable of withstanding industrial conditions. There is also a strong push towards utilizing low-cost and sustainable feedstocks, aligning with global efforts to reduce dependence on fossil-based resources.
Another key objective is the development of novel applications for propionic acid and its derivatives. This includes exploring its potential in biodegradable polymers, green solvents, and as a platform chemical for various industrial processes. Additionally, there is growing interest in understanding and harnessing the probiotic properties of propionic acid-producing bacteria, opening up new avenues in the fields of nutrition and healthcare.
As the biotechnology sector continues to evolve, propionic acid research is expected to play a crucial role in addressing global challenges such as sustainability, food security, and healthcare. The ongoing efforts in this field reflect a broader trend towards bio-based solutions and circular economy principles, positioning propionic acid as a key player in the future of industrial biotechnology.
The evolution of propionic acid biotechnology can be traced through several key milestones. In the 1960s and 1970s, scientists focused on isolating and characterizing propionic acid-producing bacteria, primarily from the genus Propionibacterium. This laid the foundation for understanding the metabolic pathways involved in propionic acid production. The 1980s and 1990s saw significant improvements in fermentation processes, with researchers optimizing culture conditions and developing more efficient bioreactors.
The turn of the millennium marked a new era in propionic acid biotechnology with the advent of metabolic engineering and synthetic biology. These cutting-edge techniques allowed scientists to manipulate microbial genomes to enhance propionic acid production. Researchers began to explore alternative substrates, including renewable resources and waste streams, to make the production process more sustainable and cost-effective.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing high-yield strains and improving downstream processing techniques. The integration of advanced analytical tools and bioinformatics has accelerated strain development and process optimization. Moreover, the growing interest in bio-based chemicals has propelled propionic acid to the forefront of industrial biotechnology, with applications expanding beyond traditional uses in food preservation to include bioplastics, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
The current objectives in propionic acid biotechnology are multifaceted and ambitious. Researchers aim to further increase production yields and efficiency, with a particular emphasis on developing robust microbial strains capable of withstanding industrial conditions. There is also a strong push towards utilizing low-cost and sustainable feedstocks, aligning with global efforts to reduce dependence on fossil-based resources.
Another key objective is the development of novel applications for propionic acid and its derivatives. This includes exploring its potential in biodegradable polymers, green solvents, and as a platform chemical for various industrial processes. Additionally, there is growing interest in understanding and harnessing the probiotic properties of propionic acid-producing bacteria, opening up new avenues in the fields of nutrition and healthcare.
As the biotechnology sector continues to evolve, propionic acid research is expected to play a crucial role in addressing global challenges such as sustainability, food security, and healthcare. The ongoing efforts in this field reflect a broader trend towards bio-based solutions and circular economy principles, positioning propionic acid as a key player in the future of industrial biotechnology.
Market Analysis for Propionic Acid in Biotechnology
The market for propionic acid in biotechnology has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by its diverse applications and increasing demand across various industries. The global propionic acid market size was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $2.1 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of around 5.2% during the forecast period.
In the biotechnology sector, propionic acid plays a crucial role in several applications, including food preservation, animal feed additives, and pharmaceuticals. The food industry remains the largest consumer of propionic acid, accounting for over 40% of the market share. The increasing demand for packaged and processed foods, coupled with growing concerns about food safety and shelf life extension, has been a major driver for propionic acid usage in this sector.
The animal feed industry is another significant market for propionic acid in biotechnology. As a feed preservative, propionic acid helps prevent mold growth and bacterial contamination, thereby improving the shelf life and nutritional value of animal feed. This application segment is expected to witness substantial growth, driven by the rising global meat consumption and the need for efficient livestock management practices.
In the pharmaceutical industry, propionic acid and its derivatives are used in the production of various medications, including anti-inflammatory drugs and antifungal agents. The growing emphasis on healthcare and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases are contributing to the expansion of this market segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the propionic acid market, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and changing dietary habits in countries like China and India.
Key market players in the propionic acid industry include BASF SE, Dow Inc., Eastman Chemical Company, and Perstorp Holding AB. These companies are focusing on research and development activities to enhance product quality and expand their application portfolio in the biotechnology sector.
