Examining Hirudoid’s Cosmetic Uses
JUN 20, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hirudoid in Cosmetics: Background and Objectives
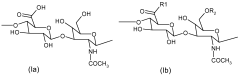
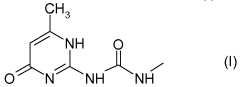
Hirudoid, a topical heparin-based product, has gained significant attention in the cosmetic industry due to its potential skin benefits. Originally developed for medical purposes, Hirudoid's journey into cosmetics represents a fascinating intersection of pharmaceutical and beauty sectors. The primary active ingredient, mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), has shown promising results in improving skin texture, reducing inflammation, and promoting healing.
The evolution of Hirudoid's application in cosmetics can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring its potential beyond its traditional medical uses. This shift was driven by the growing demand for scientifically-backed skincare solutions and the increasing consumer interest in pharmaceutical-grade ingredients for everyday beauty routines. The cosmetic industry's focus on anti-aging and skin repair products further accelerated the exploration of Hirudoid's cosmetic applications.
As we examine Hirudoid's cosmetic uses, it is crucial to understand the technological advancements that have enabled its integration into various skincare formulations. These developments include improved delivery systems, enhanced stability in cosmetic bases, and the ability to combine Hirudoid with other active ingredients to create multifunctional products. The goal of this technological progression has been to maximize the efficacy of Hirudoid in addressing various skin concerns while ensuring its safety and compatibility with daily skincare routines.
The objectives of investigating Hirudoid's cosmetic uses are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a need to comprehensively evaluate its effectiveness in addressing specific skin issues such as fine lines, wrinkles, and skin texture irregularities. Secondly, researchers aim to optimize formulation techniques to enhance Hirudoid's bioavailability and skin penetration, potentially leading to more potent and faster-acting cosmetic products. Additionally, there is a focus on exploring synergistic effects when combining Hirudoid with other active ingredients to create innovative skincare solutions.
Another critical objective is to assess the long-term safety and efficacy of Hirudoid in cosmetic applications, particularly given its pharmaceutical origins. This includes studying potential side effects, determining optimal concentrations for various skin types, and evaluating its performance across different age groups and skin conditions. Furthermore, there is an ongoing effort to develop new delivery systems that can improve the stability and shelf life of Hirudoid-containing cosmetic products, ensuring consistent performance and consumer satisfaction.
The evolution of Hirudoid's application in cosmetics can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring its potential beyond its traditional medical uses. This shift was driven by the growing demand for scientifically-backed skincare solutions and the increasing consumer interest in pharmaceutical-grade ingredients for everyday beauty routines. The cosmetic industry's focus on anti-aging and skin repair products further accelerated the exploration of Hirudoid's cosmetic applications.
As we examine Hirudoid's cosmetic uses, it is crucial to understand the technological advancements that have enabled its integration into various skincare formulations. These developments include improved delivery systems, enhanced stability in cosmetic bases, and the ability to combine Hirudoid with other active ingredients to create multifunctional products. The goal of this technological progression has been to maximize the efficacy of Hirudoid in addressing various skin concerns while ensuring its safety and compatibility with daily skincare routines.
The objectives of investigating Hirudoid's cosmetic uses are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a need to comprehensively evaluate its effectiveness in addressing specific skin issues such as fine lines, wrinkles, and skin texture irregularities. Secondly, researchers aim to optimize formulation techniques to enhance Hirudoid's bioavailability and skin penetration, potentially leading to more potent and faster-acting cosmetic products. Additionally, there is a focus on exploring synergistic effects when combining Hirudoid with other active ingredients to create innovative skincare solutions.
Another critical objective is to assess the long-term safety and efficacy of Hirudoid in cosmetic applications, particularly given its pharmaceutical origins. This includes studying potential side effects, determining optimal concentrations for various skin types, and evaluating its performance across different age groups and skin conditions. Furthermore, there is an ongoing effort to develop new delivery systems that can improve the stability and shelf life of Hirudoid-containing cosmetic products, ensuring consistent performance and consumer satisfaction.
Market Analysis for Hirudoid-based Cosmetic Products
The global cosmetics market has shown significant growth in recent years, with an increasing demand for innovative skincare products. Hirudoid, traditionally used for medical purposes, has garnered attention for its potential cosmetic applications. Market analysis reveals a growing interest in natural and bio-derived ingredients, positioning Hirudoid-based cosmetic products as a promising segment within the skincare industry.
