How Decane Supports Multi-Phase Chemical Separation
JUL 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Decane Separation Background and Objectives
Decane, a straight-chain alkane hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C10H22, has emerged as a crucial component in multi-phase chemical separation processes. The evolution of decane's application in this field can be traced back to the early 20th century when the petroleum industry began to explore more efficient methods for separating complex hydrocarbon mixtures.
The primary objective of utilizing decane in multi-phase chemical separation is to enhance the efficiency and selectivity of separation processes, particularly in the extraction of valuable compounds from complex mixtures. This aliphatic hydrocarbon's unique properties, including its low solubility in water, moderate boiling point, and excellent solvating capabilities for non-polar substances, make it an ideal candidate for various separation techniques.
Over the years, the role of decane in chemical separation has expanded beyond the petroleum industry. It has found applications in pharmaceutical manufacturing, environmental remediation, and the production of fine chemicals. The increasing demand for high-purity compounds in these sectors has driven the development of more sophisticated separation techniques involving decane.
One of the key trends in the evolution of decane-based separation processes is the focus on sustainability and environmental impact. Researchers and industry professionals are exploring ways to minimize the use of harmful solvents and reduce energy consumption in separation processes. Decane, being a relatively benign hydrocarbon, aligns well with these sustainability goals.
The technological advancements in analytical chemistry and process engineering have significantly contributed to the refinement of decane-based separation methods. The integration of advanced spectroscopic techniques, computational modeling, and process intensification strategies has led to more precise and efficient separation processes.
Looking ahead, the objectives for decane in multi-phase chemical separation are multifaceted. There is a growing emphasis on developing novel separation techniques that can handle increasingly complex mixtures with higher selectivity and throughput. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of decane in emerging fields such as nanotechnology and advanced materials processing.
Another important goal is to optimize the recovery and recycling of decane in separation processes, thereby improving the overall sustainability and cost-effectiveness of these operations. This aligns with the broader industry trend towards circular economy principles and waste reduction.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of decane in multi-phase chemical separation reflect a journey of continuous innovation and adaptation to evolving industrial needs. From its roots in petroleum refining to its current status as a versatile separation medium, decane continues to play a crucial role in advancing the field of chemical separation technology.
The primary objective of utilizing decane in multi-phase chemical separation is to enhance the efficiency and selectivity of separation processes, particularly in the extraction of valuable compounds from complex mixtures. This aliphatic hydrocarbon's unique properties, including its low solubility in water, moderate boiling point, and excellent solvating capabilities for non-polar substances, make it an ideal candidate for various separation techniques.
Over the years, the role of decane in chemical separation has expanded beyond the petroleum industry. It has found applications in pharmaceutical manufacturing, environmental remediation, and the production of fine chemicals. The increasing demand for high-purity compounds in these sectors has driven the development of more sophisticated separation techniques involving decane.
One of the key trends in the evolution of decane-based separation processes is the focus on sustainability and environmental impact. Researchers and industry professionals are exploring ways to minimize the use of harmful solvents and reduce energy consumption in separation processes. Decane, being a relatively benign hydrocarbon, aligns well with these sustainability goals.
The technological advancements in analytical chemistry and process engineering have significantly contributed to the refinement of decane-based separation methods. The integration of advanced spectroscopic techniques, computational modeling, and process intensification strategies has led to more precise and efficient separation processes.
Looking ahead, the objectives for decane in multi-phase chemical separation are multifaceted. There is a growing emphasis on developing novel separation techniques that can handle increasingly complex mixtures with higher selectivity and throughput. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of decane in emerging fields such as nanotechnology and advanced materials processing.
Another important goal is to optimize the recovery and recycling of decane in separation processes, thereby improving the overall sustainability and cost-effectiveness of these operations. This aligns with the broader industry trend towards circular economy principles and waste reduction.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of decane in multi-phase chemical separation reflect a journey of continuous innovation and adaptation to evolving industrial needs. From its roots in petroleum refining to its current status as a versatile separation medium, decane continues to play a crucial role in advancing the field of chemical separation technology.
Market Analysis for Decane-Based Separation
The market for decane-based separation technologies has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for efficient and cost-effective chemical separation processes across various industries. Decane, a versatile hydrocarbon, has emerged as a key player in multi-phase chemical separation due to its unique properties and wide-ranging applications.
