Hirudoid: Transforming Scar Management
JUN 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hirudoid in Scar Management: Background and Objectives
Hirudoid, a topical medication containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), has emerged as a promising agent in the field of scar management. The evolution of scar treatment has been driven by the need to improve both functional and aesthetic outcomes for patients. Historically, scar management has progressed from basic wound care to more sophisticated approaches involving various pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions.
The primary objective of researching Hirudoid in scar management is to explore its potential to transform current treatment paradigms. This investigation aims to evaluate the efficacy of Hirudoid in reducing scar formation, improving scar appearance, and enhancing overall tissue healing. By focusing on Hirudoid, researchers seek to address the limitations of existing scar management techniques and potentially offer a more effective, accessible, and patient-friendly solution.
Scar formation is a complex biological process involving multiple cellular and molecular mechanisms. Traditional scar management strategies have often yielded inconsistent results, highlighting the need for innovative approaches. Hirudoid's unique composition, particularly its mucopolysaccharide polysulfate content, presents an opportunity to target specific aspects of the scarring process, potentially leading to superior outcomes.
The technical landscape surrounding scar management has seen significant advancements in recent years, with a growing emphasis on understanding the underlying pathophysiology of scar formation. This has led to the development of targeted therapies, including topical agents, that aim to modulate the wound healing process and minimize excessive scarring. Hirudoid's potential in this arena stems from its ability to influence various aspects of tissue repair and regeneration.
As the global burden of scars continues to grow, driven by factors such as increased surgical procedures and traumatic injuries, the demand for effective scar management solutions has intensified. This has created a fertile ground for research into novel treatments like Hirudoid. The exploration of Hirudoid's role in scar management aligns with the broader trend towards personalized medicine and targeted therapeutic approaches in dermatology and wound care.
By investigating Hirudoid's mechanisms of action, optimal application protocols, and long-term efficacy, this research aims to establish a comprehensive understanding of its potential in transforming scar management. The ultimate goal is to develop evidence-based guidelines for incorporating Hirudoid into clinical practice, potentially revolutionizing the approach to scar prevention and treatment across various medical specialties.
The primary objective of researching Hirudoid in scar management is to explore its potential to transform current treatment paradigms. This investigation aims to evaluate the efficacy of Hirudoid in reducing scar formation, improving scar appearance, and enhancing overall tissue healing. By focusing on Hirudoid, researchers seek to address the limitations of existing scar management techniques and potentially offer a more effective, accessible, and patient-friendly solution.
Scar formation is a complex biological process involving multiple cellular and molecular mechanisms. Traditional scar management strategies have often yielded inconsistent results, highlighting the need for innovative approaches. Hirudoid's unique composition, particularly its mucopolysaccharide polysulfate content, presents an opportunity to target specific aspects of the scarring process, potentially leading to superior outcomes.
The technical landscape surrounding scar management has seen significant advancements in recent years, with a growing emphasis on understanding the underlying pathophysiology of scar formation. This has led to the development of targeted therapies, including topical agents, that aim to modulate the wound healing process and minimize excessive scarring. Hirudoid's potential in this arena stems from its ability to influence various aspects of tissue repair and regeneration.
As the global burden of scars continues to grow, driven by factors such as increased surgical procedures and traumatic injuries, the demand for effective scar management solutions has intensified. This has created a fertile ground for research into novel treatments like Hirudoid. The exploration of Hirudoid's role in scar management aligns with the broader trend towards personalized medicine and targeted therapeutic approaches in dermatology and wound care.
By investigating Hirudoid's mechanisms of action, optimal application protocols, and long-term efficacy, this research aims to establish a comprehensive understanding of its potential in transforming scar management. The ultimate goal is to develop evidence-based guidelines for incorporating Hirudoid into clinical practice, potentially revolutionizing the approach to scar prevention and treatment across various medical specialties.
Market Analysis for Advanced Scar Treatment Solutions
The global market for advanced scar treatment solutions has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of aesthetic concerns and the rising prevalence of skin injuries and surgeries. The scar management market, which includes products like Hirudoid, is expected to continue its upward trajectory due to several key factors.
