Implementing Dolby Vision in Advanced Cinematography Techniques
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dolby Vision Evolution and Objectives
Dolby Vision, a cutting-edge High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology, has revolutionized the cinematography landscape since its inception in 2014. This advanced imaging format has evolved significantly, pushing the boundaries of visual storytelling and enhancing the viewer experience. The primary objective of Dolby Vision in advanced cinematography techniques is to capture, process, and display a wider range of colors and brightness levels, resulting in more lifelike and immersive visuals.
The evolution of Dolby Vision can be traced through several key milestones. Initially, it focused on expanding the color gamut and increasing the bit depth of digital images. This allowed for a more accurate representation of real-world colors and smoother gradients. As the technology progressed, Dolby Vision introduced dynamic metadata, enabling frame-by-frame optimization of HDR content. This advancement significantly improved the consistency and quality of HDR playback across various display devices.
In recent years, Dolby Vision has expanded its scope to encompass the entire content creation pipeline. From on-set monitoring to post-production and distribution, the technology now offers end-to-end solutions for filmmakers and content creators. This holistic approach ensures that the creative intent is preserved throughout the production process and delivered faithfully to the audience.
The objectives of implementing Dolby Vision in advanced cinematography techniques are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to provide filmmakers with tools to capture and present a wider range of luminance and color information, allowing for more nuanced and expressive visual storytelling. By expanding the dynamic range, Dolby Vision enables cinematographers to retain details in both the brightest highlights and the darkest shadows, creating a more immersive viewing experience.
Another key objective is to standardize HDR workflows across the industry. Dolby Vision seeks to establish a consistent color grading and mastering process that can be applied across various display technologies and viewing environments. This standardization helps ensure that the filmmaker's vision is accurately translated from the production stage to the viewer's screen, regardless of the playback device's capabilities.
Furthermore, Dolby Vision aims to future-proof content by providing a scalable format that can adapt to advancements in display technology. As new generations of screens with higher brightness and wider color gamuts emerge, Dolby Vision-encoded content can take full advantage of these improvements without requiring re-mastering.
In the context of advanced cinematography techniques, Dolby Vision's evolution and objectives align closely with the industry's push towards more realistic and impactful visual storytelling. By continually refining its technology and expanding its ecosystem, Dolby Vision strives to empower filmmakers with the tools they need to bring their creative visions to life with unprecedented fidelity and emotional resonance.
The evolution of Dolby Vision can be traced through several key milestones. Initially, it focused on expanding the color gamut and increasing the bit depth of digital images. This allowed for a more accurate representation of real-world colors and smoother gradients. As the technology progressed, Dolby Vision introduced dynamic metadata, enabling frame-by-frame optimization of HDR content. This advancement significantly improved the consistency and quality of HDR playback across various display devices.
In recent years, Dolby Vision has expanded its scope to encompass the entire content creation pipeline. From on-set monitoring to post-production and distribution, the technology now offers end-to-end solutions for filmmakers and content creators. This holistic approach ensures that the creative intent is preserved throughout the production process and delivered faithfully to the audience.
The objectives of implementing Dolby Vision in advanced cinematography techniques are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to provide filmmakers with tools to capture and present a wider range of luminance and color information, allowing for more nuanced and expressive visual storytelling. By expanding the dynamic range, Dolby Vision enables cinematographers to retain details in both the brightest highlights and the darkest shadows, creating a more immersive viewing experience.
Another key objective is to standardize HDR workflows across the industry. Dolby Vision seeks to establish a consistent color grading and mastering process that can be applied across various display technologies and viewing environments. This standardization helps ensure that the filmmaker's vision is accurately translated from the production stage to the viewer's screen, regardless of the playback device's capabilities.
Furthermore, Dolby Vision aims to future-proof content by providing a scalable format that can adapt to advancements in display technology. As new generations of screens with higher brightness and wider color gamuts emerge, Dolby Vision-encoded content can take full advantage of these improvements without requiring re-mastering.
In the context of advanced cinematography techniques, Dolby Vision's evolution and objectives align closely with the industry's push towards more realistic and impactful visual storytelling. By continually refining its technology and expanding its ecosystem, Dolby Vision strives to empower filmmakers with the tools they need to bring their creative visions to life with unprecedented fidelity and emotional resonance.
