Exploring Dolby Vision in High-Dynamic-Range Imaging Software
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dolby Vision HDR Evolution and Objectives
Dolby Vision, a cutting-edge High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology, has revolutionized the imaging industry since its introduction in 2014. This advanced HDR format has evolved significantly, pushing the boundaries of visual fidelity and color accuracy in digital content. The technology's development can be traced back to Dolby Laboratories' extensive research in human visual perception and color science.
The evolution of Dolby Vision has been driven by the increasing demand for more immersive and lifelike visual experiences across various platforms, including cinema, television, and mobile devices. Initially focused on professional cinema applications, Dolby Vision has expanded its reach to consumer electronics, streaming services, and content creation tools.
A key objective of Dolby Vision has been to overcome the limitations of standard dynamic range (SDR) imaging by significantly expanding the range of brightness and color that can be displayed. This includes the ability to render deeper blacks, brighter highlights, and a wider color gamut, resulting in images that more closely resemble what the human eye can perceive in the real world.
Throughout its development, Dolby Vision has aimed to provide a consistent viewing experience across different devices and viewing environments. This has led to the implementation of dynamic metadata, which allows for scene-by-scene and even frame-by-frame optimization of content, ensuring that the creator's intent is preserved regardless of the display capabilities.
Another crucial objective has been backward compatibility with existing SDR systems, allowing Dolby Vision content to be viewed on non-HDR displays without significant loss of quality. This has been instrumental in facilitating wider adoption and integration into existing workflows.
The technology has also focused on improving efficiency in content creation and distribution. Dolby Vision's single-stream approach, which embeds HDR data within a standard video signal, has simplified the production and delivery of HDR content, making it more accessible to content creators and distributors.
As the technology continues to evolve, Dolby Vision aims to push the boundaries of image quality even further. Current objectives include expanding support for higher frame rates, increased bit depth, and enhanced color volume, as well as improving algorithms for tone mapping and color management to deliver even more precise and lifelike images.
The evolution of Dolby Vision has been driven by the increasing demand for more immersive and lifelike visual experiences across various platforms, including cinema, television, and mobile devices. Initially focused on professional cinema applications, Dolby Vision has expanded its reach to consumer electronics, streaming services, and content creation tools.
A key objective of Dolby Vision has been to overcome the limitations of standard dynamic range (SDR) imaging by significantly expanding the range of brightness and color that can be displayed. This includes the ability to render deeper blacks, brighter highlights, and a wider color gamut, resulting in images that more closely resemble what the human eye can perceive in the real world.
Throughout its development, Dolby Vision has aimed to provide a consistent viewing experience across different devices and viewing environments. This has led to the implementation of dynamic metadata, which allows for scene-by-scene and even frame-by-frame optimization of content, ensuring that the creator's intent is preserved regardless of the display capabilities.
Another crucial objective has been backward compatibility with existing SDR systems, allowing Dolby Vision content to be viewed on non-HDR displays without significant loss of quality. This has been instrumental in facilitating wider adoption and integration into existing workflows.
The technology has also focused on improving efficiency in content creation and distribution. Dolby Vision's single-stream approach, which embeds HDR data within a standard video signal, has simplified the production and delivery of HDR content, making it more accessible to content creators and distributors.
As the technology continues to evolve, Dolby Vision aims to push the boundaries of image quality even further. Current objectives include expanding support for higher frame rates, increased bit depth, and enhanced color volume, as well as improving algorithms for tone mapping and color management to deliver even more precise and lifelike images.
Market Demand for HDR Imaging Solutions
The market demand for High Dynamic Range (HDR) imaging solutions has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing consumer appetite for more immersive and lifelike visual experiences. This trend is particularly evident in the entertainment and media industries, where content creators and distributors are constantly seeking ways to enhance the quality of their offerings.
The adoption of HDR technology in various sectors has been a key factor in fueling this demand. The film and television industry has been at the forefront, with major streaming platforms and broadcasters investing heavily in HDR content production and delivery. This has created a ripple effect, influencing consumer expectations and driving demand for HDR-capable devices and software solutions.
In the consumer electronics market, there has been a notable surge in the sales of HDR-compatible televisions, monitors, and mobile devices. This growth is not only limited to high-end products but is also penetrating mid-range offerings, making HDR technology more accessible to a broader consumer base. The increasing availability of HDR content across various platforms has further accelerated this trend.
