Propionic Acid's Role in Future Food Production Technologies
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Overview and Production Goals
Propionic acid, a short-chain fatty acid, has emerged as a crucial component in the future of food production technologies. This organic compound, naturally occurring in some foods and produced by gut bacteria, has gained significant attention for its multifaceted applications in the food industry. The primary goal of propionic acid production is to meet the growing demand for natural food preservatives and enhance the overall quality and safety of food products.
The evolution of propionic acid in food technology can be traced back to its discovery in the late 19th century. Since then, its importance has steadily increased, driven by the food industry's need for effective, natural preservatives. The current technological trend focuses on developing more efficient and sustainable production methods to meet the escalating demand for propionic acid in various food applications.
One of the key objectives in propionic acid production is to optimize fermentation processes. This involves enhancing the efficiency of microbial strains used in fermentation, improving bioreactor designs, and refining downstream processing techniques. The aim is to increase yield, reduce production costs, and minimize environmental impact, aligning with the broader goals of sustainable food production.
Another significant goal is to expand the application scope of propionic acid in food preservation. Research is ongoing to explore its potential in extending the shelf life of a wider range of food products, particularly in the dairy, bakery, and meat industries. This includes investigating synergistic effects with other preservatives and developing novel formulations to enhance its efficacy.
The development of propionic acid-based active packaging materials represents another frontier in food production technologies. These innovative packaging solutions aim to incorporate propionic acid or its derivatives into packaging materials, creating an additional barrier against microbial growth and extending product shelf life.
Furthermore, there is a growing interest in exploring the potential health benefits of propionic acid in functional foods. Research is being conducted to understand its role in gut health, metabolism, and potential anti-inflammatory properties. This opens up new avenues for incorporating propionic acid into functional food products, aligning with the increasing consumer demand for health-promoting foods.
As the food industry continues to evolve, the goals for propionic acid production are also shifting towards more sustainable and eco-friendly practices. This includes exploring bio-based production methods, utilizing waste streams as feedstock, and developing closed-loop production systems. These initiatives aim to reduce the carbon footprint of propionic acid production and contribute to the overall sustainability of the food supply chain.
The evolution of propionic acid in food technology can be traced back to its discovery in the late 19th century. Since then, its importance has steadily increased, driven by the food industry's need for effective, natural preservatives. The current technological trend focuses on developing more efficient and sustainable production methods to meet the escalating demand for propionic acid in various food applications.
One of the key objectives in propionic acid production is to optimize fermentation processes. This involves enhancing the efficiency of microbial strains used in fermentation, improving bioreactor designs, and refining downstream processing techniques. The aim is to increase yield, reduce production costs, and minimize environmental impact, aligning with the broader goals of sustainable food production.
Another significant goal is to expand the application scope of propionic acid in food preservation. Research is ongoing to explore its potential in extending the shelf life of a wider range of food products, particularly in the dairy, bakery, and meat industries. This includes investigating synergistic effects with other preservatives and developing novel formulations to enhance its efficacy.
The development of propionic acid-based active packaging materials represents another frontier in food production technologies. These innovative packaging solutions aim to incorporate propionic acid or its derivatives into packaging materials, creating an additional barrier against microbial growth and extending product shelf life.
Furthermore, there is a growing interest in exploring the potential health benefits of propionic acid in functional foods. Research is being conducted to understand its role in gut health, metabolism, and potential anti-inflammatory properties. This opens up new avenues for incorporating propionic acid into functional food products, aligning with the increasing consumer demand for health-promoting foods.
As the food industry continues to evolve, the goals for propionic acid production are also shifting towards more sustainable and eco-friendly practices. This includes exploring bio-based production methods, utilizing waste streams as feedstock, and developing closed-loop production systems. These initiatives aim to reduce the carbon footprint of propionic acid production and contribute to the overall sustainability of the food supply chain.
Market Analysis for Propionic Acid in Food Industry
The global market for propionic acid in the food industry has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for food preservatives and rising consumer awareness about food safety. Propionic acid, known for its antimicrobial properties, plays a crucial role in extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly bakery goods, cheese, and animal feed.
In recent years, the market has witnessed a significant uptick in demand due to the growing preference for natural and clean-label food preservatives. Propionic acid, being a naturally occurring substance, aligns well with this consumer trend. The bakery sector remains the largest application segment for propionic acid, accounting for a substantial portion of the market share. The increasing consumption of packaged and convenience foods in developing economies has further bolstered the demand for propionic acid as a preservative.