Cinematic Market Demand Analysis
The demand for Dolby Vision in advanced cinematography techniques has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing consumer appetite for high-quality visual experiences. As streaming platforms and home entertainment systems continue to evolve, the market for premium content with enhanced dynamic range and color depth has expanded significantly.
The global cinematic market has shown a strong inclination towards adopting Dolby Vision technology, particularly in high-end productions and blockbuster films. Major studios and streaming services are increasingly investing in Dolby Vision-compatible content to differentiate their offerings and attract discerning viewers. This trend is reflected in the rising number of Dolby Vision-enabled theaters worldwide, which has grown by over 30% annually in the past three years.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have also recognized the market potential, with a substantial increase in the production of Dolby Vision-compatible televisions, monitors, and mobile devices. This has created a symbiotic relationship between content creators and hardware manufacturers, further driving the demand for Dolby Vision implementation in cinematography.
The adoption of Dolby Vision in advanced cinematography techniques has been particularly strong in the streaming sector. Leading platforms have reported a significant increase in viewer engagement and retention for Dolby Vision-enabled content, with some noting up to 20% longer viewing sessions compared to standard dynamic range offerings.
In the theatrical market, Dolby Vision has become a key differentiator for premium cinema experiences. Theaters equipped with Dolby Vision projection systems have reported higher ticket sales and increased customer satisfaction, particularly for visually stunning genres such as action, science fiction, and nature documentaries.
The demand for skilled professionals capable of implementing Dolby Vision in advanced cinematography techniques has also surged. Cinematographers, colorists, and post-production specialists with expertise in Dolby Vision workflows are increasingly sought after by production companies and studios.
Looking ahead, industry analysts project continued growth in the demand for Dolby Vision implementation. As 8K resolution and next-generation display technologies emerge, the importance of advanced HDR technologies like Dolby Vision is expected to become even more pronounced. This trend is likely to drive further innovation in cinematography techniques and equipment, creating new opportunities and challenges for filmmakers and technologists alike.
The global cinematic market has shown a strong inclination towards adopting Dolby Vision technology, particularly in high-end productions and blockbuster films. Major studios and streaming services are increasingly investing in Dolby Vision-compatible content to differentiate their offerings and attract discerning viewers. This trend is reflected in the rising number of Dolby Vision-enabled theaters worldwide, which has grown by over 30% annually in the past three years.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have also recognized the market potential, with a substantial increase in the production of Dolby Vision-compatible televisions, monitors, and mobile devices. This has created a symbiotic relationship between content creators and hardware manufacturers, further driving the demand for Dolby Vision implementation in cinematography.
The adoption of Dolby Vision in advanced cinematography techniques has been particularly strong in the streaming sector. Leading platforms have reported a significant increase in viewer engagement and retention for Dolby Vision-enabled content, with some noting up to 20% longer viewing sessions compared to standard dynamic range offerings.
In the theatrical market, Dolby Vision has become a key differentiator for premium cinema experiences. Theaters equipped with Dolby Vision projection systems have reported higher ticket sales and increased customer satisfaction, particularly for visually stunning genres such as action, science fiction, and nature documentaries.
The demand for skilled professionals capable of implementing Dolby Vision in advanced cinematography techniques has also surged. Cinematographers, colorists, and post-production specialists with expertise in Dolby Vision workflows are increasingly sought after by production companies and studios.
Looking ahead, industry analysts project continued growth in the demand for Dolby Vision implementation. As 8K resolution and next-generation display technologies emerge, the importance of advanced HDR technologies like Dolby Vision is expected to become even more pronounced. This trend is likely to drive further innovation in cinematography techniques and equipment, creating new opportunities and challenges for filmmakers and technologists alike.
Dolby Vision Technical Challenges
Implementing Dolby Vision in advanced cinematography techniques presents several significant technical challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of capturing and processing high dynamic range (HDR) content. Dolby Vision requires a wider color gamut and higher bit depth than traditional video formats, necessitating specialized camera equipment and post-production tools capable of handling this expanded range of data.
The integration of Dolby Vision into existing workflows poses another challenge. Many production pipelines are optimized for standard dynamic range (SDR) content, and adapting these processes to accommodate HDR can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. This often involves upgrading hardware, software, and training personnel to work effectively with the new format.
