Self-Lubricating Materials For Check Valves
NOV 13, 20244 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Technology Background and Goals
The primary objective is to provide a comprehensive overview of the development history and evolution trends in the field of self-lubricating materials for check valves. This includes examining the key milestones and technological breakthroughs that have shaped the progress of this technology over time. Additionally, it aims to clearly define the expected technological goals and advancements that are anticipated to be achieved in this domain.
By thoroughly analyzing the historical trajectory and future projections, this section lays the foundation for understanding the current state, challenges, and potential directions for self-lubricating materials in check valve applications. It establishes the context and rationale for the subsequent sections of the technology research report.
By thoroughly analyzing the historical trajectory and future projections, this section lays the foundation for understanding the current state, challenges, and potential directions for self-lubricating materials in check valve applications. It establishes the context and rationale for the subsequent sections of the technology research report.
Market Demand Analysis
- Market Size and Growth
The global market for check valves is substantial, driven by widespread applications across industries like oil and gas, water treatment, chemical processing, and power generation. Self-lubricating materials can enhance valve performance and extend service life, creating significant demand. - Industry Trends
There is a growing emphasis on reducing maintenance costs, improving operational efficiency, and minimizing environmental impact. Self-lubricating materials align with these trends by reducing friction, wear, and the need for external lubrication. - Regulatory Compliance
Stringent regulations regarding emissions, safety, and environmental protection are driving the adoption of self-lubricating materials in check valves. These materials can help meet regulatory requirements while ensuring reliable valve operation. - Cost Savings
Self-lubricating materials can significantly reduce the costs associated with valve maintenance, lubrication, and downtime. This cost-saving potential is a major driver for their adoption across various industries. - Harsh Environments
Many applications involve harsh environments with extreme temperatures, pressures, or corrosive media. Self-lubricating materials can provide superior performance and durability in these challenging conditions, creating demand for their use in check valves.
Check Valve Self-Lubricating Materials Status and Challenges
- Material Composition
Self-lubricating materials for check valves typically consist of a polymer matrix reinforced with solid lubricants like PTFE, graphite, or molybdenum disulfide. - Lubrication Mechanism
The solid lubricants form a transfer film on the valve surfaces, reducing friction and wear during operation. - Challenges
- Achieving optimal balance between lubricity and mechanical strength
- Ensuring long-term stability and durability of the lubricating film
- Compatibility with various media and operating conditions
- Current Solutions
Commercially available self-lubricating materials include PTFE-based composites, PEEK-based compounds, and engineered plastics with solid lubricant fillers.
Check Valve Self-Lubricating Materials Current Technical Solutions
01 Polymer Coated Self-lubricating Valves
Check valves with self-lubricating polymer coatings like PTFE, PEEK, or other low-friction polymers, allowing smooth operation without external lubrication.- Self-lubricating Polymer Coatings: Check valves with self-lubricating polymer coatings or linings like PTFE, PEEK, or other low-friction polymers to reduce friction and wear during operation.
- Integrated Lubrication Systems: Check valves with integrated lubrication systems, including grease reservoirs, lubricant channels, or mechanisms to distribute lubricant to critical areas during operation.
- Self-lubricating Materials: Check valves made from inherently self-lubricating materials like graphite-filled or carbon-filled polymers, exhibiting low friction properties without additional lubrication.
- Lubricant Reservoirs: Check valves with lubricant reservoirs or chambers that hold and gradually release lubricant to the moving parts during operation.
- Self-lubricating Seals: Check valves with self-lubricating seals or gaskets made from materials like PTFE or other low-friction polymers, reducing friction and wear between components and sealing surfaces.
