Advanced Techniques for Phospholipid Analysis
JUL 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Phospholipid Analysis Evolution and Objectives
Phospholipid analysis has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially, thin-layer chromatography (TLC) was the primary method for separating and identifying phospholipids. This technique, while groundbreaking at the time, offered limited resolution and quantitative capabilities.
The advent of gas chromatography (GC) in the 1960s marked a significant leap forward, allowing for more precise separation and quantification of fatty acid components. However, GC required derivatization of phospholipids, which could potentially alter their structure and composition.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) emerged in the 1970s as a powerful tool for phospholipid analysis, offering improved separation and the ability to analyze intact molecules. This technique has since become a cornerstone in phospholipid research, with various detection methods such as UV, fluorescence, and evaporative light scattering being developed to enhance its capabilities.
The introduction of mass spectrometry (MS) coupled with chromatographic techniques in the 1980s and 1990s revolutionized phospholipid analysis. Electrospray ionization (ESI) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) techniques enabled the analysis of intact phospholipids with unprecedented sensitivity and specificity.
Recent years have seen the development of advanced MS techniques such as tandem MS (MS/MS) and high-resolution MS, which allow for detailed structural characterization and accurate quantification of phospholipids. These methods have greatly expanded our understanding of lipid metabolism, membrane biology, and disease processes.
The objectives of modern phospholipid analysis techniques are multifaceted. Researchers aim to achieve higher sensitivity, enabling the detection and quantification of low-abundance phospholipid species. Improved resolution is crucial for separating structurally similar phospholipids, particularly those with identical molecular weights but different fatty acid compositions or positional isomers.
Another key objective is to develop high-throughput methods capable of analyzing complex lipid mixtures in biological samples rapidly and comprehensively. This is particularly important in the emerging field of lipidomics, which seeks to characterize the entire lipid profile of cells, tissues, or organisms.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on developing non-destructive, in situ analysis techniques that can provide spatial information about phospholipid distribution within cells and tissues. Techniques such as imaging mass spectrometry and Raman spectroscopy are being explored for this purpose.
Ultimately, the goal of advanced phospholipid analysis techniques is to provide a more complete understanding of lipid biology, from molecular structure to cellular function, and to translate this knowledge into practical applications in fields such as medicine, nutrition, and biotechnology.
The advent of gas chromatography (GC) in the 1960s marked a significant leap forward, allowing for more precise separation and quantification of fatty acid components. However, GC required derivatization of phospholipids, which could potentially alter their structure and composition.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) emerged in the 1970s as a powerful tool for phospholipid analysis, offering improved separation and the ability to analyze intact molecules. This technique has since become a cornerstone in phospholipid research, with various detection methods such as UV, fluorescence, and evaporative light scattering being developed to enhance its capabilities.
The introduction of mass spectrometry (MS) coupled with chromatographic techniques in the 1980s and 1990s revolutionized phospholipid analysis. Electrospray ionization (ESI) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) techniques enabled the analysis of intact phospholipids with unprecedented sensitivity and specificity.
Recent years have seen the development of advanced MS techniques such as tandem MS (MS/MS) and high-resolution MS, which allow for detailed structural characterization and accurate quantification of phospholipids. These methods have greatly expanded our understanding of lipid metabolism, membrane biology, and disease processes.
The objectives of modern phospholipid analysis techniques are multifaceted. Researchers aim to achieve higher sensitivity, enabling the detection and quantification of low-abundance phospholipid species. Improved resolution is crucial for separating structurally similar phospholipids, particularly those with identical molecular weights but different fatty acid compositions or positional isomers.
Another key objective is to develop high-throughput methods capable of analyzing complex lipid mixtures in biological samples rapidly and comprehensively. This is particularly important in the emerging field of lipidomics, which seeks to characterize the entire lipid profile of cells, tissues, or organisms.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on developing non-destructive, in situ analysis techniques that can provide spatial information about phospholipid distribution within cells and tissues. Techniques such as imaging mass spectrometry and Raman spectroscopy are being explored for this purpose.
