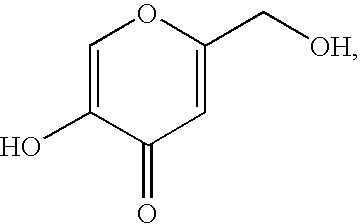
How to Use Hirudoid for Skin Discoloration?
JUN 23, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hirudoid Background and Objectives
Hirudoid, a topical medication containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), has been widely used in dermatology for its anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant properties. Originally developed for treating thrombophlebitis and superficial vein thrombosis, Hirudoid has gained attention for its potential in addressing skin discoloration issues. This report aims to explore the application of Hirudoid in treating skin discoloration, examining its efficacy, mechanisms of action, and potential benefits.
The primary objective of this investigation is to evaluate the effectiveness of Hirudoid in reducing various forms of skin discoloration, including post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, melasma, and age spots. By analyzing existing research and clinical data, we seek to understand the underlying mechanisms through which Hirudoid may influence melanin production and distribution in the skin.
Skin discoloration is a common dermatological concern affecting millions of people worldwide. It can result from various factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, and aging. Traditional treatments often involve topical agents such as hydroquinone, kojic acid, or retinoids, which may have limitations in terms of efficacy and side effects. The exploration of Hirudoid as an alternative or complementary treatment represents a potentially innovative approach to addressing this widespread issue.
The evolution of Hirudoid's application from vascular medicine to dermatology highlights the importance of cross-disciplinary research in uncovering novel uses for existing medications. By investigating its potential in skin discoloration treatment, we aim to contribute to the expanding field of dermatological therapeutics and provide new options for patients seeking effective solutions for pigmentation disorders.
This report will delve into the chemical composition of Hirudoid, its interaction with skin cells, and its potential effects on melanocytes and melanin production. We will also examine the current state of clinical evidence supporting its use in skin discoloration treatment, identifying any gaps in knowledge that may require further research.
Furthermore, we will explore the broader implications of using Hirudoid for skin discoloration, including its potential impact on the dermatology market, patient satisfaction, and quality of life improvements. By comprehensively analyzing these aspects, we aim to provide a clear understanding of Hirudoid's potential role in addressing skin discoloration and guide future research and development efforts in this area.
The primary objective of this investigation is to evaluate the effectiveness of Hirudoid in reducing various forms of skin discoloration, including post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, melasma, and age spots. By analyzing existing research and clinical data, we seek to understand the underlying mechanisms through which Hirudoid may influence melanin production and distribution in the skin.
Skin discoloration is a common dermatological concern affecting millions of people worldwide. It can result from various factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, and aging. Traditional treatments often involve topical agents such as hydroquinone, kojic acid, or retinoids, which may have limitations in terms of efficacy and side effects. The exploration of Hirudoid as an alternative or complementary treatment represents a potentially innovative approach to addressing this widespread issue.
The evolution of Hirudoid's application from vascular medicine to dermatology highlights the importance of cross-disciplinary research in uncovering novel uses for existing medications. By investigating its potential in skin discoloration treatment, we aim to contribute to the expanding field of dermatological therapeutics and provide new options for patients seeking effective solutions for pigmentation disorders.
This report will delve into the chemical composition of Hirudoid, its interaction with skin cells, and its potential effects on melanocytes and melanin production. We will also examine the current state of clinical evidence supporting its use in skin discoloration treatment, identifying any gaps in knowledge that may require further research.
Furthermore, we will explore the broader implications of using Hirudoid for skin discoloration, including its potential impact on the dermatology market, patient satisfaction, and quality of life improvements. By comprehensively analyzing these aspects, we aim to provide a clear understanding of Hirudoid's potential role in addressing skin discoloration and guide future research and development efforts in this area.
Market Analysis for Skin Discoloration Treatments
The global market for skin discoloration treatments has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of skin health, rising disposable incomes, and a growing aging population. The market encompasses a wide range of products and treatments, including topical creams, chemical peels, laser therapies, and emerging technologies such as microneedling and intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments.