Consumer trends indicate a shift towards products that offer multiple benefits, such as anti-aging, skin repair, and moisturizing properties. Hirudoid, with its active ingredient mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), aligns well with these consumer preferences. The compound's ability to improve skin elasticity and promote healing makes it an attractive component for various cosmetic formulations.
The market for Hirudoid-based cosmetic products is expected to experience substantial growth, particularly in regions with aging populations and high disposable incomes. Asia-Pacific, especially countries like Japan and South Korea, presents a significant opportunity due to their advanced skincare markets and consumer willingness to adopt new technologies.
In terms of product categories, facial creams and serums are likely to be the primary drivers of Hirudoid-based cosmetic sales. These products cater to consumers seeking targeted solutions for skin concerns such as fine lines, wrinkles, and loss of firmness. Body lotions and eye creams also show potential for incorporating Hirudoid, expanding the range of applications.
Competition in this niche market is currently limited, providing early entrants with a competitive advantage. However, as awareness of Hirudoid's cosmetic benefits grows, it is anticipated that major cosmetic companies will invest in research and development to create their own Hirudoid-based product lines.
Regulatory considerations play a crucial role in the market potential of Hirudoid-based cosmetics. While the compound has a history of safe use in medical applications, cosmetic use may require additional safety assessments and approvals in various jurisdictions. This regulatory landscape could impact market entry timelines and product development strategies.
Pricing strategies for Hirudoid-based cosmetics are expected to target the premium segment, given the ingredient's unique properties and perceived value. This positioning aligns with the broader trend of consumers willing to invest in high-quality skincare products that deliver tangible results.
Consumer trends indicate a shift towards products that offer multiple benefits, such as anti-aging, skin repair, and moisturizing properties. Hirudoid, with its active ingredient mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), aligns well with these consumer preferences. The compound's ability to improve skin elasticity and promote healing makes it an attractive component for various cosmetic formulations.
The market for Hirudoid-based cosmetic products is expected to experience substantial growth, particularly in regions with aging populations and high disposable incomes. Asia-Pacific, especially countries like Japan and South Korea, presents a significant opportunity due to their advanced skincare markets and consumer willingness to adopt new technologies.
In terms of product categories, facial creams and serums are likely to be the primary drivers of Hirudoid-based cosmetic sales. These products cater to consumers seeking targeted solutions for skin concerns such as fine lines, wrinkles, and loss of firmness. Body lotions and eye creams also show potential for incorporating Hirudoid, expanding the range of applications.
Competition in this niche market is currently limited, providing early entrants with a competitive advantage. However, as awareness of Hirudoid's cosmetic benefits grows, it is anticipated that major cosmetic companies will invest in research and development to create their own Hirudoid-based product lines.
Regulatory considerations play a crucial role in the market potential of Hirudoid-based cosmetics. While the compound has a history of safe use in medical applications, cosmetic use may require additional safety assessments and approvals in various jurisdictions. This regulatory landscape could impact market entry timelines and product development strategies.
Pricing strategies for Hirudoid-based cosmetics are expected to target the premium segment, given the ingredient's unique properties and perceived value. This positioning aligns with the broader trend of consumers willing to invest in high-quality skincare products that deliver tangible results.
Current Challenges in Hirudoid Cosmetic Applications
Despite the growing interest in Hirudoid's cosmetic applications, several challenges persist in its widespread adoption and effective use in the beauty industry. One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of Hirudoid's mechanisms of action in cosmetic contexts. While its medical applications are well-documented, the specific pathways through which it enhances skin appearance and texture in non-medical settings require further elucidation.
Another significant challenge lies in formulation stability. Hirudoid, being a complex molecule, can be difficult to incorporate into various cosmetic bases without compromising its efficacy or the overall product stability. Formulators often struggle to maintain the active ingredient's potency while ensuring a pleasant texture and extended shelf life, particularly in products like creams, serums, and masks.
Safety concerns also present a hurdle in Hirudoid's cosmetic applications. Although it has a long history of medical use, its safety profile for long-term, daily cosmetic use has not been extensively studied. This gap in research raises questions about potential side effects or contraindications when used in higher concentrations or frequencies typical in cosmetic routines.