Firstly, the growing number of surgical procedures worldwide is a major driver for the scar treatment market. As more people undergo both elective and non-elective surgeries, the demand for effective scar management solutions increases. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed countries with aging populations and in emerging economies where access to medical procedures is expanding.
Additionally, the rising incidence of skin injuries from accidents, burns, and various dermatological conditions contributes to the market's growth. These injuries often result in scarring, creating a sustained demand for advanced treatment options. The increasing focus on personal appearance and the psychological impact of visible scars further fuels the market, as consumers seek solutions to improve their quality of life and self-esteem.
The market for scar treatment is also benefiting from technological advancements in the field. Innovative products like Hirudoid, which contains mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), represent a shift towards more effective and scientifically-backed solutions. These advanced treatments offer improved outcomes compared to traditional methods, attracting both medical professionals and patients.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards non-invasive and minimally invasive treatments, which aligns well with topical solutions like Hirudoid. This trend is supported by the growing desire for treatments that offer effective results with minimal downtime and reduced risk of complications.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms. Competition is intensifying as companies invest in research and development to create more effective scar management products. This competitive environment is likely to drive further innovation and potentially lead to more affordable treatment options in the future.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the scar treatment market, owing to high healthcare expenditure and greater awareness of advanced treatment options. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a significant growth area, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing adoption of Western beauty standards.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of advanced treatments and varying regulatory standards across different regions. These factors can limit market penetration, particularly in developing economies. However, ongoing research and development efforts are expected to address these challenges, potentially expanding market access and improving treatment efficacy.
Firstly, the growing number of surgical procedures worldwide is a major driver for the scar treatment market. As more people undergo both elective and non-elective surgeries, the demand for effective scar management solutions increases. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed countries with aging populations and in emerging economies where access to medical procedures is expanding.
Additionally, the rising incidence of skin injuries from accidents, burns, and various dermatological conditions contributes to the market's growth. These injuries often result in scarring, creating a sustained demand for advanced treatment options. The increasing focus on personal appearance and the psychological impact of visible scars further fuels the market, as consumers seek solutions to improve their quality of life and self-esteem.
The market for scar treatment is also benefiting from technological advancements in the field. Innovative products like Hirudoid, which contains mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), represent a shift towards more effective and scientifically-backed solutions. These advanced treatments offer improved outcomes compared to traditional methods, attracting both medical professionals and patients.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards non-invasive and minimally invasive treatments, which aligns well with topical solutions like Hirudoid. This trend is supported by the growing desire for treatments that offer effective results with minimal downtime and reduced risk of complications.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms. Competition is intensifying as companies invest in research and development to create more effective scar management products. This competitive environment is likely to drive further innovation and potentially lead to more affordable treatment options in the future.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the scar treatment market, owing to high healthcare expenditure and greater awareness of advanced treatment options. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a significant growth area, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing adoption of Western beauty standards.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of advanced treatments and varying regulatory standards across different regions. These factors can limit market penetration, particularly in developing economies. However, ongoing research and development efforts are expected to address these challenges, potentially expanding market access and improving treatment efficacy.
Current Challenges in Scar Management Therapies
Scar management remains a significant challenge in modern medicine, with current therapies facing several limitations. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of scar formation, which involves intricate biological processes that are not fully understood. This lack of comprehensive knowledge hinders the development of targeted and effective treatments.
The heterogeneity of scars presents another major challenge. Different types of scars, such as hypertrophic scars, keloids, and atrophic scars, require distinct approaches. This diversity makes it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all solution, necessitating personalized treatment strategies that are often time-consuming and costly.
Current therapies also struggle with balancing efficacy and safety. Many existing treatments, such as corticosteroid injections or laser therapy, can be effective but may carry risks of side effects or complications. Finding interventions that provide significant improvement without compromising patient safety remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
The long-term nature of scar management poses additional difficulties. Scars can continue to evolve for months or even years after the initial injury, requiring prolonged treatment periods. This extended timeline not only impacts patient compliance but also complicates the assessment of treatment efficacy, as improvements may be gradual and difficult to quantify.