In the oil and gas industry, decane-based separation techniques have gained traction for their ability to enhance the recovery of valuable hydrocarbons from complex mixtures. This has led to improved efficiency in refining processes and increased yield of high-value products. The petrochemical sector has also witnessed a surge in demand for decane-based separation methods, particularly in the production of specialty chemicals and polymers.
The pharmaceutical industry has embraced decane-based separation technologies for their effectiveness in purifying active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates. The ability of decane to facilitate precise separation of compounds with similar properties has made it invaluable in drug development and manufacturing processes. This has contributed to the overall growth of the pharmaceutical separation market, which is projected to expand at a steady rate in the coming years.
Environmental applications of decane-based separation have also seen a rise, particularly in water treatment and pollution control. The increasing focus on sustainability and environmental regulations has driven the adoption of decane-based technologies for removing organic contaminants from water and industrial effluents. This trend is expected to continue as governments worldwide implement stricter environmental policies.
The global market for decane-based separation technologies is characterized by a diverse range of end-users, including chemical manufacturers, pharmaceutical companies, and environmental service providers. North America and Europe currently dominate the market, owing to their advanced industrial infrastructure and stringent quality standards. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, fueled by industrialization and increasing investments in chemical and pharmaceutical sectors.
Key market drivers include the growing emphasis on process optimization, the need for high-purity products, and the increasing complexity of chemical mixtures requiring separation. Additionally, the rising demand for sustainable and eco-friendly separation processes has spurred innovation in decane-based technologies, leading to the development of more efficient and environmentally compatible solutions.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for specialized expertise in implementing decane-based separation systems may hinder market growth to some extent. However, ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these technologies are expected to address these challenges and further expand the market potential of decane-based separation in the coming years.
In the oil and gas industry, decane-based separation techniques have gained traction for their ability to enhance the recovery of valuable hydrocarbons from complex mixtures. This has led to improved efficiency in refining processes and increased yield of high-value products. The petrochemical sector has also witnessed a surge in demand for decane-based separation methods, particularly in the production of specialty chemicals and polymers.
The pharmaceutical industry has embraced decane-based separation technologies for their effectiveness in purifying active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates. The ability of decane to facilitate precise separation of compounds with similar properties has made it invaluable in drug development and manufacturing processes. This has contributed to the overall growth of the pharmaceutical separation market, which is projected to expand at a steady rate in the coming years.
Environmental applications of decane-based separation have also seen a rise, particularly in water treatment and pollution control. The increasing focus on sustainability and environmental regulations has driven the adoption of decane-based technologies for removing organic contaminants from water and industrial effluents. This trend is expected to continue as governments worldwide implement stricter environmental policies.
The global market for decane-based separation technologies is characterized by a diverse range of end-users, including chemical manufacturers, pharmaceutical companies, and environmental service providers. North America and Europe currently dominate the market, owing to their advanced industrial infrastructure and stringent quality standards. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, fueled by industrialization and increasing investments in chemical and pharmaceutical sectors.
Key market drivers include the growing emphasis on process optimization, the need for high-purity products, and the increasing complexity of chemical mixtures requiring separation. Additionally, the rising demand for sustainable and eco-friendly separation processes has spurred innovation in decane-based technologies, leading to the development of more efficient and environmentally compatible solutions.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for specialized expertise in implementing decane-based separation systems may hinder market growth to some extent. However, ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these technologies are expected to address these challenges and further expand the market potential of decane-based separation in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Multi-Phase Chemical Separation
Multi-phase chemical separation faces several significant challenges in today's industrial and research environments. One of the primary issues is the complexity of separating multiple components simultaneously, especially when dealing with mixtures containing both organic and inorganic substances. The presence of emulsions and the formation of stable interfaces between different phases often hinder efficient separation processes.
Another major challenge is the energy intensity of traditional separation methods. Many current techniques, such as distillation and crystallization, require substantial energy inputs, leading to high operational costs and environmental concerns. This has sparked a growing interest in developing more energy-efficient separation technologies that can maintain or improve separation efficiency while reducing energy consumption.
The scalability of separation processes from laboratory to industrial scale presents another hurdle. Methods that work well at small scales may encounter unforeseen difficulties when scaled up, such as changes in fluid dynamics, heat transfer, and mass transfer rates. This scaling issue often necessitates significant re-engineering and optimization efforts, increasing the time and cost of implementing new separation technologies.
Selectivity and purity of separated components remain critical challenges, particularly in industries such as pharmaceuticals and electronics, where even trace impurities can have significant impacts. Achieving high selectivity while maintaining throughput is a delicate balance that often requires innovative approaches and advanced materials.
