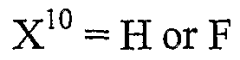Hirudoid and Future Directions in Therapy
JUN 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hirudoid Background and Therapeutic Goals
Hirudoid, a topical medication containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), has a rich history in therapeutic applications dating back to the mid-20th century. Initially developed as an anticoagulant, its potential in treating various dermatological and vascular conditions has been increasingly recognized over the decades. The evolution of Hirudoid's use reflects the growing understanding of its mechanism of action and the expanding scope of its clinical applications.
The primary active ingredient, MPS, is a semisynthetic compound that mimics the structure of naturally occurring glycosaminoglycans. This similarity allows Hirudoid to interact with various biological processes, particularly those involved in inflammation, tissue repair, and vascular health. As research progressed, the multifaceted nature of Hirudoid's therapeutic effects became apparent, leading to its application in a diverse range of medical conditions.
In recent years, the focus of Hirudoid research has shifted towards exploring its potential in addressing more complex and chronic conditions. This includes investigations into its efficacy in managing venous insufficiency, reducing the appearance of scars and stretch marks, and even potential applications in sports medicine for treating soft tissue injuries. The ongoing research aims to fully elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying Hirudoid's therapeutic actions and to optimize its formulation for enhanced efficacy and targeted delivery.
The current therapeutic goals for Hirudoid research encompass several key areas. Firstly, there is a drive to expand its approved indications, particularly in the realm of wound healing and scar management. Researchers are exploring ways to enhance Hirudoid's penetration through the skin barrier to improve its effectiveness in treating deeper tissue injuries. Additionally, there is growing interest in combining Hirudoid with other active ingredients to create more potent and versatile formulations.
Another significant goal is to develop novel delivery systems for Hirudoid. This includes investigating the potential of nanocarriers and transdermal patches to improve the drug's bioavailability and provide more controlled release profiles. Such advancements could potentially extend the duration of Hirudoid's therapeutic effects and reduce the frequency of application, thereby improving patient compliance and treatment outcomes.
Furthermore, there is an increasing focus on personalized medicine approaches in Hirudoid therapy. Researchers are exploring genetic and molecular markers that may predict individual responses to Hirudoid treatment, paving the way for more tailored therapeutic regimens. This personalized approach aims to optimize treatment efficacy while minimizing potential side effects, ultimately enhancing patient care and outcomes in various dermatological and vascular conditions.
The primary active ingredient, MPS, is a semisynthetic compound that mimics the structure of naturally occurring glycosaminoglycans. This similarity allows Hirudoid to interact with various biological processes, particularly those involved in inflammation, tissue repair, and vascular health. As research progressed, the multifaceted nature of Hirudoid's therapeutic effects became apparent, leading to its application in a diverse range of medical conditions.
In recent years, the focus of Hirudoid research has shifted towards exploring its potential in addressing more complex and chronic conditions. This includes investigations into its efficacy in managing venous insufficiency, reducing the appearance of scars and stretch marks, and even potential applications in sports medicine for treating soft tissue injuries. The ongoing research aims to fully elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying Hirudoid's therapeutic actions and to optimize its formulation for enhanced efficacy and targeted delivery.
The current therapeutic goals for Hirudoid research encompass several key areas. Firstly, there is a drive to expand its approved indications, particularly in the realm of wound healing and scar management. Researchers are exploring ways to enhance Hirudoid's penetration through the skin barrier to improve its effectiveness in treating deeper tissue injuries. Additionally, there is growing interest in combining Hirudoid with other active ingredients to create more potent and versatile formulations.
Another significant goal is to develop novel delivery systems for Hirudoid. This includes investigating the potential of nanocarriers and transdermal patches to improve the drug's bioavailability and provide more controlled release profiles. Such advancements could potentially extend the duration of Hirudoid's therapeutic effects and reduce the frequency of application, thereby improving patient compliance and treatment outcomes.
Furthermore, there is an increasing focus on personalized medicine approaches in Hirudoid therapy. Researchers are exploring genetic and molecular markers that may predict individual responses to Hirudoid treatment, paving the way for more tailored therapeutic regimens. This personalized approach aims to optimize treatment efficacy while minimizing potential side effects, ultimately enhancing patient care and outcomes in various dermatological and vascular conditions.
Market Analysis for Hirudoid-based Treatments
The market for Hirudoid-based treatments has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of its therapeutic benefits and a growing aging population. Hirudoid, a topical medication containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), has established itself as a key player in the treatment of various skin conditions and superficial thrombophlebitis.
