Hirudoid’s Potential in Treating Hemorrhoids
JUN 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hirudoid Background
Hirudoid, also known as mucopolysaccharide polysulfate, is a semi-synthetic glycosaminoglycan with a long history in medical applications. Originally derived from mammalian tissues, it has been used for decades in various therapeutic contexts, particularly in the treatment of vascular disorders and inflammatory conditions.
The development of Hirudoid can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers began exploring the potential of glycosaminoglycans in medicine. Its structure is similar to naturally occurring heparin, but with modifications that enhance its stability and reduce anticoagulant effects. This unique composition allows Hirudoid to retain beneficial properties while minimizing potential side effects associated with heparin.
Hirudoid's mechanism of action primarily involves its interaction with the extracellular matrix and cell surfaces. It has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous, and fibrinolytic properties. These characteristics make it particularly useful in treating conditions involving localized inflammation and vascular complications.
In the context of hemorrhoid treatment, Hirudoid's potential stems from its ability to address multiple aspects of the condition. Hemorrhoids are characterized by swollen and inflamed blood vessels in the anal and rectal areas, often accompanied by pain, itching, and bleeding. The anti-inflammatory properties of Hirudoid may help reduce swelling and discomfort, while its effects on vascular health could potentially improve blood flow in the affected area.
Over the years, Hirudoid has been formulated into various topical preparations, including creams, gels, and ointments. These formulations have been used to treat a range of conditions, from superficial thrombophlebitis to bruises and sports injuries. The application of Hirudoid in hemorrhoid treatment represents an extension of its established uses in vascular and inflammatory disorders.
Research into Hirudoid's efficacy for hemorrhoids has been ongoing, with several studies exploring its potential benefits. While it has shown promise in alleviating symptoms associated with hemorrhoids, its exact role in the treatment protocol is still being defined. The medical community continues to investigate optimal dosing, duration of treatment, and potential combinations with other therapeutic agents to maximize its effectiveness in managing hemorrhoids.
As with any medical treatment, the use of Hirudoid for hemorrhoids must be considered in the context of overall patient care. Factors such as the severity of the condition, patient history, and potential contraindications need to be carefully evaluated. The ongoing research and clinical trials aim to provide a more comprehensive understanding of Hirudoid's role in hemorrhoid management, potentially leading to improved treatment strategies for this common and often distressing condition.
The development of Hirudoid can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers began exploring the potential of glycosaminoglycans in medicine. Its structure is similar to naturally occurring heparin, but with modifications that enhance its stability and reduce anticoagulant effects. This unique composition allows Hirudoid to retain beneficial properties while minimizing potential side effects associated with heparin.
Hirudoid's mechanism of action primarily involves its interaction with the extracellular matrix and cell surfaces. It has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous, and fibrinolytic properties. These characteristics make it particularly useful in treating conditions involving localized inflammation and vascular complications.
In the context of hemorrhoid treatment, Hirudoid's potential stems from its ability to address multiple aspects of the condition. Hemorrhoids are characterized by swollen and inflamed blood vessels in the anal and rectal areas, often accompanied by pain, itching, and bleeding. The anti-inflammatory properties of Hirudoid may help reduce swelling and discomfort, while its effects on vascular health could potentially improve blood flow in the affected area.
Over the years, Hirudoid has been formulated into various topical preparations, including creams, gels, and ointments. These formulations have been used to treat a range of conditions, from superficial thrombophlebitis to bruises and sports injuries. The application of Hirudoid in hemorrhoid treatment represents an extension of its established uses in vascular and inflammatory disorders.
Research into Hirudoid's efficacy for hemorrhoids has been ongoing, with several studies exploring its potential benefits. While it has shown promise in alleviating symptoms associated with hemorrhoids, its exact role in the treatment protocol is still being defined. The medical community continues to investigate optimal dosing, duration of treatment, and potential combinations with other therapeutic agents to maximize its effectiveness in managing hemorrhoids.
As with any medical treatment, the use of Hirudoid for hemorrhoids must be considered in the context of overall patient care. Factors such as the severity of the condition, patient history, and potential contraindications need to be carefully evaluated. The ongoing research and clinical trials aim to provide a more comprehensive understanding of Hirudoid's role in hemorrhoid management, potentially leading to improved treatment strategies for this common and often distressing condition.
