Best Practices for Phospholipid Characterization Methods
JUL 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Phospholipid Analysis Background and Objectives
Phospholipid characterization has been a critical area of research in biochemistry and molecular biology for decades. The study of these essential biomolecules has evolved significantly, driven by advancements in analytical techniques and the growing understanding of their roles in cellular processes. Phospholipids, as key components of cell membranes and signaling molecules, play crucial roles in various biological functions, including membrane structure, cellular communication, and lipid metabolism.
The field of phospholipid analysis has its roots in the early 20th century, with rudimentary extraction and separation techniques. However, the past few decades have witnessed a rapid acceleration in the development of sophisticated analytical methods. This progress has been fueled by the increasing recognition of phospholipids' importance in health and disease, as well as the need for more precise and comprehensive characterization techniques.
The primary objective of phospholipid characterization is to accurately identify and quantify the diverse range of phospholipid species present in biological samples. This includes determining their molecular structures, fatty acid compositions, and spatial distributions within cellular environments. As research has progressed, the goals have expanded to include understanding the dynamic changes in phospholipid profiles under various physiological and pathological conditions.
Recent technological advancements have significantly enhanced our ability to analyze phospholipids with unprecedented detail and efficiency. Mass spectrometry-based techniques, particularly lipidomics approaches, have revolutionized the field by enabling the simultaneous analysis of hundreds of phospholipid species. These high-throughput methods have opened new avenues for exploring the complexity of the lipidome and its relationship to cellular function and disease states.
The evolution of phospholipid characterization methods reflects a broader trend towards more sensitive, specific, and comprehensive analytical techniques. From traditional thin-layer chromatography to modern hyphenated techniques combining chromatography with mass spectrometry, the field has continuously adapted to meet the growing demands of lipid research. This progression has been driven by the need to address challenges such as sample complexity, low abundance of certain phospholipid species, and the requirement for quantitative analysis in diverse biological matrices.
As we look towards the future, the objectives of phospholipid characterization continue to expand. There is a growing emphasis on developing standardized protocols and best practices to ensure reproducibility and comparability of results across different laboratories and studies. Additionally, there is a push towards integrating phospholipid analysis with other omics approaches, such as genomics and proteomics, to gain a more holistic understanding of cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
The field of phospholipid analysis has its roots in the early 20th century, with rudimentary extraction and separation techniques. However, the past few decades have witnessed a rapid acceleration in the development of sophisticated analytical methods. This progress has been fueled by the increasing recognition of phospholipids' importance in health and disease, as well as the need for more precise and comprehensive characterization techniques.
The primary objective of phospholipid characterization is to accurately identify and quantify the diverse range of phospholipid species present in biological samples. This includes determining their molecular structures, fatty acid compositions, and spatial distributions within cellular environments. As research has progressed, the goals have expanded to include understanding the dynamic changes in phospholipid profiles under various physiological and pathological conditions.
Recent technological advancements have significantly enhanced our ability to analyze phospholipids with unprecedented detail and efficiency. Mass spectrometry-based techniques, particularly lipidomics approaches, have revolutionized the field by enabling the simultaneous analysis of hundreds of phospholipid species. These high-throughput methods have opened new avenues for exploring the complexity of the lipidome and its relationship to cellular function and disease states.
The evolution of phospholipid characterization methods reflects a broader trend towards more sensitive, specific, and comprehensive analytical techniques. From traditional thin-layer chromatography to modern hyphenated techniques combining chromatography with mass spectrometry, the field has continuously adapted to meet the growing demands of lipid research. This progression has been driven by the need to address challenges such as sample complexity, low abundance of certain phospholipid species, and the requirement for quantitative analysis in diverse biological matrices.
As we look towards the future, the objectives of phospholipid characterization continue to expand. There is a growing emphasis on developing standardized protocols and best practices to ensure reproducibility and comparability of results across different laboratories and studies. Additionally, there is a push towards integrating phospholipid analysis with other omics approaches, such as genomics and proteomics, to gain a more holistic understanding of cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
Market Demand for Phospholipid Characterization
The market demand for phospholipid characterization methods has been steadily increasing due to the growing importance of lipids in various industries, particularly in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and food science. Phospholipids play crucial roles in cellular membranes, drug delivery systems, and food emulsions, driving the need for accurate and reliable characterization techniques.
