How to Use Hirudoid as a Preventative Measure?
JUN 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hirudoid Background and Objectives
Hirudoid, a topical gel containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), has a rich history in medical applications, particularly in the treatment of venous disorders and bruising. Originally developed in the mid-20th century, this compound has gained significant attention for its potential preventative properties. The evolution of Hirudoid's use has been driven by a growing understanding of its mechanism of action and the increasing prevalence of conditions it may help prevent.
The primary objective in exploring Hirudoid as a preventative measure is to leverage its anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant properties to mitigate the risk of various vascular and soft tissue complications. This goal aligns with the broader trend in healthcare towards proactive disease prevention rather than reactive treatment. By investigating Hirudoid's preventative applications, researchers aim to expand its utility beyond its traditional therapeutic roles.
The technical progression of Hirudoid has been marked by advancements in formulation and delivery methods. Initial versions were basic topical preparations, but over time, enhanced formulations have been developed to improve skin penetration and extend the duration of action. These improvements have opened up new possibilities for preventative use, particularly in high-risk populations or situations where vascular or soft tissue damage is anticipated.
Current research objectives focus on elucidating the optimal dosing regimens and application methods for preventative use. This includes investigating the frequency of application, the ideal timing relative to potential injury or stress, and the duration of preventative treatment needed to achieve meaningful outcomes. Additionally, there is a growing interest in understanding how Hirudoid's preventative effects may vary across different patient populations and risk factors.
The exploration of Hirudoid as a preventative measure also intersects with broader technological trends in personalized medicine and wearable health monitoring devices. There is potential for integrating Hirudoid application with real-time health data to optimize its preventative efficacy. This convergence of pharmaceutical and digital health technologies represents an exciting frontier in the evolution of Hirudoid's use.
As research progresses, the technical goals extend to developing more sophisticated delivery systems, such as transdermal patches or micro-needle arrays, which could provide controlled, sustained release of the active compound. These innovations aim to enhance the convenience and efficacy of Hirudoid as a preventative tool, potentially expanding its application to a wider range of scenarios and user groups.
The primary objective in exploring Hirudoid as a preventative measure is to leverage its anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant properties to mitigate the risk of various vascular and soft tissue complications. This goal aligns with the broader trend in healthcare towards proactive disease prevention rather than reactive treatment. By investigating Hirudoid's preventative applications, researchers aim to expand its utility beyond its traditional therapeutic roles.
The technical progression of Hirudoid has been marked by advancements in formulation and delivery methods. Initial versions were basic topical preparations, but over time, enhanced formulations have been developed to improve skin penetration and extend the duration of action. These improvements have opened up new possibilities for preventative use, particularly in high-risk populations or situations where vascular or soft tissue damage is anticipated.
Current research objectives focus on elucidating the optimal dosing regimens and application methods for preventative use. This includes investigating the frequency of application, the ideal timing relative to potential injury or stress, and the duration of preventative treatment needed to achieve meaningful outcomes. Additionally, there is a growing interest in understanding how Hirudoid's preventative effects may vary across different patient populations and risk factors.
The exploration of Hirudoid as a preventative measure also intersects with broader technological trends in personalized medicine and wearable health monitoring devices. There is potential for integrating Hirudoid application with real-time health data to optimize its preventative efficacy. This convergence of pharmaceutical and digital health technologies represents an exciting frontier in the evolution of Hirudoid's use.
As research progresses, the technical goals extend to developing more sophisticated delivery systems, such as transdermal patches or micro-needle arrays, which could provide controlled, sustained release of the active compound. These innovations aim to enhance the convenience and efficacy of Hirudoid as a preventative tool, potentially expanding its application to a wider range of scenarios and user groups.
Market Analysis for Preventative Hirudoid Use
The market for preventative use of Hirudoid presents significant growth potential, driven by increasing awareness of its benefits in reducing bruising and swelling. The global market for topical heparin products, including Hirudoid, is expected to expand as consumers seek proactive measures to maintain skin health and prevent complications from minor injuries.
A key driver of market growth is the aging population, particularly in developed countries. Older adults are more prone to bruising and slower healing, making them a prime target demographic for preventative Hirudoid use. This demographic trend aligns with the growing emphasis on preventive healthcare, creating a favorable environment for market expansion.
The sports and fitness industry represents another substantial market segment. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are increasingly looking for products that can help prevent or minimize bruising from intense physical activities. Hirudoid's potential to reduce the appearance and duration of bruises makes it an attractive option for this consumer group.