Ultimately, the goal of advanced phospholipid analysis techniques is to provide a more complete understanding of lipid biology, from molecular structure to cellular function, and to translate this knowledge into practical applications in fields such as medicine, nutrition, and biotechnology.
Market Demand for Phospholipid Analysis
The market demand for advanced phospholipid analysis techniques has been steadily growing, driven by several key factors across various industries. In the pharmaceutical sector, there is an increasing need for precise lipid profiling in drug development and quality control processes. Phospholipids play crucial roles in drug delivery systems, and their accurate analysis is essential for optimizing formulations and ensuring product efficacy.
The nutraceutical and functional food industries have also contributed significantly to the rising demand for phospholipid analysis. As consumers become more health-conscious, there is a growing interest in products enriched with specific phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine, known for their potential cognitive and cardiovascular benefits. This trend has spurred manufacturers to invest in advanced analytical techniques to validate their product claims and ensure quality.
In the field of biomedical research, the importance of phospholipids in cellular signaling, membrane dynamics, and disease pathology has led to increased funding for lipidomics studies. This has created a substantial market for sophisticated phospholipid analysis tools and services, particularly in academic and research institutions.
The cosmetics and personal care industry has also emerged as a significant driver of demand for phospholipid analysis. With the rise of "clean beauty" and natural product trends, manufacturers are focusing on plant-derived phospholipids for their emollient and moisturizing properties. Advanced analytical techniques are required to characterize these natural ingredients and ensure their stability in formulations.
Environmental monitoring represents another growing application area for phospholipid analysis. The detection and characterization of microbial phospholipids in soil and water samples provide valuable information about ecosystem health and contamination levels. This has led to increased adoption of phospholipid analysis techniques in environmental laboratories and regulatory agencies.
The global market for lipidomics, which encompasses phospholipid analysis, is experiencing robust growth. While specific market size figures for phospholipid analysis are not readily available, the broader lipidomics market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by technological advancements in mass spectrometry and chromatography, as well as the increasing integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in data analysis.
As the demand for more sensitive, high-throughput, and cost-effective phospholipid analysis techniques continues to rise, there is a clear opportunity for innovation in this field. Companies and research institutions that can develop novel methods or improve existing techniques to address the specific needs of different industries are likely to capture significant market share in this evolving landscape.
The nutraceutical and functional food industries have also contributed significantly to the rising demand for phospholipid analysis. As consumers become more health-conscious, there is a growing interest in products enriched with specific phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine, known for their potential cognitive and cardiovascular benefits. This trend has spurred manufacturers to invest in advanced analytical techniques to validate their product claims and ensure quality.
In the field of biomedical research, the importance of phospholipids in cellular signaling, membrane dynamics, and disease pathology has led to increased funding for lipidomics studies. This has created a substantial market for sophisticated phospholipid analysis tools and services, particularly in academic and research institutions.
The cosmetics and personal care industry has also emerged as a significant driver of demand for phospholipid analysis. With the rise of "clean beauty" and natural product trends, manufacturers are focusing on plant-derived phospholipids for their emollient and moisturizing properties. Advanced analytical techniques are required to characterize these natural ingredients and ensure their stability in formulations.
Environmental monitoring represents another growing application area for phospholipid analysis. The detection and characterization of microbial phospholipids in soil and water samples provide valuable information about ecosystem health and contamination levels. This has led to increased adoption of phospholipid analysis techniques in environmental laboratories and regulatory agencies.
The global market for lipidomics, which encompasses phospholipid analysis, is experiencing robust growth. While specific market size figures for phospholipid analysis are not readily available, the broader lipidomics market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by technological advancements in mass spectrometry and chromatography, as well as the increasing integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in data analysis.
As the demand for more sensitive, high-throughput, and cost-effective phospholipid analysis techniques continues to rise, there is a clear opportunity for innovation in this field. Companies and research institutions that can develop novel methods or improve existing techniques to address the specific needs of different industries are likely to capture significant market share in this evolving landscape.