In the pharmaceutical sector, the demand for phospholipid characterization is primarily driven by the development of liposomal drug delivery systems. These systems offer improved drug efficacy and reduced side effects, making them increasingly popular in targeted therapies. As a result, pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in advanced characterization methods to ensure the quality and consistency of their liposomal formulations.
The nutraceutical industry has also witnessed a surge in demand for phospholipid characterization. With the rising consumer interest in functional foods and dietary supplements, manufacturers are incorporating phospholipids into their products for their potential health benefits. This trend has created a need for robust analytical methods to verify the composition and purity of phospholipid ingredients.
In the food industry, phospholipid characterization is essential for developing and improving emulsion-based products. Food manufacturers rely on accurate characterization techniques to optimize the stability and texture of their products, particularly in dairy, bakery, and confectionery applications. The growing consumer demand for clean-label and natural ingredients has further intensified the need for precise phospholipid analysis in food formulations.
The biotechnology sector is another significant driver of market demand for phospholipid characterization. As research in areas such as membrane biology and lipid-protein interactions advances, there is an increasing need for sophisticated analytical tools to study complex lipid systems. This has led to the development of more sensitive and high-throughput characterization methods.
Environmental and agricultural industries are also contributing to the market demand. Phospholipid analysis is crucial in assessing soil health, studying plant-microbe interactions, and monitoring environmental pollutants. As sustainability becomes a global priority, the demand for phospholipid characterization in these sectors is expected to grow further.
The market for phospholipid characterization methods is also influenced by regulatory requirements. Stringent quality control standards in the pharmaceutical and food industries necessitate the use of validated analytical techniques. This regulatory pressure drives the adoption of advanced characterization methods and fuels ongoing research and development in this field.
In the pharmaceutical sector, the demand for phospholipid characterization is primarily driven by the development of liposomal drug delivery systems. These systems offer improved drug efficacy and reduced side effects, making them increasingly popular in targeted therapies. As a result, pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in advanced characterization methods to ensure the quality and consistency of their liposomal formulations.
The nutraceutical industry has also witnessed a surge in demand for phospholipid characterization. With the rising consumer interest in functional foods and dietary supplements, manufacturers are incorporating phospholipids into their products for their potential health benefits. This trend has created a need for robust analytical methods to verify the composition and purity of phospholipid ingredients.
In the food industry, phospholipid characterization is essential for developing and improving emulsion-based products. Food manufacturers rely on accurate characterization techniques to optimize the stability and texture of their products, particularly in dairy, bakery, and confectionery applications. The growing consumer demand for clean-label and natural ingredients has further intensified the need for precise phospholipid analysis in food formulations.
The biotechnology sector is another significant driver of market demand for phospholipid characterization. As research in areas such as membrane biology and lipid-protein interactions advances, there is an increasing need for sophisticated analytical tools to study complex lipid systems. This has led to the development of more sensitive and high-throughput characterization methods.
Environmental and agricultural industries are also contributing to the market demand. Phospholipid analysis is crucial in assessing soil health, studying plant-microbe interactions, and monitoring environmental pollutants. As sustainability becomes a global priority, the demand for phospholipid characterization in these sectors is expected to grow further.
The market for phospholipid characterization methods is also influenced by regulatory requirements. Stringent quality control standards in the pharmaceutical and food industries necessitate the use of validated analytical techniques. This regulatory pressure drives the adoption of advanced characterization methods and fuels ongoing research and development in this field.
Current Challenges in Phospholipid Analysis
Phospholipid analysis faces several significant challenges that hinder accurate characterization and quantification. One of the primary obstacles is the structural complexity and diversity of phospholipids. These molecules exhibit a wide range of variations in their fatty acid chains, head groups, and overall molecular structures, making comprehensive analysis difficult. The sheer number of potential phospholipid species in biological samples further complicates the analytical process.
Sample preparation remains a critical challenge in phospholipid analysis. Extracting phospholipids from complex biological matrices while maintaining their integrity and avoiding degradation or oxidation is a delicate process. The choice of extraction method can significantly impact the recovery and representation of different phospholipid classes, potentially leading to biased results. Additionally, the presence of interfering compounds in biological samples can mask or suppress phospholipid signals, necessitating careful sample clean-up procedures.