The cosmetic and aesthetic medicine sector also shows promise for preventative Hirudoid use. As minimally invasive cosmetic procedures become more popular, there is a growing demand for products that can reduce post-procedure bruising and swelling. Hirudoid's properties make it a valuable addition to post-treatment care protocols.
Geographically, developed markets such as North America and Europe are expected to lead in adoption due to higher healthcare spending and greater consumer awareness. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America present significant growth opportunities as healthcare standards improve and disposable incomes rise.
The over-the-counter (OTC) segment is likely to drive much of the market growth for preventative Hirudoid use. Easy accessibility and the trend towards self-care are encouraging consumers to incorporate such products into their daily routines without the need for a prescription.
Market challenges include competition from alternative products such as arnica-based creams and the need for extensive consumer education about the benefits of preventative use. Additionally, regulatory considerations regarding marketing claims for preventative use may impact market strategies in some regions.
Overall, the market for preventative Hirudoid use shows strong potential for growth, supported by demographic trends, increasing health consciousness, and expanding applications across various consumer segments. To capitalize on this potential, manufacturers and marketers will need to focus on consumer education, product innovation, and strategic partnerships within the healthcare and wellness industries.
A key driver of market growth is the aging population, particularly in developed countries. Older adults are more prone to bruising and slower healing, making them a prime target demographic for preventative Hirudoid use. This demographic trend aligns with the growing emphasis on preventive healthcare, creating a favorable environment for market expansion.
The sports and fitness industry represents another substantial market segment. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are increasingly looking for products that can help prevent or minimize bruising from intense physical activities. Hirudoid's potential to reduce the appearance and duration of bruises makes it an attractive option for this consumer group.
The cosmetic and aesthetic medicine sector also shows promise for preventative Hirudoid use. As minimally invasive cosmetic procedures become more popular, there is a growing demand for products that can reduce post-procedure bruising and swelling. Hirudoid's properties make it a valuable addition to post-treatment care protocols.
Geographically, developed markets such as North America and Europe are expected to lead in adoption due to higher healthcare spending and greater consumer awareness. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America present significant growth opportunities as healthcare standards improve and disposable incomes rise.
The over-the-counter (OTC) segment is likely to drive much of the market growth for preventative Hirudoid use. Easy accessibility and the trend towards self-care are encouraging consumers to incorporate such products into their daily routines without the need for a prescription.
Market challenges include competition from alternative products such as arnica-based creams and the need for extensive consumer education about the benefits of preventative use. Additionally, regulatory considerations regarding marketing claims for preventative use may impact market strategies in some regions.
Overall, the market for preventative Hirudoid use shows strong potential for growth, supported by demographic trends, increasing health consciousness, and expanding applications across various consumer segments. To capitalize on this potential, manufacturers and marketers will need to focus on consumer education, product innovation, and strategic partnerships within the healthcare and wellness industries.
Current Challenges in Preventative Hirudoid Application
The preventative application of Hirudoid faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and effectiveness. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of comprehensive clinical studies specifically focused on its preventative use. While Hirudoid has been extensively studied for its therapeutic effects on existing conditions, there is a dearth of robust scientific evidence supporting its efficacy as a preventative measure.
Another challenge lies in determining the optimal dosage and frequency of application for preventative purposes. The current guidelines for Hirudoid use are primarily tailored for treating existing conditions, and there is uncertainty regarding the appropriate regimen for prevention. This lack of standardization makes it difficult for healthcare providers to confidently prescribe Hirudoid as a preventative measure.
The potential for side effects and long-term consequences of prolonged preventative use of Hirudoid is also a concern. While the medication is generally well-tolerated, the effects of continuous, long-term application for prevention have not been thoroughly investigated. This uncertainty raises questions about the safety profile of Hirudoid when used preventatively over extended periods.
Cost-effectiveness is another significant challenge. Preventative use of Hirudoid would likely require ongoing application, which could result in substantial cumulative costs for patients. Without clear evidence of its preventative efficacy, it becomes difficult to justify these expenses, especially when compared to other preventative measures or treatments.
Regulatory hurdles also pose a challenge to the preventative use of Hirudoid. Most regulatory approvals for the medication are based on its therapeutic applications, and expanding its use to prevention may require additional clinical trials and regulatory reviews. This process can be time-consuming and expensive, potentially deterring manufacturers from pursuing this avenue.
Patient compliance and adherence to a preventative Hirudoid regimen present another challenge. Unlike acute treatments, preventative measures often require long-term commitment from patients. Ensuring consistent application over extended periods can be difficult, particularly if immediate benefits are not apparent.