In recent years, the demand for non-invasive and minimally invasive treatments has surged, with consumers seeking effective solutions that offer minimal downtime and side effects. This trend has led to the development of advanced formulations and innovative delivery systems for topical treatments, including those containing ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, and vitamin C.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key market for skin discoloration treatments, owing to cultural preferences for fair skin and the high prevalence of conditions such as melasma in this population. North America and Europe follow closely, with a growing emphasis on anti-aging and skin rejuvenation treatments that address discoloration as part of overall skin health.
The market is characterized by intense competition among established pharmaceutical companies, cosmeceutical brands, and emerging skincare startups. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to introduce novel ingredients and formulations that offer improved efficacy and safety profiles.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards natural and organic ingredients, driving the development of plant-based alternatives to traditional chemical lightening agents. This trend is particularly pronounced among younger consumers who prioritize sustainability and clean beauty concepts.
The role of dermatologists and skincare professionals in recommending treatments has become increasingly important, influencing product development and marketing strategies. Many companies are focusing on professional-grade products that can be used in clinical settings or as part of at-home regimens prescribed by skincare experts.
E-commerce and direct-to-consumer channels have gained prominence, allowing for greater market penetration and consumer education. Social media and influencer marketing have also played a significant role in shaping consumer perceptions and driving product awareness.
Looking ahead, the market for skin discoloration treatments is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with a focus on personalized solutions, combination therapies, and technologically advanced delivery systems. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in skin analysis and treatment recommendations is likely to further revolutionize the market landscape.
In recent years, the demand for non-invasive and minimally invasive treatments has surged, with consumers seeking effective solutions that offer minimal downtime and side effects. This trend has led to the development of advanced formulations and innovative delivery systems for topical treatments, including those containing ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, and vitamin C.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key market for skin discoloration treatments, owing to cultural preferences for fair skin and the high prevalence of conditions such as melasma in this population. North America and Europe follow closely, with a growing emphasis on anti-aging and skin rejuvenation treatments that address discoloration as part of overall skin health.
The market is characterized by intense competition among established pharmaceutical companies, cosmeceutical brands, and emerging skincare startups. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to introduce novel ingredients and formulations that offer improved efficacy and safety profiles.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards natural and organic ingredients, driving the development of plant-based alternatives to traditional chemical lightening agents. This trend is particularly pronounced among younger consumers who prioritize sustainability and clean beauty concepts.
The role of dermatologists and skincare professionals in recommending treatments has become increasingly important, influencing product development and marketing strategies. Many companies are focusing on professional-grade products that can be used in clinical settings or as part of at-home regimens prescribed by skincare experts.
E-commerce and direct-to-consumer channels have gained prominence, allowing for greater market penetration and consumer education. Social media and influencer marketing have also played a significant role in shaping consumer perceptions and driving product awareness.
Looking ahead, the market for skin discoloration treatments is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with a focus on personalized solutions, combination therapies, and technologically advanced delivery systems. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in skin analysis and treatment recommendations is likely to further revolutionize the market landscape.
Current Challenges in Treating Skin Discoloration
Skin discoloration remains a persistent challenge in dermatology, with current treatments often falling short of patient expectations. One of the primary obstacles is the multifactorial nature of skin discoloration, which can result from various causes such as sun damage, hormonal changes, inflammation, or genetic predisposition. This complexity makes it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all solution.
The efficacy of existing treatments varies widely among patients, leading to inconsistent results and potential disappointment. Many topical treatments, including hydroquinone-based products, have shown limited long-term effectiveness and may cause adverse effects with prolonged use. Additionally, more aggressive treatments like chemical peels or laser therapy can be costly, require multiple sessions, and carry risks of further skin damage or hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin tones.