The limitations of current analytical techniques pose another set of challenges. While mass spectrometry has emerged as a powerful tool for phospholipid analysis, issues such as ion suppression, matrix effects, and the need for appropriate internal standards persist. Chromatographic separation techniques, crucial for resolving complex phospholipid mixtures, often struggle with achieving complete separation of all species, particularly for isomeric and isobaric compounds.
Quantification of phospholipids presents its own set of difficulties. The lack of commercially available standards for all phospholipid species hampers absolute quantification efforts. Relative quantification methods are often employed but can be affected by differences in ionization efficiencies and response factors among various phospholipid classes and species. This challenge is particularly pronounced when comparing samples across different matrices or analytical conditions.
Data analysis and interpretation represent another significant hurdle in phospholipid characterization. The complexity of mass spectrometric data, coupled with the vast number of potential phospholipid species, requires sophisticated bioinformatics tools and databases. However, current software solutions often struggle with accurate peak assignment, especially for low-abundance species or in the presence of interfering compounds. The integration of multi-omics data for comprehensive lipid profiling adds another layer of complexity to data analysis and interpretation.
Standardization and method validation across different laboratories and analytical platforms remain ongoing challenges in the field. The lack of universally accepted protocols for sample preparation, analysis, and data processing hinders inter-laboratory comparisons and the establishment of reference ranges for phospholipid profiles in various biological contexts. This limitation impedes the translation of phospholipid analysis from research settings to clinical applications, where robust and reproducible methods are essential.
Sample preparation remains a critical challenge in phospholipid analysis. Extracting phospholipids from complex biological matrices while maintaining their integrity and avoiding degradation or oxidation is a delicate process. The choice of extraction method can significantly impact the recovery and representation of different phospholipid classes, potentially leading to biased results. Additionally, the presence of interfering compounds in biological samples can mask or suppress phospholipid signals, necessitating careful sample clean-up procedures.
The limitations of current analytical techniques pose another set of challenges. While mass spectrometry has emerged as a powerful tool for phospholipid analysis, issues such as ion suppression, matrix effects, and the need for appropriate internal standards persist. Chromatographic separation techniques, crucial for resolving complex phospholipid mixtures, often struggle with achieving complete separation of all species, particularly for isomeric and isobaric compounds.
Quantification of phospholipids presents its own set of difficulties. The lack of commercially available standards for all phospholipid species hampers absolute quantification efforts. Relative quantification methods are often employed but can be affected by differences in ionization efficiencies and response factors among various phospholipid classes and species. This challenge is particularly pronounced when comparing samples across different matrices or analytical conditions.
Data analysis and interpretation represent another significant hurdle in phospholipid characterization. The complexity of mass spectrometric data, coupled with the vast number of potential phospholipid species, requires sophisticated bioinformatics tools and databases. However, current software solutions often struggle with accurate peak assignment, especially for low-abundance species or in the presence of interfering compounds. The integration of multi-omics data for comprehensive lipid profiling adds another layer of complexity to data analysis and interpretation.
Standardization and method validation across different laboratories and analytical platforms remain ongoing challenges in the field. The lack of universally accepted protocols for sample preparation, analysis, and data processing hinders inter-laboratory comparisons and the establishment of reference ranges for phospholipid profiles in various biological contexts. This limitation impedes the translation of phospholipid analysis from research settings to clinical applications, where robust and reproducible methods are essential.
Existing Phospholipid Characterization Methods
01 Spectroscopic methods for phospholipid characterization
Various spectroscopic techniques are employed to characterize phospholipids, including NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and infrared spectroscopy. These methods provide detailed information about the molecular structure, composition, and interactions of phospholipids in biological systems and formulations.- Spectroscopic methods for phospholipid characterization: Various spectroscopic techniques are employed to characterize phospholipids, including NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and infrared spectroscopy. These methods provide detailed information about the molecular structure, composition, and interactions of phospholipids in biological systems and synthetic formulations.
- Chromatographic techniques for phospholipid analysis: Chromatographic methods, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and thin-layer chromatography (TLC), are used to separate and identify different phospholipid species. These techniques allow for the quantification and characterization of complex phospholipid mixtures in biological samples and pharmaceutical formulations.