The professional photography and videography sectors have also shown a growing interest in HDR imaging solutions. As the technology becomes more sophisticated and user-friendly, photographers and videographers are increasingly incorporating HDR techniques into their workflows to capture and produce more dynamic and visually striking images.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for HDR imaging solutions, particularly in the development of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. HDR cameras and displays are becoming crucial components in these systems, enhancing visibility and safety in various lighting conditions.
The gaming industry has also embraced HDR technology, with game developers and console manufacturers leveraging its capabilities to create more immersive and visually stunning gaming experiences. This has led to an increased demand for HDR-compatible gaming monitors and software solutions that can effectively render HDR content.
As the market for HDR imaging solutions continues to expand, there is a growing need for software that can efficiently process, edit, and display HDR content. This includes tools for color grading, image processing, and content creation that can handle the expanded dynamic range and color gamut offered by HDR technology. The demand for such software spans across various industries, from post-production houses in the film industry to individual content creators and prosumers.
The adoption of HDR technology in various sectors has been a key factor in fueling this demand. The film and television industry has been at the forefront, with major streaming platforms and broadcasters investing heavily in HDR content production and delivery. This has created a ripple effect, influencing consumer expectations and driving demand for HDR-capable devices and software solutions.
In the consumer electronics market, there has been a notable surge in the sales of HDR-compatible televisions, monitors, and mobile devices. This growth is not only limited to high-end products but is also penetrating mid-range offerings, making HDR technology more accessible to a broader consumer base. The increasing availability of HDR content across various platforms has further accelerated this trend.
The professional photography and videography sectors have also shown a growing interest in HDR imaging solutions. As the technology becomes more sophisticated and user-friendly, photographers and videographers are increasingly incorporating HDR techniques into their workflows to capture and produce more dynamic and visually striking images.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for HDR imaging solutions, particularly in the development of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. HDR cameras and displays are becoming crucial components in these systems, enhancing visibility and safety in various lighting conditions.
The gaming industry has also embraced HDR technology, with game developers and console manufacturers leveraging its capabilities to create more immersive and visually stunning gaming experiences. This has led to an increased demand for HDR-compatible gaming monitors and software solutions that can effectively render HDR content.
As the market for HDR imaging solutions continues to expand, there is a growing need for software that can efficiently process, edit, and display HDR content. This includes tools for color grading, image processing, and content creation that can handle the expanded dynamic range and color gamut offered by HDR technology. The demand for such software spans across various industries, from post-production houses in the film industry to individual content creators and prosumers.
Current HDR Technology Landscape
High Dynamic Range (HDR) imaging has revolutionized the way we capture, process, and display visual content. The current HDR technology landscape is characterized by a diverse array of standards, formats, and implementations, each striving to deliver superior image quality and a more immersive viewing experience.
At the forefront of HDR technology is Dolby Vision, a proprietary format developed by Dolby Laboratories. Dolby Vision stands out for its ability to provide dynamic metadata on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis, allowing for precise control over brightness, color, and contrast. This dynamic approach enables content creators to maintain their artistic intent across various display devices, ensuring consistent visual quality.
Competing with Dolby Vision is HDR10, an open standard widely adopted in the industry. HDR10 uses static metadata, which applies a single set of parameters to an entire piece of content. While less flexible than Dolby Vision, HDR10's open nature has led to its widespread adoption in consumer electronics and content distribution.
HDR10+ represents an evolution of HDR10, introducing dynamic metadata similar to Dolby Vision. Developed by Samsung in collaboration with Amazon, HDR10+ aims to provide a royalty-free alternative to Dolby Vision while offering comparable image quality enhancements.
Another notable player in the HDR space is Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG), jointly developed by the BBC and NHK. HLG is designed to be backward compatible with standard dynamic range (SDR) displays, making it particularly suitable for broadcast applications.
In terms of software implementation, various tools and frameworks have emerged to support HDR content creation and processing. Adobe's Creative Suite, including Premiere Pro and After Effects, has integrated HDR workflows, allowing professionals to edit and color grade HDR footage. DaVinci Resolve, known for its color correction capabilities, offers comprehensive HDR support across multiple formats.
Open-source initiatives like OpenColorIO (OCIO) provide color management solutions that can handle HDR color spaces, facilitating consistent color reproduction across different software and hardware environments. Similarly, OpenEXR, an open standard for HDR image files, has gained traction in the visual effects and animation industries.
The current landscape also sees increasing integration of HDR technologies in real-time rendering engines such as Unreal Engine and Unity. These engines now support HDR rendering pipelines, enabling game developers and virtual production teams to create more visually stunning and realistic environments.