Challenges facing the market include fluctuating raw material prices, stringent regulations regarding food additives, and the growing trend towards natural and organic products. However, ongoing research into sustainable production methods and novel applications in biotechnology is expected to create new opportunities for market growth in the coming years.
In the biotechnology sector, propionic acid plays a crucial role in several applications, including food preservation, animal feed additives, and pharmaceuticals. The food industry remains the largest consumer of propionic acid, accounting for over 40% of the market share. The increasing demand for packaged and processed foods, coupled with growing concerns about food safety and shelf life extension, has been a major driver for propionic acid usage in this sector.
The animal feed industry is another significant market for propionic acid in biotechnology. As a feed preservative, propionic acid helps prevent mold growth and bacterial contamination, thereby improving the shelf life and nutritional value of animal feed. This application segment is expected to witness substantial growth, driven by the rising global meat consumption and the need for efficient livestock management practices.
In the pharmaceutical industry, propionic acid and its derivatives are used in the production of various medications, including anti-inflammatory drugs and antifungal agents. The growing emphasis on healthcare and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases are contributing to the expansion of this market segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the propionic acid market, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and changing dietary habits in countries like China and India.
Key market players in the propionic acid industry include BASF SE, Dow Inc., Eastman Chemical Company, and Perstorp Holding AB. These companies are focusing on research and development activities to enhance product quality and expand their application portfolio in the biotechnology sector.
Challenges facing the market include fluctuating raw material prices, stringent regulations regarding food additives, and the growing trend towards natural and organic products. However, ongoing research into sustainable production methods and novel applications in biotechnology is expected to create new opportunities for market growth in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Propionic Acid Biosynthesis
Propionic acid biosynthesis faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread industrial application. One of the primary obstacles is the low yield and productivity of current microbial fermentation processes. Despite extensive research, the production rates and final concentrations of propionic acid remain suboptimal for commercial viability. This limitation is largely attributed to the metabolic constraints of the microorganisms used, particularly Propionibacterium species, which are the most common producers.
Another major challenge is the inhibitory effect of propionic acid on the producing microorganisms. As the concentration of propionic acid increases during fermentation, it creates an acidic environment that negatively impacts cell growth and metabolism. This feedback inhibition significantly limits the maximum achievable titer and necessitates complex downstream processing to continuously remove the product, adding to production costs.
The selectivity of the biosynthetic pathways presents an additional hurdle. Current fermentation processes often result in the formation of by-products such as acetic acid and succinic acid, which reduce the overall yield of propionic acid and complicate purification procedures. Improving pathway specificity and redirecting carbon flux towards propionic acid production remains a key focus area for researchers.
Substrate utilization efficiency is another critical challenge. Many propionic acid-producing strains have limited ability to metabolize diverse carbon sources, particularly low-cost agricultural and industrial by-products. Enhancing the substrate spectrum of production strains could significantly reduce raw material costs and improve the economic feasibility of bio-based propionic acid production.
Furthermore, the genetic tools and techniques for manipulating propionic acid-producing microorganisms are less developed compared to model organisms like Escherichia coli. This limitation hampers rapid strain improvement and metabolic engineering efforts. Developing more efficient genetic modification methods for Propionibacterium and other potential host organisms is crucial for overcoming current production bottlenecks.
Lastly, scaling up laboratory-scale fermentation processes to industrial levels presents its own set of challenges. Maintaining optimal conditions for propionic acid production in large bioreactors, including pH control, oxygen transfer, and substrate feeding strategies, requires significant process engineering efforts. Addressing these scale-up issues is essential for translating research advancements into commercially viable production systems.
Another major challenge is the inhibitory effect of propionic acid on the producing microorganisms. As the concentration of propionic acid increases during fermentation, it creates an acidic environment that negatively impacts cell growth and metabolism. This feedback inhibition significantly limits the maximum achievable titer and necessitates complex downstream processing to continuously remove the product, adding to production costs.
The selectivity of the biosynthetic pathways presents an additional hurdle. Current fermentation processes often result in the formation of by-products such as acetic acid and succinic acid, which reduce the overall yield of propionic acid and complicate purification procedures. Improving pathway specificity and redirecting carbon flux towards propionic acid production remains a key focus area for researchers.