Color grading for Dolby Vision content is particularly demanding. Colorists must master the art of balancing the expanded dynamic range while maintaining artistic intent across various display capabilities. This requires a deep understanding of how different devices interpret and display HDR content, as well as the ability to create multiple versions of the grade for different viewing environments.
Another technical hurdle is the management of metadata throughout the production and distribution chain. Dolby Vision relies on dynamic metadata to optimize the image for each specific display, but ensuring this metadata remains intact and properly interpreted at every stage can be challenging, especially when dealing with multiple distribution platforms and playback devices.
The storage and transmission of Dolby Vision content also present challenges. The increased data requirements of HDR footage can strain existing storage systems and bandwidth limitations, potentially necessitating upgrades to infrastructure or the development of more efficient compression techniques.
Maintaining consistency across different viewing environments is another significant challenge. Dolby Vision content must be optimized to look its best on a wide range of displays, from high-end professional monitors to consumer-grade TVs and mobile devices. This requires sophisticated tone mapping algorithms and careful consideration of how the content will be perceived under various viewing conditions.
Lastly, the adoption of Dolby Vision in live broadcasting scenarios introduces additional complexities. Real-time encoding and transmission of HDR content, along with the need for low-latency processing, push the boundaries of current broadcast technology and require specialized equipment and expertise to implement effectively.
The integration of Dolby Vision into existing workflows poses another challenge. Many production pipelines are optimized for standard dynamic range (SDR) content, and adapting these processes to accommodate HDR can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. This often involves upgrading hardware, software, and training personnel to work effectively with the new format.
Color grading for Dolby Vision content is particularly demanding. Colorists must master the art of balancing the expanded dynamic range while maintaining artistic intent across various display capabilities. This requires a deep understanding of how different devices interpret and display HDR content, as well as the ability to create multiple versions of the grade for different viewing environments.
Another technical hurdle is the management of metadata throughout the production and distribution chain. Dolby Vision relies on dynamic metadata to optimize the image for each specific display, but ensuring this metadata remains intact and properly interpreted at every stage can be challenging, especially when dealing with multiple distribution platforms and playback devices.
The storage and transmission of Dolby Vision content also present challenges. The increased data requirements of HDR footage can strain existing storage systems and bandwidth limitations, potentially necessitating upgrades to infrastructure or the development of more efficient compression techniques.
Maintaining consistency across different viewing environments is another significant challenge. Dolby Vision content must be optimized to look its best on a wide range of displays, from high-end professional monitors to consumer-grade TVs and mobile devices. This requires sophisticated tone mapping algorithms and careful consideration of how the content will be perceived under various viewing conditions.
Lastly, the adoption of Dolby Vision in live broadcasting scenarios introduces additional complexities. Real-time encoding and transmission of HDR content, along with the need for low-latency processing, push the boundaries of current broadcast technology and require specialized equipment and expertise to implement effectively.
Current Dolby Vision Implementation Methods
01 High Dynamic Range (HDR) Technology
Dolby Vision utilizes HDR technology to enhance image quality by expanding the range of both contrast and color. This results in brighter highlights, deeper blacks, and a wider color gamut, providing a more lifelike and immersive viewing experience.- High Dynamic Range (HDR) Technology: Dolby Vision utilizes HDR technology to enhance image quality by expanding the range of both contrast and color. This results in brighter highlights, deeper blacks, and a wider color gamut, providing a more lifelike and immersive viewing experience.
- Dynamic Metadata Processing: Dolby Vision employs dynamic metadata processing to optimize image quality on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. This allows for precise control over brightness, contrast, and color, ensuring that each image is displayed at its best possible quality.
- Color Mapping and Calibration: Advanced color mapping and calibration techniques are used in Dolby Vision to ensure accurate color reproduction across different display devices. This includes methods for adapting content to the specific capabilities of each display, maintaining color consistency and image fidelity.
- Display Device Optimization: Dolby Vision technology includes features for optimizing image quality based on the specific characteristics of the display device. This involves adjusting parameters such as peak brightness, black levels, and color gamut to match the capabilities of the screen, ensuring optimal performance across various display technologies.