Hemorrhoid Market Analysis
The global hemorrhoid treatment market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing prevalence of hemorrhoids, growing awareness about available treatments, and advancements in medical technologies. The market size was valued at approximately $2.1 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period.
Hemorrhoids affect a significant portion of the adult population worldwide, with estimates suggesting that up to 50% of individuals over the age of 50 experience hemorrhoid symptoms at some point in their lives. This high prevalence rate contributes significantly to the market demand for effective treatments.
The market is segmented based on treatment type, including over-the-counter (OTC) medications, surgical procedures, and prescription medications. OTC treatments, including creams, ointments, and suppositories, currently dominate the market due to their easy accessibility and lower cost. However, prescription medications like Hirudoid are gaining traction due to their potential for more effective symptom relief.
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, accounts for a significant portion of the global market due to its high healthcare expenditure and advanced medical infrastructure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising disposable incomes.
Key market trends include a shift towards minimally invasive treatment options, increasing adoption of combination therapies, and growing demand for natural and herbal remedies. There is also a rising focus on developing novel drug delivery systems to enhance the efficacy of existing treatments.
The competitive landscape of the hemorrhoid treatment market is characterized by the presence of both established pharmaceutical companies and emerging players. Major companies are investing in research and development to introduce innovative products and gain a competitive edge. Strategic collaborations, mergers, and acquisitions are common strategies employed by market players to expand their product portfolios and geographical presence.
Challenges facing the market include the social stigma associated with hemorrhoids, which often leads to underreporting and delayed treatment seeking. Additionally, the availability of alternative treatment options, such as dietary and lifestyle changes, may impact market growth to some extent.
Hemorrhoids affect a significant portion of the adult population worldwide, with estimates suggesting that up to 50% of individuals over the age of 50 experience hemorrhoid symptoms at some point in their lives. This high prevalence rate contributes significantly to the market demand for effective treatments.
The market is segmented based on treatment type, including over-the-counter (OTC) medications, surgical procedures, and prescription medications. OTC treatments, including creams, ointments, and suppositories, currently dominate the market due to their easy accessibility and lower cost. However, prescription medications like Hirudoid are gaining traction due to their potential for more effective symptom relief.
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, accounts for a significant portion of the global market due to its high healthcare expenditure and advanced medical infrastructure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising disposable incomes.
Key market trends include a shift towards minimally invasive treatment options, increasing adoption of combination therapies, and growing demand for natural and herbal remedies. There is also a rising focus on developing novel drug delivery systems to enhance the efficacy of existing treatments.
The competitive landscape of the hemorrhoid treatment market is characterized by the presence of both established pharmaceutical companies and emerging players. Major companies are investing in research and development to introduce innovative products and gain a competitive edge. Strategic collaborations, mergers, and acquisitions are common strategies employed by market players to expand their product portfolios and geographical presence.
Challenges facing the market include the social stigma associated with hemorrhoids, which often leads to underreporting and delayed treatment seeking. Additionally, the availability of alternative treatment options, such as dietary and lifestyle changes, may impact market growth to some extent.
Hirudoid Challenges
Despite the potential benefits of Hirudoid in treating hemorrhoids, several challenges exist in its widespread adoption and efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the limited clinical evidence supporting its use specifically for hemorrhoid treatment. While Hirudoid has shown promise in treating various vascular conditions, robust, large-scale clinical trials focusing on its efficacy in hemorrhoid management are lacking. This gap in research makes it difficult for healthcare providers to confidently prescribe Hirudoid as a primary treatment option.
Another significant challenge is the variability in patient response to Hirudoid treatment. Hemorrhoids can vary greatly in severity and underlying causes, and not all patients may experience the same level of relief from Hirudoid application. This inconsistency in outcomes can lead to skepticism among both patients and healthcare professionals, potentially limiting its adoption as a standard treatment protocol.
The formulation and delivery method of Hirudoid also present challenges. The current topical application may not always provide optimal penetration to reach the affected hemorrhoidal tissues effectively. This limitation could result in reduced efficacy, especially for internal hemorrhoids or more severe cases. Developing more advanced delivery systems or formulations that enhance tissue penetration and retention could be crucial for improving Hirudoid's effectiveness in hemorrhoid treatment.
