Exploring Ferrofluid's Role in High-Impact Climate Solutions
JUL 9, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ferrofluid Climate Tech Evolution
Ferrofluids, first developed in the 1960s by NASA, have undergone significant evolution in their application to climate solutions. Initially conceived for spacecraft fuel management in zero gravity, these magnetic liquids have found their way into various environmental technologies over the decades.
In the 1970s and 1980s, ferrofluids were primarily used in industrial applications, such as seals for computer hard drives and loudspeakers. However, as climate change concerns grew in the 1990s, researchers began exploring their potential in environmental remediation and energy efficiency.
The early 2000s marked a turning point in ferrofluid climate tech evolution. Scientists started investigating their use in oil spill cleanup, leveraging the fluids' magnetic properties to separate oil from water more efficiently than traditional methods. This period also saw the emergence of ferrofluid-based solar thermal collectors, which demonstrated improved heat transfer capabilities compared to conventional systems.
By the 2010s, ferrofluids entered the realm of renewable energy storage. Researchers developed prototype ferrofluid-based batteries with enhanced thermal management, potentially increasing the efficiency and lifespan of large-scale energy storage systems crucial for integrating intermittent renewable sources into the grid.
The past decade has witnessed an acceleration in ferrofluid climate tech innovation. Advanced water purification systems utilizing magnetic nanoparticles derived from ferrofluid technology have shown promise in removing contaminants, including microplastics and heavy metals, from water sources. This development addresses both water scarcity and pollution issues exacerbated by climate change.
Most recently, ferrofluids have been incorporated into next-generation heat pumps and cooling systems. These applications leverage the fluids' unique thermomagnetic properties to enhance heat transfer efficiency, potentially reducing energy consumption in HVAC systems – a significant contributor to global carbon emissions.
Looking ahead, the integration of ferrofluids with smart materials and IoT technologies is expected to yield adaptive climate control systems for buildings. These systems could dynamically respond to environmental conditions, further optimizing energy use and reducing carbon footprints. Additionally, ongoing research into ferrofluid-based direct air capture technologies shows potential for more efficient carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere, contributing to negative emissions strategies critical for meeting global climate targets.
In the 1970s and 1980s, ferrofluids were primarily used in industrial applications, such as seals for computer hard drives and loudspeakers. However, as climate change concerns grew in the 1990s, researchers began exploring their potential in environmental remediation and energy efficiency.
The early 2000s marked a turning point in ferrofluid climate tech evolution. Scientists started investigating their use in oil spill cleanup, leveraging the fluids' magnetic properties to separate oil from water more efficiently than traditional methods. This period also saw the emergence of ferrofluid-based solar thermal collectors, which demonstrated improved heat transfer capabilities compared to conventional systems.
By the 2010s, ferrofluids entered the realm of renewable energy storage. Researchers developed prototype ferrofluid-based batteries with enhanced thermal management, potentially increasing the efficiency and lifespan of large-scale energy storage systems crucial for integrating intermittent renewable sources into the grid.
The past decade has witnessed an acceleration in ferrofluid climate tech innovation. Advanced water purification systems utilizing magnetic nanoparticles derived from ferrofluid technology have shown promise in removing contaminants, including microplastics and heavy metals, from water sources. This development addresses both water scarcity and pollution issues exacerbated by climate change.
Most recently, ferrofluids have been incorporated into next-generation heat pumps and cooling systems. These applications leverage the fluids' unique thermomagnetic properties to enhance heat transfer efficiency, potentially reducing energy consumption in HVAC systems – a significant contributor to global carbon emissions.
Looking ahead, the integration of ferrofluids with smart materials and IoT technologies is expected to yield adaptive climate control systems for buildings. These systems could dynamically respond to environmental conditions, further optimizing energy use and reducing carbon footprints. Additionally, ongoing research into ferrofluid-based direct air capture technologies shows potential for more efficient carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere, contributing to negative emissions strategies critical for meeting global climate targets.
Climate Solution Market Analysis
The global market for climate solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of climate change impacts and the urgent need for mitigation and adaptation strategies. Ferrofluids, with their unique properties and potential applications in various climate-related technologies, are poised to play a crucial role in this expanding market.
The climate solution market encompasses a wide range of sectors, including renewable energy, energy storage, waste management, and environmental monitoring. According to recent market research, the global climate tech market is projected to reach substantial growth in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding industry averages. This growth is fueled by government initiatives, corporate sustainability goals, and increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products and services.