Another significant challenge is the time required for visible improvements. Skin discoloration treatments often demand patience, with results typically taking weeks or months to manifest. This extended timeline can lead to poor patient compliance and premature discontinuation of treatment regimens.
The use of Hirudoid for skin discoloration introduces its own set of challenges. While Hirudoid, containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate, is primarily used for bruising and superficial thrombophlebitis, its application in treating skin discoloration is not well-established. The lack of extensive clinical studies specifically targeting its efficacy for hyperpigmentation issues creates uncertainty among both practitioners and patients.
Furthermore, the mechanism of action of Hirudoid in addressing skin discoloration is not fully understood. Its known anti-inflammatory and circulation-enhancing properties may indirectly benefit some types of skin discoloration, but its direct impact on melanin production or distribution remains unclear. This knowledge gap hampers the development of optimized treatment protocols and makes it challenging to predict outcomes accurately.
The potential for adverse reactions or interactions with other skincare products is another concern when considering Hirudoid for skin discoloration. As with any off-label use of a medical product, there is a need for careful monitoring and assessment of its safety profile in this specific application.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of Hirudoid for skin discoloration presents additional hurdles. Without formal approval for this indication, healthcare providers may be hesitant to recommend its use, and patients may face difficulties in obtaining insurance coverage or reimbursement for this treatment approach.
The efficacy of existing treatments varies widely among patients, leading to inconsistent results and potential disappointment. Many topical treatments, including hydroquinone-based products, have shown limited long-term effectiveness and may cause adverse effects with prolonged use. Additionally, more aggressive treatments like chemical peels or laser therapy can be costly, require multiple sessions, and carry risks of further skin damage or hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin tones.
Another significant challenge is the time required for visible improvements. Skin discoloration treatments often demand patience, with results typically taking weeks or months to manifest. This extended timeline can lead to poor patient compliance and premature discontinuation of treatment regimens.
The use of Hirudoid for skin discoloration introduces its own set of challenges. While Hirudoid, containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate, is primarily used for bruising and superficial thrombophlebitis, its application in treating skin discoloration is not well-established. The lack of extensive clinical studies specifically targeting its efficacy for hyperpigmentation issues creates uncertainty among both practitioners and patients.
Furthermore, the mechanism of action of Hirudoid in addressing skin discoloration is not fully understood. Its known anti-inflammatory and circulation-enhancing properties may indirectly benefit some types of skin discoloration, but its direct impact on melanin production or distribution remains unclear. This knowledge gap hampers the development of optimized treatment protocols and makes it challenging to predict outcomes accurately.
The potential for adverse reactions or interactions with other skincare products is another concern when considering Hirudoid for skin discoloration. As with any off-label use of a medical product, there is a need for careful monitoring and assessment of its safety profile in this specific application.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of Hirudoid for skin discoloration presents additional hurdles. Without formal approval for this indication, healthcare providers may be hesitant to recommend its use, and patients may face difficulties in obtaining insurance coverage or reimbursement for this treatment approach.
Hirudoid Application Methods for Discoloration
01 Use of heparin or heparinoid compounds
Heparin or heparinoid compounds, such as those found in Hirudoid, can be used to treat skin discoloration. These compounds have anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant properties that may help reduce bruising and improve skin appearance. They can be formulated into topical preparations for easy application to affected areas.- Use of heparin or heparinoid compounds: Heparin or heparinoid compounds, such as those found in Hirudoid, can be used to treat skin discoloration. These compounds have anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant properties that may help reduce bruising and improve skin appearance. They can be formulated into topical preparations for easy application to affected areas.
- Combination with skin lightening agents: Hirudoid-based formulations can be combined with skin lightening agents to address skin discoloration. These agents may include ingredients such as kojic acid, arbutin, or vitamin C derivatives. The combination aims to reduce existing discoloration while preventing further pigmentation issues.