Additionally, there are concerns regarding the long-term safety and potential side effects of prolonged Hirudoid use for hemorrhoid management. While the drug has a generally good safety profile, extended application to sensitive rectal tissues may lead to unforeseen complications or adverse reactions in some patients. Comprehensive long-term safety studies specific to hemorrhoid treatment are needed to address these concerns and establish clear guidelines for safe, extended use.
The cost-effectiveness of Hirudoid compared to other hemorrhoid treatments is another challenge. With various over-the-counter and prescription options available, including creams, suppositories, and surgical interventions, Hirudoid must demonstrate superior efficacy or cost-benefit ratio to justify its use. This economic aspect is particularly important for healthcare systems and insurance providers when considering coverage and reimbursement policies.
Lastly, regulatory hurdles and approval processes for new indications can pose significant challenges. While Hirudoid is approved for various uses, obtaining specific approval for hemorrhoid treatment may require additional clinical trials and regulatory submissions. This process can be time-consuming and costly, potentially delaying its availability as a recognized treatment option for hemorrhoids in some regions or healthcare systems.
Another significant challenge is the variability in patient response to Hirudoid treatment. Hemorrhoids can vary greatly in severity and underlying causes, and not all patients may experience the same level of relief from Hirudoid application. This inconsistency in outcomes can lead to skepticism among both patients and healthcare professionals, potentially limiting its adoption as a standard treatment protocol.
The formulation and delivery method of Hirudoid also present challenges. The current topical application may not always provide optimal penetration to reach the affected hemorrhoidal tissues effectively. This limitation could result in reduced efficacy, especially for internal hemorrhoids or more severe cases. Developing more advanced delivery systems or formulations that enhance tissue penetration and retention could be crucial for improving Hirudoid's effectiveness in hemorrhoid treatment.
Additionally, there are concerns regarding the long-term safety and potential side effects of prolonged Hirudoid use for hemorrhoid management. While the drug has a generally good safety profile, extended application to sensitive rectal tissues may lead to unforeseen complications or adverse reactions in some patients. Comprehensive long-term safety studies specific to hemorrhoid treatment are needed to address these concerns and establish clear guidelines for safe, extended use.
The cost-effectiveness of Hirudoid compared to other hemorrhoid treatments is another challenge. With various over-the-counter and prescription options available, including creams, suppositories, and surgical interventions, Hirudoid must demonstrate superior efficacy or cost-benefit ratio to justify its use. This economic aspect is particularly important for healthcare systems and insurance providers when considering coverage and reimbursement policies.
Lastly, regulatory hurdles and approval processes for new indications can pose significant challenges. While Hirudoid is approved for various uses, obtaining specific approval for hemorrhoid treatment may require additional clinical trials and regulatory submissions. This process can be time-consuming and costly, potentially delaying its availability as a recognized treatment option for hemorrhoids in some regions or healthcare systems.
Key Pharmaceutical Players
The market for Hirudoid in treating hemorrhoids is in a growth phase, driven by increasing prevalence of the condition and growing awareness of treatment options. The global hemorrhoid treatment market is expected to reach significant size in the coming years. Technologically, the use of Hirudoid for this application is moderately mature, with ongoing research to optimize its efficacy. Key players like Johnson & Johnson, Sanofi, and AstraZeneca are investing in R&D to enhance formulations and delivery methods. Regional companies such as Jiangsu Yangtze River Pharmaceutical Group and Lunan Pharmaceutical Group are also contributing to market expansion, particularly in emerging economies. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical giants and specialized regional manufacturers, indicating a dynamic and evolving market.
Sanofi
Technical Solution: Sanofi has explored the potential of Hirudoid in treating hemorrhoids through their advanced drug delivery systems. Their approach involves incorporating the active ingredient of Hirudoid (MPS) into a novel nanoparticle-based formulation. This technology aims to enhance the penetration and retention of the drug in the affected tissues, potentially improving its efficacy and duration of action. Sanofi's research team has conducted preclinical studies to optimize the formulation and assess its safety profile. They are also investigating the possibility of combining MPS with other anti-inflammatory agents to create a more comprehensive hemorrhoid treatment.