Current Challenges in Phospholipid Analysis
Phospholipid analysis faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread application and accuracy. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of phospholipid structures, which makes their identification and quantification particularly difficult. The diverse range of fatty acid compositions and head groups creates a vast array of possible molecular species, requiring sophisticated analytical techniques to differentiate and characterize them accurately.
Sample preparation remains a critical challenge in phospholipid analysis. The extraction and purification of phospholipids from biological matrices often lead to sample loss or degradation, potentially altering the original lipid profile. Additionally, the presence of interfering compounds in complex biological samples can mask or distort the signals of target phospholipids, necessitating more advanced separation techniques.
The sensitivity and resolution of current analytical methods pose another significant challenge. While techniques such as mass spectrometry have greatly improved the detection of phospholipids, achieving consistent and reliable quantification across a wide dynamic range remains problematic. This is particularly evident when dealing with low-abundance phospholipid species or when analyzing samples with high lipid complexity.
Standardization and reproducibility issues continue to plague phospholipid analysis. The lack of universally accepted protocols for sample preparation, analysis, and data interpretation makes it difficult to compare results across different laboratories or studies. This variability hampers the establishment of reliable reference ranges and complicates the translation of phospholipid analysis into clinical or industrial applications.
The analysis of intact phospholipids presents unique challenges due to their susceptibility to fragmentation during ionization processes. This fragmentation can lead to the loss of structural information, particularly regarding the position and stereochemistry of fatty acyl chains. Developing ionization techniques that preserve the structural integrity of phospholipids while maintaining high sensitivity is an ongoing area of research.
Data analysis and interpretation remain formidable challenges in phospholipid research. The sheer volume of data generated by modern analytical platforms, coupled with the complexity of phospholipid structures, necessitates advanced bioinformatics tools and databases. However, current software solutions often struggle to keep pace with the rapid advancements in analytical technologies, creating a bottleneck in data processing and interpretation.
Lastly, the dynamic nature of phospholipids in biological systems presents a significant challenge. Phospholipid compositions can change rapidly in response to various stimuli or disease states, making it difficult to capture a representative snapshot of the lipidome at any given time. Developing methods that can accurately track these dynamic changes in real-time remains a key challenge in advancing phospholipid analysis techniques.
Sample preparation remains a critical challenge in phospholipid analysis. The extraction and purification of phospholipids from biological matrices often lead to sample loss or degradation, potentially altering the original lipid profile. Additionally, the presence of interfering compounds in complex biological samples can mask or distort the signals of target phospholipids, necessitating more advanced separation techniques.
The sensitivity and resolution of current analytical methods pose another significant challenge. While techniques such as mass spectrometry have greatly improved the detection of phospholipids, achieving consistent and reliable quantification across a wide dynamic range remains problematic. This is particularly evident when dealing with low-abundance phospholipid species or when analyzing samples with high lipid complexity.
Standardization and reproducibility issues continue to plague phospholipid analysis. The lack of universally accepted protocols for sample preparation, analysis, and data interpretation makes it difficult to compare results across different laboratories or studies. This variability hampers the establishment of reliable reference ranges and complicates the translation of phospholipid analysis into clinical or industrial applications.
The analysis of intact phospholipids presents unique challenges due to their susceptibility to fragmentation during ionization processes. This fragmentation can lead to the loss of structural information, particularly regarding the position and stereochemistry of fatty acyl chains. Developing ionization techniques that preserve the structural integrity of phospholipids while maintaining high sensitivity is an ongoing area of research.
Data analysis and interpretation remain formidable challenges in phospholipid research. The sheer volume of data generated by modern analytical platforms, coupled with the complexity of phospholipid structures, necessitates advanced bioinformatics tools and databases. However, current software solutions often struggle to keep pace with the rapid advancements in analytical technologies, creating a bottleneck in data processing and interpretation.
