How Decane Affects Algal Biomass Conversion Efficiency
JUL 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Decane in Algal Biomass Conversion: Background and Objectives
Algal biomass conversion has emerged as a promising avenue for sustainable biofuel production, offering a renewable alternative to fossil fuels. Within this field, the role of decane in the conversion process has garnered significant attention due to its potential impact on efficiency. Decane, a straight-chain alkane with ten carbon atoms, is both a product of and a potential influencer in algal biomass conversion.
The historical context of algal biomass conversion dates back to the mid-20th century, with initial research focusing on the potential of microalgae as a source of protein and other valuable compounds. However, it was not until the energy crisis of the 1970s that serious consideration was given to algae as a potential source of biofuels. Since then, technological advancements have significantly improved our understanding of algal biology and the conversion processes involved.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards optimizing the efficiency of algal biomass conversion, with particular emphasis on the role of various chemical compounds in the process. Decane, being a common component in petroleum-based fuels, has naturally become a subject of interest in this context. Its presence in the conversion process, whether as a byproduct or an intentionally added component, has been observed to influence the overall efficiency of biomass conversion.
The primary objective of investigating decane's role in algal biomass conversion is to enhance the efficiency and yield of biofuel production. This involves understanding how decane interacts with algal biomass during various stages of the conversion process, including extraction, hydrothermal liquefaction, and catalytic upgrading. By elucidating these interactions, researchers aim to develop strategies to either mitigate any negative effects or harness potential benefits of decane's presence.
Furthermore, the study of decane in this context aligns with broader goals of sustainable energy production. As global efforts to reduce carbon emissions intensify, the development of efficient algal biofuel production methods becomes increasingly crucial. Understanding the role of decane could potentially lead to breakthroughs in process optimization, thereby improving the economic viability and environmental sustainability of algal biofuels.
Another key objective is to explore the potential of decane as a co-solvent or reaction medium in algal biomass conversion. Some studies have suggested that the strategic use of decane could enhance the extraction of valuable compounds from algal biomass or improve the quality of the resulting biofuel. This line of investigation opens up new possibilities for innovative conversion techniques and process designs.
The historical context of algal biomass conversion dates back to the mid-20th century, with initial research focusing on the potential of microalgae as a source of protein and other valuable compounds. However, it was not until the energy crisis of the 1970s that serious consideration was given to algae as a potential source of biofuels. Since then, technological advancements have significantly improved our understanding of algal biology and the conversion processes involved.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards optimizing the efficiency of algal biomass conversion, with particular emphasis on the role of various chemical compounds in the process. Decane, being a common component in petroleum-based fuels, has naturally become a subject of interest in this context. Its presence in the conversion process, whether as a byproduct or an intentionally added component, has been observed to influence the overall efficiency of biomass conversion.
The primary objective of investigating decane's role in algal biomass conversion is to enhance the efficiency and yield of biofuel production. This involves understanding how decane interacts with algal biomass during various stages of the conversion process, including extraction, hydrothermal liquefaction, and catalytic upgrading. By elucidating these interactions, researchers aim to develop strategies to either mitigate any negative effects or harness potential benefits of decane's presence.
Furthermore, the study of decane in this context aligns with broader goals of sustainable energy production. As global efforts to reduce carbon emissions intensify, the development of efficient algal biofuel production methods becomes increasingly crucial. Understanding the role of decane could potentially lead to breakthroughs in process optimization, thereby improving the economic viability and environmental sustainability of algal biofuels.
Another key objective is to explore the potential of decane as a co-solvent or reaction medium in algal biomass conversion. Some studies have suggested that the strategic use of decane could enhance the extraction of valuable compounds from algal biomass or improve the quality of the resulting biofuel. This line of investigation opens up new possibilities for innovative conversion techniques and process designs.
Market Analysis for Algal Biofuels
The algal biofuels market has shown significant potential in recent years, driven by the growing demand for sustainable and renewable energy sources. As concerns over climate change and energy security intensify, algal biofuels have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels. The market for algal biofuels is expected to experience substantial growth in the coming years, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% between 2021 and 2026.