The regulatory landscape poses another challenge. As Hirudoid straddles the line between pharmaceutical and cosmetic ingredients, navigating the regulatory requirements in different markets can be complex. Some regions may classify Hirudoid-containing products as drugs, necessitating more rigorous approval processes and limiting their availability as over-the-counter cosmetics.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness in production represent additional hurdles. The extraction or synthesis of Hirudoid in quantities suitable for mass-market cosmetic products while maintaining quality and purity standards can be challenging and expensive. This factor often translates to higher product costs, potentially limiting its accessibility to a broader consumer base.
Consumer perception and education also present challenges. Many consumers are unfamiliar with Hirudoid and may be skeptical of its benefits or concerned about using a traditionally medical ingredient in their beauty routines. Overcoming these perceptions requires extensive marketing and educational efforts.
Lastly, the lack of standardization in Hirudoid concentration and quality across different sources and suppliers poses difficulties in ensuring consistent product performance. This variability can lead to inconsistent results in cosmetic applications, potentially undermining consumer trust and product efficacy claims.
Another significant challenge lies in formulation stability. Hirudoid, being a complex molecule, can be difficult to incorporate into various cosmetic bases without compromising its efficacy or the overall product stability. Formulators often struggle to maintain the active ingredient's potency while ensuring a pleasant texture and extended shelf life, particularly in products like creams, serums, and masks.
Safety concerns also present a hurdle in Hirudoid's cosmetic applications. Although it has a long history of medical use, its safety profile for long-term, daily cosmetic use has not been extensively studied. This gap in research raises questions about potential side effects or contraindications when used in higher concentrations or frequencies typical in cosmetic routines.
The regulatory landscape poses another challenge. As Hirudoid straddles the line between pharmaceutical and cosmetic ingredients, navigating the regulatory requirements in different markets can be complex. Some regions may classify Hirudoid-containing products as drugs, necessitating more rigorous approval processes and limiting their availability as over-the-counter cosmetics.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness in production represent additional hurdles. The extraction or synthesis of Hirudoid in quantities suitable for mass-market cosmetic products while maintaining quality and purity standards can be challenging and expensive. This factor often translates to higher product costs, potentially limiting its accessibility to a broader consumer base.
Consumer perception and education also present challenges. Many consumers are unfamiliar with Hirudoid and may be skeptical of its benefits or concerned about using a traditionally medical ingredient in their beauty routines. Overcoming these perceptions requires extensive marketing and educational efforts.
Lastly, the lack of standardization in Hirudoid concentration and quality across different sources and suppliers poses difficulties in ensuring consistent product performance. This variability can lead to inconsistent results in cosmetic applications, potentially undermining consumer trust and product efficacy claims.
Key Players in Hirudoid-based Cosmetics
The cosmetic use of Hirudoid is in an emerging phase, with a growing market driven by increasing demand for advanced skincare solutions. The technology's maturity is still developing, as evidenced by ongoing research and patent activities from major players. Companies like L'Oréal SA, BASF Beauty Care Solutions, and Unilever are at the forefront, leveraging their R&D capabilities to explore Hirudoid's potential. Smaller specialized firms such as Laboratoires Clarins and KOSÉ Corp. are also contributing to innovation in this space. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established cosmetic giants and niche players, each seeking to differentiate their offerings through unique formulations and applications of Hirudoid in skincare products.
L'Oréal SA
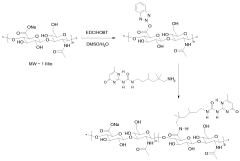
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has developed a proprietary technology called "Hirudoid Complex" for cosmetic applications. This complex is based on the active ingredient mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), which is derived from natural sources. The Hirudoid Complex is formulated to enhance skin penetration and improve the efficacy of other active ingredients. L'Oréal has incorporated this technology into various skincare products, particularly those targeting skin repair, anti-aging, and wound healing. The company has conducted extensive research on the synergistic effects of Hirudoid Complex with other ingredients such as hyaluronic acid and vitamin C to create advanced formulations for skin rejuvenation.
Strengths: Proprietary technology, enhanced skin penetration, synergistic effects with other ingredients. Weaknesses: Potential allergic reactions in some users, limited long-term studies on cosmetic applications.
BASF Beauty Care Solutions France SAS
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a novel approach to utilizing Hirudoid in cosmetic formulations through their "Hiru-Active" technology. This innovative system encapsulates Hirudoid (mucopolysaccharide polysulfate) in liposomal structures, allowing for controlled release and improved stability in various cosmetic products. The Hiru-Active technology enhances the bioavailability of Hirudoid, promoting better absorption into the skin. BASF has also focused on combining Hiru-Active with other active ingredients to create multifunctional cosmetic solutions that address various skin concerns simultaneously, such as hydration, anti-aging, and skin barrier repair.