Lastly, the dynamic nature of phospholipids in biological systems presents a significant challenge. Phospholipid compositions can change rapidly in response to various stimuli or disease states, making it difficult to capture a representative snapshot of the lipidome at any given time. Developing methods that can accurately track these dynamic changes in real-time remains a key challenge in advancing phospholipid analysis techniques.
Current Phospholipid Analysis Methodologies
01 Phospholipid synthesis and extraction methods
Various methods for synthesizing and extracting phospholipids from natural sources or through chemical processes. These techniques aim to produce high-quality phospholipids for use in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food industries.- Phospholipid synthesis and modification: Various methods for synthesizing and modifying phospholipids are described. These include chemical synthesis routes, enzymatic modifications, and techniques for altering the structure or properties of phospholipids. Such processes can be used to create novel phospholipids with specific characteristics for use in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, or other applications.
- Phospholipid-based drug delivery systems: Phospholipids are utilized in the development of drug delivery systems, such as liposomes and nanoparticles. These systems can improve the solubility, stability, and bioavailability of various drugs. The phospholipid-based carriers can be designed to target specific tissues or cells, enhancing therapeutic efficacy while reducing side effects.
- Analytical methods for phospholipids: Various analytical techniques are employed for the characterization and quantification of phospholipids. These methods include chromatography, mass spectrometry, and spectroscopic techniques. Such analytical approaches are crucial for quality control, research, and development in industries utilizing phospholipids.
- Phospholipids in food and nutrition: Phospholipids play important roles in food and nutrition applications. They are used as emulsifiers, stabilizers, and nutritional supplements. Research focuses on the extraction, purification, and modification of phospholipids from natural sources for use in functional foods and nutraceuticals.
- Phospholipids in membrane biology and biotechnology: Phospholipids are essential components of biological membranes and are studied extensively in membrane biology. They are also used in biotechnological applications, such as the creation of artificial membranes, biosensors, and cell culture systems. Research in this area focuses on understanding membrane dynamics and developing novel biotechnological tools.
02 Phospholipid-based drug delivery systems
Development of drug delivery systems using phospholipids as carriers. These systems enhance drug solubility, stability, and bioavailability, improving therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects.Expand Specific Solutions03 Phospholipid analysis and characterization techniques
Advanced analytical methods for identifying, quantifying, and characterizing phospholipids in various samples. These techniques include mass spectrometry, chromatography, and spectroscopic methods to determine phospholipid composition and structure.Expand Specific Solutions04 Phospholipid applications in cosmetics and personal care
Utilization of phospholipids in cosmetic and personal care products for their emulsifying, moisturizing, and skin-barrier enhancing properties. These applications include formulations for skincare, haircare, and anti-aging products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Phospholipid-based liposome formulations
Development of liposomal formulations using phospholipids for encapsulating various active ingredients. These formulations improve stability, controlled release, and targeted delivery of drugs, nutrients, and other bioactive compounds.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Phospholipid Analysis Industry
The advanced techniques for phospholipid analysis market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in pharmaceutical, food, and biotechnology industries. The global market size is estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars, with steady annual growth projected. Technologically, the field is rapidly evolving, with innovations in mass spectrometry and chromatography techniques leading the way. Key players like Waters Technology Corp. and Shimadzu Corp. are at the forefront, developing high-resolution analytical instruments. Academic institutions such as the University of Tokyo and Nagoya University are contributing significantly to research advancements. Emerging companies like Stemirna Therapeutics are exploring novel applications in drug delivery systems, indicating a dynamic and competitive landscape with opportunities for further innovation and market expansion.
Waters Technology Corp.