Strengths: Advanced drug delivery technology, potential for improved efficacy and duration of action, strong research and development capabilities. Weaknesses: Still in early stages of development for hemorrhoid treatment, potential regulatory hurdles for novel formulations.
Uniderm Farmaceutici Srl
Technical Solution: Uniderm Farmaceutici Srl has developed a proprietary formulation of Hirudoid for treating hemorrhoids. Their approach involves a topical cream or ointment containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), the active ingredient in Hirudoid. This formulation is designed to reduce inflammation, improve blood circulation, and promote healing of the affected area. The company has conducted clinical trials to demonstrate the efficacy of their Hirudoid-based product in alleviating hemorrhoid symptoms, including pain, itching, and swelling.
Strengths: Proven efficacy of MPS in treating vascular conditions, non-invasive topical application, potential for rapid symptom relief. Weaknesses: Limited long-term data on effectiveness for hemorrhoids specifically, potential for skin irritation in some users.
Hirudoid Core Mechanisms
Pharmaceutical composition for treating hemorrhoidal disaese
PatentActiveEP3461490A1
Innovation
- A pharmaceutical composition combining Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 and Pentapeptide-18 with plant extracts like Hippocastanum, Centella, and Hamamelis, which have microcirculation activity, to reduce clinical symptoms and improve trophism of hemorrhoidal vascular tissue, offering a synergistic effect that enhances the treatment's efficacy.
Herbal pharmaceutical compositions and method of preparation thereof
PatentActiveUS20200254045A1
Innovation
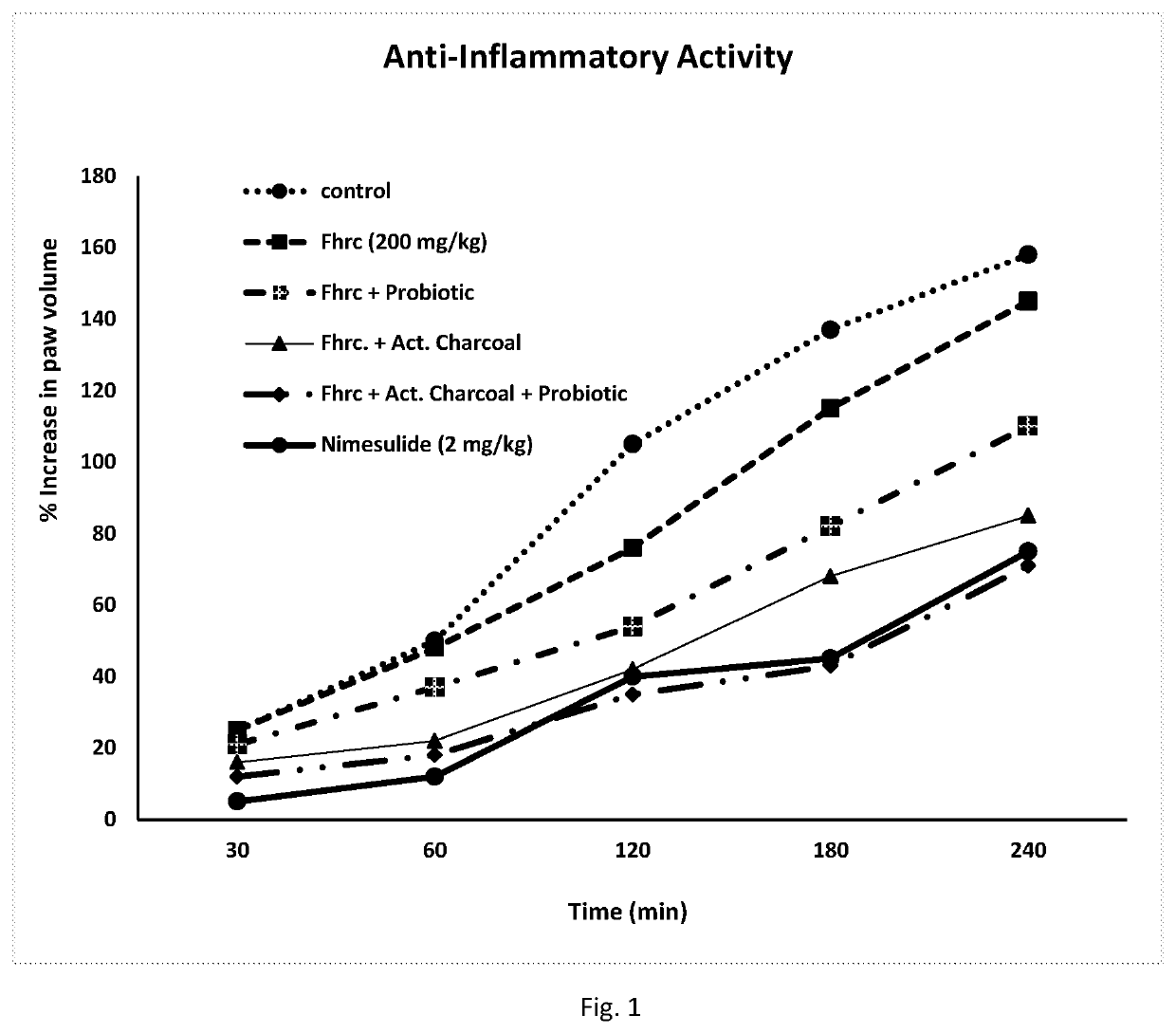
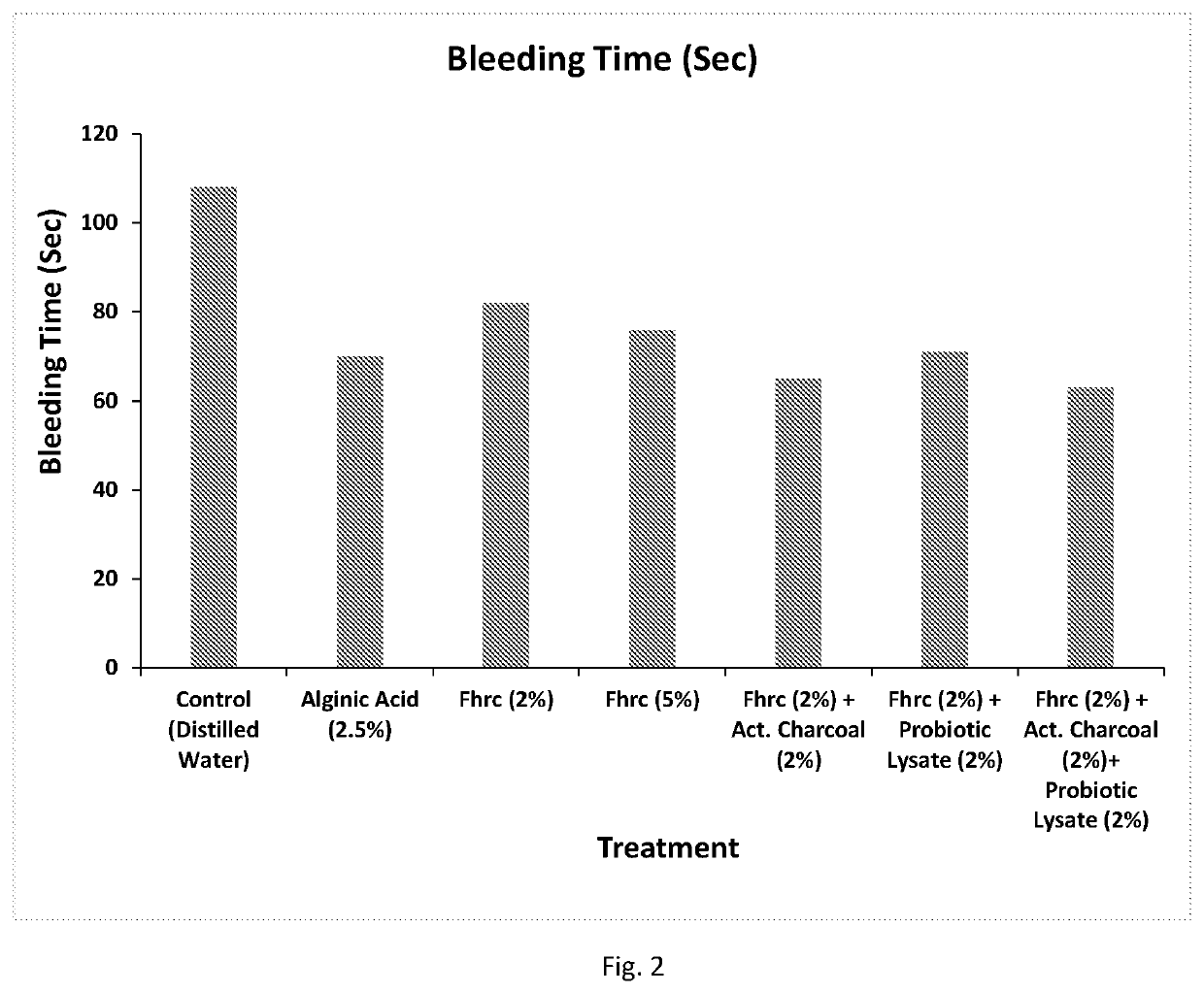
- A novel herbal pharmaceutical composition combining flavonoid-rich herbal extracts with activated charcoal and probiotics, which are formulated into tablets or capsules, offering anti-inflammatory, wound-healing, and hemostatic properties to treat hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and fistula, while minimizing side effects and providing long-term management.
Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape for Hirudoid in the treatment of hemorrhoids is complex and varies across different regions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies Hirudoid as a medical device due to its mechanism of action. As such, it falls under the regulatory framework for medical devices, requiring manufacturers to demonstrate safety and efficacy through clinical trials before obtaining market approval. The FDA may require a Premarket Approval (PMA) application or a 510(k) clearance, depending on the specific claims and intended use of the product.
In the European Union, Hirudoid is regulated under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745. This regulation imposes stringent requirements on manufacturers, including the need for a comprehensive quality management system, post-market surveillance, and clinical evaluation reports. The CE marking process involves assessment by a Notified Body, which evaluates the product's conformity with essential safety and performance requirements.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has its own regulatory pathway for medical devices like Hirudoid. Manufacturers must obtain approval through the PMDA's review process, which includes evaluation of clinical data and quality management systems. The Japanese regulatory framework emphasizes the importance of local clinical data, which may necessitate additional studies specific to the Japanese population.
In emerging markets, such as China and India, regulatory requirements for Hirudoid may be less established but are rapidly evolving. These countries are developing more robust regulatory frameworks for medical devices, often modeled after international standards. Manufacturers seeking to enter these markets should be prepared for potentially lengthy approval processes and the need for local clinical data.
Globally, manufacturers must navigate varying requirements for labeling, packaging, and post-market surveillance. Many countries require adverse event reporting and periodic safety update reports. Additionally, some regions may have specific requirements for the disposal or environmental impact of Hirudoid products, particularly considering its organic components.
Regulatory considerations also extend to manufacturing practices. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance is essential in most markets, with inspections of manufacturing facilities being a common requirement. The sourcing of raw materials, particularly if derived from animal sources, may be subject to additional scrutiny and documentation requirements.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, manufacturers must stay abreast of changes in different markets. This may involve ongoing communication with regulatory bodies, participation in industry forums, and continuous monitoring of regulatory updates. The global nature of the medical device market necessitates a comprehensive and adaptable regulatory strategy for Hirudoid in the treatment of hemorrhoids.
In the European Union, Hirudoid is regulated under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745. This regulation imposes stringent requirements on manufacturers, including the need for a comprehensive quality management system, post-market surveillance, and clinical evaluation reports. The CE marking process involves assessment by a Notified Body, which evaluates the product's conformity with essential safety and performance requirements.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has its own regulatory pathway for medical devices like Hirudoid. Manufacturers must obtain approval through the PMDA's review process, which includes evaluation of clinical data and quality management systems. The Japanese regulatory framework emphasizes the importance of local clinical data, which may necessitate additional studies specific to the Japanese population.
In emerging markets, such as China and India, regulatory requirements for Hirudoid may be less established but are rapidly evolving. These countries are developing more robust regulatory frameworks for medical devices, often modeled after international standards. Manufacturers seeking to enter these markets should be prepared for potentially lengthy approval processes and the need for local clinical data.
