Robust Techniques to Validate Hypochlorous Acid Purity and Concentration
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl Purity Analysis
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) purity analysis is a critical aspect of quality control in various industries, including water treatment, healthcare, and food processing. The validation of HOCl purity and concentration requires robust techniques that ensure accuracy, reliability, and reproducibility. These methods are essential for maintaining product efficacy and safety standards.
One of the primary techniques used for HOCl purity analysis is high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). This method offers high sensitivity and selectivity, allowing for the precise quantification of HOCl and potential impurities. HPLC can detect trace amounts of contaminants, such as chlorate and perchlorate, which may form during the production or storage of HOCl solutions. The use of UV-vis detectors in conjunction with HPLC enhances the ability to identify and quantify various chlorine species.
Spectrophotometric methods provide another valuable approach for HOCl purity analysis. UV-visible spectroscopy can be used to measure the absorbance of HOCl at specific wavelengths, typically around 230-235 nm. This technique allows for rapid and non-destructive analysis of HOCl concentration. However, it is important to note that other chlorine species may interfere with the measurements, necessitating careful calibration and validation of the method.
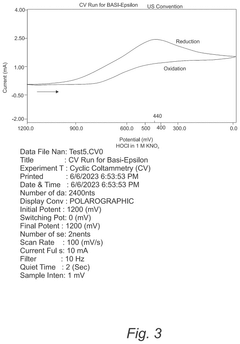
Electrochemical techniques, such as amperometry and potentiometry, offer real-time monitoring capabilities for HOCl concentration. These methods are particularly useful for continuous process control in industrial settings. Amperometric sensors can provide rapid and accurate measurements of free available chlorine, which includes HOCl. Potentiometric methods, using ion-selective electrodes, can also be employed to determine HOCl concentration based on the oxidation-reduction potential of the solution.
Titration methods, while traditional, remain relevant for HOCl purity analysis. Iodometric titration is commonly used to determine the available chlorine content in HOCl solutions. This method involves the reduction of HOCl by iodide, followed by titration of the liberated iodine with a standardized thiosulfate solution. While titration methods can be time-consuming, they offer a reliable and cost-effective approach for routine analysis.
Advanced analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry (MS) coupled with chromatography, provide powerful tools for in-depth purity analysis of HOCl solutions. These methods can identify and quantify trace impurities and degradation products with high precision. LC-MS or GC-MS techniques are particularly useful for investigating the stability and degradation pathways of HOCl under various storage conditions.
The selection of appropriate analytical techniques for HOCl purity analysis depends on factors such as required sensitivity, specificity, sample throughput, and available resources. A comprehensive approach often involves combining multiple techniques to ensure thorough characterization of HOCl solutions. Validation of these analytical methods is crucial to establish their reliability and suitability for the intended purpose.
One of the primary techniques used for HOCl purity analysis is high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). This method offers high sensitivity and selectivity, allowing for the precise quantification of HOCl and potential impurities. HPLC can detect trace amounts of contaminants, such as chlorate and perchlorate, which may form during the production or storage of HOCl solutions. The use of UV-vis detectors in conjunction with HPLC enhances the ability to identify and quantify various chlorine species.
Spectrophotometric methods provide another valuable approach for HOCl purity analysis. UV-visible spectroscopy can be used to measure the absorbance of HOCl at specific wavelengths, typically around 230-235 nm. This technique allows for rapid and non-destructive analysis of HOCl concentration. However, it is important to note that other chlorine species may interfere with the measurements, necessitating careful calibration and validation of the method.
Electrochemical techniques, such as amperometry and potentiometry, offer real-time monitoring capabilities for HOCl concentration. These methods are particularly useful for continuous process control in industrial settings. Amperometric sensors can provide rapid and accurate measurements of free available chlorine, which includes HOCl. Potentiometric methods, using ion-selective electrodes, can also be employed to determine HOCl concentration based on the oxidation-reduction potential of the solution.
Titration methods, while traditional, remain relevant for HOCl purity analysis. Iodometric titration is commonly used to determine the available chlorine content in HOCl solutions. This method involves the reduction of HOCl by iodide, followed by titration of the liberated iodine with a standardized thiosulfate solution. While titration methods can be time-consuming, they offer a reliable and cost-effective approach for routine analysis.