Technical Solution: Waters Corporation has developed cutting-edge techniques for phospholipid analysis, leveraging their expertise in chromatography and mass spectrometry. Their ACQUITY UPLC I-Class PLUS system, combined with the Xevo G2-XS QTof Mass Spectrometer, enables ultra-high resolution separation and detection of phospholipids[8]. Waters has introduced a novel class-specific separation technique using their ACQUITY UPLC CSH C18 columns, which provides enhanced resolution of phospholipid species based on their head groups and fatty acid compositions[9]. The company's ion mobility-enabled SYNAPT XS mass spectrometer adds an extra dimension of separation, allowing for improved differentiation of isomeric and isobaric phospholipid species[10]. Waters has also developed specialized software solutions, such as Progenesis QI for metabolomics and lipidomics, which offers advanced data processing capabilities and streamlined workflows for phospholipid identification and quantification[11].
Strengths: High-resolution separation and detection, class-specific analysis capabilities, and advanced data processing software. Weaknesses: Potentially high cost of instrumentation and consumables.
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Agilent Technologies has pioneered advanced techniques for phospholipid analysis through their innovative LC-MS and GC-MS platforms. Their Infinity II UHPLC system, when coupled with the 6546 Q-TOF LC/MS, offers high-resolution separation and accurate mass detection for comprehensive phospholipid profiling[4]. Agilent has developed a novel reversed-phase HPLC method that allows for improved separation of phospholipid classes and species, including those with similar structures[5]. The company's LipidQuan solution provides targeted quantification of hundreds of lipid species in a single run, utilizing multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) on their triple quadrupole LC/MS systems[6]. Furthermore, Agilent has introduced advanced data analysis software, such as MassHunter Lipid Annotator, which employs machine learning algorithms to enhance lipid identification accuracy and reduce analysis time[7].
Strengths: Comprehensive lipid profiling capabilities, targeted quantification methods, and advanced data analysis tools. Weaknesses: Potential for high operational costs and need for specialized training.
Innovative Phospholipid Analysis Techniques
Phosphopeptide analysis method
PatentInactiveUS7892846B2
Innovation
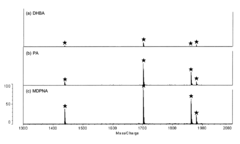
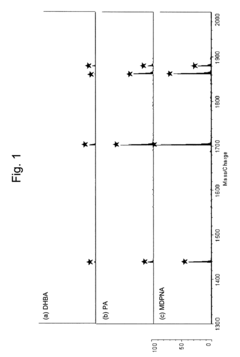
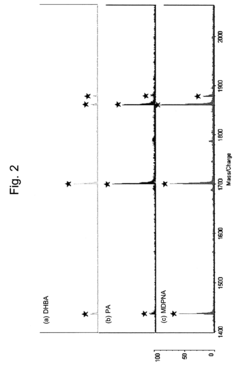
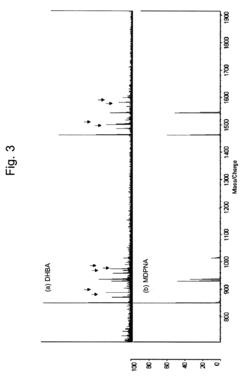
- Using a matrix additive containing phosphonic acid groups, such as methylenediphosphonic acid, with 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid in sample preparation for MALDI mass spectrometry to enhance phosphopeptide detection sensitivity and suppress alkali metal-adduct ions.
A novel and cost effective method of detecting phospholipids in the neurodegenerative disease
PatentPendingIN201741021839A
Innovation
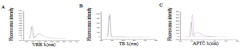
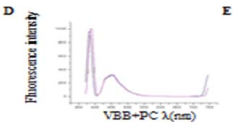
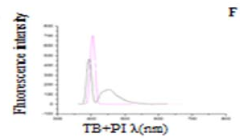
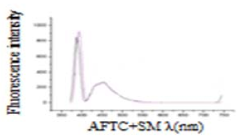
- A novel method involving the formation of lipid-dye complexes using organic dyes like Victoria blue-B, Toluidine blue, and ammonium ferrothiocyanate, which exhibit differential peaks spectroscopically, allowing for quantitative determination of phospholipids without the need for expensive equipment or hazardous materials.
