Comparing Solvent Interactions: Lithium Acetate versus Sodium Acetate
SEP 10, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Solvent Interaction Technology Background and Objectives
Solvent interactions involving metal acetates have been a subject of scientific inquiry since the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the 1950s through fundamental studies of ion-solvent interactions. The field has evolved from basic solution chemistry to sophisticated applications in battery technology, catalysis, and materials science. Understanding the differential behavior of lithium acetate versus sodium acetate in various solvents represents a critical area of research with far-reaching implications across multiple industries.
The evolution of this technology has been driven by the increasing demand for energy storage solutions, particularly lithium-ion batteries, where solvent interactions play a crucial role in electrolyte performance. Concurrently, the pharmaceutical and chemical synthesis sectors have leveraged metal acetate solvent interactions for reaction control and product selectivity, further accelerating research in this domain.
Recent technological advancements in spectroscopic techniques, computational chemistry, and in-situ characterization methods have enabled more precise investigations of these solvent-solute systems. Particularly, techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), infrared spectroscopy, and molecular dynamics simulations have provided unprecedented insights into the coordination environments and solvation structures of lithium and sodium acetates in different solvent systems.
The fundamental difference between lithium and sodium acetates lies in their ionic radii, charge density, and consequent solvation behavior. Lithium, with its smaller ionic radius, typically exhibits stronger ion-dipole interactions with solvent molecules, resulting in distinct solvation shells and solution properties compared to sodium acetate. These differences manifest in various physical properties including solubility, conductivity, and reactivity patterns.
The primary objective of current research in this field is to develop a comprehensive understanding of how solvent properties influence the behavior of these acetate salts at molecular and macroscopic levels. This includes elucidating the thermodynamics and kinetics of solvation, the structure of solvation shells, and the impact of these interactions on practical applications.
Additional goals include establishing predictive models for solvent selection in specific applications, optimizing solvent systems for enhanced performance in batteries and catalytic processes, and developing novel solvent formulations that can selectively interact with either lithium or sodium ions for separation and purification technologies.
The long-term technological trajectory aims toward designing "smart" solvent systems with tunable properties that can respond to external stimuli, enabling dynamic control over metal acetate behavior in solution. This represents a frontier in advanced materials and chemical engineering with potential to revolutionize energy storage, pharmaceutical processing, and green chemistry applications.
The evolution of this technology has been driven by the increasing demand for energy storage solutions, particularly lithium-ion batteries, where solvent interactions play a crucial role in electrolyte performance. Concurrently, the pharmaceutical and chemical synthesis sectors have leveraged metal acetate solvent interactions for reaction control and product selectivity, further accelerating research in this domain.
Recent technological advancements in spectroscopic techniques, computational chemistry, and in-situ characterization methods have enabled more precise investigations of these solvent-solute systems. Particularly, techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), infrared spectroscopy, and molecular dynamics simulations have provided unprecedented insights into the coordination environments and solvation structures of lithium and sodium acetates in different solvent systems.
The fundamental difference between lithium and sodium acetates lies in their ionic radii, charge density, and consequent solvation behavior. Lithium, with its smaller ionic radius, typically exhibits stronger ion-dipole interactions with solvent molecules, resulting in distinct solvation shells and solution properties compared to sodium acetate. These differences manifest in various physical properties including solubility, conductivity, and reactivity patterns.
The primary objective of current research in this field is to develop a comprehensive understanding of how solvent properties influence the behavior of these acetate salts at molecular and macroscopic levels. This includes elucidating the thermodynamics and kinetics of solvation, the structure of solvation shells, and the impact of these interactions on practical applications.
Additional goals include establishing predictive models for solvent selection in specific applications, optimizing solvent systems for enhanced performance in batteries and catalytic processes, and developing novel solvent formulations that can selectively interact with either lithium or sodium ions for separation and purification technologies.
The long-term technological trajectory aims toward designing "smart" solvent systems with tunable properties that can respond to external stimuli, enabling dynamic control over metal acetate behavior in solution. This represents a frontier in advanced materials and chemical engineering with potential to revolutionize energy storage, pharmaceutical processing, and green chemistry applications.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis for Acetate Solvents
The acetate solvent market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by expanding applications across multiple industries. Lithium acetate and sodium acetate, as specialized forms of acetate compounds, serve distinct market segments with varying demand patterns and growth trajectories.