Substrate utilization efficiency is another critical challenge. Many propionic acid-producing strains have limited ability to metabolize diverse carbon sources, particularly low-cost agricultural and industrial by-products. Enhancing the substrate spectrum of production strains could significantly reduce raw material costs and improve the economic feasibility of bio-based propionic acid production.
Furthermore, the genetic tools and techniques for manipulating propionic acid-producing microorganisms are less developed compared to model organisms like Escherichia coli. This limitation hampers rapid strain improvement and metabolic engineering efforts. Developing more efficient genetic modification methods for Propionibacterium and other potential host organisms is crucial for overcoming current production bottlenecks.
Lastly, scaling up laboratory-scale fermentation processes to industrial levels presents its own set of challenges. Maintaining optimal conditions for propionic acid production in large bioreactors, including pH control, oxygen transfer, and substrate feeding strategies, requires significant process engineering efforts. Addressing these scale-up issues is essential for translating research advancements into commercially viable production systems.
Current Biosynthetic Pathways for Propionic Acid
01 Production methods of propionic acid
Various methods for producing propionic acid are described, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis routes, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of propionic acid production for industrial applications.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid is widely used as a food preservative due to its antimicrobial properties. It is effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical industry: Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the synthesis of various drugs, as intermediates in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients, and in some cases, as therapeutic agents themselves.
- Environmental and industrial applications: Propionic acid has diverse applications in environmental and industrial sectors. It is used in the production of herbicides, as a chemical intermediate in various industrial processes, and in the treatment of industrial wastewater. Its properties make it suitable for use in de-icing fluids and as a solvent in certain applications.
- Purification and recovery methods: Various techniques are employed for the purification and recovery of propionic acid from reaction mixtures or fermentation broths. These methods may include distillation, extraction, membrane separation, or other advanced separation techniques to obtain high-purity propionic acid for commercial use.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective against molds and some bacteria, extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in bakery items and dairy products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations
Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in pharmaceutical formulations. They are used as excipients, pH adjusters, and in some cases, as active pharmaceutical ingredients for various therapeutic purposes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial applications of propionic acid
Propionic acid has diverse industrial applications beyond food and pharmaceuticals. It is used in the production of plastics, herbicides, and as a chemical intermediate in various manufacturing processes. The acid also finds use in the production of cellulose acetate propionate and other specialty chemicals.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling
The handling, storage, and disposal of propionic acid require specific safety measures due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Innovations in this area focus on developing safer handling methods, reducing environmental footprint, and improving workplace safety in industries using propionic acid.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Propionic Acid Biotechnology
The propionic acid biotechnology market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable production methods and applications in various industries. The market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with research institutions like Jiangnan University, Nanjing Tech University, and The Ohio State University leading academic efforts. Companies such as Evonik Operations GmbH, Arkema France SA, and Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd. are at the forefront of commercial development, investing in R&D to improve production efficiency and expand applications. The involvement of both academic and industrial players suggests a maturing technology landscape, with ongoing efforts to optimize fermentation processes, enhance yield, and develop novel applications across food, agriculture, and pharmaceutical sectors.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed advanced biotechnological processes for the production of propionic acid. Their approach involves engineered Propionibacterium strains capable of fermenting glucose and other renewable feedstocks to produce propionic acid with high yield and selectivity. The company has optimized fermentation conditions and downstream processing to achieve industrial-scale production. Evonik's bio-based propionic acid demonstrates comparable quality to petrochemical-derived alternatives, with a significantly reduced carbon footprint[1][3]. They have also explored the use of lignocellulosic biomass as a feedstock, potentially improving the sustainability and cost-effectiveness of the process[2].
Strengths: Established industrial-scale production, reduced carbon footprint, potential for using renewable feedstocks. Weaknesses: May face competition from traditional petrochemical routes, dependent on feedstock prices and availability.
Arkema France SA
Technical Solution: Arkema has invested in research to develop bio-based propionic acid production methods. Their approach focuses on the use of glycerol, a byproduct of biodiesel production, as a renewable feedstock for propionic acid synthesis. The company has engineered microbial strains, likely Propionibacterium or related species, to efficiently convert glycerol to propionic acid. Arkema's process includes optimized fermentation conditions and innovative separation techniques to achieve high purity propionic acid. This bio-based route aligns with the company's commitment to sustainable chemistry and circular economy principles[4][5]. Arkema is also exploring the integration of this process with their existing acrylics production to create a more sustainable value chain.