Lastly, there is a need for better understanding of the specific conditions and patient populations that would benefit most from preventative Hirudoid use. Without clear guidelines on target groups, healthcare providers may struggle to identify appropriate candidates for preventative application, leading to potential overuse or underutilization of the medication.
Another challenge lies in determining the optimal dosage and frequency of application for preventative purposes. The current guidelines for Hirudoid use are primarily tailored for treating existing conditions, and there is uncertainty regarding the appropriate regimen for prevention. This lack of standardization makes it difficult for healthcare providers to confidently prescribe Hirudoid as a preventative measure.
The potential for side effects and long-term consequences of prolonged preventative use of Hirudoid is also a concern. While the medication is generally well-tolerated, the effects of continuous, long-term application for prevention have not been thoroughly investigated. This uncertainty raises questions about the safety profile of Hirudoid when used preventatively over extended periods.
Cost-effectiveness is another significant challenge. Preventative use of Hirudoid would likely require ongoing application, which could result in substantial cumulative costs for patients. Without clear evidence of its preventative efficacy, it becomes difficult to justify these expenses, especially when compared to other preventative measures or treatments.
Regulatory hurdles also pose a challenge to the preventative use of Hirudoid. Most regulatory approvals for the medication are based on its therapeutic applications, and expanding its use to prevention may require additional clinical trials and regulatory reviews. This process can be time-consuming and expensive, potentially deterring manufacturers from pursuing this avenue.
Patient compliance and adherence to a preventative Hirudoid regimen present another challenge. Unlike acute treatments, preventative measures often require long-term commitment from patients. Ensuring consistent application over extended periods can be difficult, particularly if immediate benefits are not apparent.
Lastly, there is a need for better understanding of the specific conditions and patient populations that would benefit most from preventative Hirudoid use. Without clear guidelines on target groups, healthcare providers may struggle to identify appropriate candidates for preventative application, leading to potential overuse or underutilization of the medication.
Key Players in Hirudoid Production
The use of Hirudoid as a preventative measure is currently in an early development stage, with a growing market potential due to increased interest in proactive healthcare. The global market for such preventative treatments is expanding, driven by aging populations and a focus on wellness. Technologically, the application is still evolving, with companies like Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Novartis AG, and GlaxoSmithKline Intellectual Property Development Ltd. leading research efforts. These firms are exploring innovative formulations and delivery methods to enhance Hirudoid's preventative efficacy. However, the technology's maturity varies across different preventative applications, with some areas more advanced than others.
Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Takeda has developed a proprietary formulation of Hirudoid that enhances its preventative effects. Their approach involves incorporating the active ingredient, mucopolysaccharide polysulfate, into a novel delivery system that improves skin penetration and prolongs the duration of action. This formulation is designed to be applied as a preventative measure, creating a protective barrier on the skin that helps prevent bruising, swelling, and inflammation before they occur. The company has conducted clinical trials to demonstrate the efficacy of this preventative application, showing significant reductions in the incidence and severity of bruising in high-risk patients.
Strengths: Enhanced skin penetration, prolonged duration of action, and clinically proven preventative efficacy. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to advanced formulation, may require more frequent application for optimal prevention.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis has developed an innovative approach to using Hirudoid as a preventative measure by combining it with their patented nanoparticle technology. This method encapsulates the mucopolysaccharide polysulfate in biodegradable nanoparticles, allowing for a controlled release of the active ingredient over an extended period. The nanoparticles are designed to penetrate deeper into the skin layers, providing a more comprehensive preventative effect. Novartis has also incorporated antioxidants and skin-nourishing ingredients into the formulation to enhance its overall protective properties. Clinical studies have shown that this advanced formulation significantly reduces the risk of bruising and promotes faster healing when applied preventatively.
Strengths: Controlled release technology, deeper skin penetration, and added skin-nourishing benefits. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process may lead to higher production costs, potential for nanoparticle accumulation in long-term use.
Core Research on Hirudoid Efficacy
Sphingolipids in treatment and prevention of steatosis and of steatosis or of hepatotoxicity and its sequelae
PatentInactiveEP1830829A1
Innovation
- The use of sphingolipids, such as phytosphingosine, sphingosine, sphinganine, ceramide, and sphingomyelin, in food items and medicaments to prevent and treat hepatic steatosis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis by modulating lipid metabolism and reducing liver toxicity.