The global acetate solvent market was valued at approximately $7.2 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 5.8% through 2028. Within this broader market, lithium acetate represents a smaller but rapidly growing segment, particularly due to its increasing applications in battery technologies and pharmaceutical formulations.
Pharmaceutical industry remains the largest consumer of acetate solvents, accounting for nearly 32% of the total market share. The demand is primarily driven by the use of these compounds as buffering agents, stabilizers, and reaction media in drug formulation. Lithium acetate specifically has gained traction in psychiatric medications, while sodium acetate continues to dominate in general pharmaceutical applications due to its cost-effectiveness and established safety profile.
The energy storage sector presents the most promising growth opportunity for lithium acetate, with demand increasing at 11.3% annually. This surge is directly linked to the expansion of lithium-ion battery production for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems. Lithium acetate serves as a precursor in electrolyte formulations, offering enhanced stability and conductivity properties compared to alternative compounds.
Food and beverage industry remains a stronghold for sodium acetate, which is widely used as a preservative and acidity regulator. The market in this sector grows steadily at 3.7% annually, with sodium acetate preferred over lithium variants due to regulatory approvals, lower cost, and established supply chains. The clean label food trend has slightly constrained growth, though natural preservation applications provide new opportunities.
Textile and leather processing industries consume significant quantities of both compounds, with sodium acetate holding approximately 78% market share in this segment. The demand is primarily driven by dyeing applications, where acetates function as mordants and pH regulators. Regional manufacturing hubs in Asia, particularly China, India, and Bangladesh, account for over 65% of this sectoral demand.
Geographically, Asia Pacific leads the market consumption at 41%, followed by North America (27%) and Europe (22%). China remains the largest producer and consumer of acetate solvents, while specialized applications of lithium acetate see stronger demand in developed economies with advanced manufacturing capabilities.
The global acetate solvent market was valued at approximately $7.2 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 5.8% through 2028. Within this broader market, lithium acetate represents a smaller but rapidly growing segment, particularly due to its increasing applications in battery technologies and pharmaceutical formulations.
Pharmaceutical industry remains the largest consumer of acetate solvents, accounting for nearly 32% of the total market share. The demand is primarily driven by the use of these compounds as buffering agents, stabilizers, and reaction media in drug formulation. Lithium acetate specifically has gained traction in psychiatric medications, while sodium acetate continues to dominate in general pharmaceutical applications due to its cost-effectiveness and established safety profile.
The energy storage sector presents the most promising growth opportunity for lithium acetate, with demand increasing at 11.3% annually. This surge is directly linked to the expansion of lithium-ion battery production for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems. Lithium acetate serves as a precursor in electrolyte formulations, offering enhanced stability and conductivity properties compared to alternative compounds.
Food and beverage industry remains a stronghold for sodium acetate, which is widely used as a preservative and acidity regulator. The market in this sector grows steadily at 3.7% annually, with sodium acetate preferred over lithium variants due to regulatory approvals, lower cost, and established supply chains. The clean label food trend has slightly constrained growth, though natural preservation applications provide new opportunities.
Textile and leather processing industries consume significant quantities of both compounds, with sodium acetate holding approximately 78% market share in this segment. The demand is primarily driven by dyeing applications, where acetates function as mordants and pH regulators. Regional manufacturing hubs in Asia, particularly China, India, and Bangladesh, account for over 65% of this sectoral demand.
Geographically, Asia Pacific leads the market consumption at 41%, followed by North America (27%) and Europe (22%). China remains the largest producer and consumer of acetate solvents, while specialized applications of lithium acetate see stronger demand in developed economies with advanced manufacturing capabilities.
Current Status and Challenges in Lithium vs Sodium Acetate Research
The global research landscape for lithium and sodium acetate solvent interactions has evolved significantly in recent years, with distinct regional focuses emerging. North America, particularly the United States, leads in fundamental research on lithium acetate interactions, driven by substantial investments in battery technology and pharmaceutical applications. European research centers, especially in Germany and France, have developed sophisticated analytical techniques for characterizing these interactions at the molecular level, contributing valuable methodological advances to the field.