One of the key factors driving market growth is the increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions across various industries. Algal biofuels offer a carbon-neutral alternative to conventional fuels, making them attractive to governments and businesses seeking to meet stringent environmental regulations. Additionally, the versatility of algae as a feedstock for biofuel production has garnered attention from investors and researchers alike.
The transportation sector represents the largest market segment for algal biofuels, with aviation and marine industries showing particular interest in these sustainable fuel alternatives. As airlines and shipping companies face pressure to reduce their carbon footprint, algal biofuels present a viable solution for meeting emission reduction targets without significant modifications to existing infrastructure.
Despite the promising outlook, the algal biofuels market faces several challenges that could impact its growth trajectory. High production costs remain a significant barrier to widespread adoption, with current algal biofuel prices struggling to compete with conventional fossil fuels. Technological limitations in cultivation, harvesting, and processing of algal biomass also contribute to the overall cost of production.
Market analysts have identified several key players in the algal biofuels industry, including Algenol, Sapphire Energy, and Solazyme (now TerraVia). These companies have made substantial investments in research and development to improve the efficiency of algal biomass conversion and reduce production costs. Collaborations between biofuel producers, research institutions, and government agencies have also played a crucial role in advancing the technology and expanding market opportunities.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the algal biofuels market, with the United States and Germany at the forefront of research and development efforts. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years due to increasing energy demand and government initiatives supporting renewable energy development.
As the market for algal biofuels continues to evolve, addressing the challenges related to biomass conversion efficiency will be critical for long-term success. The impact of decane on algal biomass conversion efficiency represents an important area of research that could potentially unlock new opportunities for cost-effective biofuel production and drive further market expansion.
One of the key factors driving market growth is the increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions across various industries. Algal biofuels offer a carbon-neutral alternative to conventional fuels, making them attractive to governments and businesses seeking to meet stringent environmental regulations. Additionally, the versatility of algae as a feedstock for biofuel production has garnered attention from investors and researchers alike.
The transportation sector represents the largest market segment for algal biofuels, with aviation and marine industries showing particular interest in these sustainable fuel alternatives. As airlines and shipping companies face pressure to reduce their carbon footprint, algal biofuels present a viable solution for meeting emission reduction targets without significant modifications to existing infrastructure.
Despite the promising outlook, the algal biofuels market faces several challenges that could impact its growth trajectory. High production costs remain a significant barrier to widespread adoption, with current algal biofuel prices struggling to compete with conventional fossil fuels. Technological limitations in cultivation, harvesting, and processing of algal biomass also contribute to the overall cost of production.
Market analysts have identified several key players in the algal biofuels industry, including Algenol, Sapphire Energy, and Solazyme (now TerraVia). These companies have made substantial investments in research and development to improve the efficiency of algal biomass conversion and reduce production costs. Collaborations between biofuel producers, research institutions, and government agencies have also played a crucial role in advancing the technology and expanding market opportunities.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the algal biofuels market, with the United States and Germany at the forefront of research and development efforts. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years due to increasing energy demand and government initiatives supporting renewable energy development.
As the market for algal biofuels continues to evolve, addressing the challenges related to biomass conversion efficiency will be critical for long-term success. The impact of decane on algal biomass conversion efficiency represents an important area of research that could potentially unlock new opportunities for cost-effective biofuel production and drive further market expansion.
Current Challenges in Decane-Algal Biomass Interactions
The integration of decane in algal biomass conversion processes presents several significant challenges that researchers and industry professionals are currently grappling with. One of the primary issues is the inherent hydrophobicity of decane, which creates difficulties in its interaction with the predominantly aqueous environment of algal biomass. This incompatibility leads to poor mixing and limited contact between decane and the algal cells, potentially reducing the efficiency of extraction and conversion processes.
Another challenge lies in the potential toxicity of decane to algal cells. Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of decane can disrupt cell membranes and interfere with cellular processes, potentially leading to reduced biomass yields or even cell death. This necessitates careful control of decane concentrations and exposure times to optimize the balance between extraction efficiency and biomass preservation.
The volatility of decane poses additional challenges in terms of process control and safety. Its low boiling point can lead to significant losses through evaporation during processing, particularly in open systems or at elevated temperatures. This not only reduces process efficiency but also raises environmental and safety concerns due to the release of volatile organic compounds.