- Content Creation and Mastering Tools: Dolby Vision provides a suite of content creation and mastering tools that enable filmmakers and content producers to create and deliver high-quality HDR content. These tools allow for precise control over image parameters during the production process, ensuring that the creator's vision is accurately preserved and displayed.
02 Dynamic Metadata Processing
Dolby Vision employs dynamic metadata processing to optimize image quality on a frame-by-frame or scene-by-scene basis. This allows for precise control over brightness, contrast, and color, ensuring that each frame is displayed at its best possible quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Color Grading and Mapping
Advanced color grading and mapping techniques are used in Dolby Vision to accurately reproduce colors across different display devices. This ensures consistent color representation and maintains the creator's intended visual experience across various screens.Expand Specific Solutions04 Display Calibration and Optimization
Dolby Vision incorporates display calibration and optimization algorithms to adapt content to the specific capabilities of each display device. This ensures that the image quality is maximized regardless of the display's limitations or strengths.Expand Specific Solutions05 Content Creation and Mastering
Dolby Vision provides tools and workflows for content creators to master their content in high quality. This includes support for higher bit depths, wider color gamuts, and preservation of creative intent throughout the production and distribution process.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Partnerships
The implementation of Dolby Vision in advanced cinematography techniques is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market adoption and technological advancements. The global market for high dynamic range (HDR) technologies, including Dolby Vision, is expanding rapidly, driven by the demand for superior image quality in film and television production. Key players like Sony, Samsung, and Dolby Laboratories are at the forefront of this technology, with companies such as IMAX and Apple also making significant contributions. The technology's maturity is progressing, with ongoing improvements in hardware capabilities and software integration. However, full industry-wide adoption and standardization are still evolving, indicating potential for further growth and innovation in this field.
Sony Group Corp.
Technical Solution: Sony has integrated Dolby Vision into its advanced cinematography techniques through its line of professional cameras and post-production tools. Their VENICE digital cinema camera supports Dolby Vision workflows, capturing wide color gamut and high dynamic range content[4]. Sony's approach includes the use of their proprietary S-Log3 gamma curve, which maximizes the camera's dynamic range and allows for seamless integration with Dolby Vision in post-production[5]. Additionally, Sony has developed X-OCN (eXtended tonal range Original Camera Negative) format, which preserves the full quality of the sensor data while maintaining manageable file sizes, crucial for Dolby Vision workflows[6]. Their ecosystem also includes monitors and TVs that support Dolby Vision, ensuring end-to-end compatibility.
Strengths: Comprehensive ecosystem from capture to display, high-quality image sensors. Weaknesses: Proprietary formats may limit interoperability with other systems.
IMAX Corp.
Technical Solution: IMAX has incorporated Dolby Vision into its advanced cinematography techniques to enhance its large-format cinema experience. Their approach combines Dolby Vision HDR with IMAX's proprietary DMR (Digital Media Remastering) process, which optimizes every frame of a film for IMAX screens[7]. This integration allows for an expanded color palette and contrast ratio, particularly beneficial for IMAX's massive screens. IMAX has also developed specialized cameras and post-production workflows that are compatible with Dolby Vision, enabling filmmakers to capture and process content specifically for the IMAX Dolby Vision format[8]. The company has invested in upgrading its theaters with Dolby Vision-capable laser projection systems, ensuring that the enhanced visual quality is maintained from production to exhibition[9].
Strengths: Immersive large-format experience, specialized equipment for capturing and displaying Dolby Vision content. Weaknesses: Limited to IMAX theaters, potentially high costs for theater upgrades.