Regulatory Considerations for Phospholipid Analysis
Regulatory considerations play a crucial role in the development and implementation of advanced techniques for phospholipid analysis. As these techniques become more sophisticated and widely used in various industries, regulatory bodies have established guidelines to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and safety of phospholipid analysis methods.
In the pharmaceutical industry, regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have set forth specific requirements for phospholipid analysis in drug development and quality control. These guidelines often emphasize the need for validated analytical methods, including liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, to accurately identify and quantify phospholipids in drug formulations.
The food industry also faces regulatory scrutiny regarding phospholipid analysis, particularly in the context of food safety and nutritional labeling. Regulatory bodies like the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) have established standards for the analysis of phospholipids in food products, focusing on issues such as contamination detection and accurate nutritional content reporting.
In the field of environmental monitoring, regulatory agencies have implemented guidelines for the analysis of phospholipids in environmental samples. These regulations often address the detection and quantification of phospholipids as biomarkers for microbial activity in soil, water, and sediment samples. Compliance with these guidelines is essential for environmental impact assessments and remediation efforts.
The clinical diagnostics sector is subject to stringent regulatory oversight concerning phospholipid analysis techniques. Regulatory bodies such as the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) in the United States have established standards for the use of phospholipid analysis in diagnostic tests, particularly in the context of lipid disorders and cardiovascular disease risk assessment.
As advanced techniques for phospholipid analysis continue to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to keep pace with technological advancements. This includes the development of new guidelines for emerging technologies such as high-resolution mass spectrometry and advanced imaging techniques for phospholipid analysis. Regulatory bodies are also addressing the challenges posed by the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in data analysis and interpretation.
Compliance with regulatory requirements often necessitates the implementation of robust quality management systems, including standard operating procedures (SOPs) for sample preparation, instrument calibration, and data analysis. Additionally, regulatory agencies may require laboratories to participate in proficiency testing programs to demonstrate the accuracy and reliability of their phospholipid analysis techniques.
In the pharmaceutical industry, regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have set forth specific requirements for phospholipid analysis in drug development and quality control. These guidelines often emphasize the need for validated analytical methods, including liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, to accurately identify and quantify phospholipids in drug formulations.
The food industry also faces regulatory scrutiny regarding phospholipid analysis, particularly in the context of food safety and nutritional labeling. Regulatory bodies like the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) have established standards for the analysis of phospholipids in food products, focusing on issues such as contamination detection and accurate nutritional content reporting.
In the field of environmental monitoring, regulatory agencies have implemented guidelines for the analysis of phospholipids in environmental samples. These regulations often address the detection and quantification of phospholipids as biomarkers for microbial activity in soil, water, and sediment samples. Compliance with these guidelines is essential for environmental impact assessments and remediation efforts.
The clinical diagnostics sector is subject to stringent regulatory oversight concerning phospholipid analysis techniques. Regulatory bodies such as the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) in the United States have established standards for the use of phospholipid analysis in diagnostic tests, particularly in the context of lipid disorders and cardiovascular disease risk assessment.
As advanced techniques for phospholipid analysis continue to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to keep pace with technological advancements. This includes the development of new guidelines for emerging technologies such as high-resolution mass spectrometry and advanced imaging techniques for phospholipid analysis. Regulatory bodies are also addressing the challenges posed by the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in data analysis and interpretation.
Compliance with regulatory requirements often necessitates the implementation of robust quality management systems, including standard operating procedures (SOPs) for sample preparation, instrument calibration, and data analysis. Additionally, regulatory agencies may require laboratories to participate in proficiency testing programs to demonstrate the accuracy and reliability of their phospholipid analysis techniques.
Environmental Impact of Phospholipid Analysis Methods
The environmental impact of phospholipid analysis methods is a critical consideration in the field of advanced techniques for phospholipid analysis. Traditional methods often involve the use of harmful solvents and generate significant amounts of chemical waste. However, recent advancements have led to more environmentally friendly approaches.