The global market for Hirudoid and similar MPS-based products is estimated to be substantial, with strong demand in both developed and emerging markets. Europe and North America currently dominate the market share, but rapid growth is observed in Asia-Pacific regions, particularly in countries like China and Japan, where there is a rising prevalence of venous disorders and an increasing focus on advanced wound care.
One of the primary drivers of market growth is the expanding application of Hirudoid in various therapeutic areas. While traditionally used for treating bruises and hematomas, recent clinical studies have demonstrated its efficacy in managing conditions such as superficial thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, and certain types of scars. This broadening of therapeutic applications has significantly expanded the potential market for Hirudoid-based treatments.
The aging population worldwide is another crucial factor contributing to market growth. As the elderly population increases, there is a corresponding rise in age-related skin conditions and vascular disorders, which are prime targets for Hirudoid therapy. This demographic shift is expected to sustain long-term demand for Hirudoid and similar products.
In terms of market segmentation, hospitals and clinics remain the largest end-users of Hirudoid-based treatments. However, there is a growing trend towards self-administration and home care, particularly for long-term management of chronic conditions. This shift is driving the development of more user-friendly formulations and delivery systems, potentially opening up new market segments.
Competition in the Hirudoid market is intensifying, with several pharmaceutical companies developing similar MPS-based products or alternative formulations. This competitive landscape is likely to drive innovation in product development, potentially leading to more effective or convenient treatment options for patients.
Regulatory factors play a significant role in shaping the market. Stringent approval processes in key markets like the United States and Europe can impact the introduction of new Hirudoid-based products or expanded indications for existing ones. However, once approved, these regulatory hurdles can also serve as barriers to entry for new competitors, potentially benefiting established players in the market.
Looking ahead, the market for Hirudoid-based treatments is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Emerging trends such as combination therapies, where Hirudoid is used in conjunction with other treatments, and the development of novel delivery systems, are likely to drive further market expansion and diversification.
The global market for Hirudoid and similar MPS-based products is estimated to be substantial, with strong demand in both developed and emerging markets. Europe and North America currently dominate the market share, but rapid growth is observed in Asia-Pacific regions, particularly in countries like China and Japan, where there is a rising prevalence of venous disorders and an increasing focus on advanced wound care.
One of the primary drivers of market growth is the expanding application of Hirudoid in various therapeutic areas. While traditionally used for treating bruises and hematomas, recent clinical studies have demonstrated its efficacy in managing conditions such as superficial thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, and certain types of scars. This broadening of therapeutic applications has significantly expanded the potential market for Hirudoid-based treatments.
The aging population worldwide is another crucial factor contributing to market growth. As the elderly population increases, there is a corresponding rise in age-related skin conditions and vascular disorders, which are prime targets for Hirudoid therapy. This demographic shift is expected to sustain long-term demand for Hirudoid and similar products.
In terms of market segmentation, hospitals and clinics remain the largest end-users of Hirudoid-based treatments. However, there is a growing trend towards self-administration and home care, particularly for long-term management of chronic conditions. This shift is driving the development of more user-friendly formulations and delivery systems, potentially opening up new market segments.
Competition in the Hirudoid market is intensifying, with several pharmaceutical companies developing similar MPS-based products or alternative formulations. This competitive landscape is likely to drive innovation in product development, potentially leading to more effective or convenient treatment options for patients.
Regulatory factors play a significant role in shaping the market. Stringent approval processes in key markets like the United States and Europe can impact the introduction of new Hirudoid-based products or expanded indications for existing ones. However, once approved, these regulatory hurdles can also serve as barriers to entry for new competitors, potentially benefiting established players in the market.
Looking ahead, the market for Hirudoid-based treatments is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Emerging trends such as combination therapies, where Hirudoid is used in conjunction with other treatments, and the development of novel delivery systems, are likely to drive further market expansion and diversification.
Current Challenges in Hirudoid Research
Despite significant advancements in Hirudoid research, several challenges persist in fully understanding and harnessing its therapeutic potential. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of its mechanism of action. While Hirudoid is known to have anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic properties, the exact molecular pathways through which it exerts these effects remain incompletely elucidated. This gap in knowledge hinders the development of more targeted and efficient therapies.
Another challenge lies in optimizing the delivery and bioavailability of Hirudoid. Current formulations, primarily topical, may not achieve optimal penetration or systemic distribution for certain indications. Developing novel drug delivery systems that enhance absorption and maintain therapeutic concentrations at target sites is crucial for expanding its clinical applications.