Environmental and safety concerns also pose challenges to multi-phase chemical separation. The use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other hazardous substances in some separation processes raises safety risks and environmental issues. There is a growing need for greener separation technologies that minimize the use of harmful chemicals and reduce waste generation.
The development of robust and fouling-resistant separation materials is another ongoing challenge. Many separation processes, especially those involving membranes or adsorbents, suffer from performance degradation over time due to fouling, scaling, or chemical degradation. Enhancing the longevity and stability of separation materials is crucial for improving process efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
Lastly, the integration of separation processes with other unit operations in a chemical plant or laboratory setting presents logistical and engineering challenges. Optimizing the entire process chain while ensuring efficient separation at each stage requires a holistic approach to process design and control, often necessitating advanced modeling and simulation techniques.
Another major challenge is the energy intensity of traditional separation methods. Many current techniques, such as distillation and crystallization, require substantial energy inputs, leading to high operational costs and environmental concerns. This has sparked a growing interest in developing more energy-efficient separation technologies that can maintain or improve separation efficiency while reducing energy consumption.
The scalability of separation processes from laboratory to industrial scale presents another hurdle. Methods that work well at small scales may encounter unforeseen difficulties when scaled up, such as changes in fluid dynamics, heat transfer, and mass transfer rates. This scaling issue often necessitates significant re-engineering and optimization efforts, increasing the time and cost of implementing new separation technologies.
Selectivity and purity of separated components remain critical challenges, particularly in industries such as pharmaceuticals and electronics, where even trace impurities can have significant impacts. Achieving high selectivity while maintaining throughput is a delicate balance that often requires innovative approaches and advanced materials.
Environmental and safety concerns also pose challenges to multi-phase chemical separation. The use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other hazardous substances in some separation processes raises safety risks and environmental issues. There is a growing need for greener separation technologies that minimize the use of harmful chemicals and reduce waste generation.
The development of robust and fouling-resistant separation materials is another ongoing challenge. Many separation processes, especially those involving membranes or adsorbents, suffer from performance degradation over time due to fouling, scaling, or chemical degradation. Enhancing the longevity and stability of separation materials is crucial for improving process efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
Lastly, the integration of separation processes with other unit operations in a chemical plant or laboratory setting presents logistical and engineering challenges. Optimizing the entire process chain while ensuring efficient separation at each stage requires a holistic approach to process design and control, often necessitating advanced modeling and simulation techniques.
Existing Decane-Based Separation Solutions
01 Distillation techniques for decane separation
Various distillation methods are employed for the separation of decane from other hydrocarbons. These techniques may include fractional distillation, vacuum distillation, or azeotropic distillation, depending on the specific mixture and desired purity. The process typically involves heating the mixture to different boiling points, allowing for the separation of decane based on its unique vapor pressure characteristics.- Distillation techniques for decane separation: Various distillation methods are employed for the separation of decane from other hydrocarbons. These techniques may include fractional distillation, vacuum distillation, or azeotropic distillation, depending on the specific mixture and desired purity. The process typically involves heating the mixture to different boiling points, allowing for the separation of decane based on its unique vapor pressure characteristics.
- Chromatographic separation of decane: Chromatography is utilized for the separation and analysis of decane in complex mixtures. This method may involve gas chromatography, liquid chromatography, or other specialized chromatographic techniques. The separation is based on the differential partitioning of decane between the mobile and stationary phases, allowing for its isolation from other components.
- Membrane-based separation of decane: Membrane technology is applied for the selective separation of decane from other hydrocarbons or solvents. This method utilizes specialized membranes with specific pore sizes or chemical affinities to allow the passage of decane while retaining other components. The process may involve pervaporation, nanofiltration, or other membrane-based techniques to achieve efficient separation.
- Adsorption-based decane separation: Adsorption processes are employed to separate decane from mixtures by utilizing materials with high affinity for specific components. This may involve the use of activated carbon, zeolites, or other specialized adsorbents. The separation is achieved through selective adsorption of decane or other components, followed by desorption steps to recover the purified decane.
- Extraction methods for decane isolation: Various extraction techniques are used to isolate decane from complex mixtures. These may include liquid-liquid extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, or solid-phase extraction. The process involves the selective transfer of decane between different phases based on its solubility or affinity, allowing for its separation from other components in the mixture.