In the context of ferrofluids, their potential applications in climate solutions span multiple sectors. In the renewable energy sector, ferrofluids show promise in enhancing the efficiency of solar thermal systems and improving the performance of wind turbines. The energy storage market, particularly in the development of advanced heat transfer systems and thermal management solutions, presents another significant opportunity for ferrofluid technologies.
Environmental monitoring and remediation represent another key area where ferrofluids could make a substantial impact. Their unique magnetic properties make them ideal for developing advanced sensors and cleanup technologies for oil spills and other environmental contaminants. This aligns with the growing demand for more effective and efficient environmental protection solutions.
The market for ferrofluid-based climate solutions is still in its early stages, with considerable room for growth and innovation. As research and development in this field progress, we can expect to see an increase in commercial applications and market penetration. The adaptability of ferrofluids to various climate-related challenges positions them as a versatile technology with cross-sector potential.
However, it's important to note that the ferrofluid market faces competition from other emerging technologies in the climate solution space. To succeed, ferrofluid-based solutions will need to demonstrate clear advantages in terms of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scalability compared to existing alternatives.
Overall, the market analysis suggests a positive outlook for ferrofluids in climate solutions. The technology's unique properties, combined with the urgent global need for innovative climate mitigation and adaptation strategies, create a favorable environment for growth and adoption. As the climate solution market continues to expand, ferrofluids have the potential to carve out a significant niche, contributing to the development of more effective and efficient climate technologies.
The climate solution market encompasses a wide range of sectors, including renewable energy, energy storage, waste management, and environmental monitoring. According to recent market research, the global climate tech market is projected to reach substantial growth in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding industry averages. This growth is fueled by government initiatives, corporate sustainability goals, and increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products and services.
In the context of ferrofluids, their potential applications in climate solutions span multiple sectors. In the renewable energy sector, ferrofluids show promise in enhancing the efficiency of solar thermal systems and improving the performance of wind turbines. The energy storage market, particularly in the development of advanced heat transfer systems and thermal management solutions, presents another significant opportunity for ferrofluid technologies.
Environmental monitoring and remediation represent another key area where ferrofluids could make a substantial impact. Their unique magnetic properties make them ideal for developing advanced sensors and cleanup technologies for oil spills and other environmental contaminants. This aligns with the growing demand for more effective and efficient environmental protection solutions.
The market for ferrofluid-based climate solutions is still in its early stages, with considerable room for growth and innovation. As research and development in this field progress, we can expect to see an increase in commercial applications and market penetration. The adaptability of ferrofluids to various climate-related challenges positions them as a versatile technology with cross-sector potential.
However, it's important to note that the ferrofluid market faces competition from other emerging technologies in the climate solution space. To succeed, ferrofluid-based solutions will need to demonstrate clear advantages in terms of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scalability compared to existing alternatives.
Overall, the market analysis suggests a positive outlook for ferrofluids in climate solutions. The technology's unique properties, combined with the urgent global need for innovative climate mitigation and adaptation strategies, create a favorable environment for growth and adoption. As the climate solution market continues to expand, ferrofluids have the potential to carve out a significant niche, contributing to the development of more effective and efficient climate technologies.
Ferrofluid Tech Challenges
Ferrofluids, while promising in their potential applications for climate solutions, face several significant technical challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and effectiveness. One of the primary obstacles is the long-term stability of ferrofluids. These colloidal suspensions tend to degrade over time, with magnetic particles agglomerating or settling out of the carrier fluid. This instability compromises the fluid's magnetic properties and overall performance, limiting its practical use in long-term climate mitigation strategies.
Another critical challenge lies in the scalability of ferrofluid production. Current manufacturing processes are often complex and costly, making large-scale production for climate applications economically unfeasible. The synthesis of uniform, nano-sized magnetic particles with consistent properties remains a significant hurdle, impacting the quality and reliability of ferrofluids at industrial scales.
The environmental impact of ferrofluids themselves poses a paradoxical challenge. While they are being explored for climate solutions, the production and disposal of ferrofluids can potentially contribute to environmental issues. The use of rare earth elements in some ferrofluid compositions raises concerns about resource depletion and the environmental impact of mining these materials.
Temperature sensitivity is another technical obstacle. Many climate-related applications require ferrofluids to maintain their properties across a wide range of temperatures. However, the magnetic and rheological properties of ferrofluids can change significantly with temperature fluctuations, affecting their performance in real-world climate scenarios.