Advanced analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry (MS) coupled with chromatography, provide powerful tools for in-depth purity analysis of HOCl solutions. These methods can identify and quantify trace impurities and degradation products with high precision. LC-MS or GC-MS techniques are particularly useful for investigating the stability and degradation pathways of HOCl under various storage conditions.
The selection of appropriate analytical techniques for HOCl purity analysis depends on factors such as required sensitivity, specificity, sample throughput, and available resources. A comprehensive approach often involves combining multiple techniques to ensure thorough characterization of HOCl solutions. Validation of these analytical methods is crucial to establish their reliability and suitability for the intended purpose.
Market Demand for HOCl
The market demand for hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has been steadily increasing across various industries due to its powerful disinfectant properties and eco-friendly nature. Healthcare sectors, including hospitals, clinics, and dental practices, have shown significant interest in HOCl for its effectiveness against a wide range of pathogens while being gentle on human tissues. This demand has been further amplified by the global focus on hygiene and sanitation in the wake of recent health crises.
In the food and beverage industry, HOCl has gained traction as a safe and effective sanitizer for food processing equipment, surfaces, and even direct food contact applications. Its ability to eliminate harmful microorganisms without leaving harmful residues aligns well with the industry's stringent safety standards and consumer preferences for chemical-free products.
The agriculture sector has also recognized the potential of HOCl in crop protection and post-harvest treatment. Farmers and agribusinesses are increasingly adopting HOCl solutions for irrigation systems, seed treatment, and produce washing, driven by the need for sustainable and non-toxic alternatives to traditional chemical pesticides and fungicides.
Water treatment facilities have shown growing interest in HOCl as an alternative to chlorine-based disinfectants. Its effectiveness in water purification, coupled with reduced environmental impact and lower risk of harmful by-product formation, makes it an attractive option for both municipal water systems and industrial wastewater treatment plants.
The personal care and cosmetics industry has begun exploring HOCl for its antimicrobial properties in skincare products, particularly for acne treatment and wound healing applications. This emerging market segment presents significant growth potential as consumers increasingly seek natural and gentle yet effective skincare solutions.
In the veterinary and animal husbandry sectors, HOCl has found applications in wound care, surface disinfection, and water treatment for livestock. The non-toxic nature of HOCl makes it particularly suitable for use around animals, addressing concerns about chemical residues in animal products.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for HOCl across various sectors, particularly in public spaces, transportation, and hospitality industries. Its proven efficacy against viruses, including coronaviruses, has positioned HOCl as a preferred disinfectant for high-traffic areas and frequently touched surfaces.
As environmental regulations become more stringent and public awareness of chemical safety increases, the market for HOCl is expected to expand further. Industries are actively seeking alternatives to traditional chemical disinfectants, driving innovation in HOCl production, storage, and application technologies.
In the food and beverage industry, HOCl has gained traction as a safe and effective sanitizer for food processing equipment, surfaces, and even direct food contact applications. Its ability to eliminate harmful microorganisms without leaving harmful residues aligns well with the industry's stringent safety standards and consumer preferences for chemical-free products.
The agriculture sector has also recognized the potential of HOCl in crop protection and post-harvest treatment. Farmers and agribusinesses are increasingly adopting HOCl solutions for irrigation systems, seed treatment, and produce washing, driven by the need for sustainable and non-toxic alternatives to traditional chemical pesticides and fungicides.
Water treatment facilities have shown growing interest in HOCl as an alternative to chlorine-based disinfectants. Its effectiveness in water purification, coupled with reduced environmental impact and lower risk of harmful by-product formation, makes it an attractive option for both municipal water systems and industrial wastewater treatment plants.
The personal care and cosmetics industry has begun exploring HOCl for its antimicrobial properties in skincare products, particularly for acne treatment and wound healing applications. This emerging market segment presents significant growth potential as consumers increasingly seek natural and gentle yet effective skincare solutions.
In the veterinary and animal husbandry sectors, HOCl has found applications in wound care, surface disinfection, and water treatment for livestock. The non-toxic nature of HOCl makes it particularly suitable for use around animals, addressing concerns about chemical residues in animal products.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for HOCl across various sectors, particularly in public spaces, transportation, and hospitality industries. Its proven efficacy against viruses, including coronaviruses, has positioned HOCl as a preferred disinfectant for high-traffic areas and frequently touched surfaces.