Globally, manufacturers must navigate varying requirements for labeling, packaging, and post-market surveillance. Many countries require adverse event reporting and periodic safety update reports. Additionally, some regions may have specific requirements for the disposal or environmental impact of Hirudoid products, particularly considering its organic components.
Regulatory considerations also extend to manufacturing practices. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance is essential in most markets, with inspections of manufacturing facilities being a common requirement. The sourcing of raw materials, particularly if derived from animal sources, may be subject to additional scrutiny and documentation requirements.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, manufacturers must stay abreast of changes in different markets. This may involve ongoing communication with regulatory bodies, participation in industry forums, and continuous monitoring of regulatory updates. The global nature of the medical device market necessitates a comprehensive and adaptable regulatory strategy for Hirudoid in the treatment of hemorrhoids.
Safety and Side Effects
Hirudoid, a topical medication containing mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS), has shown promise in treating hemorrhoids. However, as with any medical treatment, safety considerations and potential side effects must be thoroughly evaluated. Clinical studies have demonstrated that Hirudoid is generally well-tolerated when used as directed, with a low incidence of adverse reactions.
The most commonly reported side effects of Hirudoid are mild and localized, including temporary skin irritation, itching, or redness at the application site. These reactions typically subside within a few days of continued use. In rare cases, patients may experience more severe allergic reactions, such as hives or swelling. It is crucial for patients to discontinue use and seek medical attention if they experience any signs of an allergic response.
One of the key safety advantages of Hirudoid is its topical application, which minimizes systemic absorption and reduces the risk of systemic side effects. This localized action makes it particularly suitable for treating hemorrhoids, as it can deliver the active ingredient directly to the affected area without significant systemic exposure.
Long-term safety data on Hirudoid for hemorrhoid treatment is limited, and further research is needed to fully assess its safety profile for extended use. However, existing studies have not identified any significant long-term risks associated with its use. It is important to note that Hirudoid should not be used internally or on open wounds, as this may increase the risk of adverse effects.
Precautions should be taken when using Hirudoid in certain patient populations. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before using the medication, as its safety in these groups has not been extensively studied. Similarly, individuals with a history of allergic reactions to MPS or other components of the formulation should avoid using Hirudoid.
To ensure safe and effective use, patients should follow the recommended dosage and application instructions provided by their healthcare provider or the product label. Overuse or prolonged application beyond the recommended duration may increase the risk of side effects without providing additional therapeutic benefits.
In conclusion, while Hirudoid appears to have a favorable safety profile for treating hemorrhoids, ongoing monitoring and further research are essential to fully understand its long-term safety implications. Healthcare providers should carefully consider individual patient factors and potential risks when recommending Hirudoid for hemorrhoid treatment.
The most commonly reported side effects of Hirudoid are mild and localized, including temporary skin irritation, itching, or redness at the application site. These reactions typically subside within a few days of continued use. In rare cases, patients may experience more severe allergic reactions, such as hives or swelling. It is crucial for patients to discontinue use and seek medical attention if they experience any signs of an allergic response.
One of the key safety advantages of Hirudoid is its topical application, which minimizes systemic absorption and reduces the risk of systemic side effects. This localized action makes it particularly suitable for treating hemorrhoids, as it can deliver the active ingredient directly to the affected area without significant systemic exposure.
Long-term safety data on Hirudoid for hemorrhoid treatment is limited, and further research is needed to fully assess its safety profile for extended use. However, existing studies have not identified any significant long-term risks associated with its use. It is important to note that Hirudoid should not be used internally or on open wounds, as this may increase the risk of adverse effects.
Precautions should be taken when using Hirudoid in certain patient populations. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before using the medication, as its safety in these groups has not been extensively studied. Similarly, individuals with a history of allergic reactions to MPS or other components of the formulation should avoid using Hirudoid.
To ensure safe and effective use, patients should follow the recommended dosage and application instructions provided by their healthcare provider or the product label. Overuse or prolonged application beyond the recommended duration may increase the risk of side effects without providing additional therapeutic benefits.
In conclusion, while Hirudoid appears to have a favorable safety profile for treating hemorrhoids, ongoing monitoring and further research are essential to fully understand its long-term safety implications. Healthcare providers should carefully consider individual patient factors and potential risks when recommending Hirudoid for hemorrhoid treatment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!