The interaction between ferrofluids and other materials in climate solution systems presents additional challenges. Compatibility issues with various surfaces and materials can lead to corrosion, degradation, or altered performance of both the ferrofluid and the surrounding components. This complicates the design and implementation of ferrofluid-based climate technologies.
Controlling the behavior of ferrofluids in complex, dynamic environments is yet another technical hurdle. Climate applications often involve unpredictable and varying conditions, requiring precise control over ferrofluid properties. Achieving this level of control, especially in large-scale systems, remains a significant engineering challenge.
Lastly, the lack of standardized testing and characterization methods for ferrofluids in climate-related applications hinders their development and adoption. Without consistent benchmarks and performance metrics, it becomes difficult to compare different ferrofluid formulations and assess their suitability for specific climate solutions. This gap in standardization also complicates regulatory approval processes, further slowing the integration of ferrofluid technologies into climate mitigation strategies.
Another critical challenge lies in the scalability of ferrofluid production. Current manufacturing processes are often complex and costly, making large-scale production for climate applications economically unfeasible. The synthesis of uniform, nano-sized magnetic particles with consistent properties remains a significant hurdle, impacting the quality and reliability of ferrofluids at industrial scales.
The environmental impact of ferrofluids themselves poses a paradoxical challenge. While they are being explored for climate solutions, the production and disposal of ferrofluids can potentially contribute to environmental issues. The use of rare earth elements in some ferrofluid compositions raises concerns about resource depletion and the environmental impact of mining these materials.
Temperature sensitivity is another technical obstacle. Many climate-related applications require ferrofluids to maintain their properties across a wide range of temperatures. However, the magnetic and rheological properties of ferrofluids can change significantly with temperature fluctuations, affecting their performance in real-world climate scenarios.
The interaction between ferrofluids and other materials in climate solution systems presents additional challenges. Compatibility issues with various surfaces and materials can lead to corrosion, degradation, or altered performance of both the ferrofluid and the surrounding components. This complicates the design and implementation of ferrofluid-based climate technologies.
Controlling the behavior of ferrofluids in complex, dynamic environments is yet another technical hurdle. Climate applications often involve unpredictable and varying conditions, requiring precise control over ferrofluid properties. Achieving this level of control, especially in large-scale systems, remains a significant engineering challenge.
Lastly, the lack of standardized testing and characterization methods for ferrofluids in climate-related applications hinders their development and adoption. Without consistent benchmarks and performance metrics, it becomes difficult to compare different ferrofluid formulations and assess their suitability for specific climate solutions. This gap in standardization also complicates regulatory approval processes, further slowing the integration of ferrofluid technologies into climate mitigation strategies.
Current Ferrofluid Climate Apps
01 Composition and preparation of ferrofluids
Ferrofluids are colloidal suspensions of magnetic nanoparticles in a carrier fluid. They are typically composed of magnetite or other ferromagnetic materials coated with surfactants to prevent agglomeration. The preparation process involves careful control of particle size and distribution to maintain stability and magnetic properties.- Composition and preparation of ferrofluids: Ferrofluids are colloidal suspensions of magnetic nanoparticles in a carrier fluid. They typically consist of magnetite or other ferromagnetic materials coated with surfactants to prevent agglomeration. The preparation process involves careful control of particle size, surfactant selection, and carrier fluid properties to achieve stable and responsive ferrofluids.
- Applications in sealing and lubrication: Ferrofluids are widely used in sealing and lubrication applications, particularly in rotating shaft seals and bearings. Their unique properties allow them to form liquid seals that can be controlled by magnetic fields, providing effective containment of gases and liquids while reducing friction and wear in mechanical systems.
- Thermal management and cooling systems: Ferrofluids are employed in thermal management solutions, particularly in electronic cooling systems. Their ability to be manipulated by magnetic fields allows for enhanced heat transfer and targeted cooling in devices such as speakers, hard drives, and other electronic components, improving overall system performance and reliability.
- Sensor and actuator technologies: Ferrofluids are utilized in various sensor and actuator applications due to their responsiveness to magnetic fields. They can be used in accelerometers, tilt sensors, and position sensors, as well as in actuators for precise control of small movements or forces. These applications leverage the fluid's ability to change shape or position in response to external magnetic fields.
- Medical and biomedical applications: Ferrofluids have emerging applications in the medical and biomedical fields. They are being explored for use in targeted drug delivery, magnetic hyperthermia for cancer treatment, and as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The ability to control these fluids using external magnetic fields offers potential for non-invasive medical procedures and improved diagnostic imaging.