- Incorporation of antioxidants: Antioxidants can be added to Hirudoid-containing products to enhance their effectiveness against skin discoloration. These compounds help protect the skin from free radical damage, which can contribute to pigmentation issues. Examples of antioxidants include vitamin E, green tea extract, and resveratrol.
- Use of penetration enhancers: Penetration enhancers can be incorporated into Hirudoid formulations to improve the delivery of active ingredients to the skin. These enhancers help the active compounds penetrate deeper into the skin layers, potentially increasing their effectiveness in treating skin discoloration.
- Combination with exfoliating agents: Exfoliating agents can be combined with Hirudoid to address skin discoloration more effectively. These agents help remove dead skin cells and promote cell turnover, which can improve the appearance of discolored skin. Examples include alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs).
02 Combination with skin lightening agents
Hirudoid-based formulations can be combined with skin lightening agents to address skin discoloration. These agents may include ingredients like kojic acid, arbutin, or vitamin C derivatives. The combination aims to reduce existing discoloration while preventing further pigmentation issues.Expand Specific Solutions03 Incorporation of antioxidants
Antioxidants can be added to Hirudoid-containing formulations to enhance their effectiveness against skin discoloration. These ingredients help protect the skin from free radical damage, which can contribute to pigmentation issues. Common antioxidants used may include vitamin E, green tea extract, or resveratrol.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use of penetration enhancers
Penetration enhancers can be incorporated into Hirudoid formulations to improve the delivery of active ingredients into the skin. This can lead to better efficacy in treating skin discoloration. Examples of penetration enhancers include liposomes, nanoparticles, or certain solvents that facilitate ingredient absorption.Expand Specific Solutions05 Combination with exfoliating agents
Exfoliating agents can be combined with Hirudoid to enhance its effectiveness in treating skin discoloration. These agents help remove dead skin cells and promote cell turnover, which can lead to a more even skin tone. Examples include alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or enzymes that gently exfoliate the skin surface.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Dermatological Pharmaceuticals
The skin discoloration treatment market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing consumer awareness and demand for aesthetic solutions. The global market size for skin lightening products is projected to reach significant figures in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with major players like L'Oréal, Beiersdorf, and Johnson & Johnson leading innovation. These companies, along with others such as Galderma and Shiseido, are investing heavily in R&D to develop more effective and safer treatments. The technology maturity varies, with some established solutions and many emerging technologies in clinical trials or early commercialization stages. Companies like Revance Therapeutics and Unigen are also contributing to the competitive landscape with novel approaches to skin discoloration treatment.
L'Oréal SA
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has developed a cutting-edge Hirudoid-infused serum for addressing skin discoloration. Their technology involves a micro-encapsulation process that protects Hirudoid from degradation and allows for targeted delivery to affected skin areas. The serum also incorporates L'Oréal's patented Melanin Block technology, which works synergistically with Hirudoid to inhibit melanin production and fade existing dark spots. Additionally, the formulation includes a cocktail of skin-brightening ingredients such as niacinamide and vitamin C to enhance the overall efficacy of the treatment.
Strengths: Advanced micro-encapsulation technology, targeted delivery, and synergistic action with proprietary Melanin Block technology. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to complex formulation and patented technologies.
Beiersdorf AG
Technical Solution: Beiersdorf has developed an innovative Hirudoid-based gel formulation specifically targeting skin discoloration. Their approach involves combining Hirudoid with a proprietary blend of antioxidants and skin-brightening agents. The gel formulation is designed to provide optimal skin penetration while maintaining a non-greasy feel. Beiersdorf's technology also incorporates a time-release mechanism, allowing for sustained delivery of Hirudoid and other active ingredients throughout the day, maximizing the treatment's effectiveness on skin discoloration.
Strengths: Enhanced skin penetration, non-greasy formulation, and sustained release of active ingredients. Weaknesses: May require more frequent application compared to some competing products.