As the HDR ecosystem continues to evolve, interoperability and standardization efforts are ongoing. Organizations like the UHD Alliance and the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) are working to establish guidelines and best practices for HDR content creation, distribution, and display.
At the forefront of HDR technology is Dolby Vision, a proprietary format developed by Dolby Laboratories. Dolby Vision stands out for its ability to provide dynamic metadata on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis, allowing for precise control over brightness, color, and contrast. This dynamic approach enables content creators to maintain their artistic intent across various display devices, ensuring consistent visual quality.
Competing with Dolby Vision is HDR10, an open standard widely adopted in the industry. HDR10 uses static metadata, which applies a single set of parameters to an entire piece of content. While less flexible than Dolby Vision, HDR10's open nature has led to its widespread adoption in consumer electronics and content distribution.
HDR10+ represents an evolution of HDR10, introducing dynamic metadata similar to Dolby Vision. Developed by Samsung in collaboration with Amazon, HDR10+ aims to provide a royalty-free alternative to Dolby Vision while offering comparable image quality enhancements.
Another notable player in the HDR space is Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG), jointly developed by the BBC and NHK. HLG is designed to be backward compatible with standard dynamic range (SDR) displays, making it particularly suitable for broadcast applications.
In terms of software implementation, various tools and frameworks have emerged to support HDR content creation and processing. Adobe's Creative Suite, including Premiere Pro and After Effects, has integrated HDR workflows, allowing professionals to edit and color grade HDR footage. DaVinci Resolve, known for its color correction capabilities, offers comprehensive HDR support across multiple formats.
Open-source initiatives like OpenColorIO (OCIO) provide color management solutions that can handle HDR color spaces, facilitating consistent color reproduction across different software and hardware environments. Similarly, OpenEXR, an open standard for HDR image files, has gained traction in the visual effects and animation industries.
The current landscape also sees increasing integration of HDR technologies in real-time rendering engines such as Unreal Engine and Unity. These engines now support HDR rendering pipelines, enabling game developers and virtual production teams to create more visually stunning and realistic environments.
As the HDR ecosystem continues to evolve, interoperability and standardization efforts are ongoing. Organizations like the UHD Alliance and the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) are working to establish guidelines and best practices for HDR content creation, distribution, and display.
Dolby Vision Implementation Strategies
01 High Dynamic Range (HDR) imaging technology
Dolby Vision utilizes HDR technology to enhance the dynamic range of images, providing a wider range of brightness, contrast, and color. This results in more lifelike and vibrant visuals, with improved detail in both bright and dark areas of the image.- High Dynamic Range (HDR) imaging technology: Dolby Vision utilizes HDR technology to enhance the dynamic range of images, providing a wider range of brightness, contrast, and color. This results in more lifelike and vibrant visuals, with improved detail in both bright and dark areas of the image.
- Dynamic metadata for scene-by-scene optimization: Dolby Vision incorporates dynamic metadata that allows for frame-by-frame or scene-by-scene optimization of the image. This enables more precise control over brightness, contrast, and color grading, resulting in a more accurate representation of the creator's intent across various display devices.
- Color gamut expansion and bit depth enhancement: The technology expands the color gamut and increases the bit depth of the image, allowing for a broader range of colors and smoother gradients. This results in more natural-looking images with reduced color banding and improved color accuracy.
- Display device calibration and adaptation: Dolby Vision includes features for calibrating and adapting content to different display devices, ensuring optimal performance across various screens. This includes adjusting for the specific capabilities of each display, such as peak brightness and black levels, to maintain image quality and consistency.
- Backward compatibility and scalability: The technology is designed to be backward compatible with standard dynamic range (SDR) content and displays while also being scalable for future advancements in display technology. This ensures that Dolby Vision content can be enjoyed on a wide range of devices while still providing benefits on more advanced displays.