The animal feed industry also represents a key growth area for propionic acid. With the rising global meat consumption and the need for efficient livestock production, propionic acid's use as a mold inhibitor in animal feed has gained traction. This application helps prevent feed spoilage and ensures better animal health, contributing to the overall market expansion.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest markets for propionic acid in the food industry. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a lucrative market, driven by rapid urbanization, changing dietary habits, and increasing disposable incomes. Countries like China and India are expected to be major contributors to the market growth in the coming years.
The market landscape is characterized by the presence of several key players, including large multinational corporations and regional manufacturers. These companies are focusing on product innovation, expanding their production capacities, and strategic partnerships to strengthen their market position. The competitive environment has led to continuous improvements in product quality and the development of new applications for propionic acid in the food industry.
Looking ahead, the market for propionic acid in the food industry is projected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as the increasing global population, rising food safety concerns, and the expansion of the processed food industry are expected to drive demand. Additionally, the growing trend towards organic and natural food preservatives presents new opportunities for propionic acid manufacturers to develop innovative, eco-friendly solutions.
In recent years, the market has witnessed a significant uptick in demand due to the growing preference for natural and clean-label food preservatives. Propionic acid, being a naturally occurring substance, aligns well with this consumer trend. The bakery sector remains the largest application segment for propionic acid, accounting for a substantial portion of the market share. The increasing consumption of packaged and convenience foods in developing economies has further bolstered the demand for propionic acid as a preservative.
The animal feed industry also represents a key growth area for propionic acid. With the rising global meat consumption and the need for efficient livestock production, propionic acid's use as a mold inhibitor in animal feed has gained traction. This application helps prevent feed spoilage and ensures better animal health, contributing to the overall market expansion.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest markets for propionic acid in the food industry. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a lucrative market, driven by rapid urbanization, changing dietary habits, and increasing disposable incomes. Countries like China and India are expected to be major contributors to the market growth in the coming years.
The market landscape is characterized by the presence of several key players, including large multinational corporations and regional manufacturers. These companies are focusing on product innovation, expanding their production capacities, and strategic partnerships to strengthen their market position. The competitive environment has led to continuous improvements in product quality and the development of new applications for propionic acid in the food industry.
Looking ahead, the market for propionic acid in the food industry is projected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as the increasing global population, rising food safety concerns, and the expansion of the processed food industry are expected to drive demand. Additionally, the growing trend towards organic and natural food preservatives presents new opportunities for propionic acid manufacturers to develop innovative, eco-friendly solutions.
Current Challenges in Propionic Acid Production
The production of propionic acid faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption in food production technologies. One of the primary issues is the high cost of production, which stems from the use of expensive raw materials and energy-intensive processes. Traditional methods of propionic acid production, such as petrochemical synthesis or fermentation of glucose, often result in low yields and require substantial energy inputs, making the process economically unfavorable for large-scale applications.
Another major challenge is the environmental impact associated with current production methods. Petrochemical-based production of propionic acid contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and relies on non-renewable resources. While fermentation processes offer a more sustainable alternative, they still face efficiency issues and often generate significant amounts of waste byproducts, which require additional treatment and disposal.
The purity of the final product also presents a considerable challenge. Food-grade propionic acid requires high levels of purity, which can be difficult to achieve consistently through current production methods. Impurities can affect the quality and safety of food products, necessitating costly purification steps that further increase production expenses.
Scalability remains a significant hurdle for propionic acid production. As demand for natural preservatives and sustainable food additives grows, manufacturers struggle to scale up production while maintaining efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This challenge is particularly acute for bio-based production methods, which often face limitations in terms of fermentation capacity and downstream processing capabilities.
Furthermore, the variability in raw material quality and availability poses challenges for consistent production. Fermentation-based processes, in particular, are sensitive to fluctuations in feedstock composition, which can affect yield and product quality. This variability makes it difficult to optimize production processes and achieve consistent results across different batches.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to propionic acid production. As food safety standards become increasingly stringent, manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of regulations governing the production and use of food additives. Meeting these requirements often necessitates additional investments in quality control measures and documentation processes.
Lastly, the development of novel production technologies faces barriers in terms of research funding and industry adoption. While innovative approaches, such as metabolic engineering of microorganisms or electrochemical synthesis, show promise for addressing some of the current challenges, they require significant investment in research and development. The conservative nature of the food industry can also slow the adoption of new production methods, as stakeholders may be hesitant to implement unproven technologies.
Another major challenge is the environmental impact associated with current production methods. Petrochemical-based production of propionic acid contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and relies on non-renewable resources. While fermentation processes offer a more sustainable alternative, they still face efficiency issues and often generate significant amounts of waste byproducts, which require additional treatment and disposal.