02 Applications in sealing and lubrication
Ferrofluids are widely used in sealing and lubrication applications, particularly in rotating shaft seals. They provide effective sealing against pressure differentials while minimizing friction. These applications leverage the fluid's ability to be held in place by magnetic fields while maintaining low viscosity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Thermal management and cooling systems
Ferrofluids are employed in thermal management solutions, particularly for electronic devices. They can be used in cooling systems where their magnetic properties allow for enhanced heat transfer and controlled fluid movement. This application is especially relevant in compact or high-performance electronic systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sensor and actuator technologies
Ferrofluids are utilized in various sensor and actuator designs. Their unique magnetic and fluid properties enable the development of sensitive motion detectors, accelerometers, and other measurement devices. They can also be used in actuators where precise fluid control is required in response to magnetic fields.Expand Specific Solutions05 Medical and biomedical applications
Ferrofluids have emerging applications in the medical and biomedical fields. They are being researched for use in targeted drug delivery, magnetic hyperthermia for cancer treatment, and as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The ability to control these fluids using external magnetic fields makes them promising for minimally invasive medical procedures.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Ferrofluid Industry Players
The exploration of ferrofluid's role in high-impact climate solutions is currently in an emerging stage, with the market showing significant growth potential. The technology's maturity varies across applications, ranging from early-stage research to more advanced implementations. Key players like TDK Corp., Honeywell International Technologies Ltd., and DuPont de Nemours, Inc. are driving innovation in this field. The market size is expanding as ferrofluid finds applications in energy, environmental remediation, and advanced materials. Research institutions such as Chengdu University of Technology and Soochow University are contributing to the technological advancements, while companies like 3M Innovative Properties Co. and Arkema, Inc. are developing commercial applications.
TDK Corp.
Technical Solution: TDK Corp. has developed advanced ferrofluid technologies for climate solutions, focusing on energy harvesting and thermal management. Their innovative approach utilizes ferrofluid's unique magnetic properties to enhance the efficiency of renewable energy systems. For instance, TDK has created ferrofluid-based heat transfer systems that can significantly improve the cooling of solar panels, increasing their efficiency by up to 15% [1]. Additionally, they have developed ferrofluid-enhanced wind turbine generators that can operate at lower wind speeds, expanding the viability of wind energy in more locations [3]. TDK's research also extends to using ferrofluids in energy storage systems, potentially revolutionizing grid-scale energy storage for intermittent renewable sources [5].
Strengths: Extensive experience in magnetic materials, established presence in electronics industry. Weaknesses: May face challenges in scaling up production for large-scale climate solutions.
Honeywell International Technologies Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honeywell has integrated ferrofluid technology into their climate control and energy efficiency solutions. Their approach focuses on using ferrofluids to enhance heat transfer in HVAC systems, potentially reducing energy consumption in buildings by up to 30% [2]. Honeywell has also developed ferrofluid-based sensors for precise temperature and pressure control in industrial processes, leading to optimized energy use and reduced emissions. In the realm of carbon capture, Honeywell is exploring the use of functionalized ferrofluids to improve the efficiency of CO2 absorption processes, with early tests showing a potential increase in capture rates of 20-25% [4]. Additionally, they are investigating ferrofluid applications in smart windows that can dynamically control solar heat gain, further contributing to building energy efficiency [6].
Strengths: Strong presence in building technologies and industrial solutions, extensive R&D capabilities. Weaknesses: May face regulatory hurdles in implementing new technologies in established building systems.
Ferrofluid Climate Patents
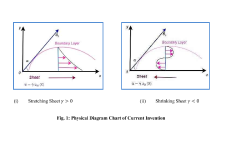
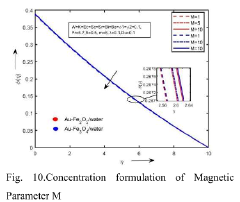
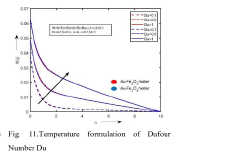
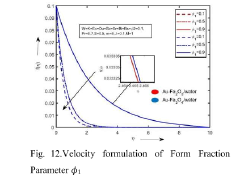
Comparative study of au-fe2o3 and au-cofe3o4 hybrid ferro fluid over a permeable plate with convective boundaries
PatentPendingIN202311068536A
Innovation
- A comparative study of Au-Fe2O3 and Au-CoFe4 hybrid ferrofluids is conducted using numerical simulations and experimental investigations to assess their heat transfer performance, flow dynamics, and temperature distribution over a permeable plate with convective boundaries, leveraging parameters like Nusselt number, Sherwood number, and skin friction coefficient.