- Liposome characterization methods: Techniques for characterizing liposomes, which are phospholipid-based vesicles, include dynamic light scattering, zeta potential measurements, and electron microscopy. These methods provide information about liposome size, stability, and surface properties, which are crucial for their applications in drug delivery and biotechnology.
- Enzymatic assays for phospholipid characterization: Enzymatic assays are used to characterize specific phospholipid classes and their metabolites. These assays employ enzymes such as phospholipases to cleave phospholipids at specific sites, allowing for the identification and quantification of different phospholipid species in biological samples.
- Biophysical techniques for membrane characterization: Biophysical methods, including atomic force microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, and X-ray diffraction, are used to study phospholipid membranes and their properties. These techniques provide insights into membrane structure, fluidity, and interactions with other molecules, which are essential for understanding cellular processes and developing drug delivery systems.
02 Chromatographic techniques for phospholipid analysis
Chromatographic methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), thin-layer chromatography (TLC), and gas chromatography (GC) are used to separate and analyze phospholipids. These techniques allow for the identification and quantification of different phospholipid species in complex mixtures.Expand Specific Solutions03 Enzymatic assays for phospholipid characterization
Enzymatic methods are developed to characterize specific phospholipids or their metabolites. These assays often involve the use of phospholipases or other enzymes that can selectively cleave or modify phospholipids, allowing for their identification and quantification.Expand Specific Solutions04 Liposome-based techniques for phospholipid studies
Liposomes are used as model systems to study phospholipid properties and interactions. Techniques such as dynamic light scattering, zeta potential measurements, and fluorescence spectroscopy are employed to characterize phospholipid behavior in these artificial membrane systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Computational methods for phospholipid characterization
Computational approaches, including molecular dynamics simulations and machine learning algorithms, are utilized to predict and analyze phospholipid properties, interactions, and behavior in complex biological systems. These methods complement experimental techniques and provide insights into phospholipid structure-function relationships.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Phospholipid Analysis Industry
The phospholipid characterization methods market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for advanced analytical techniques in pharmaceutical and biotechnology research. The global market size is estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars, with steady expansion projected. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with major players like Life Technologies, Waters Technology, and Shimadzu Corporation leading innovation in mass spectrometry and chromatography techniques. Academic institutions such as the University of Michigan and Ohio State University are also contributing significantly to method development. The technology is maturing, but there's still room for improvement in accuracy, sensitivity, and high-throughput capabilities.
Life Technologies Corp.
Technical Solution: Life Technologies Corp. (now part of Thermo Fisher Scientific) has developed a multi-omics approach for phospholipid characterization, integrating lipidomics with genomics and proteomics. Their method utilizes high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry for comprehensive lipid profiling, combined with next-generation sequencing and proteomics analysis to provide a holistic view of cellular lipid metabolism[7]. The company has also introduced novel lipid extraction protocols optimized for various sample types, including challenging matrices like brain tissue and plasma[8]. Life Technologies' approach incorporates stable isotope labeling techniques for dynamic phospholipid analysis, enabling the study of lipid turnover and metabolism in living systems[9].
Strengths: Integrated multi-omics approach, optimized extraction protocols for various sample types, and capability for dynamic lipid analysis. Weaknesses: Complex data integration and interpretation may require specialized bioinformatics expertise.
Shimadzu Corp.
Technical Solution: Shimadzu Corp. has developed a comprehensive phospholipid characterization method using their Nexera UHPLC system coupled with LCMS-8060 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer. Their approach utilizes multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) for targeted phospholipid analysis, allowing for high-sensitivity quantification of specific phospholipid species[4]. Shimadzu's method incorporates a novel LIPID-MAPS database, which enhances lipid identification accuracy. The company has also introduced automated sample preparation techniques, including robotic liquid handling systems, to improve reproducibility and throughput in phospholipid analysis[5]. Additionally, Shimadzu has developed specialized software for lipid data processing and interpretation, streamlining the analysis workflow[6].
Strengths: High-sensitivity quantification, automated sample preparation, and integrated data analysis software. Weaknesses: May be less suitable for untargeted lipidomics approaches compared to high-resolution MS systems.