02 Dynamic metadata for scene-by-scene optimization
Dolby Vision incorporates dynamic metadata that allows for frame-by-frame or scene-by-scene optimization of the image. This enables more precise control over brightness, contrast, and color grading, resulting in a more accurate representation of the creator's intent across various display devices.Expand Specific Solutions03 Wide color gamut support
Dolby Vision supports a wide color gamut, allowing for the reproduction of a broader range of colors than traditional display technologies. This results in more vivid and accurate color representation, enhancing the overall visual experience.Expand Specific Solutions04 Adaptive display mapping
Dolby Vision employs adaptive display mapping techniques to optimize content for different display capabilities. This ensures that the HDR content is appropriately rendered on various devices, from high-end TVs to mobile screens, while maintaining the intended visual quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Backward compatibility and content delivery
Dolby Vision is designed to be backward compatible with standard dynamic range (SDR) displays and content. It also includes efficient content delivery methods to ensure that the enhanced visual experience can be transmitted and displayed across various devices and platforms.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HDR Technology
The high-dynamic-range imaging software market, particularly in the context of Dolby Vision, is in a mature growth phase with increasing adoption across various industries. The market size is substantial, driven by the growing demand for enhanced visual experiences in entertainment, consumer electronics, and professional applications. Technologically, the field is well-developed but continues to evolve, with key players like Dolby Laboratories, Adobe, and Microsoft leading innovation. Companies such as OPPO, Samsung, and Huawei are integrating these technologies into their devices, while research institutions like Wuhan University and Peking University contribute to advancing the field. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established tech giants and specialized firms, each contributing to the ongoing refinement and expansion of HDR imaging capabilities.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Vision, developed by Dolby Laboratories, is a cutting-edge HDR technology that enhances image quality by optimizing brightness, contrast, and color. It utilizes dynamic metadata to adjust content on a scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame basis, ensuring optimal display across various devices[1]. The technology supports up to 12-bit color depth, allowing for a potential 68 billion colors, far exceeding standard HDR10's capabilities[2]. Dolby Vision's perceptual quantizer (PQ) curve enables a peak brightness of up to 10,000 nits, significantly surpassing traditional SDR displays[3]. Additionally, Dolby Vision IQ adapts HDR performance based on ambient light conditions, further enhancing viewing experiences in various environments[4].
Strengths: Industry-leading HDR technology with wide adoption, superior color depth, and dynamic metadata for optimal display across devices. Weaknesses: Requires licensing, which may limit adoption in some markets, and necessitates compatible hardware for full functionality.
Adobe, Inc.
Technical Solution: Adobe has integrated Dolby Vision support into its creative software suite, particularly in Premiere Pro and After Effects. Their approach focuses on providing content creators with tools to produce, edit, and deliver Dolby Vision content efficiently. Adobe's implementation includes features such as automatic conversion of SDR projects to HDR, built-in Dolby Vision analysis and metadata generation tools, and export options for various Dolby Vision profiles[5]. The software utilizes GPU acceleration to handle the increased computational demands of HDR processing, ensuring smooth playback and rendering of Dolby Vision content[6]. Adobe also offers color management tools that allow precise control over the expanded color gamut and luminance range provided by Dolby Vision[7].
Strengths: Seamless integration with industry-standard creative software, powerful tools for HDR content creation and delivery. Weaknesses: Steep learning curve for new users, high system requirements for optimal performance with HDR content.
Core Dolby Vision HDR Innovations
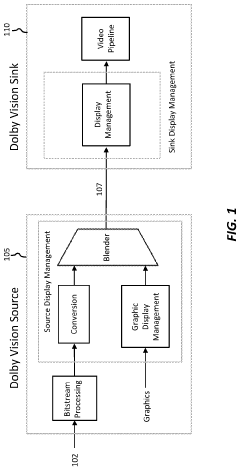
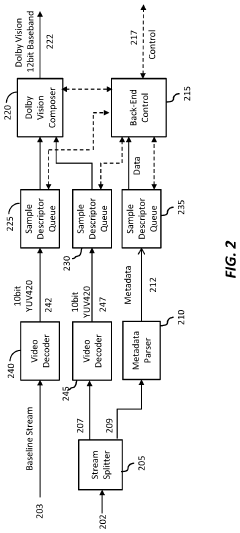
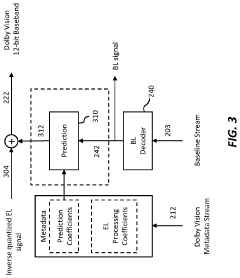
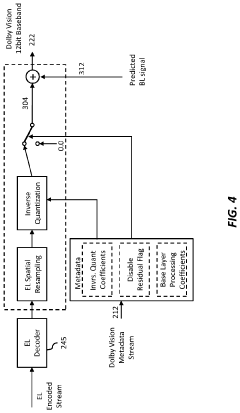
Layered representation and delivery of high dynamic range video
PatentActiveUS20190373290A1
Innovation
- The implementation of a layered representation and delivery system for HDR video, utilizing Dolby Vision technology, which includes a base layer and enhancement layer, along with metadata processing to reconstruct HDR signals, ensuring seamless playback on compatible displays.