The purity of the final product also presents a considerable challenge. Food-grade propionic acid requires high levels of purity, which can be difficult to achieve consistently through current production methods. Impurities can affect the quality and safety of food products, necessitating costly purification steps that further increase production expenses.
Scalability remains a significant hurdle for propionic acid production. As demand for natural preservatives and sustainable food additives grows, manufacturers struggle to scale up production while maintaining efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This challenge is particularly acute for bio-based production methods, which often face limitations in terms of fermentation capacity and downstream processing capabilities.
Furthermore, the variability in raw material quality and availability poses challenges for consistent production. Fermentation-based processes, in particular, are sensitive to fluctuations in feedstock composition, which can affect yield and product quality. This variability makes it difficult to optimize production processes and achieve consistent results across different batches.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to propionic acid production. As food safety standards become increasingly stringent, manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of regulations governing the production and use of food additives. Meeting these requirements often necessitates additional investments in quality control measures and documentation processes.
Lastly, the development of novel production technologies faces barriers in terms of research funding and industry adoption. While innovative approaches, such as metabolic engineering of microorganisms or electrochemical synthesis, show promise for addressing some of the current challenges, they require significant investment in research and development. The conservative nature of the food industry can also slow the adoption of new production methods, as stakeholders may be hesitant to implement unproven technologies.
Current Propionic Acid Production Methods
01 Production methods of propionic acid
Various methods for producing propionic acid are described, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis routes, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of propionic acid production for industrial applications.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods for producing propionic acid are described, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis routes, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of propionic acid production for industrial applications.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid and its salts are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in bakery items and dairy products.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations: Propionic acid and its derivatives are utilized in pharmaceutical formulations for various purposes, including as active ingredients, excipients, or pH adjusters. They may be incorporated into topical, oral, or injectable medications for different therapeutic applications.
- Industrial applications of propionic acid: Propionic acid finds diverse industrial applications beyond food and pharmaceuticals. It is used in the production of plastics, herbicides, and as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of various compounds. Its properties make it valuable in industries such as agriculture, polymers, and chemical manufacturing.
- Environmental and safety considerations of propionic acid: Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of propionic acid production and use. This includes developing eco-friendly production methods, optimizing handling procedures, and assessing potential health effects to ensure safe industrial and consumer applications.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid and its derivatives are widely used as food preservatives due to their antimicrobial properties. They are effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in bakery items and animal feed.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical formulations
Propionic acid and its salts are utilized in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. They can be incorporated into drug formulations as active ingredients or excipients, contributing to the stability and efficacy of medicinal products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Propionic acid derivatives and their synthesis
Research focuses on developing novel propionic acid derivatives and improving synthesis methods for existing compounds. These derivatives find applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid production
Efforts are made to develop environmentally friendly production processes for propionic acid, focusing on reducing waste, improving energy efficiency, and ensuring worker safety. This includes the development of green chemistry approaches and the implementation of safety measures in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Propionic Acid Manufacturing
The market for propionic acid in future food production technologies is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for natural food preservatives and sustainable production methods. The global market size is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with key players like Kemin Industries, Dow Global Technologies, and Cargill leading innovation. The technology is maturing rapidly, with universities such as Jiangnan University, Ohio State University, and Nanjing Tech University contributing to research advancements. Companies like PetroChina and Braskem are exploring bio-based production methods, indicating a shift towards more sustainable practices in this sector.
Kemin Industries, Inc.
Technical Solution: Kemin Industries has developed proprietary formulations incorporating propionic acid for use in animal nutrition and food preservation. Their research focuses on optimizing the synergistic effects of propionic acid with other organic acids and natural compounds to enhance antimicrobial efficacy[1]. The company has also invested in microencapsulation technologies to improve the stability and controlled release of propionic acid in various food matrices[2]. Kemin's approach includes the development of propionic acid-based solutions for extending the shelf life of baked goods and preventing mold growth in animal feed[3].
Strengths: Specialized knowledge in food preservation and animal nutrition, innovative formulation techniques. Weaknesses: Limited focus on propionic acid production, reliance on external suppliers for raw materials.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies has developed advanced catalytic processes for the production of propionic acid from renewable feedstocks. Their technology utilizes heterogeneous catalysts to convert bio-based ethylene and carbon monoxide into propionic acid with high selectivity and yield[1]. The company has also explored the integration of propionic acid production with existing petrochemical processes to improve overall efficiency and reduce carbon footprint[2]. Dow's research extends to the development of novel propionic acid derivatives for use in polymers, coatings, and other industrial applications, expanding the potential market for bio-based propionic acid[3].