Innovative Approaches in Phospholipid Analysis
Phosphopeptide analysis method
PatentInactiveUS7892846B2
Innovation
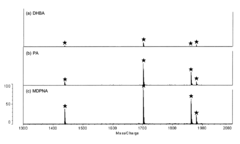
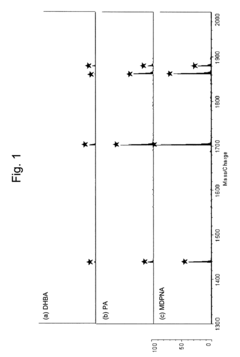
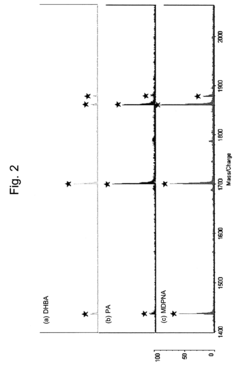
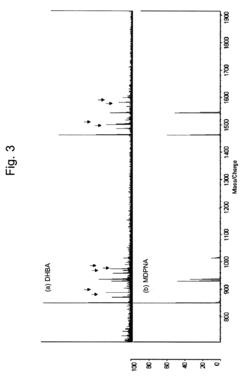
- Using a matrix additive containing phosphonic acid groups, such as methylenediphosphonic acid, with 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid in sample preparation for MALDI mass spectrometry to enhance phosphopeptide detection sensitivity and suppress alkali metal-adduct ions.
Phospholipid quantitating method
PatentInactiveJP2012194132A
Innovation
- A method that involves determining the content of phospholipids, measuring fatty acid composition, calculating sensitivity differences for each category, and correcting the measured content to achieve precise quantification using HPLC and GC techniques.
Regulatory Considerations for Phospholipid Analysis
Regulatory considerations play a crucial role in phospholipid analysis, particularly in the pharmaceutical and food industries. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have established guidelines for the characterization and analysis of phospholipids in drug products and food additives. These regulatory bodies emphasize the importance of using validated analytical methods to ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of products containing phospholipids.
One of the key regulatory requirements is the implementation of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in phospholipid analysis. This includes maintaining proper documentation, using calibrated instruments, and following standard operating procedures (SOPs) for sample preparation and analysis. Regulatory agencies also require the use of reference standards and quality control samples to ensure the accuracy and precision of analytical results.
The FDA's Guidance for Industry on Liposome Drug Products provides specific recommendations for the characterization of phospholipids in liposomal formulations. This guidance emphasizes the need for comprehensive physicochemical characterization, including lipid composition, particle size distribution, and surface charge. Similarly, the EMA has published guidelines on the quality of liposomal products, which include requirements for phospholipid analysis.
In the food industry, regulatory bodies such as the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have established guidelines for the use of phospholipids as food additives. These guidelines specify the analytical methods to be used for the identification and quantification of phospholipids in food products. Compliance with these regulations is essential for obtaining approval for the use of phospholipids in food applications.
Regulatory agencies also require the validation of analytical methods used for phospholipid characterization. This includes demonstrating the specificity, accuracy, precision, linearity, and robustness of the chosen methods. Method validation ensures that the analytical results are reliable and reproducible, which is critical for regulatory compliance and product quality assurance.
Furthermore, regulatory considerations extend to the reporting and documentation of phospholipid analysis results. Detailed records of analytical procedures, raw data, and final reports must be maintained and made available for regulatory inspections. This documentation should include information on method validation, instrument calibration, and quality control measures.
One of the key regulatory requirements is the implementation of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in phospholipid analysis. This includes maintaining proper documentation, using calibrated instruments, and following standard operating procedures (SOPs) for sample preparation and analysis. Regulatory agencies also require the use of reference standards and quality control samples to ensure the accuracy and precision of analytical results.
The FDA's Guidance for Industry on Liposome Drug Products provides specific recommendations for the characterization of phospholipids in liposomal formulations. This guidance emphasizes the need for comprehensive physicochemical characterization, including lipid composition, particle size distribution, and surface charge. Similarly, the EMA has published guidelines on the quality of liposomal products, which include requirements for phospholipid analysis.
In the food industry, regulatory bodies such as the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have established guidelines for the use of phospholipids as food additives. These guidelines specify the analytical methods to be used for the identification and quantification of phospholipids in food products. Compliance with these regulations is essential for obtaining approval for the use of phospholipids in food applications.