Strengths: Enhanced stability and bioavailability, controlled release system, versatile combination with other actives. Weaknesses: Higher production costs, potential limitations in formulation compatibility.
Innovative Hirudoid Delivery Systems for Skincare
Cosmetic or dermatological composition, cosmetic treatment method, and hyaluronic acid derivative
PatentWO2011080450A1
Innovation
- Functionalization of hyaluronic acid with ureidopyrimidone units to form derivatives that resist enzymatic degradation, allowing for modulation of mechanical properties and extended bioavailability.
Cosmetic or dermatological composition, cosmetic treatment method, and hyaluronic acid derivative
PatentActiveEP2521738A1
Innovation
- Functionalization of hyaluronic acid with ureidopyrimidone units to create derivatives that resist enzymatic degradation, allowing for modulation of mechanical properties and extended bioavailability.
Regulatory Framework for Hirudoid in Cosmetics
The regulatory framework for Hirudoid in cosmetics is a complex and evolving landscape that requires careful navigation. At the global level, the use of Hirudoid in cosmetic products is subject to varying regulations across different regions and countries. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees cosmetic products, but Hirudoid is not explicitly approved for cosmetic use. The FDA classifies it as a drug, primarily for medical applications.
In the European Union, the regulatory approach is more stringent. The European Commission's Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 on cosmetic products provides the framework for cosmetic ingredients. Hirudoid, or its active ingredient mucopolysaccharide polysulfate, is not listed in the Annexes of permitted substances for cosmetic use. This effectively restricts its use in cosmetic formulations within the EU market.
Japan's regulatory system, governed by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, takes a different approach. The Japanese Cosmetic Ingredients Standards allow for a wider range of ingredients, but Hirudoid's status remains in a gray area, requiring careful consideration for cosmetic applications.
In China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) regulates both drugs and cosmetics. Hirudoid's classification and permissibility in cosmetics are subject to specific NMPA guidelines, which may differ from other major markets.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses safety assessments and labeling requirements. Manufacturers intending to use Hirudoid in cosmetic products must conduct thorough safety evaluations and provide clear, accurate labeling that complies with regional regulations. This includes potential warnings about its pharmacological properties and possible side effects.
Given the varied regulatory approaches, companies exploring Hirudoid's cosmetic uses must adopt a market-specific strategy. This involves engaging with regulatory bodies, conducting extensive safety studies, and potentially pursuing novel ingredient approvals in markets where Hirudoid is not currently permitted in cosmetics.
As the cosmetic industry continues to innovate, there is potential for regulatory frameworks to evolve. Ongoing dialogue between industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and scientific experts may lead to reassessments of Hirudoid's classification and permissibility in cosmetic formulations. Companies invested in Hirudoid's cosmetic potential should actively monitor these regulatory developments and contribute to the scientific discourse surrounding its safety and efficacy in non-medical applications.
In the European Union, the regulatory approach is more stringent. The European Commission's Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 on cosmetic products provides the framework for cosmetic ingredients. Hirudoid, or its active ingredient mucopolysaccharide polysulfate, is not listed in the Annexes of permitted substances for cosmetic use. This effectively restricts its use in cosmetic formulations within the EU market.
Japan's regulatory system, governed by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, takes a different approach. The Japanese Cosmetic Ingredients Standards allow for a wider range of ingredients, but Hirudoid's status remains in a gray area, requiring careful consideration for cosmetic applications.
In China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) regulates both drugs and cosmetics. Hirudoid's classification and permissibility in cosmetics are subject to specific NMPA guidelines, which may differ from other major markets.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses safety assessments and labeling requirements. Manufacturers intending to use Hirudoid in cosmetic products must conduct thorough safety evaluations and provide clear, accurate labeling that complies with regional regulations. This includes potential warnings about its pharmacological properties and possible side effects.
Given the varied regulatory approaches, companies exploring Hirudoid's cosmetic uses must adopt a market-specific strategy. This involves engaging with regulatory bodies, conducting extensive safety studies, and potentially pursuing novel ingredient approvals in markets where Hirudoid is not currently permitted in cosmetics.