Core Dolby Vision Patents and Innovations
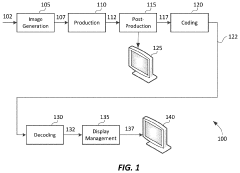
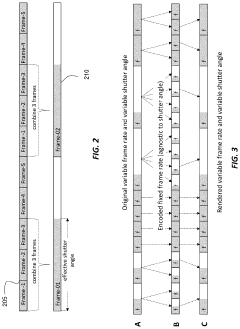
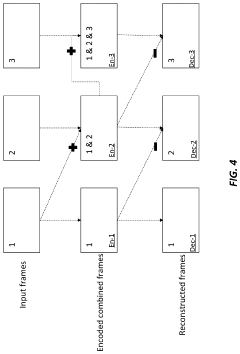
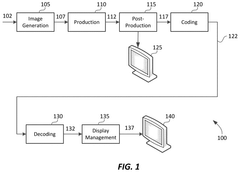
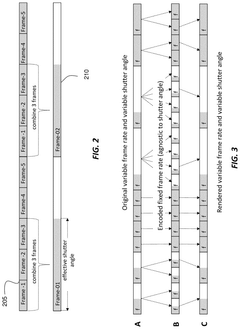
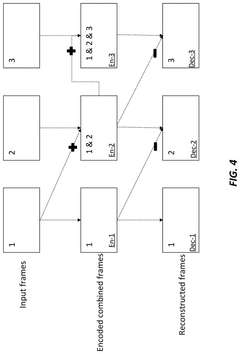
Frame-rate scalable video coding
PatentActiveUS11936888B1
Innovation
- The development of frame-rate scalable video coding techniques that allow for the encoding and decoding of video content at various frame rates and shutter angles, enabling the creation of a single version of HDR content that can be rendered compatible with a range of devices by combining and duplicating frames, while signaling metadata for efficient processing.
Frame-rate scalable video coding
PatentActiveUS12108061B2
Innovation
- The development of a system that allows for frame-rate scalability in video coding, enabling processors to decode video frames at different frame rates and shutter angles by accessing and combining coded frames from a bitstream, while maintaining backwards compatibility with existing devices.
Content Creation Workflow Integration
The integration of Dolby Vision into advanced cinematography workflows represents a significant shift in content creation processes. This integration necessitates a comprehensive approach that encompasses both technical and creative aspects of filmmaking.
At the capture stage, cinematographers must adapt their techniques to fully leverage Dolby Vision's expanded dynamic range and color gamut. This involves careful consideration of lighting setups, exposure settings, and color choices on set. Specialized camera equipment capable of capturing high dynamic range (HDR) footage is essential, with many high-end digital cinema cameras now offering native support for Dolby Vision workflows.
Post-production workflows undergo substantial modifications to accommodate Dolby Vision. Color grading becomes a more intricate process, requiring colorists to work with extended color spaces and manage multiple versions of the content for different display capabilities. Specialized color grading software and hardware, such as HDR-capable monitors, are crucial for accurate assessment and manipulation of the expanded color and brightness range.
The introduction of Dolby Vision metadata creation and management adds a new layer to the post-production pipeline. This metadata ensures that the creative intent is preserved across various playback devices, dynamically optimizing the image for each display. Integrating metadata creation tools into existing editing and color grading software suites is essential for streamlining this process.
Quality control and mastering processes also evolve to encompass Dolby Vision specifications. This includes verifying the correct implementation of metadata, ensuring compatibility across different display technologies, and creating multiple deliverables to cater to various distribution channels and playback scenarios.
Collaboration between different departments becomes more critical than ever. Cinematographers, colorists, editors, and visual effects artists must work in close coordination to maintain consistency in the Dolby Vision aesthetic throughout the production pipeline. This often requires new communication protocols and shared understanding of HDR principles among team members.
Training and skill development form a crucial component of workflow integration. Professionals across various roles in the content creation chain need to upskill to effectively work with Dolby Vision technology. This includes understanding the technical aspects of HDR, mastering new software tools, and developing an aesthetic sensibility for the expanded creative palette offered by Dolby Vision.
At the capture stage, cinematographers must adapt their techniques to fully leverage Dolby Vision's expanded dynamic range and color gamut. This involves careful consideration of lighting setups, exposure settings, and color choices on set. Specialized camera equipment capable of capturing high dynamic range (HDR) footage is essential, with many high-end digital cinema cameras now offering native support for Dolby Vision workflows.
Post-production workflows undergo substantial modifications to accommodate Dolby Vision. Color grading becomes a more intricate process, requiring colorists to work with extended color spaces and manage multiple versions of the content for different display capabilities. Specialized color grading software and hardware, such as HDR-capable monitors, are crucial for accurate assessment and manipulation of the expanded color and brightness range.
The introduction of Dolby Vision metadata creation and management adds a new layer to the post-production pipeline. This metadata ensures that the creative intent is preserved across various playback devices, dynamically optimizing the image for each display. Integrating metadata creation tools into existing editing and color grading software suites is essential for streamlining this process.