Another significant hurdle is the limited ability to prevent scar formation entirely. While some interventions can improve the appearance of scars, completely avoiding their formation, especially in cases of severe injuries or surgeries, remains elusive. This gap in preventive measures highlights the need for innovative approaches that can intervene in the early stages of wound healing.
The psychological impact of scars adds another layer of complexity to management strategies. Beyond physical appearance, scars can significantly affect a patient's quality of life, self-esteem, and mental health. Addressing these psychological aspects alongside physical treatment is crucial but often overlooked in current therapies.
Lastly, the cost and accessibility of advanced scar management treatments present significant challenges. Many effective therapies, such as advanced laser treatments or specialized dressings, can be expensive and not widely available, limiting their use to a small portion of patients who need them. This disparity in access to optimal care underscores the need for more cost-effective and widely accessible treatment options.
The heterogeneity of scars presents another major challenge. Different types of scars, such as hypertrophic scars, keloids, and atrophic scars, require distinct approaches. This diversity makes it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all solution, necessitating personalized treatment strategies that are often time-consuming and costly.
Current therapies also struggle with balancing efficacy and safety. Many existing treatments, such as corticosteroid injections or laser therapy, can be effective but may carry risks of side effects or complications. Finding interventions that provide significant improvement without compromising patient safety remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
The long-term nature of scar management poses additional difficulties. Scars can continue to evolve for months or even years after the initial injury, requiring prolonged treatment periods. This extended timeline not only impacts patient compliance but also complicates the assessment of treatment efficacy, as improvements may be gradual and difficult to quantify.
Another significant hurdle is the limited ability to prevent scar formation entirely. While some interventions can improve the appearance of scars, completely avoiding their formation, especially in cases of severe injuries or surgeries, remains elusive. This gap in preventive measures highlights the need for innovative approaches that can intervene in the early stages of wound healing.
The psychological impact of scars adds another layer of complexity to management strategies. Beyond physical appearance, scars can significantly affect a patient's quality of life, self-esteem, and mental health. Addressing these psychological aspects alongside physical treatment is crucial but often overlooked in current therapies.
Lastly, the cost and accessibility of advanced scar management treatments present significant challenges. Many effective therapies, such as advanced laser treatments or specialized dressings, can be expensive and not widely available, limiting their use to a small portion of patients who need them. This disparity in access to optimal care underscores the need for more cost-effective and widely accessible treatment options.
Existing Hirudoid-based Scar Treatment Approaches
01 Topical formulations for scar management
Various topical formulations containing active ingredients such as heparin, allantoin, and other compounds are used for scar management. These formulations can help improve the appearance of scars, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. They may be applied directly to the affected area to enhance skin regeneration and minimize scar formation.- Topical formulations for scar management: Various topical formulations containing active ingredients such as hirudoid, silicone, and other compounds are used for scar management. These formulations can help improve the appearance of scars, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. They may be applied directly to the affected area and are often used in combination with other scar management techniques.
- Wound dressings and patches for scar treatment: Specialized wound dressings and patches are designed for scar management. These products may incorporate active ingredients or provide a protective barrier to promote healing and reduce scarring. Some dressings may use advanced materials or technologies to enhance their effectiveness in scar treatment.
- Combination therapies for scar management: Combination therapies involving multiple treatment modalities are used for comprehensive scar management. These may include a combination of topical treatments, physical therapies, and advanced technologies such as laser therapy or microneedling. The synergistic effects of combined treatments can lead to improved outcomes in scar reduction and skin healing.
- Bioactive compounds for scar reduction: Various bioactive compounds, including natural extracts and synthetic molecules, are being researched and developed for their potential in scar management. These compounds may target specific aspects of the wound healing process or influence collagen production and remodeling to improve scar appearance and texture.
- Devices and methods for scar treatment: Innovative devices and methods are being developed for scar treatment, including advanced applicators, delivery systems, and physical therapy tools. These may include devices for controlled drug delivery, massage tools for scar tissue manipulation, or instruments for precise application of treatments to affected areas.