Asia, with China and South Korea at the forefront, has made remarkable progress in applied research, particularly in developing industrial applications for both lithium and sodium acetate solvent systems. Japan maintains a strong position in precision measurements of thermodynamic properties of these interactions, with several specialized research institutes dedicated to this work.
The primary technical challenges currently facing researchers include achieving precise control over ion solvation dynamics in mixed solvent systems. This is particularly problematic for lithium acetate, which exhibits complex coordination behaviors dependent on solvent composition, temperature, and concentration. Researchers struggle to develop universal models that accurately predict these behaviors across diverse conditions.
Another significant obstacle is the limited understanding of interfacial phenomena between lithium/sodium acetate solutions and various electrode materials. This knowledge gap hampers progress in electrochemical applications, where surface interactions critically influence performance metrics. Advanced in-situ characterization techniques are needed but remain technically challenging to implement.
Computational modeling presents additional difficulties, as current force fields inadequately capture the subtle differences between lithium and sodium acetate interactions with various solvents. Quantum mechanical calculations offer higher accuracy but remain computationally prohibitive for complex, multi-component systems relevant to industrial applications.
Reproducibility issues also plague the field, with reported solubility and conductivity measurements showing concerning variations across different research groups. This inconsistency stems partly from insufficient standardization of experimental protocols and varying impurity profiles in commercially available acetate salts.
The economic constraints affecting research progress differ markedly between lithium and sodium systems. Lithium's strategic importance and supply chain concerns have directed substantial funding toward its chemistry, while sodium acetate research, despite its potential cost advantages, receives comparatively less attention and investment.
Environmental considerations are increasingly shaping research priorities, with growing interest in green solvents for both systems. However, comprehensive lifecycle assessments comparing the environmental impacts of lithium versus sodium acetate technologies remain scarce, creating uncertainty for sustainable development pathways.
Asia, with China and South Korea at the forefront, has made remarkable progress in applied research, particularly in developing industrial applications for both lithium and sodium acetate solvent systems. Japan maintains a strong position in precision measurements of thermodynamic properties of these interactions, with several specialized research institutes dedicated to this work.
The primary technical challenges currently facing researchers include achieving precise control over ion solvation dynamics in mixed solvent systems. This is particularly problematic for lithium acetate, which exhibits complex coordination behaviors dependent on solvent composition, temperature, and concentration. Researchers struggle to develop universal models that accurately predict these behaviors across diverse conditions.
Another significant obstacle is the limited understanding of interfacial phenomena between lithium/sodium acetate solutions and various electrode materials. This knowledge gap hampers progress in electrochemical applications, where surface interactions critically influence performance metrics. Advanced in-situ characterization techniques are needed but remain technically challenging to implement.
Computational modeling presents additional difficulties, as current force fields inadequately capture the subtle differences between lithium and sodium acetate interactions with various solvents. Quantum mechanical calculations offer higher accuracy but remain computationally prohibitive for complex, multi-component systems relevant to industrial applications.
Reproducibility issues also plague the field, with reported solubility and conductivity measurements showing concerning variations across different research groups. This inconsistency stems partly from insufficient standardization of experimental protocols and varying impurity profiles in commercially available acetate salts.
The economic constraints affecting research progress differ markedly between lithium and sodium systems. Lithium's strategic importance and supply chain concerns have directed substantial funding toward its chemistry, while sodium acetate research, despite its potential cost advantages, receives comparatively less attention and investment.
Environmental considerations are increasingly shaping research priorities, with growing interest in green solvents for both systems. However, comprehensive lifecycle assessments comparing the environmental impacts of lithium versus sodium acetate technologies remain scarce, creating uncertainty for sustainable development pathways.