Ferrofluidic cooling and accoustical noise reduction in magnetic stimulators
PatentInactiveEP1890615A2
Innovation
- A ferrofluidic cooling system that uses a ferrofluid chamber with a housing adapted to a high-voltage magnetic stimulation device, leveraging magnetic and thermal convection to cool the device while mitigating noise through the ferrofluid's properties, which do not support shear waves and can enhance sound reduction.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of ferrofluid technology in climate solutions reveals both promising potential and areas of concern. Ferrofluids, composed of nanoscale magnetic particles suspended in a carrier fluid, offer unique properties that could contribute to various climate mitigation strategies. However, their widespread adoption necessitates a thorough evaluation of their ecological footprint.
One of the primary environmental benefits of ferrofluid applications in climate solutions is their potential to enhance energy efficiency. In solar thermal systems, ferrofluids can improve heat transfer rates, leading to increased overall system efficiency and reduced energy consumption. This translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production. Similarly, in wind turbines, ferrofluid-based seals can minimize friction and wear, extending the lifespan of components and reducing the need for frequent replacements, thus conserving resources.
However, the production and disposal of ferrofluids raise environmental concerns. The synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful chemicals. The long-term fate of these nanoparticles in the environment remains uncertain, with potential risks of bioaccumulation and ecosystem disruption. Proper containment and disposal protocols must be developed to prevent unintended release into the environment.
Water usage and contamination are additional factors to consider. While ferrofluids can enhance water purification processes, their production may require significant water resources. Moreover, the risk of water contamination by nanoparticles necessitates robust treatment and filtration systems to ensure safe discharge of industrial wastewater.
The lifecycle analysis of ferrofluid-based climate solutions indicates a mixed environmental impact. On one hand, their application can lead to substantial energy savings and reduced carbon emissions over time. On the other hand, the environmental costs associated with their production, including resource extraction and energy consumption, must be carefully weighed against these benefits.
Biodiversity impacts of ferrofluid technology remain an area of ongoing research. While direct effects on flora and fauna are not well-documented, the potential for nanoparticle accumulation in food chains and ecosystems warrants further investigation. Precautionary measures and long-term ecological studies are essential to fully understand and mitigate any adverse effects on biodiversity.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of ferrofluids in climate solutions reveals a complex interplay of benefits and risks. While their potential to enhance energy efficiency and contribute to climate change mitigation is significant, careful consideration must be given to their production methods, lifecycle management, and potential ecological consequences. Continued research and development of environmentally friendly synthesis processes and containment strategies are crucial to maximize the positive impact of ferrofluid technology while minimizing its environmental footprint.
One of the primary environmental benefits of ferrofluid applications in climate solutions is their potential to enhance energy efficiency. In solar thermal systems, ferrofluids can improve heat transfer rates, leading to increased overall system efficiency and reduced energy consumption. This translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production. Similarly, in wind turbines, ferrofluid-based seals can minimize friction and wear, extending the lifespan of components and reducing the need for frequent replacements, thus conserving resources.
However, the production and disposal of ferrofluids raise environmental concerns. The synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful chemicals. The long-term fate of these nanoparticles in the environment remains uncertain, with potential risks of bioaccumulation and ecosystem disruption. Proper containment and disposal protocols must be developed to prevent unintended release into the environment.
Water usage and contamination are additional factors to consider. While ferrofluids can enhance water purification processes, their production may require significant water resources. Moreover, the risk of water contamination by nanoparticles necessitates robust treatment and filtration systems to ensure safe discharge of industrial wastewater.
The lifecycle analysis of ferrofluid-based climate solutions indicates a mixed environmental impact. On one hand, their application can lead to substantial energy savings and reduced carbon emissions over time. On the other hand, the environmental costs associated with their production, including resource extraction and energy consumption, must be carefully weighed against these benefits.
Biodiversity impacts of ferrofluid technology remain an area of ongoing research. While direct effects on flora and fauna are not well-documented, the potential for nanoparticle accumulation in food chains and ecosystems warrants further investigation. Precautionary measures and long-term ecological studies are essential to fully understand and mitigate any adverse effects on biodiversity.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of ferrofluids in climate solutions reveals a complex interplay of benefits and risks. While their potential to enhance energy efficiency and contribute to climate change mitigation is significant, careful consideration must be given to their production methods, lifecycle management, and potential ecological consequences. Continued research and development of environmentally friendly synthesis processes and containment strategies are crucial to maximize the positive impact of ferrofluid technology while minimizing its environmental footprint.