As environmental regulations become more stringent and public awareness of chemical safety increases, the market for HOCl is expected to expand further. Industries are actively seeking alternatives to traditional chemical disinfectants, driving innovation in HOCl production, storage, and application technologies.
Current Challenges
The validation of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) purity and concentration faces several significant challenges in current practice. One of the primary issues is the inherent instability of HOCl solutions. These solutions are prone to rapid degradation, especially when exposed to light, heat, or contaminants. This instability makes it difficult to maintain consistent concentration levels over time, complicating the validation process and potentially leading to inaccurate results.
Another challenge lies in the lack of standardized methods for HOCl analysis across different industries and applications. While various techniques exist, there is no universally accepted protocol for measuring HOCl purity and concentration. This absence of standardization can lead to inconsistencies in results between different laboratories or testing facilities, making it challenging to compare data and establish reliable benchmarks.
The presence of interfering substances in HOCl solutions presents an additional hurdle. Chlorine-based compounds, such as chlorine dioxide or hypochlorite ions, can coexist with HOCl and interfere with analytical measurements. Distinguishing between these species and accurately quantifying HOCl alone requires sophisticated analytical techniques that may not be readily available or easily implemented in all settings.
Furthermore, the low concentration levels at which HOCl is typically used in many applications pose a challenge for accurate detection and quantification. Many conventional analytical methods struggle to provide reliable results at these low concentrations, necessitating the development and validation of highly sensitive techniques.
The environmental and safety concerns associated with HOCl analysis also contribute to the current challenges. Some traditional methods for chlorine analysis involve the use of hazardous reagents or generate toxic by-products. This has led to a push for greener, safer analytical techniques, which in turn requires extensive validation and optimization to ensure they meet the necessary performance criteria.
Lastly, the diverse range of matrices in which HOCl is used – from water treatment systems to medical disinfectants and food processing applications – adds complexity to the validation process. Each matrix may introduce unique interferences or require specific sample preparation steps, making it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all approach to HOCl validation. This variability necessitates the development of robust, versatile techniques that can accurately measure HOCl purity and concentration across a wide range of sample types and conditions.
Another challenge lies in the lack of standardized methods for HOCl analysis across different industries and applications. While various techniques exist, there is no universally accepted protocol for measuring HOCl purity and concentration. This absence of standardization can lead to inconsistencies in results between different laboratories or testing facilities, making it challenging to compare data and establish reliable benchmarks.
The presence of interfering substances in HOCl solutions presents an additional hurdle. Chlorine-based compounds, such as chlorine dioxide or hypochlorite ions, can coexist with HOCl and interfere with analytical measurements. Distinguishing between these species and accurately quantifying HOCl alone requires sophisticated analytical techniques that may not be readily available or easily implemented in all settings.
Furthermore, the low concentration levels at which HOCl is typically used in many applications pose a challenge for accurate detection and quantification. Many conventional analytical methods struggle to provide reliable results at these low concentrations, necessitating the development and validation of highly sensitive techniques.
The environmental and safety concerns associated with HOCl analysis also contribute to the current challenges. Some traditional methods for chlorine analysis involve the use of hazardous reagents or generate toxic by-products. This has led to a push for greener, safer analytical techniques, which in turn requires extensive validation and optimization to ensure they meet the necessary performance criteria.
Lastly, the diverse range of matrices in which HOCl is used – from water treatment systems to medical disinfectants and food processing applications – adds complexity to the validation process. Each matrix may introduce unique interferences or require specific sample preparation steps, making it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all approach to HOCl validation. This variability necessitates the development of robust, versatile techniques that can accurately measure HOCl purity and concentration across a wide range of sample types and conditions.
Existing Validation
01 Production methods for high-purity hypochlorous acid
Various methods are employed to produce high-purity hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and advanced purification techniques. These methods aim to minimize impurities and achieve consistent concentration levels, which are crucial for applications requiring precise and stable hypochlorous acid solutions.- Production methods for high-purity hypochlorous acid: Various methods are employed to produce high-purity hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions, and membrane separation techniques. These methods aim to minimize impurities and achieve consistent concentration levels, which are crucial for applications requiring precise control of hypochlorous acid purity.