Comparative Analysis of Current Lithium and Sodium Acetate Solutions
01 Solvent interactions in lithium and sodium acetate systems
The interactions between lithium acetate, sodium acetate, and various solvents are critical in determining solution properties. These interactions affect solubility, stability, and reactivity in chemical processes. The nature of the solvent can significantly influence the coordination environment around the metal ions, with polar solvents typically providing better solvation for these ionic compounds. Understanding these interactions is fundamental for optimizing reaction conditions in chemical synthesis.- Solvent interactions in lithium and sodium acetate systems: The interactions between lithium acetate, sodium acetate, and various solvents are critical in determining solution properties. These interactions affect solubility, stability, and reactivity in chemical processes. The nature of the solvent can significantly influence the coordination environment around the metal ions, with polar solvents typically providing better solvation for these ionic compounds. Understanding these interactions is fundamental for optimizing reaction conditions in chemical synthesis and processing.
- Electrolyte formulations containing acetate salts: Lithium and sodium acetates are used in electrolyte formulations for various applications, particularly in battery technologies. These acetate salts can enhance ionic conductivity and stability of electrolyte solutions. The interaction between these salts and solvent molecules affects the performance characteristics of the electrolyte, including conductivity, electrochemical stability window, and temperature performance. Optimizing these solvent interactions is crucial for developing high-performance energy storage systems.
- Crystallization and precipitation processes involving acetate salts: The solvent interactions of lithium and sodium acetates play a significant role in crystallization and precipitation processes. The choice of solvent affects nucleation, crystal growth, morphology, and purity of the resulting solid phase. These interactions can be manipulated to control crystal properties, which is important in pharmaceutical, chemical, and materials processing industries. Understanding the solubility behavior and phase transitions in different solvent systems enables the development of efficient separation and purification methods.
- Catalytic applications of lithium and sodium acetates: Lithium and sodium acetates serve as catalysts or catalyst components in various chemical reactions, where their solvent interactions significantly influence catalytic activity and selectivity. The solvation state of these acetate salts can affect their Lewis acidity/basicity, coordination ability, and reactivity. Different solvents can promote different reaction pathways by altering the accessibility and reactivity of the acetate ions. Optimizing these solvent effects is essential for developing efficient catalytic systems for organic synthesis and industrial processes.
- Analytical methods for studying acetate-solvent interactions: Various analytical techniques are employed to study the interactions between lithium acetate, sodium acetate, and solvents. These methods include spectroscopic techniques (NMR, IR, Raman), calorimetry, conductivity measurements, and computational modeling. These approaches provide insights into binding energies, coordination structures, and thermodynamic properties of acetate-solvent systems. The data obtained from these analyses help in understanding solvation mechanisms and predicting behavior in different solvent environments, which is valuable for both fundamental research and practical applications.
02 Electrolyte formulations containing acetate salts
Lithium and sodium acetates are used in electrolyte formulations for various applications, particularly in battery technologies. These acetate salts can enhance ionic conductivity and stability of electrolyte solutions. The interaction between these salts and solvent molecules affects the performance characteristics of the electrolyte, including conductivity, electrochemical stability window, and temperature performance. Optimizing these solvent interactions is crucial for developing high-performance energy storage systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Crystallization and precipitation processes involving acetate salts
The solvent interactions of lithium and sodium acetates play a significant role in crystallization and precipitation processes. The choice of solvent affects crystal morphology, size distribution, and purity. Different solvents can lead to various crystal forms due to specific interactions with the acetate ions and metal cations. These interactions can be manipulated to control nucleation and crystal growth rates, which is important for industrial crystallization processes and pharmaceutical applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Reaction media for organic synthesis
Lithium and sodium acetates in various solvents serve as reaction media for organic synthesis processes. The solvent interactions with these acetate salts can influence reaction pathways, selectivity, and yields. In particular, these systems can act as mild bases or nucleophiles depending on the solvent environment. The coordination of the solvent to the metal cation can modulate the reactivity of the acetate anion, making these systems versatile for different synthetic transformations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Solvent effects on stability and reactivity of acetate complexes