Treatment and/or prevention of a viral infection
PatentPendingUS20230355602A1
Innovation
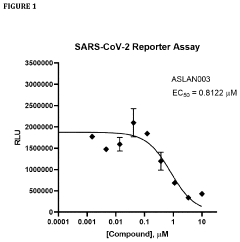
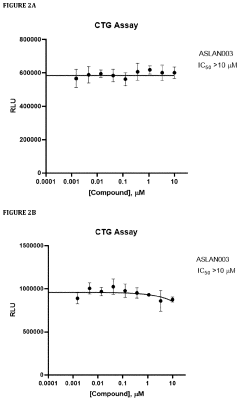
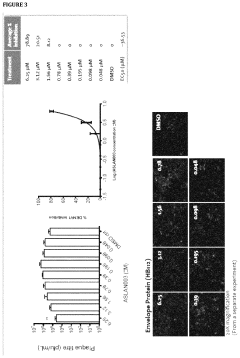
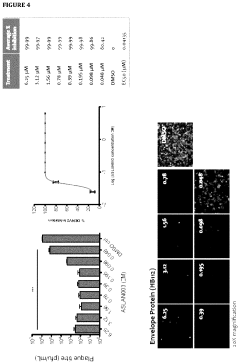
- Administration of a DHODH inhibitor, specifically 2-(3,5-difluoro-3′methoxybiphenyl-4-ylamino)nicotinic acid (ASLAN003), which targets host cell metabolism to inhibit viral replication, activate innate immune responses, and reduce inflammatory responses, thereby providing a broad-spectrum antiviral effect independent of virus type or mutation.
Regulatory Framework for Hirudoid Use
The regulatory framework for Hirudoid use as a preventative measure is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental bodies and healthcare organizations. At the federal level, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the approval, marketing, and distribution of Hirudoid. The FDA classifies Hirudoid as a prescription drug, which means its use must be under the supervision of a licensed healthcare professional.
State medical boards and pharmacy boards also contribute to the regulatory landscape by establishing guidelines for prescribing and dispensing Hirudoid. These boards may have specific protocols in place for off-label use of medications, which could apply to the preventative use of Hirudoid. Healthcare providers must adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance and patient safety.
Insurance companies and healthcare payers also influence the regulatory framework by determining coverage policies for preventative use of Hirudoid. These policies often require evidence of medical necessity and may limit the duration or frequency of preventative treatments. Providers and patients must navigate these coverage requirements when considering Hirudoid for preventative purposes.
International regulatory bodies, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA), have their own frameworks for Hirudoid use. These regulations may differ from those in the United States, potentially affecting global research and development efforts related to preventative applications of Hirudoid.
Professional medical associations, such as dermatology and vascular medicine societies, contribute to the regulatory landscape by issuing clinical practice guidelines. These guidelines often inform regulatory decisions and shape the standard of care for preventative treatments. Providers looking to use Hirudoid preventatively should consult these guidelines to ensure their practices align with current recommendations.
Clinical trial regulations also play a significant role in shaping the use of Hirudoid as a preventative measure. The FDA's Investigational New Drug (IND) program governs the conduct of clinical trials for new indications of approved drugs. Researchers exploring preventative applications of Hirudoid must navigate these regulations to generate the necessary evidence for regulatory approval.
Pharmacovigilance regulations require ongoing monitoring and reporting of adverse events associated with Hirudoid use. This system helps regulatory bodies assess the long-term safety profile of the drug, particularly when used in novel preventative applications. Healthcare providers and manufacturers must comply with these reporting requirements to support the continued safe use of Hirudoid.
State medical boards and pharmacy boards also contribute to the regulatory landscape by establishing guidelines for prescribing and dispensing Hirudoid. These boards may have specific protocols in place for off-label use of medications, which could apply to the preventative use of Hirudoid. Healthcare providers must adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance and patient safety.
Insurance companies and healthcare payers also influence the regulatory framework by determining coverage policies for preventative use of Hirudoid. These policies often require evidence of medical necessity and may limit the duration or frequency of preventative treatments. Providers and patients must navigate these coverage requirements when considering Hirudoid for preventative purposes.
International regulatory bodies, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA), have their own frameworks for Hirudoid use. These regulations may differ from those in the United States, potentially affecting global research and development efforts related to preventative applications of Hirudoid.
Professional medical associations, such as dermatology and vascular medicine societies, contribute to the regulatory landscape by issuing clinical practice guidelines. These guidelines often inform regulatory decisions and shape the standard of care for preventative treatments. Providers looking to use Hirudoid preventatively should consult these guidelines to ensure their practices align with current recommendations.