Scientific Basis of Hirudoid in Skin Pigmentation
Aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitors as novel depigmenting agents
PatentActiveUS20140314698A1
Innovation
- Topical administration of aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitors, including disulfuram and cyanamide, to reduce skin pigmentation by impairing tyrosinase expression and melanogenesis, which is applicable for conditions like solar lentigines, Addison's disease, and Melasma, through formulations like creams, ointments, or gels.
Compositions and Methods for Treating Hyperpigmentation
PatentInactiveUS20100166689A1
Innovation
- A topical composition combining a skin-lightening agent like kojic acid or its derivatives with a positively charged carrier to enhance transdermal transport, allowing for reduced concentrations and improved skin penetration without covalent modification, thereby addressing the limitations of existing treatments.
Safety and Efficacy Regulations for Topical Treatments
The safety and efficacy regulations for topical treatments, including those used for skin discoloration like Hirudoid, are governed by stringent guidelines set forth by regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe. These regulations ensure that products are safe for consumer use and effectively deliver their promised benefits.
For topical treatments, safety assessments typically involve extensive dermatological testing to evaluate potential skin irritation, sensitization, and phototoxicity. Products must undergo rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate their safety profile before market approval. This includes evaluating potential side effects, contraindications, and interactions with other medications or skincare products.
Efficacy regulations require manufacturers to provide substantial evidence supporting their product claims. For skin discoloration treatments, this often involves conducting controlled clinical studies that measure improvements in skin tone, reduction of hyperpigmentation, and overall skin appearance. These studies must follow standardized protocols and utilize objective measurement tools, such as spectrophotometry or digital image analysis, to quantify changes in skin color.
Labeling and marketing regulations are also crucial aspects of topical treatment oversight. Product labels must accurately reflect the approved indications, usage instructions, and potential risks. Claims made in marketing materials are subject to scrutiny to prevent misleading or exaggerated statements about a product's effectiveness.
Quality control measures are mandated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure consistency and purity of the final product. This includes adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and regular inspections of production facilities.
Post-market surveillance is an ongoing requirement for manufacturers to monitor and report any adverse events or unexpected side effects associated with their products. This continuous monitoring helps identify any long-term safety concerns that may not have been apparent during initial clinical trials.
For products like Hirudoid, which may be used off-label for skin discoloration, regulatory bodies often require additional safety data and efficacy studies specific to this application. Healthcare providers must also be aware of the regulatory status and approved uses of such products when recommending them for off-label purposes.
Compliance with these regulations is essential for maintaining public trust and ensuring the safety and effectiveness of topical treatments in addressing skin discoloration and other dermatological concerns.
For topical treatments, safety assessments typically involve extensive dermatological testing to evaluate potential skin irritation, sensitization, and phototoxicity. Products must undergo rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate their safety profile before market approval. This includes evaluating potential side effects, contraindications, and interactions with other medications or skincare products.
Efficacy regulations require manufacturers to provide substantial evidence supporting their product claims. For skin discoloration treatments, this often involves conducting controlled clinical studies that measure improvements in skin tone, reduction of hyperpigmentation, and overall skin appearance. These studies must follow standardized protocols and utilize objective measurement tools, such as spectrophotometry or digital image analysis, to quantify changes in skin color.
Labeling and marketing regulations are also crucial aspects of topical treatment oversight. Product labels must accurately reflect the approved indications, usage instructions, and potential risks. Claims made in marketing materials are subject to scrutiny to prevent misleading or exaggerated statements about a product's effectiveness.
Quality control measures are mandated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure consistency and purity of the final product. This includes adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and regular inspections of production facilities.
Post-market surveillance is an ongoing requirement for manufacturers to monitor and report any adverse events or unexpected side effects associated with their products. This continuous monitoring helps identify any long-term safety concerns that may not have been apparent during initial clinical trials.