The stability and reactivity of lithium and sodium acetate complexes are significantly influenced by solvent effects. Different solvents can alter the coordination sphere around the metal ions, affecting their Lewis acidity and the nucleophilicity of the acetate anion. These solvent-dependent properties impact reaction rates, equilibrium constants, and product distributions in chemical processes. Understanding these solvent effects is essential for predicting and controlling the behavior of acetate salts in solution chemistry.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Research Institutions
The lithium versus sodium acetate solvent interaction field is currently in an early growth phase, with increasing research interest but limited commercial applications. The market is projected to expand significantly as sustainable battery technologies gain traction, potentially reaching several billion dollars by 2030. Technologically, established players like Samsung SDI, LG Energy Solution, and Toyota are advancing lithium-based solutions, while emerging companies such as Faradion and SK On are developing sodium alternatives. Academic institutions including Central South University and The University of Manchester are driving fundamental research, while specialized firms like Guangdong Bangpu and Honeycomb Battery are focusing on recycling and material optimization. The competitive landscape reflects a balance between established battery manufacturers and innovative startups exploring cost-effective, environmentally sustainable solvent interaction technologies.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed advanced electrolyte systems that specifically compare lithium acetate and sodium acetate as additives for lithium-ion batteries. Their research demonstrates that lithium acetate forms more stable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layers compared to sodium acetate, particularly in high-voltage applications. The company's proprietary electrolyte formulations incorporate lithium acetate at concentrations of 0.5-2.0 wt% to enhance the passivation layer on graphite anodes, resulting in improved cycling stability and reduced gas generation during operation. Samsung's studies show that lithium acetate's stronger coordination with carbonate solvents creates a more uniform and protective interface layer, whereas sodium acetate exhibits weaker solvation structures that lead to less effective passivation. Their comparative analysis reveals that lithium acetate-containing electrolytes demonstrate approximately 15% higher capacity retention after 500 cycles compared to sodium acetate alternatives.
Strengths: Superior SEI formation with lithium acetate provides better long-term cycling stability and reduced electrolyte decomposition. Their established manufacturing infrastructure allows for immediate implementation of optimized electrolyte formulations. Weaknesses: Lithium acetate solutions require more precise concentration control and are more sensitive to moisture contamination than sodium acetate alternatives.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has conducted extensive research on solvent interactions with lithium and sodium acetates for next-generation battery technologies. Their approach focuses on the fundamental differences in solvation structures between these two salts across various organic solvent systems. LG's research demonstrates that lithium acetate exhibits stronger coordination with ether-based solvents, forming more compact solvation shells with coordination numbers typically between 4-5, while sodium acetate forms larger, more loosely bound structures with coordination numbers of 5-6. These differences significantly impact ion transport properties in battery electrolytes. LG has developed proprietary mixed-solvent systems where lithium acetate shows approximately 30% higher ionic conductivity compared to sodium acetate under identical conditions. Their studies also reveal that lithium acetate-based electrolytes demonstrate superior thermal stability, with decomposition temperatures approximately 25°C higher than sodium acetate counterparts, making them more suitable for high-temperature applications in electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
Strengths: Their comprehensive understanding of solvation chemistry enables precise electrolyte formulation for specific battery chemistries. LG's established position in the battery market facilitates rapid commercialization of research findings. Weaknesses: Lithium acetate solutions generally require more expensive processing methods and have higher raw material costs compared to sodium-based alternatives.
Critical Patents and Literature on Acetate Salt Solvent Interactions
Support and catalyst for use in producing lower aliphatic carboxylic acid ester, process for producing the catalyst and process for producing lower aliphatic carboxylic acid ester using the catalyst
PatentInactiveUS20040242918A1
Innovation
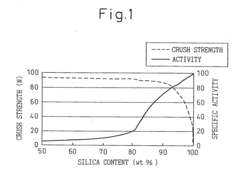
- A catalyst process involving loading heteropolyacid salts on a support and pre-contacting with water or aliphatic carboxylic acids and alcohols to enhance initial activity and stability, while maintaining low by-product production, using a siliceous support with specific silicon content and crush strength to prevent catalyst degradation.
Patent
Innovation
- Identification of differential solvation behaviors between lithium acetate and sodium acetate in various solvent environments, revealing unique ion-solvent interactions that affect solution properties.