02 Integrated Lubrication Systems
Check valves with integrated lubrication systems like grease fittings, oil reservoirs, or mechanisms to supply lubricant to moving parts, reducing friction and extending service life.Expand Specific Solutions03 Self-lubricating Seals and Seats
Check valve seals and seats made from self-lubricating materials or coatings like carbon-reinforced PTFE, graphite-filled PEEK, or other low-friction compounds, minimizing friction and wear without external lubricants.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lubricant-impregnated Components
Check valves with components impregnated or filled with lubricants like grease or oil, continuously releasing small amounts to the moving parts for consistent lubrication and reduced friction.Expand Specific Solutions05 Self-adjusting Lubrication Mechanisms
Check valves with self-adjusting lubrication mechanisms that automatically adjust lubricant supply based on factors like temperature, pressure, or operating conditions, maintaining optimal lubrication levels.Expand Specific Solutions
Check Valve Self-Lubricating Materials Main Player Analysis
The self-lubricating materials market for check valves is diverse, with established players like Halkey-Roberts Corp., Cameron International Corp., and Proserv Gilmore Valve LLC, as well as emerging companies like Zhejiang Changsheng Sliding Bearings Co., Ltd. and Yancheng Shengtai Valve Co. Ltd. Research institutions like Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics and California Institute of Technology contribute to innovation. The market is growing due to demand for efficient and durable valve solutions, with technological advancements driving material performance improvements.
Halkey-Roberts Corp.
Technical Solution:
Zhejiang Changsheng Sliding Bearings Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Zhejiang Changsheng specializes in self-lubricating bearings with composite materials for low friction and high wear resistance, ensuring long-term performance without external lubrication.
Strength: High wear resistance and low friction. Weakness: Limited material compositions.
Check Valve Self-Lubricating Materials Key Technology Interpretation
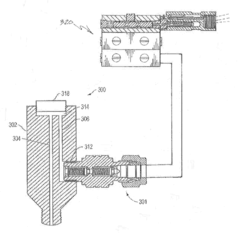
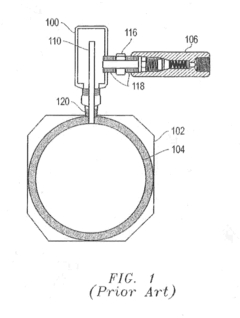
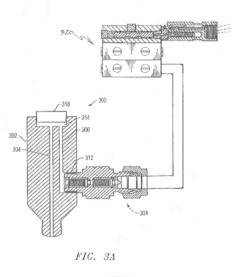
Check Valve and Method and Apparatus for Extending Life of Check Valve
PatentActiveUS20160186736A1
Innovation
- Reducing check valve failures: the invention addresses the root cause of check valve failures in gas compressors and other applications. by providing a fluid barrier to protect the check valve, it extends the life of the equipment.
- Small internal volume: the device has a small internal volume to prevent delaying lubricant from reaching the compressor upon start up. this ensures that the lubricant reaches the compressor cylinder in a timely manner, preventing any damage or contamination.
- Applicability to different applications: the invention is not limited to gas compressors but can be applied to any application where the check valve is exposed to hot, corrosive, or contaminated fluids. this makes the invention highly versatile and applicable in various industries.
Check Valve Self-Lubricating Materials Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of self-lubricating materials for check valves is a crucial consideration. These materials often contain hazardous substances like heavy metals or persistent organic compounds that can leach into the surrounding environment during use or disposal. Proper material selection and responsible handling practices are essential to mitigate potential risks. Additionally, the manufacturing processes involved may generate emissions or waste streams that require careful management. A comprehensive life cycle assessment should be conducted to identify and address environmental concerns at every stage, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal or recycling. Ultimately, the goal should be to develop eco-friendly, sustainable self-lubricating solutions that minimize environmental harm while ensuring reliable valve performance.
Check Valve Self-Lubricating Materials Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Regulatory and compliance issues surrounding self-lubricating materials for check valves are crucial considerations. These materials must adhere to industry standards and regulations to ensure safe and reliable operation. Key aspects include material composition, environmental impact, and compatibility with the specific application. Compliance with relevant guidelines, such as those set by regulatory bodies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), is essential. Additionally, certifications from recognized organizations may be required for certain applications or industries. Thorough testing and documentation are necessary to demonstrate adherence to regulations and facilitate approval processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!