- Concentration control and stabilization techniques: Maintaining the desired concentration of hypochlorous acid is essential for its effectiveness. Techniques such as pH adjustment, temperature control, and the addition of stabilizing agents are used to prevent degradation and maintain the desired concentration over time. These methods help extend the shelf life and ensure consistent performance of hypochlorous acid solutions.
- Analytical methods for purity and concentration determination: Accurate measurement of hypochlorous acid purity and concentration is crucial for quality control and application purposes. Various analytical techniques are employed, including spectrophotometry, titration, and electrochemical methods. These techniques allow for precise quantification of hypochlorous acid content and the detection of impurities.
- Applications of high-purity hypochlorous acid: High-purity hypochlorous acid finds applications in various fields, including water treatment, disinfection, medical devices, and personal care products. The purity and concentration of hypochlorous acid are tailored to specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and safety in each use case.
- Storage and packaging solutions for maintaining purity: Proper storage and packaging are essential for maintaining the purity and concentration of hypochlorous acid. Specialized containers, light-protective materials, and inert gas environments are used to prevent degradation and contamination. These solutions help preserve the quality of hypochlorous acid during storage and transportation.
02 Concentration control and stabilization techniques
Maintaining the desired concentration of hypochlorous acid is essential for its effectiveness. Techniques such as pH adjustment, temperature control, and the addition of stabilizing agents are used to prevent degradation and maintain the desired concentration over time. These methods help extend the shelf life and ensure consistent performance of hypochlorous acid solutions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Analytical methods for purity and concentration measurement
Accurate measurement of hypochlorous acid purity and concentration is crucial for quality control and application purposes. Various analytical techniques are employed, including spectrophotometry, titration methods, and electrochemical sensors. These methods allow for precise determination of hypochlorous acid content and the detection of impurities.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of high-purity hypochlorous acid
High-purity hypochlorous acid finds applications in various fields, including disinfection, water treatment, medical devices, and personal care products. The purity and concentration of hypochlorous acid are critical factors in determining its efficacy and safety for different applications, with specific requirements varying depending on the intended use.Expand Specific Solutions05 Storage and packaging solutions for maintaining purity and concentration
Proper storage and packaging are essential for maintaining the purity and concentration of hypochlorous acid solutions. Specialized containers, light-protective materials, and innovative packaging designs are used to prevent degradation and contamination. These solutions help preserve the stability and effectiveness of hypochlorous acid during storage and transportation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for robust techniques to validate hypochlorous acid purity and concentration is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for effective disinfection solutions across various industries. The global market size for hypochlorous acid is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a growing emphasis on quality control and validation methods. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Panasonic Intellectual Property Management Co. Ltd., WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB, and Versitech Ltd. leading innovation in measurement and validation techniques. Academic institutions such as Hunan University of Science & Technology and Qilu University of Technology are contributing to research and development, enhancing the overall technological maturity of the sector.
Aquaox, Inc.
Technical Solution: Aquaox has developed a proprietary electrochemical activation (ECA) technology for producing high-purity hypochlorous acid (HOCl). Their process involves electrolysis of salt water in a specialized cell, resulting in a stable HOCl solution with a pH range of 6.2-6.5 and an oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) of +800 to +1000 mV [1]. To validate purity and concentration, Aquaox employs a multi-step approach: 1) In-line monitoring of pH, ORP, and free available chlorine (FAC) during production; 2) Spectrophotometric analysis using DPD (N,N-diethyl-p-phenylenediamine) method for precise FAC measurement; 3) Ion chromatography to detect and quantify potential impurities like chlorate and perchlorate [2][3]. Additionally, they use advanced analytical techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to confirm the molecular structure and purity of HOCl [4].