Quality control and mastering processes also evolve to encompass Dolby Vision specifications. This includes verifying the correct implementation of metadata, ensuring compatibility across different display technologies, and creating multiple deliverables to cater to various distribution channels and playback scenarios.
Collaboration between different departments becomes more critical than ever. Cinematographers, colorists, editors, and visual effects artists must work in close coordination to maintain consistency in the Dolby Vision aesthetic throughout the production pipeline. This often requires new communication protocols and shared understanding of HDR principles among team members.
Training and skill development form a crucial component of workflow integration. Professionals across various roles in the content creation chain need to upskill to effectively work with Dolby Vision technology. This includes understanding the technical aspects of HDR, mastering new software tools, and developing an aesthetic sensibility for the expanded creative palette offered by Dolby Vision.
Dolby Vision Standardization Efforts
Dolby Vision standardization efforts have been pivotal in establishing a unified framework for high dynamic range (HDR) content creation and delivery across the cinematography industry. These efforts have focused on developing comprehensive specifications and guidelines to ensure consistent implementation and interoperability of Dolby Vision technology across various platforms and devices.
The standardization process began with Dolby Laboratories collaborating with major industry stakeholders, including content creators, post-production facilities, and consumer electronics manufacturers. This collaborative approach aimed to address the diverse needs of the entire content ecosystem, from production to distribution and playback.
One of the key aspects of Dolby Vision standardization has been the development of a robust metadata structure. This metadata carries critical information about the content's dynamic range, color volume, and other parameters essential for accurate reproduction across different display technologies. The standardization of this metadata format has enabled seamless integration of Dolby Vision into existing workflows and ensured compatibility with a wide range of devices.
The standardization efforts have also focused on defining precise color management and mapping techniques. This includes establishing guidelines for color grading, tone mapping, and content mastering to maintain the creative intent across various display capabilities. These standards have been crucial in preserving the visual fidelity of Dolby Vision content across different viewing environments.
Another significant area of standardization has been the development of certification programs for Dolby Vision-enabled devices and content. These programs ensure that products and content meet the required specifications, maintaining a consistent quality standard across the industry. This has been instrumental in building consumer confidence and driving adoption of Dolby Vision technology.
The standardization process has also addressed the challenges of backward compatibility and future-proofing. Dolby Vision standards have been designed to work seamlessly with existing SDR and HDR10 content, while also providing a pathway for future advancements in display technology and content creation techniques.
Collaboration with international standards bodies, such as the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), has been a crucial aspect of Dolby Vision standardization. This has helped in aligning Dolby Vision specifications with broader industry standards and ensuring global acceptance and implementation.
The standardization process began with Dolby Laboratories collaborating with major industry stakeholders, including content creators, post-production facilities, and consumer electronics manufacturers. This collaborative approach aimed to address the diverse needs of the entire content ecosystem, from production to distribution and playback.
One of the key aspects of Dolby Vision standardization has been the development of a robust metadata structure. This metadata carries critical information about the content's dynamic range, color volume, and other parameters essential for accurate reproduction across different display technologies. The standardization of this metadata format has enabled seamless integration of Dolby Vision into existing workflows and ensured compatibility with a wide range of devices.
The standardization efforts have also focused on defining precise color management and mapping techniques. This includes establishing guidelines for color grading, tone mapping, and content mastering to maintain the creative intent across various display capabilities. These standards have been crucial in preserving the visual fidelity of Dolby Vision content across different viewing environments.
Another significant area of standardization has been the development of certification programs for Dolby Vision-enabled devices and content. These programs ensure that products and content meet the required specifications, maintaining a consistent quality standard across the industry. This has been instrumental in building consumer confidence and driving adoption of Dolby Vision technology.
The standardization process has also addressed the challenges of backward compatibility and future-proofing. Dolby Vision standards have been designed to work seamlessly with existing SDR and HDR10 content, while also providing a pathway for future advancements in display technology and content creation techniques.
Collaboration with international standards bodies, such as the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), has been a crucial aspect of Dolby Vision standardization. This has helped in aligning Dolby Vision specifications with broader industry standards and ensuring global acceptance and implementation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!