Clinical trial regulations also play a significant role in shaping the use of Hirudoid as a preventative measure. The FDA's Investigational New Drug (IND) program governs the conduct of clinical trials for new indications of approved drugs. Researchers exploring preventative applications of Hirudoid must navigate these regulations to generate the necessary evidence for regulatory approval.
Pharmacovigilance regulations require ongoing monitoring and reporting of adverse events associated with Hirudoid use. This system helps regulatory bodies assess the long-term safety profile of the drug, particularly when used in novel preventative applications. Healthcare providers and manufacturers must comply with these reporting requirements to support the continued safe use of Hirudoid.
Safety and Side Effects of Preventative Hirudoid
The use of Hirudoid as a preventative measure requires careful consideration of its safety profile and potential side effects. While Hirudoid, containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate, has been widely used for its anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic properties, its long-term preventative use necessitates a thorough understanding of associated risks.
Topical application of Hirudoid is generally well-tolerated, with minimal systemic absorption. However, prolonged use may lead to skin sensitization in some individuals. Users should be aware of potential allergic reactions, which may manifest as localized redness, itching, or rash. These symptoms typically subside upon discontinuation of the product.
In rare cases, more severe allergic reactions have been reported, including angioedema and urticaria. Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to mucopolysaccharide polysulfate or any other components of Hirudoid should avoid its use. Healthcare providers should carefully assess individual risk factors before recommending preventative use.
The anticoagulant properties of Hirudoid, while beneficial in certain therapeutic contexts, may pose risks when used preventatively over extended periods. There is a theoretical risk of increased bleeding tendency, particularly in individuals with pre-existing coagulation disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications. Careful monitoring may be necessary for such patients.
Long-term preventative use of Hirudoid has not been extensively studied, and the potential for cumulative effects remains uncertain. Some concerns have been raised regarding the possibility of skin thinning or local atrophy with prolonged application, although evidence for this is limited.
Systemic side effects are rare due to the low absorption rate of topically applied Hirudoid. However, caution is advised in patients with impaired renal function, as the excretion of absorbed mucopolysaccharide polysulfate may be affected.
To mitigate risks, it is recommended to use Hirudoid intermittently rather than continuously for preventative purposes. Regular skin examinations and periodic reassessment of the need for ongoing use should be part of the preventative regimen.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult healthcare providers before using Hirudoid preventatively, as safety data in these populations is limited. While no specific adverse effects have been reported, caution is warranted.
In conclusion, while Hirudoid shows promise as a preventative measure, its use should be balanced against potential risks. Individualized assessment, proper patient education, and regular monitoring are essential to ensure safe and effective preventative application of Hirudoid.
Topical application of Hirudoid is generally well-tolerated, with minimal systemic absorption. However, prolonged use may lead to skin sensitization in some individuals. Users should be aware of potential allergic reactions, which may manifest as localized redness, itching, or rash. These symptoms typically subside upon discontinuation of the product.
In rare cases, more severe allergic reactions have been reported, including angioedema and urticaria. Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to mucopolysaccharide polysulfate or any other components of Hirudoid should avoid its use. Healthcare providers should carefully assess individual risk factors before recommending preventative use.
The anticoagulant properties of Hirudoid, while beneficial in certain therapeutic contexts, may pose risks when used preventatively over extended periods. There is a theoretical risk of increased bleeding tendency, particularly in individuals with pre-existing coagulation disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications. Careful monitoring may be necessary for such patients.
Long-term preventative use of Hirudoid has not been extensively studied, and the potential for cumulative effects remains uncertain. Some concerns have been raised regarding the possibility of skin thinning or local atrophy with prolonged application, although evidence for this is limited.
Systemic side effects are rare due to the low absorption rate of topically applied Hirudoid. However, caution is advised in patients with impaired renal function, as the excretion of absorbed mucopolysaccharide polysulfate may be affected.
To mitigate risks, it is recommended to use Hirudoid intermittently rather than continuously for preventative purposes. Regular skin examinations and periodic reassessment of the need for ongoing use should be part of the preventative regimen.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult healthcare providers before using Hirudoid preventatively, as safety data in these populations is limited. While no specific adverse effects have been reported, caution is warranted.
In conclusion, while Hirudoid shows promise as a preventative measure, its use should be balanced against potential risks. Individualized assessment, proper patient education, and regular monitoring are essential to ensure safe and effective preventative application of Hirudoid.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!