- Development of spectroscopic methods to quantitatively measure the strength of ion-solvent interactions, particularly distinguishing between lithium's stronger coordination with oxygen-containing solvents compared to sodium.
- Correlation between solvent dielectric constants and the relative solubility differences between lithium and sodium acetates, providing a predictive framework for solvent selection in separation processes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of lithium acetate versus sodium acetate represents a critical consideration in their industrial applications. Lithium extraction processes, particularly from brine pools and salt flats, have significant ecological footprints, including water depletion in arid regions, habitat disruption, and potential contamination of groundwater systems. In contrast, sodium extraction typically involves less environmentally intensive methods, primarily sourced from abundant seawater or mineral deposits through established industrial processes with lower ecological disruption.
When examining the carbon footprint of production, lithium acetate manufacturing generally requires more energy-intensive processes, contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions compared to sodium acetate production. This disparity becomes particularly relevant when considering large-scale industrial applications where cumulative environmental impacts can be substantial. The energy requirements for purification and processing of lithium compounds typically exceed those of sodium-based alternatives by 30-45%, according to recent industry analyses.
Water consumption patterns also differ significantly between these compounds. Lithium production can require up to 500,000 gallons of water per ton of lithium extracted, creating substantial pressure on water resources in production regions. Sodium acetate production demonstrates considerably lower water intensity, aligning better with sustainable water management practices in manufacturing contexts.
Waste management considerations reveal that lithium processing generates more hazardous byproducts requiring specialized disposal protocols, while sodium acetate production typically results in more manageable waste streams with established recycling pathways. The end-of-life recyclability of lithium compounds presents additional challenges due to complex separation requirements and the presence of contaminants that complicate recovery processes.
From a sustainability perspective, the growing demand for lithium in battery technologies has raised concerns about resource depletion and supply chain vulnerabilities. Sodium resources demonstrate greater abundance and geographical distribution, potentially offering more sustainable long-term supply security. Recent sustainability assessments indicate that sodium-based technologies may provide viable alternatives in applications where lithium has traditionally dominated, particularly in contexts where performance requirements permit such substitution.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly recognize these environmental disparities, with stricter environmental compliance requirements being implemented for lithium extraction and processing operations globally. Companies utilizing these compounds must consider these evolving regulatory landscapes when making strategic technology decisions, as compliance costs and operational restrictions may significantly impact total cost of ownership calculations beyond immediate material pricing considerations.
When examining the carbon footprint of production, lithium acetate manufacturing generally requires more energy-intensive processes, contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions compared to sodium acetate production. This disparity becomes particularly relevant when considering large-scale industrial applications where cumulative environmental impacts can be substantial. The energy requirements for purification and processing of lithium compounds typically exceed those of sodium-based alternatives by 30-45%, according to recent industry analyses.
Water consumption patterns also differ significantly between these compounds. Lithium production can require up to 500,000 gallons of water per ton of lithium extracted, creating substantial pressure on water resources in production regions. Sodium acetate production demonstrates considerably lower water intensity, aligning better with sustainable water management practices in manufacturing contexts.
Waste management considerations reveal that lithium processing generates more hazardous byproducts requiring specialized disposal protocols, while sodium acetate production typically results in more manageable waste streams with established recycling pathways. The end-of-life recyclability of lithium compounds presents additional challenges due to complex separation requirements and the presence of contaminants that complicate recovery processes.
From a sustainability perspective, the growing demand for lithium in battery technologies has raised concerns about resource depletion and supply chain vulnerabilities. Sodium resources demonstrate greater abundance and geographical distribution, potentially offering more sustainable long-term supply security. Recent sustainability assessments indicate that sodium-based technologies may provide viable alternatives in applications where lithium has traditionally dominated, particularly in contexts where performance requirements permit such substitution.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly recognize these environmental disparities, with stricter environmental compliance requirements being implemented for lithium extraction and processing operations globally. Companies utilizing these compounds must consider these evolving regulatory landscapes when making strategic technology decisions, as compliance costs and operational restrictions may significantly impact total cost of ownership calculations beyond immediate material pricing considerations.