Strengths: Extensive experience in chemical engineering and catalysis, global production and distribution network. Weaknesses: Primary focus on industrial applications rather than food production, potential competition from established petrochemical routes.
Innovative Propionic Acid Synthesis Techniques
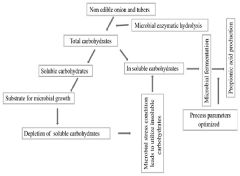
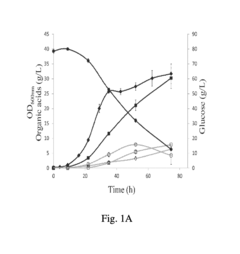
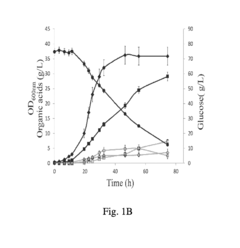
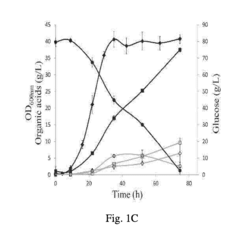
Method for production of propionic acid from inulins
PatentPendingIN202141042851A
Innovation
- A single-step process optimizing enzymatic hydrolysis of inulin from onion waste and non-edible tubers to convert insoluble carbohydrates into fermentable sugars, followed by microbial fermentation to produce propionic acid, addressing issues like bi-product formation and downstream processing through optimized microbial growth conditions and stress parameters.
Improved propionibacterium strains for the production of propionic acid
PatentInactiveUS20190071697A1
Innovation
- Selecting and combining Propionibacterium strains with high potential for propionic acid production, such as P. acidipropionici ATCC 4875 and P. acidipropionici ATCC 55737, through genome shuffling to create novel strains with improved growth rates and reduced byproduct production, such as P. acidipropionici F3E8, which achieves enhanced propionic acid yields and growth rates.
Regulatory Framework for Food Preservatives
The regulatory framework for food preservatives plays a crucial role in shaping the future of food production technologies, particularly concerning the use of propionic acid. As a widely used preservative, propionic acid is subject to stringent regulations across various jurisdictions to ensure food safety and quality.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates propionic acid under the Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status. This designation allows its use in food products within specified limits. The FDA continually reviews scientific evidence to update its guidelines, which may impact the future applications of propionic acid in food production.
The European Union, through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), has established specific regulations for propionic acid and its salts. These regulations set maximum permitted levels for different food categories and require regular safety assessments. The EU's approach to food additives, including preservatives, emphasizes the precautionary principle, which may influence future regulatory decisions on propionic acid.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international food standards that serve as a reference for many countries. Their guidelines on propionic acid usage contribute to harmonizing regulations worldwide, facilitating international trade while ensuring consumer safety.
Emerging trends in food safety regulations are likely to impact the future use of propionic acid. There is a growing emphasis on natural and clean label products, which may lead to stricter regulations or alternative preservation methods. Additionally, advancements in food production technologies may necessitate updates to existing regulatory frameworks to address new applications of propionic acid.
The regulatory landscape also considers the environmental impact of food preservatives. As sustainability becomes a key focus in food production, regulations may evolve to include criteria related to the environmental footprint of preservatives like propionic acid. This could influence production methods and usage patterns in the future.
Ongoing research into the long-term effects of food preservatives on human health may lead to regulatory changes. Regulatory bodies are likely to continue monitoring scientific studies and adjusting their guidelines accordingly. This dynamic regulatory environment requires food producers to stay informed and adaptable in their use of propionic acid and other preservatives.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates propionic acid under the Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status. This designation allows its use in food products within specified limits. The FDA continually reviews scientific evidence to update its guidelines, which may impact the future applications of propionic acid in food production.
The European Union, through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), has established specific regulations for propionic acid and its salts. These regulations set maximum permitted levels for different food categories and require regular safety assessments. The EU's approach to food additives, including preservatives, emphasizes the precautionary principle, which may influence future regulatory decisions on propionic acid.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international food standards that serve as a reference for many countries. Their guidelines on propionic acid usage contribute to harmonizing regulations worldwide, facilitating international trade while ensuring consumer safety.
Emerging trends in food safety regulations are likely to impact the future use of propionic acid. There is a growing emphasis on natural and clean label products, which may lead to stricter regulations or alternative preservation methods. Additionally, advancements in food production technologies may necessitate updates to existing regulatory frameworks to address new applications of propionic acid.
