Improving The Lubrication Effect Of Check Valves
NOV 13, 20244 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Technology Background and Goals
The primary objective is to improve the lubrication effect of check valves, which are essential components in various fluid systems. Proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction, wear, and ensuring smooth operation of check valves. This research aims to explore innovative solutions and technologies that can enhance the lubrication performance, thereby extending the service life and reliability of check valves.
Key areas of focus include developing advanced lubricant formulations, optimizing surface coatings and materials, and investigating novel lubrication mechanisms. The research will also consider the impact of operating conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and fluid properties, on the lubrication effectiveness. By addressing these challenges, the research seeks to contribute to the development of more efficient and durable check valve systems, benefiting various industries that rely on fluid handling processes.
Key areas of focus include developing advanced lubricant formulations, optimizing surface coatings and materials, and investigating novel lubrication mechanisms. The research will also consider the impact of operating conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and fluid properties, on the lubrication effectiveness. By addressing these challenges, the research seeks to contribute to the development of more efficient and durable check valve systems, benefiting various industries that rely on fluid handling processes.
Market Demand Analysis
- Market Size and Growth
The global check valve lubrication market is expected to witness significant growth in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand from various industries such as oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing. - Key Applications
Check valves are widely used in pipelines, pumps, and fluid handling systems to prevent backflow. Proper lubrication is crucial for ensuring smooth operation, reducing wear and tear, and extending the lifespan of these valves. - Industry Trends
The market is witnessing a shift towards eco-friendly and biodegradable lubricants due to stringent environmental regulations. Additionally, the demand for high-performance lubricants capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and pressures is on the rise. - Regional Dynamics
Asia-Pacific region is expected to dominate the market due to the rapid industrialization and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. North America and Europe also hold significant market shares due to the presence of established industries.
Technology Status and Challenges
- Lubrication Challenges
Check valves often experience high friction and wear due to frequent opening/closing cycles, leading to reduced efficiency and lifespan. - Existing Solutions
Current solutions include using lubricants, coatings, or specialized materials, but they have limitations in durability, compatibility, or cost. - Material Advancements
New materials like ceramics, polymers, and composites offer improved wear resistance and self-lubricating properties, but require further research for optimal performance. - Surface Engineering
Techniques like surface texturing, coatings, and ion implantation can enhance lubrication and wear resistance, but need optimization for specific applications. - Fluid Dynamics
Studying fluid flow patterns and pressure distributions can lead to improved valve designs that minimize friction and wear.
Current Technical Solutions
01 Lubrication with Fluids
Some check valves are designed to be lubricated with lubricating fluids, such as oils or greases, to reduce friction and wear between the moving parts. The lubricating fluid can be applied during assembly or through dedicated lubrication ports.- Lubrication with Fluids: Some check valves are designed to be lubricated by the flow of lubricating fluids, such as oils or greases, through the valve body. This helps reduce friction and wear between the moving parts, improving performance and extending service life.
- Self-Lubricating Materials: Certain materials, like polymers or composites, can be used in check valve construction to provide self-lubricating properties, reducing the need for external lubrication and minimizing friction and wear.
- Lubrication Grooves or Channels: Some check valve designs incorporate grooves or channels in the valve body or components to facilitate the distribution of lubricants, ensuring proper lubrication and reducing friction.
- Dedicated Lubrication Systems: Dedicated lubrication systems, including pumps, reservoirs, and distribution lines, can be integrated into check valve assemblies to deliver lubricants to the valve components at desired flow rates and pressures.
- Lubrication-Free Designs: Some check valve designs aim to minimize or eliminate the need for lubrication by using specialized materials, coatings, or surface treatments that reduce friction and wear, simplifying maintenance and reducing contamination risks.