Strengths: Highly controlled production process, comprehensive analytical validation suite, and ability to produce stable, high-purity HOCl. Weaknesses: Potential for electrode degradation over time, which may introduce trace metal contaminants, requiring regular monitoring and maintenance.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a robust analytical framework for validating hypochlorous acid purity and concentration, leveraging its extensive expertise in chemical analysis. Their approach combines multiple complementary techniques: 1) High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection for precise quantification of HOCl and potential by-products [5]; 2) Potentiometric titration for rapid determination of available chlorine content; 3) Ion-selective electrode (ISE) measurements for real-time monitoring of chlorine species [6]. BASF also employs advanced spectroscopic methods, including Raman spectroscopy, to provide molecular-level insights into HOCl solutions and detect impurities at trace levels [7]. To ensure the stability and efficacy of HOCl formulations, BASF has developed accelerated aging protocols and conducts long-term stability studies under various environmental conditions [8].
Strengths: Comprehensive analytical capabilities, advanced spectroscopic techniques, and expertise in stability testing. Weaknesses: Some methods may require expensive, specialized equipment, potentially limiting widespread adoption in smaller facilities or field applications.
Innovative Techniques
Concentration measurement method of hypobromous acid or salts thereof and stabilized hypobromous acid compositions
PatentActiveJP2019100781A
Innovation
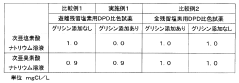
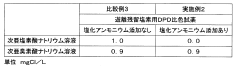
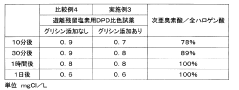
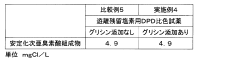
- A colorimetric method using N,N-diethyl-p-phenylenediamine or N,N'-bis(2,4-di-sulfobenzyl)toluidine tetrasodium as reagents, with an excess of ammonium salts or amino group-containing compounds like glycine to consume hypochlorous acid, allowing separate measurement of hypobromous acid concentrations.
Method of preparation and properties of pure hypochlorous acid, hocl
PatentPendingUS20250115481A1
Innovation
- A method involving the combination of sodium hypochlorite with a nonpolar solvent and a weak acid, such as acetic acid, to form a biphasic mixture, followed by agitation and separation of phases, where the nonpolar solvent is used to extract and then remove pure hypochlorous acid.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding hypochlorous acid (HOCl) validation is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the diverse applications of this compound across various industries. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating HOCl as a pesticide and disinfectant under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The EPA requires manufacturers to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of HOCl-based products through rigorous testing protocols.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also has oversight on HOCl, particularly in food processing and medical applications. The FDA's regulations focus on ensuring the purity and concentration of HOCl meet specific standards for use in food contact surfaces and medical devices. These regulations often reference analytical methods outlined in the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) for validating HOCl purity and concentration.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines on the use of HOCl in water treatment and disinfection processes. These guidelines often serve as a basis for national regulations in many countries. The European Union, through its Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), has established specific requirements for HOCl-based products, including validation of purity and concentration.
In the context of workplace safety, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S. sets exposure limits and handling guidelines for HOCl. These regulations necessitate accurate measurement and monitoring of HOCl concentrations in workplace environments.
The pharmaceutical industry faces particularly stringent regulations when using HOCl in drug formulations or as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). Regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the FDA require adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), which include validated analytical methods for HOCl purity and concentration assessment.
Environmental regulations also impact HOCl validation requirements. Many countries have established maximum residual levels for chlorine-based compounds in wastewater discharge, necessitating accurate measurement techniques to ensure compliance.
As the applications of HOCl continue to expand, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the development and standardization of robust validation techniques. This trend is driving research into more sensitive and reliable analytical methods, as well as the establishment of international standards for HOCl purity and concentration validation across different industries and applications.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also has oversight on HOCl, particularly in food processing and medical applications. The FDA's regulations focus on ensuring the purity and concentration of HOCl meet specific standards for use in food contact surfaces and medical devices. These regulations often reference analytical methods outlined in the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) for validating HOCl purity and concentration.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines on the use of HOCl in water treatment and disinfection processes. These guidelines often serve as a basis for national regulations in many countries. The European Union, through its Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), has established specific requirements for HOCl-based products, including validation of purity and concentration.
In the context of workplace safety, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S. sets exposure limits and handling guidelines for HOCl. These regulations necessitate accurate measurement and monitoring of HOCl concentrations in workplace environments.