Regulatory agencies also require the validation of analytical methods used for phospholipid characterization. This includes demonstrating the specificity, accuracy, precision, linearity, and robustness of the chosen methods. Method validation ensures that the analytical results are reliable and reproducible, which is critical for regulatory compliance and product quality assurance.
Furthermore, regulatory considerations extend to the reporting and documentation of phospholipid analysis results. Detailed records of analytical procedures, raw data, and final reports must be maintained and made available for regulatory inspections. This documentation should include information on method validation, instrument calibration, and quality control measures.
Standardization of Phospholipid Characterization Protocols
The standardization of phospholipid characterization protocols is crucial for ensuring consistency and reliability in research and industrial applications. This process involves establishing uniform methods for sample preparation, analysis, and data interpretation across different laboratories and institutions.
One key aspect of standardization is the development of reference materials and calibration standards. These materials serve as benchmarks for comparing results between different laboratories and validating analytical methods. Internationally recognized organizations, such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), play a vital role in producing and distributing certified reference materials for phospholipid analysis.
Standardized sample preparation techniques are essential for obtaining reproducible results. This includes protocols for lipid extraction, purification, and derivatization. The choice of solvents, extraction methods, and storage conditions can significantly impact the quality and quantity of phospholipids recovered from biological samples. Establishing guidelines for these procedures helps minimize variability and ensures comparability of results across different studies.
Analytical methods for phospholipid characterization also require standardization. This encompasses techniques such as thin-layer chromatography (TLC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry (MS), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Standardized protocols should specify instrument parameters, column specifications, mobile phase compositions, and detection methods. Additionally, guidelines for data acquisition, processing, and interpretation are necessary to ensure consistent results.
Quality control measures are an integral part of standardized protocols. This includes the use of internal standards, regular instrument calibration, and participation in inter-laboratory comparison studies. Such measures help identify and minimize sources of error, ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of phospholipid characterization results.
Data reporting and presentation formats should also be standardized to facilitate comparison and integration of results from different sources. This includes guidelines for expressing concentrations, reporting detection limits, and presenting structural information. Standardized nomenclature for phospholipid species is particularly important, as it enables clear communication and avoids confusion in the scientific literature.
Lastly, the standardization process should be dynamic and responsive to technological advancements. Regular review and updating of protocols are necessary to incorporate new analytical techniques and address emerging challenges in phospholipid characterization. Collaboration between academic institutions, industry partners, and regulatory bodies is essential for developing and implementing these standards on a global scale.
One key aspect of standardization is the development of reference materials and calibration standards. These materials serve as benchmarks for comparing results between different laboratories and validating analytical methods. Internationally recognized organizations, such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), play a vital role in producing and distributing certified reference materials for phospholipid analysis.
Standardized sample preparation techniques are essential for obtaining reproducible results. This includes protocols for lipid extraction, purification, and derivatization. The choice of solvents, extraction methods, and storage conditions can significantly impact the quality and quantity of phospholipids recovered from biological samples. Establishing guidelines for these procedures helps minimize variability and ensures comparability of results across different studies.
Analytical methods for phospholipid characterization also require standardization. This encompasses techniques such as thin-layer chromatography (TLC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry (MS), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Standardized protocols should specify instrument parameters, column specifications, mobile phase compositions, and detection methods. Additionally, guidelines for data acquisition, processing, and interpretation are necessary to ensure consistent results.
Quality control measures are an integral part of standardized protocols. This includes the use of internal standards, regular instrument calibration, and participation in inter-laboratory comparison studies. Such measures help identify and minimize sources of error, ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of phospholipid characterization results.
Data reporting and presentation formats should also be standardized to facilitate comparison and integration of results from different sources. This includes guidelines for expressing concentrations, reporting detection limits, and presenting structural information. Standardized nomenclature for phospholipid species is particularly important, as it enables clear communication and avoids confusion in the scientific literature.
Lastly, the standardization process should be dynamic and responsive to technological advancements. Regular review and updating of protocols are necessary to incorporate new analytical techniques and address emerging challenges in phospholipid characterization. Collaboration between academic institutions, industry partners, and regulatory bodies is essential for developing and implementing these standards on a global scale.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!