The standardization of Hirudoid preparations poses another significant hurdle. As a naturally derived compound, batch-to-batch variability can occur, potentially affecting efficacy and safety profiles. Establishing robust quality control measures and standardization protocols is essential for ensuring consistent therapeutic outcomes and facilitating regulatory approvals.
Furthermore, the limited scope of clinical trials presents a challenge in fully exploring Hirudoid's potential. While it has shown promise in treating various conditions, from venous insufficiency to bruising, large-scale, randomized controlled trials are needed to definitively establish its efficacy across a broader range of indications. This lack of comprehensive clinical data hampers its wider acceptance in mainstream medical practice.
Additionally, there is a need for more research into potential drug interactions and long-term safety profiles of Hirudoid, particularly for systemic applications. As with many naturally derived compounds, understanding how Hirudoid interacts with other medications and its effects over extended periods of use is crucial for its safe integration into treatment regimens.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for Hirudoid and similar compounds presents challenges in bringing new formulations or applications to market. Navigating the complex approval processes, especially for novel delivery systems or expanded indications, requires substantial resources and can slow the pace of innovation in this field.
Another challenge lies in optimizing the delivery and bioavailability of Hirudoid. Current formulations, primarily topical, may not achieve optimal penetration or systemic distribution for certain indications. Developing novel drug delivery systems that enhance absorption and maintain therapeutic concentrations at target sites is crucial for expanding its clinical applications.
The standardization of Hirudoid preparations poses another significant hurdle. As a naturally derived compound, batch-to-batch variability can occur, potentially affecting efficacy and safety profiles. Establishing robust quality control measures and standardization protocols is essential for ensuring consistent therapeutic outcomes and facilitating regulatory approvals.
Furthermore, the limited scope of clinical trials presents a challenge in fully exploring Hirudoid's potential. While it has shown promise in treating various conditions, from venous insufficiency to bruising, large-scale, randomized controlled trials are needed to definitively establish its efficacy across a broader range of indications. This lack of comprehensive clinical data hampers its wider acceptance in mainstream medical practice.
Additionally, there is a need for more research into potential drug interactions and long-term safety profiles of Hirudoid, particularly for systemic applications. As with many naturally derived compounds, understanding how Hirudoid interacts with other medications and its effects over extended periods of use is crucial for its safe integration into treatment regimens.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for Hirudoid and similar compounds presents challenges in bringing new formulations or applications to market. Navigating the complex approval processes, especially for novel delivery systems or expanded indications, requires substantial resources and can slow the pace of innovation in this field.
Key Players in Hirudoid Research
The research on Hirudoid and future directions in therapy is in a developing stage, with a growing market size due to increasing interest in novel therapeutic approaches. The technology maturity varies among key players, with established pharmaceutical companies like Novartis AG, Sanofi, and Merck Patent GmbH leading in advanced research and development. Emerging biotechnology firms such as Immatics Biotechnologies GmbH and OncoTherapy Science, Inc. are also making significant contributions. Academic institutions like the University of Washington and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique are driving fundamental research, while collaborations between industry and academia, exemplified by partnerships involving Amgen, Inc. and various universities, are accelerating progress in this field.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis AG has developed a novel approach to Hirudoid therapy, focusing on enhancing its anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant properties. Their research involves modifying the molecular structure of heparinoid to improve its absorption and efficacy. The company has also explored combining Hirudoid with other active ingredients to create a more potent formulation for treating various skin conditions and vascular disorders. Additionally, Novartis is investigating the potential of Hirudoid in wound healing acceleration and reducing scarring through controlled release mechanisms.
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, global reach for clinical trials, and extensive experience in drug development. Weaknesses: High development costs and potential regulatory hurdles for new formulations.
Sanofi
Technical Solution: Sanofi's research on Hirudoid focuses on expanding its therapeutic applications beyond traditional uses. They are developing a new delivery system for Hirudoid that allows for sustained release, potentially improving its effectiveness in treating chronic conditions. Sanofi is also exploring the synergistic effects of combining Hirudoid with other active ingredients to create multi-functional topical treatments. Their research extends to investigating the potential of Hirudoid in reducing post-surgical adhesions and improving outcomes in cosmetic procedures. Furthermore, Sanofi is conducting studies on the use of Hirudoid in managing diabetic foot ulcers and other chronic wounds.
Strengths: Extensive experience in pharmaceutical development and global distribution network. Weaknesses: Potential competition from generic alternatives and the need for substantial investment in clinical trials.