Strengths: Utilization of glycerol waste stream, integration with existing product lines, commitment to sustainability. Weaknesses: May face challenges in scaling up production, potential variability in glycerol supply and quality.
Innovative Approaches in Propionic Acid Production
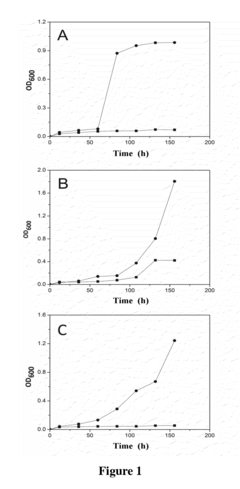
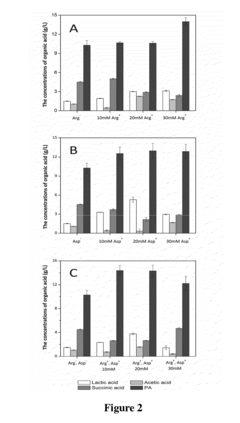
Method for Improving Acid tolerance of Propionibacterium acdipropionici
PatentInactiveUS20140178952A1
Innovation
- Adding arginine and/or aspartic acid to the culture medium during the cultivation of Propionibacterium acdipropionici to enhance acid tolerance and propionic acid productivity.
Continuous fermentation process which is useful for the simultaneous optimal production of propionic acid and vitamin B12
PatentInactiveUS6878534B1
Innovation
- A continuous two-stage fermentation process using Propionibacterium acidipropionici DSM 8250 strain, where the first stage optimizes propionic acid production under anaerobic conditions and the second stage optimizes vitamin B12 production under micro-aerobic conditions, with sucrose as a carbon substrate and specific nutrient additions, allowing for cell recycling and minimizing acetic acid formation.
Environmental Impact of Propionic Acid Bioprocesses
The environmental impact of propionic acid bioprocesses has gained increasing attention as the biotechnology industry seeks more sustainable production methods. Compared to traditional petrochemical-based production, bio-based propionic acid offers several environmental advantages. The use of renewable feedstocks, such as glucose or glycerol, reduces reliance on fossil fuels and decreases overall carbon footprint. Additionally, bioprocesses typically operate under milder conditions, requiring less energy input and generating fewer harmful byproducts.
However, the environmental benefits of bio-based propionic acid production are not without challenges. One significant concern is the potential for eutrophication due to nutrient-rich effluents from fermentation processes. Proper wastewater treatment and nutrient recovery systems are essential to mitigate this risk. Another consideration is the land use associated with growing feedstock crops, which may compete with food production or lead to deforestation if not managed sustainably.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) have been conducted to quantify the environmental impacts of bio-based propionic acid production. These studies generally indicate a lower global warming potential compared to petrochemical routes, but results can vary depending on feedstock choice and process efficiency. For instance, using waste glycerol from biodiesel production as a feedstock can significantly improve the environmental profile by valorizing a byproduct.
Water consumption is another critical factor in assessing the environmental impact of propionic acid bioprocesses. While biological production methods often require substantial water inputs, advancements in water recycling and process integration have led to improved water efficiency. Some innovative approaches, such as the use of membrane bioreactors, have shown promise in reducing water footprint and improving overall process sustainability.
The choice of microorganism for fermentation can also influence environmental outcomes. Research into more efficient bacterial strains, such as engineered Propionibacterium freudenreichii, aims to increase yield and productivity while reducing waste generation. Additionally, the development of consolidated bioprocessing techniques, where a single microorganism performs multiple steps, has the potential to simplify production and decrease environmental impact.
As the biotechnology industry continues to evolve, there is a growing focus on developing closed-loop systems for propionic acid production. These integrated biorefineries aim to maximize resource utilization and minimize waste by finding applications for all byproducts and side streams. For example, the CO2 generated during fermentation could be captured and used in other industrial processes or for greenhouse cultivation, further reducing the carbon footprint of the overall production system.