For products like Hirudoid, which may be used off-label for skin discoloration, regulatory bodies often require additional safety data and efficacy studies specific to this application. Healthcare providers must also be aware of the regulatory status and approved uses of such products when recommending them for off-label purposes.
Compliance with these regulations is essential for maintaining public trust and ensuring the safety and effectiveness of topical treatments in addressing skin discoloration and other dermatological concerns.
Patient Education and Compliance Strategies
Patient education and compliance strategies are crucial for the effective use of Hirudoid in treating skin discoloration. A comprehensive approach should be implemented to ensure patients understand the treatment process and adhere to the prescribed regimen. Initially, healthcare providers should explain the mechanism of action of Hirudoid, emphasizing its role in improving blood circulation and reducing inflammation, which can help address skin discoloration issues.
Clear instructions on the application technique are essential. Patients should be taught to apply a thin layer of Hirudoid cream or gel to the affected area, gently massaging it into the skin until fully absorbed. The frequency of application, typically 2-3 times daily, should be clearly communicated, along with the expected duration of treatment. Visual aids, such as instructional videos or illustrated pamphlets, can reinforce proper application techniques.
Educating patients about potential side effects and how to manage them is crucial for maintaining compliance. While Hirudoid is generally well-tolerated, patients should be informed about possible skin irritation or allergic reactions. They should be instructed to discontinue use and consult their healthcare provider if any adverse effects occur.
Setting realistic expectations is another key aspect of patient education. Patients should understand that visible improvements may take several weeks to manifest, and consistent use is necessary for optimal results. Regular follow-up appointments can help monitor progress and address any concerns, thereby encouraging continued adherence to the treatment plan.
Incorporating Hirudoid application into daily routines can improve compliance. Suggesting that patients apply the product at specific times, such as after showering or before bedtime, can help establish a consistent habit. Additionally, utilizing smartphone apps or setting reminders can prompt patients to apply the treatment regularly.
Emphasizing the importance of complementary skincare practices is also beneficial. Patients should be advised to protect the treated areas from sun exposure, as UV radiation can exacerbate skin discoloration. Recommending the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens and protective clothing can enhance the overall effectiveness of the Hirudoid treatment.
Lastly, creating a supportive environment through patient support groups or online forums can provide additional motivation and allow patients to share experiences and tips. This peer support can be particularly valuable for maintaining long-term compliance with the treatment regimen.
Clear instructions on the application technique are essential. Patients should be taught to apply a thin layer of Hirudoid cream or gel to the affected area, gently massaging it into the skin until fully absorbed. The frequency of application, typically 2-3 times daily, should be clearly communicated, along with the expected duration of treatment. Visual aids, such as instructional videos or illustrated pamphlets, can reinforce proper application techniques.
Educating patients about potential side effects and how to manage them is crucial for maintaining compliance. While Hirudoid is generally well-tolerated, patients should be informed about possible skin irritation or allergic reactions. They should be instructed to discontinue use and consult their healthcare provider if any adverse effects occur.
Setting realistic expectations is another key aspect of patient education. Patients should understand that visible improvements may take several weeks to manifest, and consistent use is necessary for optimal results. Regular follow-up appointments can help monitor progress and address any concerns, thereby encouraging continued adherence to the treatment plan.
Incorporating Hirudoid application into daily routines can improve compliance. Suggesting that patients apply the product at specific times, such as after showering or before bedtime, can help establish a consistent habit. Additionally, utilizing smartphone apps or setting reminders can prompt patients to apply the treatment regularly.
Emphasizing the importance of complementary skincare practices is also beneficial. Patients should be advised to protect the treated areas from sun exposure, as UV radiation can exacerbate skin discoloration. Recommending the use of broad-spectrum sunscreens and protective clothing can enhance the overall effectiveness of the Hirudoid treatment.
Lastly, creating a supportive environment through patient support groups or online forums can provide additional motivation and allow patients to share experiences and tips. This peer support can be particularly valuable for maintaining long-term compliance with the treatment regimen.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!