02 Chromatographic separation of decane
Chromatography is utilized for the separation and analysis of decane in complex mixtures. This method may involve gas chromatography, liquid chromatography, or other specialized chromatographic techniques. The separation is based on the differential partitioning of decane between the mobile and stationary phases, allowing for its isolation from other components.Expand Specific Solutions03 Membrane-based separation of decane
Membrane technology is applied for the separation of decane from other hydrocarbons or solvents. This method utilizes selective permeation through specialized membranes, which may be based on size exclusion, affinity, or other physicochemical properties. The process can be optimized for decane separation by selecting appropriate membrane materials and operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Adsorption-based decane separation
Adsorption processes are employed for the selective removal of decane from mixtures. This technique utilizes adsorbent materials with high affinity for decane, such as activated carbon, zeolites, or specialized polymers. The separation is achieved through the preferential adsorption of decane onto the adsorbent surface, followed by desorption or regeneration steps to recover the purified decane.Expand Specific Solutions05 Extraction methods for decane separation
Liquid-liquid extraction or solvent extraction techniques are used to separate decane from other components. This process involves the use of a solvent that selectively dissolves decane, allowing for its extraction from the original mixture. The choice of solvent and extraction conditions are optimized to achieve high selectivity and efficiency in decane separation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Chemical Separation
The multi-phase chemical separation technology utilizing decane is currently in a growth stage, with increasing market demand driven by the petrochemical and fine chemical industries. The global market for chemical separation technologies is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. While the technology is relatively mature, ongoing research and development efforts by key players such as Shell Oil Co., DuPont de Nemours, Inc., and BASF Corp. are focused on improving efficiency and sustainability. These companies, along with others like LyondellBasell Acetyls LLC and Lummus Technology LLC, are investing in advanced separation techniques to enhance process performance and reduce environmental impact, indicating a competitive landscape with potential for further innovation and market expansion.
Shell Oil Co.
Technical Solution: Shell Oil Co. has developed an innovative approach to multi-phase chemical separation using decane as a key component. Their method involves a liquid-liquid extraction process where decane acts as a non-polar solvent to separate organic compounds from aqueous solutions[1]. The process utilizes decane's high boiling point (174°C) and low miscibility with water to create a distinct organic phase[2]. Shell's technology incorporates a series of mixer-settler units, allowing for multiple extraction stages to enhance separation efficiency[3]. The company has also implemented advanced process control systems to optimize the separation parameters, such as temperature, flow rates, and mixing intensity, resulting in improved product purity and recovery rates[4].
Strengths: High separation efficiency, scalable process, and adaptable to various chemical mixtures. Weaknesses: Energy-intensive due to multiple extraction stages, potential environmental concerns with decane handling.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont de Nemours, Inc. has developed a state-of-the-art multi-phase chemical separation technology that leverages decane's properties. Their approach combines liquid-liquid extraction with advanced centrifugal separation techniques[1]. The process utilizes decane as a selective solvent in a counter-current extraction system, followed by high-speed centrifugal separators to achieve rapid phase disengagement[2]. DuPont has also implemented proprietary internals in their extraction columns to enhance mass transfer and increase separation efficiency[3]. The company's technology incorporates real-time process analytical tools to monitor and control key separation parameters, ensuring optimal performance and product quality[4]. This integrated system achieves high throughput and excellent separation performance while minimizing solvent losses[5].
Strengths: High separation efficiency, rapid processing, and excellent process control. Weaknesses: High energy consumption for centrifugal separation and potential mechanical wear on equipment.
Innovative Decane Separation Technologies
Facility for processing a multiphase fluid and method for characterizing said fluid online
PatentWO2014044973A1
Innovation
- A treatment installation with a main settling tank and an analysis decanter that simultaneously processes a fraction of the multiphase fluid, allowing for continuous separation and characterization of phases, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustment of flow rates and additive use without disrupting the main process.
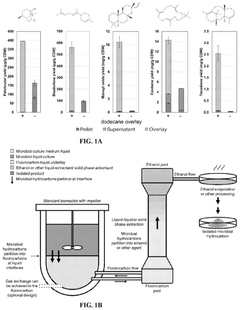
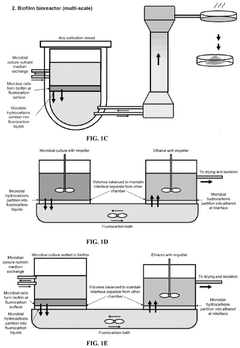
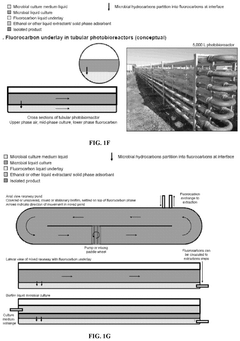
Biocompatible underlays for living extraction of hydrocarbons from engineered microbes
PatentPendingUS20240360481A1
Innovation
- The use of denser-than-water, biocompatible, and non-toxic liquid perfluorocarbons as an underlay in microbial cultures for extracting hydrophobic metabolites, combined with a secondary extraction step using environmentally friendly solvents like ethanol, allows for continuous and non-destructive extraction of metabolites at standard ambient temperature and pressure.