02 Self-Lubricating Materials
Certain check valve designs incorporate self-lubricating materials, such as polymer composites or coatings, to provide lubrication without external lubricants, reducing wear and maintenance requirements.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lubrication-Free Designs
Some check valve designs aim to eliminate the need for lubrication by using materials and configurations that minimize friction and wear without lubricants, incorporating features like low-friction coatings, optimized geometries, or reduced contact areas.Expand Specific Solutions04 Solid Lubricants
Solid lubricants, such as graphite, molybdenum disulfide, or PTFE, can be used to lubricate check valves, providing long-lasting lubrication and reducing friction when applied as coatings or incorporated into the valve components.Expand Specific Solutions05 Dedicated Lubrication Systems
Some check valve designs incorporate dedicated lubrication systems that continuously or periodically supply lubricant to the valve components, including pumps, reservoirs, and distribution channels to ensure proper lubrication during operation.Expand Specific Solutions
Technology Main Player Analysis
The competitive landscape for improving the lubrication effect of check valves involves players with varying expertise and market scales. Established companies like Chevron Oronite Co. LLC, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., and The Lubrizol Corp. offer advanced lubricants for high performance. Specialized firms like Hans Jensen Lubricators A/S and BestLine International Research, Inc. provide lubrication solutions with technical expertise. Emerging players like Texhong Valve Technology (Quanzhou) Co., Ltd. and Suzhou Kedi Liquid Science Equipment Co., Ltd. contribute to innovation in this niche market. The overall market is growing, driven by the need for enhanced efficiency and longevity of mechanical systems.
Chevron Oronite Co. LLC
Technical Solution: Chevron Oronite develops advanced lubrication additives that enhance check valve performance, reducing friction and wear for improved efficiency and lifespan, even in extreme conditions.
Strength: Proven effectiveness in extreme conditions. Weakness: High cost of additives.
Hans Jensen Lubricators A/S
Technical Solution: Hans Jensen Lubricators specializes in innovative lubrication systems for precise delivery, reducing wear and extending service life of check valves. Their customizable systems are highly efficient.
Strength: Customizable and precise. Weakness: Limited to specific applications.
Key Technology Interpretation
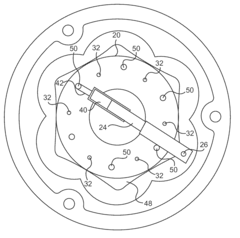
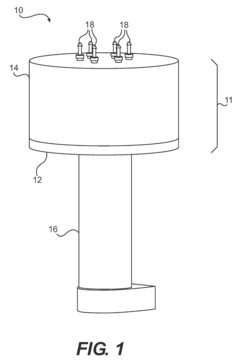
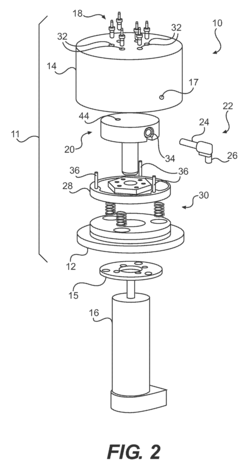
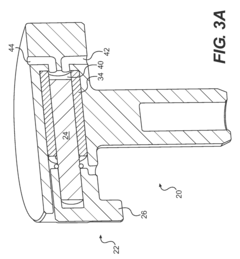
Fluid pump
PatentActiveUS8162632B2
Innovation
- Eliminating check valves that are prone to sticking at low temperatures, improving lubrication efficiency.
- Providing sequential lubrication delivery to multiple locations for more comprehensive coverage.
- Utilizing a symmetrical housing design about a central longitudinal axis for improved balance and stability.
Environmental Impact Analysis
The lubrication of check valves plays a crucial role in minimizing friction and wear, ensuring smooth operation and prolonged service life. However, the environmental impact of lubricants should be carefully evaluated. Conventional lubricants often contain hazardous substances that can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic ecosystems. Biodegradable and eco-friendly lubricants derived from renewable sources, such as vegetable oils or synthetic esters, offer a sustainable alternative. These lubricants have a lower environmental footprint and are less toxic to aquatic life. Additionally, proper disposal methods and spill prevention measures should be implemented to mitigate potential environmental risks associated with lubricant usage in check valve applications.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
In the context of improving the lubrication effect of check valves, regulatory and compliance considerations play a crucial role. Lubricants used in check valves must adhere to stringent industry standards and environmental regulations to ensure safe and reliable operation. Factors such as compatibility with valve materials, temperature and pressure ratings, and potential contamination risks must be carefully evaluated. Additionally, lubricant selection should consider environmental impact, biodegradability, and compliance with relevant regulations like REACH, RoHS, and TSCA. Proper documentation, material safety data sheets, and regular maintenance procedures are essential for maintaining regulatory compliance throughout the valve's lifecycle.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!