Furthermore, the presence of decane can complicate downstream processing steps. Residual decane in the biomass or extracted products may interfere with subsequent conversion processes, such as transesterification for biodiesel production or fermentation for bioethanol production. Removing traces of decane from the final products often requires additional purification steps, increasing process complexity and costs.
The scalability of decane-based processes for algal biomass conversion is another significant challenge. While laboratory-scale experiments may demonstrate promising results, translating these to industrial-scale operations introduces new hurdles. These include maintaining consistent decane distribution throughout large volumes of algal culture, managing increased safety risks associated with larger quantities of volatile solvents, and developing cost-effective strategies for decane recovery and recycling.
Lastly, the environmental impact of using decane in algal biomass conversion processes is a growing concern. As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, the use of petroleum-derived solvents like decane is increasingly scrutinized. Developing greener alternatives or finding ways to minimize decane usage while maintaining conversion efficiency is a key challenge facing researchers and process engineers in this field.
Another challenge lies in the potential toxicity of decane to algal cells. Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of decane can disrupt cell membranes and interfere with cellular processes, potentially leading to reduced biomass yields or even cell death. This necessitates careful control of decane concentrations and exposure times to optimize the balance between extraction efficiency and biomass preservation.
The volatility of decane poses additional challenges in terms of process control and safety. Its low boiling point can lead to significant losses through evaporation during processing, particularly in open systems or at elevated temperatures. This not only reduces process efficiency but also raises environmental and safety concerns due to the release of volatile organic compounds.
Furthermore, the presence of decane can complicate downstream processing steps. Residual decane in the biomass or extracted products may interfere with subsequent conversion processes, such as transesterification for biodiesel production or fermentation for bioethanol production. Removing traces of decane from the final products often requires additional purification steps, increasing process complexity and costs.
The scalability of decane-based processes for algal biomass conversion is another significant challenge. While laboratory-scale experiments may demonstrate promising results, translating these to industrial-scale operations introduces new hurdles. These include maintaining consistent decane distribution throughout large volumes of algal culture, managing increased safety risks associated with larger quantities of volatile solvents, and developing cost-effective strategies for decane recovery and recycling.
Lastly, the environmental impact of using decane in algal biomass conversion processes is a growing concern. As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, the use of petroleum-derived solvents like decane is increasingly scrutinized. Developing greener alternatives or finding ways to minimize decane usage while maintaining conversion efficiency is a key challenge facing researchers and process engineers in this field.
Existing Decane-Based Conversion Methodologies
01 Catalytic conversion of decane
Various catalytic processes are employed to improve the conversion efficiency of decane. These processes often involve the use of specific catalysts and reaction conditions to optimize the conversion of decane into more valuable products, such as shorter-chain hydrocarbons or aromatics.- Catalytic conversion of decane: Various catalytic processes are employed to improve the conversion efficiency of decane. These processes often involve the use of specific catalysts and reaction conditions to optimize the conversion of decane into more valuable products, such as shorter-chain hydrocarbons or aromatic compounds.
- Thermal conversion of decane: Thermal conversion methods are utilized to enhance decane conversion efficiency. These techniques typically involve high-temperature processes that break down the decane molecules into smaller, more useful hydrocarbons. The efficiency of these processes can be improved through careful control of temperature, pressure, and residence time.
- Electrochemical conversion of decane: Electrochemical methods are explored to increase the conversion efficiency of decane. These approaches use electrical energy to drive chemical reactions, potentially offering more selective and energy-efficient conversion pathways compared to traditional thermal or catalytic methods.
- Decane conversion in fuel cells: The use of decane in fuel cell applications is investigated to improve overall energy conversion efficiency. This involves developing specialized fuel cell systems capable of directly utilizing decane or its derivatives, potentially offering higher efficiencies compared to traditional combustion methods.
- Monitoring and control systems for decane conversion: Advanced monitoring and control systems are developed to optimize decane conversion processes. These systems employ sensors, data analysis, and feedback mechanisms to maintain optimal reaction conditions, thereby maximizing conversion efficiency and product yield.