The pharmaceutical industry faces particularly stringent regulations when using HOCl in drug formulations or as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). Regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the FDA require adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), which include validated analytical methods for HOCl purity and concentration assessment.
Environmental regulations also impact HOCl validation requirements. Many countries have established maximum residual levels for chlorine-based compounds in wastewater discharge, necessitating accurate measurement techniques to ensure compliance.
As the applications of HOCl continue to expand, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the development and standardization of robust validation techniques. This trend is driving research into more sensitive and reliable analytical methods, as well as the establishment of international standards for HOCl purity and concentration validation across different industries and applications.
Safety Considerations
Safety considerations are paramount when working with hypochlorous acid (HOCl) due to its reactive nature and potential health hazards. Proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures must be implemented to ensure the safety of personnel and the environment. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential, including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and appropriate respiratory protection when dealing with concentrated solutions or in poorly ventilated areas.
The concentration of HOCl is a critical factor in safety management. Higher concentrations pose greater risks and require more stringent safety measures. Regular monitoring and validation of HOCl concentration are crucial to maintain safe working conditions. Automated systems for concentration monitoring can provide real-time data and alerts, reducing the risk of exposure to unsafe levels.
Proper ventilation is essential in areas where HOCl is used or stored. The acid can release chlorine gas, which is toxic if inhaled. Facilities should be equipped with adequate ventilation systems and gas detectors to prevent the accumulation of harmful vapors. Emergency eyewash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure.
Storage considerations include using appropriate containers resistant to corrosion and degradation. HOCl should be stored in a cool, dark place away from direct sunlight and heat sources to prevent decomposition. Incompatible materials, such as certain metals and organic compounds, must be kept separate to avoid potentially dangerous reactions.
Training programs for personnel handling HOCl are crucial. These should cover proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the use of safety equipment. Regular safety audits and drills can help ensure that all staff members are prepared to respond effectively to potential incidents.
Disposal of HOCl and related waste must comply with local environmental regulations. Neutralization processes may be required before disposal, and proper documentation should be maintained. Implementing a comprehensive waste management plan can help minimize environmental impact and ensure regulatory compliance.
In the context of validation techniques, safety considerations extend to the analytical processes themselves. Methods that minimize sample handling and exposure risks should be prioritized. Automated systems and closed-loop sampling techniques can significantly reduce the potential for accidents during the validation process.
Lastly, a robust incident reporting and investigation system should be in place to learn from any safety-related events and continuously improve safety protocols. This proactive approach to safety management is essential for maintaining a safe working environment when dealing with hypochlorous acid and its validation processes.
The concentration of HOCl is a critical factor in safety management. Higher concentrations pose greater risks and require more stringent safety measures. Regular monitoring and validation of HOCl concentration are crucial to maintain safe working conditions. Automated systems for concentration monitoring can provide real-time data and alerts, reducing the risk of exposure to unsafe levels.
Proper ventilation is essential in areas where HOCl is used or stored. The acid can release chlorine gas, which is toxic if inhaled. Facilities should be equipped with adequate ventilation systems and gas detectors to prevent the accumulation of harmful vapors. Emergency eyewash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure.
Storage considerations include using appropriate containers resistant to corrosion and degradation. HOCl should be stored in a cool, dark place away from direct sunlight and heat sources to prevent decomposition. Incompatible materials, such as certain metals and organic compounds, must be kept separate to avoid potentially dangerous reactions.
Training programs for personnel handling HOCl are crucial. These should cover proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the use of safety equipment. Regular safety audits and drills can help ensure that all staff members are prepared to respond effectively to potential incidents.
Disposal of HOCl and related waste must comply with local environmental regulations. Neutralization processes may be required before disposal, and proper documentation should be maintained. Implementing a comprehensive waste management plan can help minimize environmental impact and ensure regulatory compliance.
In the context of validation techniques, safety considerations extend to the analytical processes themselves. Methods that minimize sample handling and exposure risks should be prioritized. Automated systems and closed-loop sampling techniques can significantly reduce the potential for accidents during the validation process.
Lastly, a robust incident reporting and investigation system should be in place to learn from any safety-related events and continuously improve safety protocols. This proactive approach to safety management is essential for maintaining a safe working environment when dealing with hypochlorous acid and its validation processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!