02 Wound dressings and patches for scar treatment
Specialized wound dressings and patches are designed for scar management. These products may incorporate active ingredients or utilize advanced materials to create an optimal environment for scar healing. They can help maintain moisture, protect the wound, and deliver therapeutic agents to the scar tissue.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination therapies for scar management
Combination therapies involving multiple treatment modalities are employed for comprehensive scar management. These may include the use of topical agents, physical therapies, and advanced technologies such as light-based treatments or microneedling. The synergistic effects of combined treatments can enhance overall scar improvement.Expand Specific Solutions04 Bioactive compounds for scar reduction
Various bioactive compounds, including plant extracts, peptides, and growth factors, are utilized in scar management products. These compounds can modulate the wound healing process, stimulate collagen production, and improve the overall appearance of scars. Research focuses on identifying and incorporating novel bioactive ingredients for enhanced scar treatment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Devices and methods for scar treatment
Innovative devices and methods are developed for scar management, including advanced applicators, massage tools, and therapeutic systems. These technologies aim to improve the delivery of active ingredients, enhance circulation in the scar tissue, and promote optimal healing conditions. Some devices may incorporate features like controlled pressure or temperature regulation for targeted scar treatment.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Scar Management Industry
The research on Hirudoid for transforming scar management is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global scar treatment market is expanding, driven by rising aesthetic consciousness and medical needs. Technologically, the field is progressing from traditional treatments to innovative approaches. Companies like Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, and Smith & Nephew are leading with established products, while emerging players such as CellionBioMed and Sirnaomics are introducing novel solutions. The involvement of academic institutions like MIT and Arizona State University indicates ongoing research and potential breakthroughs, suggesting a dynamic and competitive landscape with varying levels of technological maturity among participants.
Johnson & Johnson
Technical Solution: Johnson & Johnson has developed a proprietary Hirudoid-based formulation for scar management. Their approach combines Hirudoid (a mucopolysaccharide polysulfate) with other active ingredients to enhance its efficacy in scar treatment. The formulation is designed to improve the appearance of scars by promoting collagen remodeling, reducing inflammation, and increasing skin hydration. Clinical studies have shown significant improvements in scar texture, color, and overall appearance after regular application of this Hirudoid-based product.
Strengths: Extensive research and development capabilities, global distribution network, and strong brand recognition. Weaknesses: Higher product costs compared to generic alternatives, potential for side effects in some users.
Fidia Farmaceutici SpA
Technical Solution: Fidia Farmaceutici has developed an advanced Hirudoid-based gel formulation specifically for scar management. Their product incorporates a high concentration of mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS) derived from Hirudoid, combined with proprietary penetration enhancers. This formulation is designed to penetrate deep into the skin layers, targeting the underlying scar tissue. The gel works by stimulating fibroblast activity, promoting the breakdown of excessive collagen, and improving microcirculation in the affected area. Clinical trials have demonstrated significant improvements in scar elasticity, thickness, and overall appearance.
Strengths: Specialized expertise in dermatological products, innovative formulation techniques. Weaknesses: Limited market presence compared to larger pharmaceutical companies, potential for higher production costs.
Core Innovations in Hirudoid Formulations
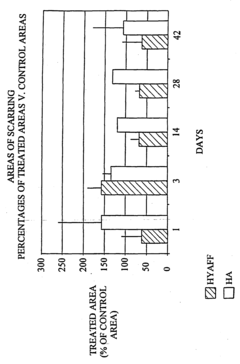
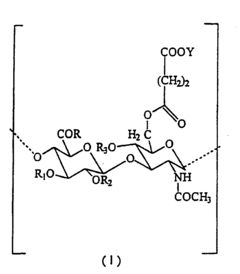
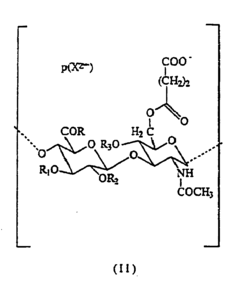
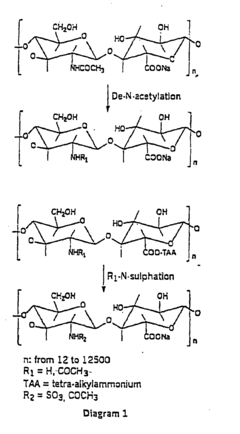
Hyaluronic acid derivatives for the prevention and treatment of cutaneous scars
PatentInactiveEP1712228A2
Innovation
- The use of hyaluronic acid derivatives, combined with pharmacologically or biologically active compounds, to reduce the area affected by scarring, where these derivatives are prepared from purified hyaluronic acid fractions with specific molecular weights and modified through esterification, cross-linking, or sulphation processes to enhance their pharmacological properties.
Pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of wounds, scars and keloids
PatentInactiveEP0619737A1
Innovation
- A pharmaceutical composition containing crosslinked glycosaminoglycans, such as hyaluronic acid and heparin, used intralesionally in the form of injectable gels or powders, which inhibit keloid formation without local overreactions or systemic effects, and are biodegradable, allowing for controlled release and prolonged effectiveness.
Regulatory Framework for Scar Treatment Products
The regulatory framework for scar treatment products plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of these medical devices. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of scar treatment products, classifying them based on their intended use and potential risks. Most scar treatment products fall under Class I or Class II medical devices, with varying levels of regulatory control.
For Class I devices, which are considered low-risk, manufacturers are generally required to register their establishment and list their products with the FDA. These products are subject to general controls, including good manufacturing practices and labeling requirements. Many over-the-counter scar treatment products, such as silicone sheets and gels, fall into this category.
Class II devices, which pose moderate risks, require more stringent controls. In addition to general controls, these products often need to obtain FDA clearance through the 510(k) premarket notification process. This process involves demonstrating that the new device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device. Some advanced scar treatment products, including certain laser devices and injectable fillers, may fall into this category.
The regulatory framework also encompasses post-market surveillance, requiring manufacturers to monitor and report adverse events associated with their products. This ongoing process helps ensure the continued safety and effectiveness of scar treatment products in real-world use.
Internationally, regulatory requirements for scar treatment products can vary significantly. The European Union, for instance, has implemented the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which provides a comprehensive framework for medical devices, including those used for scar management. The MDR emphasizes clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and traceability throughout the product lifecycle.
In emerging markets, regulatory frameworks for scar treatment products may be less developed or in the process of evolving. This can present both opportunities and challenges for manufacturers looking to expand their global reach. Companies must navigate diverse regulatory landscapes, adapting their products and documentation to meet local requirements.
As the field of scar management continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve to address new technologies and treatment modalities. This may include the development of specific guidance documents for novel scar treatment approaches, such as those involving regenerative medicine or nanotechnology. Manufacturers and researchers must stay abreast of these regulatory developments to ensure compliance and facilitate the introduction of innovative scar management solutions to the market.
For Class I devices, which are considered low-risk, manufacturers are generally required to register their establishment and list their products with the FDA. These products are subject to general controls, including good manufacturing practices and labeling requirements. Many over-the-counter scar treatment products, such as silicone sheets and gels, fall into this category.
Class II devices, which pose moderate risks, require more stringent controls. In addition to general controls, these products often need to obtain FDA clearance through the 510(k) premarket notification process. This process involves demonstrating that the new device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device. Some advanced scar treatment products, including certain laser devices and injectable fillers, may fall into this category.
The regulatory framework also encompasses post-market surveillance, requiring manufacturers to monitor and report adverse events associated with their products. This ongoing process helps ensure the continued safety and effectiveness of scar treatment products in real-world use.
Internationally, regulatory requirements for scar treatment products can vary significantly. The European Union, for instance, has implemented the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which provides a comprehensive framework for medical devices, including those used for scar management. The MDR emphasizes clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and traceability throughout the product lifecycle.
In emerging markets, regulatory frameworks for scar treatment products may be less developed or in the process of evolving. This can present both opportunities and challenges for manufacturers looking to expand their global reach. Companies must navigate diverse regulatory landscapes, adapting their products and documentation to meet local requirements.