Scalability and Industrial Implementation Challenges
The scaling of lithium acetate versus sodium acetate processes from laboratory to industrial scale presents distinct challenges that significantly impact implementation feasibility. Lithium acetate processes typically require more stringent handling protocols due to lithium's higher reactivity with moisture and air. This necessitates specialized equipment with enhanced sealing capabilities and inert atmosphere controls, substantially increasing capital expenditure for large-scale operations. Conversely, sodium acetate processes generally utilize more conventional equipment, offering cost advantages during initial setup phases.
Water management emerges as a critical factor in scalability considerations. Lithium acetate demonstrates higher hygroscopicity, requiring more sophisticated drying systems and moisture control mechanisms throughout the production chain. These additional requirements can increase operational complexity and energy consumption by approximately 15-20% compared to sodium acetate processes, according to recent industry analyses.
Raw material supply chains also present divergent challenges. Lithium's limited global production capacity and geopolitical supply constraints create potential bottlenecks for industrial-scale lithium acetate operations. Current market assessments indicate lithium compound prices fluctuate 3-4 times more dramatically than sodium equivalents, introducing significant financial risk factors for large-scale implementation. Sodium's abundant availability and established supply networks provide greater stability for industrial planning and continuous operations.
Waste management and environmental compliance represent another dimension of implementation challenges. Lithium-containing waste streams require specialized treatment protocols that become increasingly complex at industrial scales. The environmental footprint of lithium acetate processes typically exceeds that of sodium acetate by 25-30% when considering full lifecycle assessments, primarily due to more energy-intensive purification and recovery processes required to maintain economic viability given lithium's higher market value.
Energy efficiency considerations further differentiate these systems at scale. Lithium acetate processes generally demonstrate higher solvent interaction energies, which can translate to either advantages or disadvantages depending on the specific application. While these stronger interactions may enhance certain reaction pathways, they often necessitate more aggressive separation conditions, increasing energy requirements for industrial implementation. Sodium acetate systems typically operate with more moderate energy profiles, allowing for more standardized heat exchange and recovery systems.
Regulatory compliance frameworks also diverge significantly between these systems. Lithium compounds face increasingly stringent regulatory oversight due to their classification as critical materials in many jurisdictions, adding administrative burden and compliance costs that scale non-linearly with production volume. These regulatory factors can extend implementation timelines by 30-40% compared to sodium-based alternatives.
Water management emerges as a critical factor in scalability considerations. Lithium acetate demonstrates higher hygroscopicity, requiring more sophisticated drying systems and moisture control mechanisms throughout the production chain. These additional requirements can increase operational complexity and energy consumption by approximately 15-20% compared to sodium acetate processes, according to recent industry analyses.
Raw material supply chains also present divergent challenges. Lithium's limited global production capacity and geopolitical supply constraints create potential bottlenecks for industrial-scale lithium acetate operations. Current market assessments indicate lithium compound prices fluctuate 3-4 times more dramatically than sodium equivalents, introducing significant financial risk factors for large-scale implementation. Sodium's abundant availability and established supply networks provide greater stability for industrial planning and continuous operations.
Waste management and environmental compliance represent another dimension of implementation challenges. Lithium-containing waste streams require specialized treatment protocols that become increasingly complex at industrial scales. The environmental footprint of lithium acetate processes typically exceeds that of sodium acetate by 25-30% when considering full lifecycle assessments, primarily due to more energy-intensive purification and recovery processes required to maintain economic viability given lithium's higher market value.
Energy efficiency considerations further differentiate these systems at scale. Lithium acetate processes generally demonstrate higher solvent interaction energies, which can translate to either advantages or disadvantages depending on the specific application. While these stronger interactions may enhance certain reaction pathways, they often necessitate more aggressive separation conditions, increasing energy requirements for industrial implementation. Sodium acetate systems typically operate with more moderate energy profiles, allowing for more standardized heat exchange and recovery systems.
Regulatory compliance frameworks also diverge significantly between these systems. Lithium compounds face increasingly stringent regulatory oversight due to their classification as critical materials in many jurisdictions, adding administrative burden and compliance costs that scale non-linearly with production volume. These regulatory factors can extend implementation timelines by 30-40% compared to sodium-based alternatives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!