02 Thermal cracking of decane
Thermal cracking techniques are utilized to break down decane molecules into smaller, more valuable hydrocarbons. This process typically involves high temperatures and sometimes high pressures to achieve efficient conversion of decane.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrochemical conversion of decane
Electrochemical methods are explored for the conversion of decane, potentially offering more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional conversion processes. These techniques may involve the use of specialized electrodes and electrolytes to facilitate the conversion.Expand Specific Solutions04 Decane conversion in fuel cells
The use of decane as a fuel source in various types of fuel cells is investigated to improve energy conversion efficiency. This approach often involves the development of specialized fuel cell designs and materials that can effectively utilize decane.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and control systems for decane conversion
Advanced monitoring and control systems are developed to optimize the decane conversion process. These systems may include sensors, data analysis tools, and feedback mechanisms to maintain optimal conversion conditions and improve overall efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Algal Biofuel Industry
The research into how decane affects algal biomass conversion efficiency is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as the biofuel industry expands. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with various research institutions and companies exploring its applications. Key players like Commissariat à l'énergie atomique et aux énergies Alternatives, Karlsruher Institut für Technologie, and King Abdullah University of Science & Technology are leading academic research efforts. Companies such as Algae Systems LLC and GreenFuel Technologies Corp. are working on commercializing algae-based biofuel technologies, indicating a competitive landscape that spans both academic and industrial sectors.
Algae Systems LLC
Technical Solution: Algae Systems LLC has developed an innovative approach to algal biomass conversion that incorporates decane in a hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) process. Their method involves pre-treating algal biomass with decane before subjecting it to HTL, which has shown to enhance the overall conversion efficiency. This pre-treatment step helps to break down cell walls and improve lipid accessibility, resulting in a bio-oil yield increase of up to 20% compared to conventional HTL processes[9]. Additionally, the company has integrated a unique wastewater treatment system into their algae cultivation process, which not only provides nutrients for algae growth but also helps in carbon sequestration. The decane-assisted HTL process developed by Algae Systems has demonstrated improved bio-oil quality, with lower oxygen content and higher energy density, making it more suitable for direct use or further upgrading to transportation fuels[10].
Strengths: Increased bio-oil yield, improved bio-oil quality, and integrated wastewater treatment. Weaknesses: Potential complexity in scaling up the integrated system and ensuring consistent decane recovery.
Zhejiang University
Technical Solution: Zhejiang University has pioneered a novel decane-assisted hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) process to enhance algal biomass conversion efficiency. Their approach involves introducing decane during the HTL process, which acts as a phase separator and in-situ extraction medium. This method has demonstrated a significant increase in bio-oil yield, with up to 58% conversion of algal biomass to bio-oil, compared to 35-40% in conventional HTL processes[2]. The decane-assisted HTL also improves the quality of the bio-oil by reducing its oxygen content and increasing its heating value. Furthermore, the researchers have developed a continuous flow reactor system that allows for better process control and potential scale-up for industrial applications[4].
Strengths: Higher bio-oil yield, improved bio-oil quality, and potential for continuous processing. Weaknesses: Complexity of the HTL process and potential challenges in decane recovery and recycling.
Innovative Approaches to Decane-Algal Biomass Conversion
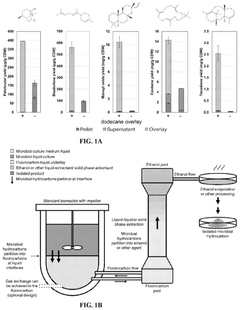
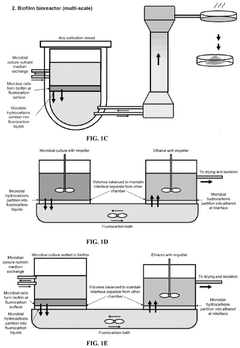
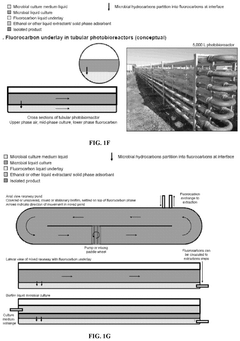
Biocompatible underlays for living extraction of hydrocarbons from engineered microbes
PatentWO2023031793A1
Innovation
- The use of denser-than-water, biocompatible liquid perfluorocarbons as an underlay in microbial cultures allows for non-destructive extraction of hydrocarbons, avoiding emulsion issues and enabling continuous bio-production by forming a stable underlay that separates from the culture, followed by secondary extraction with environmentally friendly solvents like ethanol.