As the field of scar management continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve to address new technologies and treatment modalities. This may include the development of specific guidance documents for novel scar treatment approaches, such as those involving regenerative medicine or nanotechnology. Manufacturers and researchers must stay abreast of these regulatory developments to ensure compliance and facilitate the introduction of innovative scar management solutions to the market.
Patient-Centric Considerations in Scar Management
In the realm of scar management, patient-centric considerations have become increasingly paramount. The use of Hirudoid in transforming scar management necessitates a comprehensive understanding of patient needs, preferences, and experiences. This approach ensures that treatment protocols are not only effective but also aligned with patient expectations and quality of life.
One of the primary patient-centric considerations is the psychological impact of scarring. Patients often experience emotional distress, reduced self-esteem, and social anxiety due to visible scars. Hirudoid-based treatments must address these psychological aspects alongside physical healing. Incorporating patient counseling and support services into the treatment plan can significantly enhance overall outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Pain management is another crucial factor in patient-centric scar treatment. Hirudoid's potential to reduce discomfort and itching associated with scar formation should be thoroughly evaluated. Tailoring the application frequency and dosage to individual patient needs can optimize comfort levels and improve adherence to treatment regimens.
The ease of use and convenience of Hirudoid applications must also be considered from a patient perspective. Developing user-friendly formulations and clear application instructions can enhance patient compliance and treatment effectiveness. Additionally, considering the lifestyle and daily routines of patients when designing treatment protocols can improve long-term adherence and outcomes.
Patient education plays a vital role in scar management. Providing comprehensive information about Hirudoid's mechanism of action, expected outcomes, and potential side effects empowers patients to make informed decisions about their treatment. This education should extend to proper scar care techniques, including sun protection and moisturization, to complement the effects of Hirudoid.
Long-term follow-up and patient feedback mechanisms are essential components of a patient-centric approach. Regular assessments of patient satisfaction, scar appearance, and functional improvements allow for continuous refinement of treatment strategies. This iterative process ensures that scar management protocols evolve to meet changing patient needs and preferences over time.
Lastly, considering the cost-effectiveness and accessibility of Hirudoid-based treatments from a patient perspective is crucial. Developing affordable treatment options and exploring insurance coverage possibilities can significantly impact patient adoption and long-term adherence to scar management protocols.
One of the primary patient-centric considerations is the psychological impact of scarring. Patients often experience emotional distress, reduced self-esteem, and social anxiety due to visible scars. Hirudoid-based treatments must address these psychological aspects alongside physical healing. Incorporating patient counseling and support services into the treatment plan can significantly enhance overall outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Pain management is another crucial factor in patient-centric scar treatment. Hirudoid's potential to reduce discomfort and itching associated with scar formation should be thoroughly evaluated. Tailoring the application frequency and dosage to individual patient needs can optimize comfort levels and improve adherence to treatment regimens.
The ease of use and convenience of Hirudoid applications must also be considered from a patient perspective. Developing user-friendly formulations and clear application instructions can enhance patient compliance and treatment effectiveness. Additionally, considering the lifestyle and daily routines of patients when designing treatment protocols can improve long-term adherence and outcomes.
Patient education plays a vital role in scar management. Providing comprehensive information about Hirudoid's mechanism of action, expected outcomes, and potential side effects empowers patients to make informed decisions about their treatment. This education should extend to proper scar care techniques, including sun protection and moisturization, to complement the effects of Hirudoid.
Long-term follow-up and patient feedback mechanisms are essential components of a patient-centric approach. Regular assessments of patient satisfaction, scar appearance, and functional improvements allow for continuous refinement of treatment strategies. This iterative process ensures that scar management protocols evolve to meet changing patient needs and preferences over time.
Lastly, considering the cost-effectiveness and accessibility of Hirudoid-based treatments from a patient perspective is crucial. Developing affordable treatment options and exploring insurance coverage possibilities can significantly impact patient adoption and long-term adherence to scar management protocols.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!