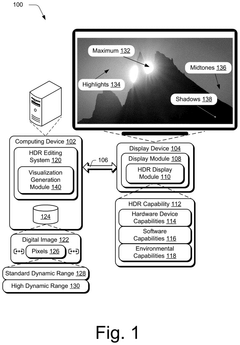
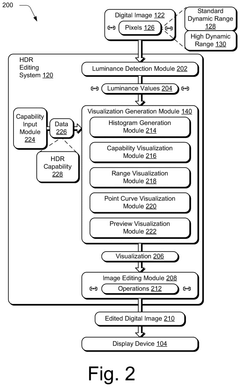
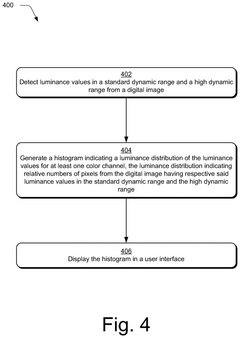
High dynamic range visualizations indicating ranges, point curves, and previews
PatentPendingUS20250117977A1
Innovation
- A high dynamic range editing system is configured to generate various visualizations, such as histograms, capability visualizations, range visualizations, point curves, and previews, to aid digital image editing and address the challenges of HDR across different devices and conditions.
Content Creation Workflow Integration
The integration of Dolby Vision into high-dynamic-range (HDR) imaging software has significantly transformed the content creation workflow, offering enhanced capabilities and streamlined processes for creators. This integration has been designed to seamlessly fit into existing production pipelines, minimizing disruption while maximizing the potential for high-quality HDR content creation.
At the heart of this integration is the Dolby Vision Content Mapping Unit (CMU), a software tool that allows content creators to analyze and grade their HDR content in real-time. The CMU enables creators to visualize how their content will appear across a wide range of displays, from high-end HDR televisions to standard dynamic range (SDR) devices. This capability ensures that the creative intent is preserved across various viewing environments.
The workflow typically begins with the capture of wide color gamut and high dynamic range footage. Dolby Vision-enabled cameras can capture this data natively, while other high-end digital cameras can also produce compatible raw files. These files are then imported into Dolby Vision-integrated editing and color grading software, such as DaVinci Resolve, Baselight, or Adobe Premiere Pro.
During the color grading process, the Dolby Vision integration allows colorists to work in a full HDR environment while simultaneously creating SDR versions. The software's algorithms analyze the HDR grade and automatically generate an SDR version, which can be fine-tuned if necessary. This dual-stream approach significantly reduces the time and effort required to create multiple deliverables.
One of the key advantages of the Dolby Vision workflow is the creation of dynamic metadata. This metadata contains frame-by-frame instructions on how to optimize the HDR content for different display capabilities. The integration of this metadata creation process into the content creation software ensures that the creator's artistic intent is preserved across a wide range of playback devices.
The final stage of the workflow involves the export of the content along with the Dolby Vision metadata. This package can then be delivered to various distribution platforms, ensuring that end-users receive the optimal viewing experience regardless of their display technology.
By integrating Dolby Vision into the content creation workflow, software developers have provided creators with powerful tools to produce high-quality HDR content efficiently. This integration not only enhances the creative possibilities but also streamlines the production process, allowing for faster turnaround times and more consistent results across different display technologies.
At the heart of this integration is the Dolby Vision Content Mapping Unit (CMU), a software tool that allows content creators to analyze and grade their HDR content in real-time. The CMU enables creators to visualize how their content will appear across a wide range of displays, from high-end HDR televisions to standard dynamic range (SDR) devices. This capability ensures that the creative intent is preserved across various viewing environments.
The workflow typically begins with the capture of wide color gamut and high dynamic range footage. Dolby Vision-enabled cameras can capture this data natively, while other high-end digital cameras can also produce compatible raw files. These files are then imported into Dolby Vision-integrated editing and color grading software, such as DaVinci Resolve, Baselight, or Adobe Premiere Pro.
During the color grading process, the Dolby Vision integration allows colorists to work in a full HDR environment while simultaneously creating SDR versions. The software's algorithms analyze the HDR grade and automatically generate an SDR version, which can be fine-tuned if necessary. This dual-stream approach significantly reduces the time and effort required to create multiple deliverables.