However, the environmental benefits of bio-based propionic acid production are not without challenges. One significant concern is the potential for eutrophication due to nutrient-rich effluents from fermentation processes. Proper wastewater treatment and nutrient recovery systems are essential to mitigate this risk. Another consideration is the land use associated with growing feedstock crops, which may compete with food production or lead to deforestation if not managed sustainably.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) have been conducted to quantify the environmental impacts of bio-based propionic acid production. These studies generally indicate a lower global warming potential compared to petrochemical routes, but results can vary depending on feedstock choice and process efficiency. For instance, using waste glycerol from biodiesel production as a feedstock can significantly improve the environmental profile by valorizing a byproduct.
Water consumption is another critical factor in assessing the environmental impact of propionic acid bioprocesses. While biological production methods often require substantial water inputs, advancements in water recycling and process integration have led to improved water efficiency. Some innovative approaches, such as the use of membrane bioreactors, have shown promise in reducing water footprint and improving overall process sustainability.
The choice of microorganism for fermentation can also influence environmental outcomes. Research into more efficient bacterial strains, such as engineered Propionibacterium freudenreichii, aims to increase yield and productivity while reducing waste generation. Additionally, the development of consolidated bioprocessing techniques, where a single microorganism performs multiple steps, has the potential to simplify production and decrease environmental impact.
As the biotechnology industry continues to evolve, there is a growing focus on developing closed-loop systems for propionic acid production. These integrated biorefineries aim to maximize resource utilization and minimize waste by finding applications for all byproducts and side streams. For example, the CO2 generated during fermentation could be captured and used in other industrial processes or for greenhouse cultivation, further reducing the carbon footprint of the overall production system.
Regulatory Framework for Biobased Propionic Acid
The regulatory framework for biobased propionic acid production and use is evolving as the biotechnology industry advances. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of propionic acid as a food additive and preservative. The Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status of propionic acid allows for its use in various food applications without additional FDA approval, provided it adheres to good manufacturing practices.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the production and environmental impact of biobased propionic acid under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Manufacturers must comply with reporting requirements and safety assessments for new biotechnology processes. The EPA also encourages the development of sustainable bio-based chemicals through its Safer Choice program, which may benefit biobased propionic acid producers.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates the safety of propionic acid and its salts for use in food products. The EU's Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation applies to the production and import of biobased propionic acid, requiring manufacturers to register substances and provide safety data.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed standards for bio-based products, including ISO 16620 for determining biobased content. These standards help ensure consistency and quality in the production of biobased propionic acid and facilitate international trade.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on sustainability and circular economy principles. The EU's Circular Economy Action Plan and similar initiatives worldwide are likely to influence future regulations for biobased chemicals, potentially favoring environmentally friendly production methods for propionic acid.
As the biotechnology sector continues to innovate, regulatory frameworks are expected to adapt. Emerging areas of focus include the development of streamlined approval processes for bio-based alternatives to traditional chemicals and the establishment of clearer guidelines for the environmental assessment of biotechnology processes. Regulatory harmonization efforts between different regions may also shape the future landscape for biobased propionic acid production and use.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the production and environmental impact of biobased propionic acid under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Manufacturers must comply with reporting requirements and safety assessments for new biotechnology processes. The EPA also encourages the development of sustainable bio-based chemicals through its Safer Choice program, which may benefit biobased propionic acid producers.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates the safety of propionic acid and its salts for use in food products. The EU's Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation applies to the production and import of biobased propionic acid, requiring manufacturers to register substances and provide safety data.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed standards for bio-based products, including ISO 16620 for determining biobased content. These standards help ensure consistency and quality in the production of biobased propionic acid and facilitate international trade.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on sustainability and circular economy principles. The EU's Circular Economy Action Plan and similar initiatives worldwide are likely to influence future regulations for biobased chemicals, potentially favoring environmentally friendly production methods for propionic acid.
As the biotechnology sector continues to innovate, regulatory frameworks are expected to adapt. Emerging areas of focus include the development of streamlined approval processes for bio-based alternatives to traditional chemicals and the establishment of clearer guidelines for the environmental assessment of biotechnology processes. Regulatory harmonization efforts between different regions may also shape the future landscape for biobased propionic acid production and use.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!