The regulatory landscape also considers the environmental impact of food preservatives. As sustainability becomes a key focus in food production, regulations may evolve to include criteria related to the environmental footprint of preservatives like propionic acid. This could influence production methods and usage patterns in the future.
Ongoing research into the long-term effects of food preservatives on human health may lead to regulatory changes. Regulatory bodies are likely to continue monitoring scientific studies and adjusting their guidelines accordingly. This dynamic regulatory environment requires food producers to stay informed and adaptable in their use of propionic acid and other preservatives.
Sustainability in Propionic Acid Production
Sustainability in propionic acid production has become a critical focus as the demand for this versatile compound continues to grow in the food industry. Traditional production methods, primarily through petrochemical processes, have raised concerns about environmental impact and long-term viability. In response, researchers and industry leaders are exploring innovative approaches to enhance the sustainability of propionic acid production.
One promising avenue is the development of bio-based production methods. These processes utilize renewable resources, such as agricultural waste or biomass, as feedstock for fermentation. By harnessing the power of microorganisms, particularly Propionibacterium species, these methods can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with propionic acid production. Additionally, the use of waste materials as feedstock contributes to a circular economy model, addressing both waste management and resource efficiency challenges.
Advancements in metabolic engineering and synthetic biology are playing a crucial role in optimizing microbial strains for improved propionic acid yields. Researchers are focusing on enhancing the efficiency of key metabolic pathways and developing robust strains capable of withstanding industrial production conditions. These efforts aim to increase productivity while minimizing energy consumption and waste generation.
Process intensification strategies are also being explored to improve the sustainability of propionic acid production. Techniques such as continuous fermentation and in situ product recovery are being implemented to reduce energy requirements and improve overall process efficiency. These approaches not only enhance productivity but also contribute to reducing the environmental impact of production facilities.
Water management is another critical aspect of sustainable propionic acid production. Innovative water recycling and treatment technologies are being integrated into production processes to minimize water consumption and reduce wastewater generation. These efforts are particularly important in regions facing water scarcity challenges.
The integration of renewable energy sources into production facilities is gaining traction as a means to further reduce the environmental footprint of propionic acid production. Solar and wind power are being harnessed to power production processes, while biogas generated from waste streams is being utilized as an additional energy source. These initiatives not only contribute to sustainability goals but also offer potential cost savings in the long term.
As the food industry increasingly prioritizes sustainability, the demand for eco-friendly propionic acid is expected to grow. This shift is driving innovation in production technologies and encouraging collaboration between academia and industry to develop scalable, sustainable solutions. The future of propionic acid production lies in the successful integration of these sustainable practices, ensuring its continued role as a vital component in food preservation and production technologies while minimizing environmental impact.
One promising avenue is the development of bio-based production methods. These processes utilize renewable resources, such as agricultural waste or biomass, as feedstock for fermentation. By harnessing the power of microorganisms, particularly Propionibacterium species, these methods can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with propionic acid production. Additionally, the use of waste materials as feedstock contributes to a circular economy model, addressing both waste management and resource efficiency challenges.
Advancements in metabolic engineering and synthetic biology are playing a crucial role in optimizing microbial strains for improved propionic acid yields. Researchers are focusing on enhancing the efficiency of key metabolic pathways and developing robust strains capable of withstanding industrial production conditions. These efforts aim to increase productivity while minimizing energy consumption and waste generation.
Process intensification strategies are also being explored to improve the sustainability of propionic acid production. Techniques such as continuous fermentation and in situ product recovery are being implemented to reduce energy requirements and improve overall process efficiency. These approaches not only enhance productivity but also contribute to reducing the environmental impact of production facilities.
Water management is another critical aspect of sustainable propionic acid production. Innovative water recycling and treatment technologies are being integrated into production processes to minimize water consumption and reduce wastewater generation. These efforts are particularly important in regions facing water scarcity challenges.
The integration of renewable energy sources into production facilities is gaining traction as a means to further reduce the environmental footprint of propionic acid production. Solar and wind power are being harnessed to power production processes, while biogas generated from waste streams is being utilized as an additional energy source. These initiatives not only contribute to sustainability goals but also offer potential cost savings in the long term.
As the food industry increasingly prioritizes sustainability, the demand for eco-friendly propionic acid is expected to grow. This shift is driving innovation in production technologies and encouraging collaboration between academia and industry to develop scalable, sustainable solutions. The future of propionic acid production lies in the successful integration of these sustainable practices, ensuring its continued role as a vital component in food preservation and production technologies while minimizing environmental impact.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!