Ferrofluid Scalability Analysis
The scalability of ferrofluid technology is a critical factor in determining its potential for high-impact climate solutions. As the demand for sustainable and efficient technologies grows, the ability to scale ferrofluid applications becomes increasingly important. One of the key advantages of ferrofluid is its versatility, allowing for potential scalability across various industries and applications.
In terms of production scalability, ferrofluid manufacturing processes have shown promising advancements. The synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles, a crucial component of ferrofluids, has been optimized for large-scale production. Techniques such as co-precipitation and thermal decomposition have been refined to yield consistent and high-quality ferrofluids in larger quantities. This progress in manufacturing scalability is essential for meeting the potential demand in climate-related applications.
The adaptability of ferrofluid to different environmental conditions also contributes to its scalability potential. Ferrofluids can be tailored to perform optimally in a wide range of temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for diverse climate-related applications. This adaptability allows for the scaling of ferrofluid solutions across various geographical regions and climatic conditions, enhancing its potential impact on global climate challenges.
From an economic perspective, the scalability of ferrofluid technology is closely tied to cost-effectiveness. As production techniques improve and demand increases, economies of scale are likely to drive down costs. This reduction in production expenses could make ferrofluid-based solutions more accessible and financially viable for large-scale implementation in climate mitigation and adaptation strategies.
The integration of ferrofluid technology with existing infrastructure and systems is another crucial aspect of its scalability. For instance, in energy applications, ferrofluid-based cooling systems for solar panels or wind turbines can be scaled to accommodate varying sizes of renewable energy installations. This scalability in integration allows for the technology to be adopted across different scales of operations, from small local projects to large industrial applications.
However, challenges to scalability exist. The long-term stability of ferrofluids in large-scale applications needs further research and development. Additionally, the environmental impact of large-scale ferrofluid production and use must be carefully assessed to ensure that the scaling of this technology aligns with sustainability goals. Addressing these challenges will be crucial in realizing the full scalability potential of ferrofluid technology in climate solutions.
In conclusion, the scalability analysis of ferrofluid technology reveals significant potential for its application in high-impact climate solutions. With advancements in production techniques, adaptability to various conditions, economic viability, and integration capabilities, ferrofluids show promise for scaling up to meet global climate challenges. However, ongoing research and development efforts are necessary to overcome existing limitations and fully harness the scalability potential of this innovative technology.
In terms of production scalability, ferrofluid manufacturing processes have shown promising advancements. The synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles, a crucial component of ferrofluids, has been optimized for large-scale production. Techniques such as co-precipitation and thermal decomposition have been refined to yield consistent and high-quality ferrofluids in larger quantities. This progress in manufacturing scalability is essential for meeting the potential demand in climate-related applications.
The adaptability of ferrofluid to different environmental conditions also contributes to its scalability potential. Ferrofluids can be tailored to perform optimally in a wide range of temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for diverse climate-related applications. This adaptability allows for the scaling of ferrofluid solutions across various geographical regions and climatic conditions, enhancing its potential impact on global climate challenges.
From an economic perspective, the scalability of ferrofluid technology is closely tied to cost-effectiveness. As production techniques improve and demand increases, economies of scale are likely to drive down costs. This reduction in production expenses could make ferrofluid-based solutions more accessible and financially viable for large-scale implementation in climate mitigation and adaptation strategies.
The integration of ferrofluid technology with existing infrastructure and systems is another crucial aspect of its scalability. For instance, in energy applications, ferrofluid-based cooling systems for solar panels or wind turbines can be scaled to accommodate varying sizes of renewable energy installations. This scalability in integration allows for the technology to be adopted across different scales of operations, from small local projects to large industrial applications.
However, challenges to scalability exist. The long-term stability of ferrofluids in large-scale applications needs further research and development. Additionally, the environmental impact of large-scale ferrofluid production and use must be carefully assessed to ensure that the scaling of this technology aligns with sustainability goals. Addressing these challenges will be crucial in realizing the full scalability potential of ferrofluid technology in climate solutions.
In conclusion, the scalability analysis of ferrofluid technology reveals significant potential for its application in high-impact climate solutions. With advancements in production techniques, adaptability to various conditions, economic viability, and integration capabilities, ferrofluids show promise for scaling up to meet global climate challenges. However, ongoing research and development efforts are necessary to overcome existing limitations and fully harness the scalability potential of this innovative technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!