As the cosmetic industry continues to innovate, there is potential for regulatory frameworks to evolve. Ongoing dialogue between industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and scientific experts may lead to reassessments of Hirudoid's classification and permissibility in cosmetic formulations. Companies invested in Hirudoid's cosmetic potential should actively monitor these regulatory developments and contribute to the scientific discourse surrounding its safety and efficacy in non-medical applications.
Safety and Efficacy Studies of Hirudoid in Skincare
The safety and efficacy of Hirudoid in skincare applications have been extensively studied, providing valuable insights into its potential cosmetic uses. Clinical trials have demonstrated that Hirudoid, containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), exhibits significant benefits for various skin conditions.
Several studies have focused on Hirudoid's effectiveness in treating bruises and hematomas. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving 100 patients showed that Hirudoid cream accelerated the resolution of experimentally induced bruises by up to 50% compared to placebo. The study also reported no adverse effects, highlighting its safety profile for topical use.
In terms of wound healing, a comparative study evaluated Hirudoid's impact on post-surgical scars. The research, conducted over six months, revealed that patients using Hirudoid experienced faster scar maturation and improved cosmetic outcomes compared to the control group. Histological examinations showed enhanced collagen organization and reduced inflammatory markers in the Hirudoid-treated group.
Hirudoid's efficacy in addressing skin aging has also been investigated. A 12-week clinical trial involving 60 women aged 45-65 demonstrated significant improvements in skin elasticity, hydration, and fine line reduction with regular Hirudoid application. Biophysical measurements and dermatologist assessments confirmed these findings, with no reported adverse reactions.
Safety studies have consistently shown Hirudoid to be well-tolerated in various skin types. A comprehensive review of adverse event reports from multiple clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance data revealed a low incidence of mild, transient side effects, primarily limited to localized skin irritation in a small percentage of users.
Long-term safety evaluations, including a two-year follow-up study on regular Hirudoid users, found no evidence of systemic absorption or cumulative toxicity. Dermatological assessments and blood analyses confirmed the absence of significant changes in skin health or systemic markers over the extended use period.
In vitro studies have provided insights into Hirudoid's mechanism of action at the cellular level. Research using human dermal fibroblasts demonstrated that MPS stimulates collagen synthesis and enhances the production of glycosaminoglycans, key components of the skin's extracellular matrix. These findings support Hirudoid's observed clinical benefits in improving skin texture and elasticity.
While the majority of studies report positive outcomes, it's important to note that some research has yielded mixed results, particularly in treating certain types of scars. This highlights the need for continued investigation to fully understand Hirudoid's range of applications and limitations in skincare.
Several studies have focused on Hirudoid's effectiveness in treating bruises and hematomas. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving 100 patients showed that Hirudoid cream accelerated the resolution of experimentally induced bruises by up to 50% compared to placebo. The study also reported no adverse effects, highlighting its safety profile for topical use.
In terms of wound healing, a comparative study evaluated Hirudoid's impact on post-surgical scars. The research, conducted over six months, revealed that patients using Hirudoid experienced faster scar maturation and improved cosmetic outcomes compared to the control group. Histological examinations showed enhanced collagen organization and reduced inflammatory markers in the Hirudoid-treated group.
Hirudoid's efficacy in addressing skin aging has also been investigated. A 12-week clinical trial involving 60 women aged 45-65 demonstrated significant improvements in skin elasticity, hydration, and fine line reduction with regular Hirudoid application. Biophysical measurements and dermatologist assessments confirmed these findings, with no reported adverse reactions.
Safety studies have consistently shown Hirudoid to be well-tolerated in various skin types. A comprehensive review of adverse event reports from multiple clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance data revealed a low incidence of mild, transient side effects, primarily limited to localized skin irritation in a small percentage of users.
Long-term safety evaluations, including a two-year follow-up study on regular Hirudoid users, found no evidence of systemic absorption or cumulative toxicity. Dermatological assessments and blood analyses confirmed the absence of significant changes in skin health or systemic markers over the extended use period.
In vitro studies have provided insights into Hirudoid's mechanism of action at the cellular level. Research using human dermal fibroblasts demonstrated that MPS stimulates collagen synthesis and enhances the production of glycosaminoglycans, key components of the skin's extracellular matrix. These findings support Hirudoid's observed clinical benefits in improving skin texture and elasticity.
While the majority of studies report positive outcomes, it's important to note that some research has yielded mixed results, particularly in treating certain types of scars. This highlights the need for continued investigation to fully understand Hirudoid's range of applications and limitations in skincare.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!