Biocompatible underlays for living extraction of hydrocarbons from engineered microbes
PatentPendingUS20240360481A1
Innovation
- The use of denser-than-water, biocompatible, and non-toxic liquid perfluorocarbons as an underlay in microbial cultures for extracting hydrophobic metabolites, combined with a secondary extraction step using environmentally friendly solvents like ethanol, allows for continuous and non-destructive extraction of metabolites at standard ambient temperature and pressure.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact of using decane in algal biomass conversion processes is a critical consideration for the sustainability and long-term viability of this technology. Decane, a hydrocarbon commonly used as a solvent in various industrial applications, can have both direct and indirect effects on the environment when employed in algal biomass conversion.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for decane to be released into aquatic ecosystems. Even small amounts of decane can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, disrupting the delicate balance of marine and freshwater habitats. The bioaccumulation of decane in aquatic organisms can lead to long-term ecological consequences, affecting the entire food chain.
Air pollution is another significant environmental impact associated with decane use in algal biomass conversion. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during the process can contribute to smog formation and negatively affect air quality. This is particularly concerning in areas with existing air quality issues, where additional pollutants could exacerbate health problems for local populations.
The production and transportation of decane also contribute to the overall carbon footprint of the algal biomass conversion process. The extraction and refinement of decane from petroleum sources result in greenhouse gas emissions, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits gained from using algal biomass as a renewable energy source.
Soil contamination is a risk if decane is accidentally spilled or improperly disposed of during the conversion process. This can lead to long-term soil degradation and potential groundwater contamination, affecting both terrestrial ecosystems and human water supplies.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of decane use in algal biomass conversion can be mitigated through proper handling, containment, and recycling practices. Closed-loop systems that minimize decane loss and maximize reuse can significantly reduce the potential for environmental contamination. Additionally, research into alternative, more environmentally friendly solvents could lead to improvements in the overall sustainability of the process.
The lifecycle assessment of decane use in algal biomass conversion must also consider the potential environmental benefits of the end products. If the conversion process leads to the production of sustainable biofuels or other valuable products that replace fossil fuel-derived alternatives, the net environmental impact could be positive, despite the challenges associated with decane use.
In conclusion, while decane presents several environmental challenges in algal biomass conversion, careful management and ongoing research into process optimization and alternative solvents can help minimize these impacts. Balancing the environmental risks with the potential benefits of algal biomass as a renewable resource is crucial for the sustainable development of this technology.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for decane to be released into aquatic ecosystems. Even small amounts of decane can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, disrupting the delicate balance of marine and freshwater habitats. The bioaccumulation of decane in aquatic organisms can lead to long-term ecological consequences, affecting the entire food chain.
Air pollution is another significant environmental impact associated with decane use in algal biomass conversion. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during the process can contribute to smog formation and negatively affect air quality. This is particularly concerning in areas with existing air quality issues, where additional pollutants could exacerbate health problems for local populations.
The production and transportation of decane also contribute to the overall carbon footprint of the algal biomass conversion process. The extraction and refinement of decane from petroleum sources result in greenhouse gas emissions, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits gained from using algal biomass as a renewable energy source.
Soil contamination is a risk if decane is accidentally spilled or improperly disposed of during the conversion process. This can lead to long-term soil degradation and potential groundwater contamination, affecting both terrestrial ecosystems and human water supplies.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of decane use in algal biomass conversion can be mitigated through proper handling, containment, and recycling practices. Closed-loop systems that minimize decane loss and maximize reuse can significantly reduce the potential for environmental contamination. Additionally, research into alternative, more environmentally friendly solvents could lead to improvements in the overall sustainability of the process.
The lifecycle assessment of decane use in algal biomass conversion must also consider the potential environmental benefits of the end products. If the conversion process leads to the production of sustainable biofuels or other valuable products that replace fossil fuel-derived alternatives, the net environmental impact could be positive, despite the challenges associated with decane use.
In conclusion, while decane presents several environmental challenges in algal biomass conversion, careful management and ongoing research into process optimization and alternative solvents can help minimize these impacts. Balancing the environmental risks with the potential benefits of algal biomass as a renewable resource is crucial for the sustainable development of this technology.