Core Patents in Hirudoid Technology
Use of hirudine and its muteines and their peg derivatives for the combined treatment of tumours
PatentInactiveEP0563209A1
Innovation
- The use of hirudin and its muteins conjugated with PEG derivatives to enhance blood flow in tumors, combined with antitumor agents, increases the concentration of these agents within the tumor, allowing for more effective treatment with reduced doses and improved oxygenation during radiation therapy.
Modified hirudin proteins and t-cell epitopes in hirudin
PatentWO2004113386A2
Innovation
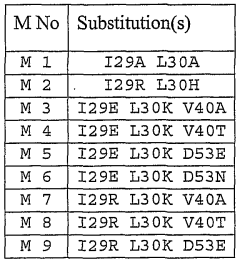
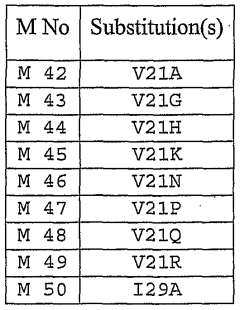
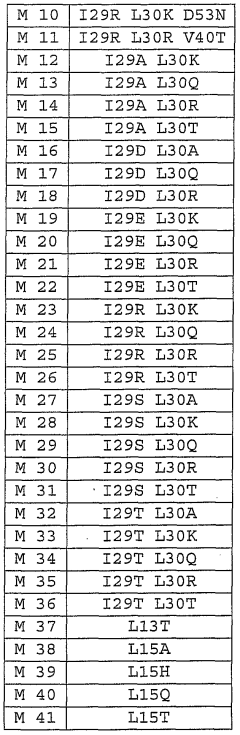
- Modified hirudin proteins with specific amino acid substitutions, particularly at positions 29 and 30, are developed to reduce immunogenicity while maintaining thrombin inhibition activity, using recombinant DNA techniques and synthetic methods to create molecules like M1 and M2, which demonstrate reduced immunogenicity in human cells and retain anticoagulant efficacy.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
Safety and efficacy are paramount considerations in the development and application of Hirudoid therapy. Extensive clinical trials have demonstrated the overall safety profile of Hirudoid, with minimal reported adverse effects. The most common side effects include mild skin irritation, itching, and redness at the application site, which typically subside without intervention. Allergic reactions are rare but have been documented in a small percentage of patients, necessitating careful patient screening and monitoring.
Efficacy studies have shown promising results in various therapeutic applications. Hirudoid has demonstrated significant effectiveness in reducing the appearance of bruises and hematomas, with studies indicating accelerated healing times compared to placebo treatments. In the management of superficial thrombophlebitis, Hirudoid has been found to alleviate symptoms such as pain, swelling, and inflammation, leading to improved patient comfort and faster recovery.
Long-term safety data on Hirudoid use is limited, particularly for extended treatment periods. This gap in knowledge highlights the need for comprehensive longitudinal studies to assess potential cumulative effects and rare adverse events that may only manifest with prolonged use. Additionally, the safety profile in specific patient populations, such as pregnant women, children, and the elderly, requires further investigation to establish clear guidelines for use in these groups.
The efficacy of Hirudoid in combination with other therapeutic modalities is an area of ongoing research. Preliminary studies suggest potential synergistic effects when used in conjunction with compression therapy for venous disorders, but more robust clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings and optimize treatment protocols. Furthermore, the comparative efficacy of Hirudoid against newer topical agents and alternative treatment modalities warrants thorough investigation to determine its place in modern therapeutic regimens.
Dosage optimization and application frequency are critical factors influencing both safety and efficacy. Current recommendations are based on limited dose-response studies, and there is a need for more precise dosing guidelines tailored to specific indications and patient characteristics. The development of novel formulations and delivery systems for Hirudoid may enhance its efficacy and safety profile, potentially expanding its therapeutic applications.
As research progresses, the integration of pharmacogenomics and personalized medicine approaches may lead to more targeted use of Hirudoid, maximizing efficacy while minimizing potential adverse effects. This personalized approach could involve genetic screening to identify patients most likely to benefit from Hirudoid therapy or those at higher risk for adverse reactions, thereby optimizing treatment outcomes and patient safety.
Efficacy studies have shown promising results in various therapeutic applications. Hirudoid has demonstrated significant effectiveness in reducing the appearance of bruises and hematomas, with studies indicating accelerated healing times compared to placebo treatments. In the management of superficial thrombophlebitis, Hirudoid has been found to alleviate symptoms such as pain, swelling, and inflammation, leading to improved patient comfort and faster recovery.