One of the key advantages of the Dolby Vision workflow is the creation of dynamic metadata. This metadata contains frame-by-frame instructions on how to optimize the HDR content for different display capabilities. The integration of this metadata creation process into the content creation software ensures that the creator's artistic intent is preserved across a wide range of playback devices.
The final stage of the workflow involves the export of the content along with the Dolby Vision metadata. This package can then be delivered to various distribution platforms, ensuring that end-users receive the optimal viewing experience regardless of their display technology.
By integrating Dolby Vision into the content creation workflow, software developers have provided creators with powerful tools to produce high-quality HDR content efficiently. This integration not only enhances the creative possibilities but also streamlines the production process, allowing for faster turnaround times and more consistent results across different display technologies.
HDR Standards and Compatibility
High Dynamic Range (HDR) imaging has revolutionized the way we capture, process, and display visual content. As the technology continues to evolve, various standards and formats have emerged to address the challenges of HDR implementation. Dolby Vision, developed by Dolby Laboratories, stands out as a prominent HDR format that has gained significant traction in the industry.
The HDR landscape is characterized by several competing standards, each with its own strengths and limitations. HDR10, an open standard, has been widely adopted due to its compatibility with a broad range of devices. However, it lacks the dynamic metadata capabilities that more advanced formats offer. HDR10+, developed by Samsung, addresses this limitation by incorporating dynamic metadata, allowing for frame-by-frame optimization of brightness and color.
Dolby Vision distinguishes itself through its support for 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata, enabling more precise control over image quality. This format has been embraced by numerous content creators and device manufacturers, contributing to its growing ecosystem. However, the proprietary nature of Dolby Vision has led to licensing requirements, which can impact its adoption in some sectors of the market.
Compatibility between different HDR standards remains a crucial consideration for software developers and hardware manufacturers. Many modern displays and playback devices support multiple HDR formats to ensure broad content compatibility. However, this approach can lead to increased complexity in both hardware design and software implementation.
The integration of Dolby Vision into high-dynamic-range imaging software presents both opportunities and challenges. Software developers must navigate the intricacies of Dolby's proprietary algorithms while ensuring seamless interoperability with other HDR standards. This often requires sophisticated color management systems and efficient metadata handling capabilities.
As the HDR ecosystem continues to evolve, efforts are being made to streamline compatibility and enhance interoperability between different standards. Industry consortiums and standardization bodies are working towards developing more unified approaches to HDR implementation. These initiatives aim to reduce fragmentation in the market and simplify the development process for content creators and software engineers.
The future of HDR standards and compatibility will likely involve a balance between innovation and consolidation. While new technologies may emerge to push the boundaries of image quality, there is also a growing need for standardization to ensure widespread adoption and seamless user experiences across different platforms and devices.
The HDR landscape is characterized by several competing standards, each with its own strengths and limitations. HDR10, an open standard, has been widely adopted due to its compatibility with a broad range of devices. However, it lacks the dynamic metadata capabilities that more advanced formats offer. HDR10+, developed by Samsung, addresses this limitation by incorporating dynamic metadata, allowing for frame-by-frame optimization of brightness and color.
Dolby Vision distinguishes itself through its support for 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata, enabling more precise control over image quality. This format has been embraced by numerous content creators and device manufacturers, contributing to its growing ecosystem. However, the proprietary nature of Dolby Vision has led to licensing requirements, which can impact its adoption in some sectors of the market.
Compatibility between different HDR standards remains a crucial consideration for software developers and hardware manufacturers. Many modern displays and playback devices support multiple HDR formats to ensure broad content compatibility. However, this approach can lead to increased complexity in both hardware design and software implementation.
The integration of Dolby Vision into high-dynamic-range imaging software presents both opportunities and challenges. Software developers must navigate the intricacies of Dolby's proprietary algorithms while ensuring seamless interoperability with other HDR standards. This often requires sophisticated color management systems and efficient metadata handling capabilities.
As the HDR ecosystem continues to evolve, efforts are being made to streamline compatibility and enhance interoperability between different standards. Industry consortiums and standardization bodies are working towards developing more unified approaches to HDR implementation. These initiatives aim to reduce fragmentation in the market and simplify the development process for content creators and software engineers.
The future of HDR standards and compatibility will likely involve a balance between innovation and consolidation. While new technologies may emerge to push the boundaries of image quality, there is also a growing need for standardization to ensure widespread adoption and seamless user experiences across different platforms and devices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!