One of the primary concerns is the extensive use of chloroform and methanol in lipid extraction processes. These solvents are known for their toxicity and potential environmental hazards. To address this issue, researchers have developed alternative extraction methods using less harmful solvents such as ethyl acetate or isopropanol. These substitutes not only reduce the environmental footprint but also enhance laboratory safety.
The advent of supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) techniques has further improved the environmental profile of phospholipid analysis. SFE, particularly using supercritical carbon dioxide, offers a green alternative to traditional solvent-based extractions. This method significantly reduces organic solvent consumption and minimizes waste generation, aligning with sustainable laboratory practices.
Mass spectrometry-based techniques have also contributed to reducing the environmental impact of phospholipid analysis. These methods require smaller sample sizes and less solvent, thereby decreasing overall waste production. Additionally, the high sensitivity of mass spectrometry allows for the detection of trace amounts of phospholipids, reducing the need for large-scale extractions.
Microfluidic devices and lab-on-a-chip technologies represent another environmentally friendly approach to phospholipid analysis. These miniaturized systems require minimal amounts of reagents and samples, drastically reducing waste generation. Furthermore, they often incorporate recycling mechanisms for solvents, further minimizing environmental impact.
The shift towards automated systems in phospholipid analysis has also contributed to improved environmental outcomes. Automated platforms optimize reagent use and reduce human error, leading to fewer repeated analyses and less waste. These systems often integrate multiple analytical steps, streamlining the process and reducing overall resource consumption.
It is worth noting that the environmental impact extends beyond the laboratory. The production and disposal of analytical instruments and consumables also contribute to the overall environmental footprint of phospholipid analysis. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing instruments with longer lifespans and recyclable components to address this aspect of environmental concern.
In conclusion, while phospholipid analysis methods have historically posed environmental challenges, recent advancements are steering the field towards more sustainable practices. The combination of green chemistry principles, innovative technologies, and improved analytical strategies is significantly reducing the environmental impact of these essential analytical techniques.
One of the primary concerns is the extensive use of chloroform and methanol in lipid extraction processes. These solvents are known for their toxicity and potential environmental hazards. To address this issue, researchers have developed alternative extraction methods using less harmful solvents such as ethyl acetate or isopropanol. These substitutes not only reduce the environmental footprint but also enhance laboratory safety.
The advent of supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) techniques has further improved the environmental profile of phospholipid analysis. SFE, particularly using supercritical carbon dioxide, offers a green alternative to traditional solvent-based extractions. This method significantly reduces organic solvent consumption and minimizes waste generation, aligning with sustainable laboratory practices.
Mass spectrometry-based techniques have also contributed to reducing the environmental impact of phospholipid analysis. These methods require smaller sample sizes and less solvent, thereby decreasing overall waste production. Additionally, the high sensitivity of mass spectrometry allows for the detection of trace amounts of phospholipids, reducing the need for large-scale extractions.
Microfluidic devices and lab-on-a-chip technologies represent another environmentally friendly approach to phospholipid analysis. These miniaturized systems require minimal amounts of reagents and samples, drastically reducing waste generation. Furthermore, they often incorporate recycling mechanisms for solvents, further minimizing environmental impact.
The shift towards automated systems in phospholipid analysis has also contributed to improved environmental outcomes. Automated platforms optimize reagent use and reduce human error, leading to fewer repeated analyses and less waste. These systems often integrate multiple analytical steps, streamlining the process and reducing overall resource consumption.
It is worth noting that the environmental impact extends beyond the laboratory. The production and disposal of analytical instruments and consumables also contribute to the overall environmental footprint of phospholipid analysis. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing instruments with longer lifespans and recyclable components to address this aspect of environmental concern.
In conclusion, while phospholipid analysis methods have historically posed environmental challenges, recent advancements are steering the field towards more sustainable practices. The combination of green chemistry principles, innovative technologies, and improved analytical strategies is significantly reducing the environmental impact of these essential analytical techniques.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!