Long-term safety data on Hirudoid use is limited, particularly for extended treatment periods. This gap in knowledge highlights the need for comprehensive longitudinal studies to assess potential cumulative effects and rare adverse events that may only manifest with prolonged use. Additionally, the safety profile in specific patient populations, such as pregnant women, children, and the elderly, requires further investigation to establish clear guidelines for use in these groups.
The efficacy of Hirudoid in combination with other therapeutic modalities is an area of ongoing research. Preliminary studies suggest potential synergistic effects when used in conjunction with compression therapy for venous disorders, but more robust clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings and optimize treatment protocols. Furthermore, the comparative efficacy of Hirudoid against newer topical agents and alternative treatment modalities warrants thorough investigation to determine its place in modern therapeutic regimens.
Dosage optimization and application frequency are critical factors influencing both safety and efficacy. Current recommendations are based on limited dose-response studies, and there is a need for more precise dosing guidelines tailored to specific indications and patient characteristics. The development of novel formulations and delivery systems for Hirudoid may enhance its efficacy and safety profile, potentially expanding its therapeutic applications.
As research progresses, the integration of pharmacogenomics and personalized medicine approaches may lead to more targeted use of Hirudoid, maximizing efficacy while minimizing potential adverse effects. This personalized approach could involve genetic screening to identify patients most likely to benefit from Hirudoid therapy or those at higher risk for adverse reactions, thereby optimizing treatment outcomes and patient safety.
Regulatory Landscape for Hirudoid Products
The regulatory landscape for Hirudoid products is complex and varies across different regions and countries. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies Hirudoid as a prescription drug, specifically as a heparinoid. This classification requires manufacturers to obtain FDA approval through rigorous clinical trials and safety assessments before marketing the product. The FDA also mandates strict labeling requirements and post-market surveillance for Hirudoid products.
In the European Union, Hirudoid is regulated under the European Medicines Agency (EMA) framework. The EMA has established specific guidelines for heparinoid-based products, including requirements for quality control, safety monitoring, and efficacy demonstration. Manufacturers must obtain marketing authorization from the EMA or national regulatory bodies before distributing Hirudoid products in EU member states.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) oversees the regulation of Hirudoid in the Japanese market. The PMDA has implemented a comprehensive review process for heparinoid products, focusing on safety, efficacy, and quality standards. Japanese regulations also emphasize the importance of post-market surveillance and adverse event reporting for Hirudoid and similar medications.
In emerging markets, such as China and India, regulatory frameworks for Hirudoid products are evolving. These countries are developing more stringent approval processes and quality control measures to align with international standards. However, the regulatory landscape in these regions may still present challenges for manufacturers due to varying requirements and potential inconsistencies in enforcement.
Global harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), are working to streamline regulatory processes for products like Hirudoid across different regions. These initiatives aim to reduce duplicative testing and expedite the approval process while maintaining high safety and efficacy standards.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of pharmaceutical products. For Hirudoid and similar heparinoid-based medications, this may lead to new requirements for assessing environmental risks and implementing sustainable manufacturing practices.
As personalized medicine advances, regulatory frameworks may need to adapt to accommodate tailored formulations of Hirudoid for specific patient populations. This could potentially lead to more nuanced regulatory pathways for specialized versions of the product.
In the European Union, Hirudoid is regulated under the European Medicines Agency (EMA) framework. The EMA has established specific guidelines for heparinoid-based products, including requirements for quality control, safety monitoring, and efficacy demonstration. Manufacturers must obtain marketing authorization from the EMA or national regulatory bodies before distributing Hirudoid products in EU member states.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) oversees the regulation of Hirudoid in the Japanese market. The PMDA has implemented a comprehensive review process for heparinoid products, focusing on safety, efficacy, and quality standards. Japanese regulations also emphasize the importance of post-market surveillance and adverse event reporting for Hirudoid and similar medications.
In emerging markets, such as China and India, regulatory frameworks for Hirudoid products are evolving. These countries are developing more stringent approval processes and quality control measures to align with international standards. However, the regulatory landscape in these regions may still present challenges for manufacturers due to varying requirements and potential inconsistencies in enforcement.
Global harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), are working to streamline regulatory processes for products like Hirudoid across different regions. These initiatives aim to reduce duplicative testing and expedite the approval process while maintaining high safety and efficacy standards.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of pharmaceutical products. For Hirudoid and similar heparinoid-based medications, this may lead to new requirements for assessing environmental risks and implementing sustainable manufacturing practices.
As personalized medicine advances, regulatory frameworks may need to adapt to accommodate tailored formulations of Hirudoid for specific patient populations. This could potentially lead to more nuanced regulatory pathways for specialized versions of the product.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!