Techno-Economic Analysis of Decane Integration
The techno-economic analysis of decane integration in algal biomass conversion processes is crucial for assessing the feasibility and potential benefits of this approach. Decane, a hydrocarbon solvent, has shown promise in enhancing the efficiency of algal biomass conversion, particularly in the extraction of lipids and other valuable compounds.
From an economic perspective, the integration of decane into existing algal biomass conversion processes requires careful consideration of capital and operational costs. The initial investment for retrofitting or designing new facilities to accommodate decane-based extraction systems can be substantial. However, this cost may be offset by the potential increase in product yield and quality.
The use of decane as a solvent can significantly improve the extraction efficiency of lipids from algal biomass. This enhanced efficiency translates to higher yields of valuable products such as biofuels and nutraceuticals. The economic impact of this increased yield must be weighed against the additional costs associated with decane procurement, handling, and recovery.
One of the key economic advantages of decane integration is the potential for reduced energy consumption during the extraction process. Decane's lower boiling point compared to traditional solvents like hexane allows for lower operating temperatures, potentially reducing energy costs. Additionally, the improved selectivity of decane for specific compounds can lead to higher-purity products, potentially commanding premium prices in the market.
The recovery and recycling of decane within the process is a critical factor in the overall economic viability. Efficient solvent recovery systems can significantly reduce operational costs and environmental impact. The development of advanced separation technologies for decane recovery is an area of ongoing research and development, with potential for further cost reductions.
From a market perspective, the integration of decane in algal biomass conversion could potentially open new avenues for high-value products. The improved extraction efficiency and selectivity may enable the production of specialty chemicals and pharmaceutical precursors that were previously uneconomical to extract from algal biomass.
However, the economic analysis must also consider potential challenges. The volatility of decane prices, which are linked to petroleum markets, could impact the long-term economic stability of decane-based processes. Additionally, regulatory considerations regarding the use of hydrocarbon solvents in food and pharmaceutical applications may influence the marketability of certain algal-derived products.
In conclusion, the techno-economic analysis of decane integration in algal biomass conversion processes reveals a complex interplay of costs, benefits, and market factors. While the potential for improved efficiency and product quality is significant, careful consideration of economic and regulatory factors is essential for successful implementation.
From an economic perspective, the integration of decane into existing algal biomass conversion processes requires careful consideration of capital and operational costs. The initial investment for retrofitting or designing new facilities to accommodate decane-based extraction systems can be substantial. However, this cost may be offset by the potential increase in product yield and quality.
The use of decane as a solvent can significantly improve the extraction efficiency of lipids from algal biomass. This enhanced efficiency translates to higher yields of valuable products such as biofuels and nutraceuticals. The economic impact of this increased yield must be weighed against the additional costs associated with decane procurement, handling, and recovery.
One of the key economic advantages of decane integration is the potential for reduced energy consumption during the extraction process. Decane's lower boiling point compared to traditional solvents like hexane allows for lower operating temperatures, potentially reducing energy costs. Additionally, the improved selectivity of decane for specific compounds can lead to higher-purity products, potentially commanding premium prices in the market.
The recovery and recycling of decane within the process is a critical factor in the overall economic viability. Efficient solvent recovery systems can significantly reduce operational costs and environmental impact. The development of advanced separation technologies for decane recovery is an area of ongoing research and development, with potential for further cost reductions.
From a market perspective, the integration of decane in algal biomass conversion could potentially open new avenues for high-value products. The improved extraction efficiency and selectivity may enable the production of specialty chemicals and pharmaceutical precursors that were previously uneconomical to extract from algal biomass.
However, the economic analysis must also consider potential challenges. The volatility of decane prices, which are linked to petroleum markets, could impact the long-term economic stability of decane-based processes. Additionally, regulatory considerations regarding the use of hydrocarbon solvents in food and pharmaceutical applications may influence the marketability of certain algal-derived products.
In conclusion, the techno-economic analysis of decane integration in algal biomass conversion processes reveals a complex interplay of costs, benefits, and market factors. While the potential for improved efficiency and product quality is significant, careful consideration of economic and regulatory factors is essential for successful implementation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!