Environmental Impact of Decane Separation
The use of decane in multi-phase chemical separation processes has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. Decane, a hydrocarbon solvent, plays a crucial role in various industrial applications, particularly in the extraction and purification of chemicals. However, its widespread use raises concerns about potential environmental impacts.
One of the primary environmental considerations is the release of decane into the atmosphere. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), decane can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog when it reacts with other pollutants in the presence of sunlight. This can lead to air quality degradation, potentially affecting human health and ecosystems in areas surrounding industrial facilities that utilize decane-based separation processes.
Water pollution is another critical environmental issue associated with decane separation. Accidental spills or improper disposal of decane-containing waste can contaminate surface water and groundwater resources. Due to its low solubility in water and tendency to form a separate phase, decane can persist in aquatic environments, potentially harming aquatic life and compromising water quality for both human and ecological uses.
Soil contamination is also a concern when decane is released into the environment. The compound can adsorb to soil particles, potentially altering soil properties and affecting plant growth. Furthermore, decane contamination in soil can lead to long-term environmental issues, as it may slowly leach into groundwater or be taken up by plants, entering the food chain.
The production and disposal of decane also contribute to its environmental footprint. The manufacturing process of decane, typically derived from petroleum, involves energy-intensive operations that result in greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the disposal of decane-contaminated materials and waste products from separation processes requires careful management to prevent environmental contamination.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, industries employing decane-based separation techniques are increasingly adopting more sustainable practices. These include implementing closed-loop systems to minimize decane emissions, improving spill prevention and response protocols, and investing in more efficient separation technologies that reduce the overall use of decane. Additionally, research into alternative, more environmentally friendly solvents is ongoing, aiming to find substitutes that can match decane's separation efficiency while minimizing ecological risks.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines and standards for the use and disposal of decane and similar solvents. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for industries to minimize their environmental impact and ensure responsible use of decane in chemical separation processes. As environmental awareness continues to grow, the development of greener separation technologies and more stringent environmental safeguards will likely shape the future of decane use in multi-phase chemical separation.
One of the primary environmental considerations is the release of decane into the atmosphere. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), decane can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog when it reacts with other pollutants in the presence of sunlight. This can lead to air quality degradation, potentially affecting human health and ecosystems in areas surrounding industrial facilities that utilize decane-based separation processes.
Water pollution is another critical environmental issue associated with decane separation. Accidental spills or improper disposal of decane-containing waste can contaminate surface water and groundwater resources. Due to its low solubility in water and tendency to form a separate phase, decane can persist in aquatic environments, potentially harming aquatic life and compromising water quality for both human and ecological uses.
Soil contamination is also a concern when decane is released into the environment. The compound can adsorb to soil particles, potentially altering soil properties and affecting plant growth. Furthermore, decane contamination in soil can lead to long-term environmental issues, as it may slowly leach into groundwater or be taken up by plants, entering the food chain.
The production and disposal of decane also contribute to its environmental footprint. The manufacturing process of decane, typically derived from petroleum, involves energy-intensive operations that result in greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the disposal of decane-contaminated materials and waste products from separation processes requires careful management to prevent environmental contamination.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, industries employing decane-based separation techniques are increasingly adopting more sustainable practices. These include implementing closed-loop systems to minimize decane emissions, improving spill prevention and response protocols, and investing in more efficient separation technologies that reduce the overall use of decane. Additionally, research into alternative, more environmentally friendly solvents is ongoing, aiming to find substitutes that can match decane's separation efficiency while minimizing ecological risks.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines and standards for the use and disposal of decane and similar solvents. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for industries to minimize their environmental impact and ensure responsible use of decane in chemical separation processes. As environmental awareness continues to grow, the development of greener separation technologies and more stringent environmental safeguards will likely shape the future of decane use in multi-phase chemical separation.
Safety Protocols in Decane-Based Processes
Safety protocols in decane-based processes are crucial for ensuring the well-being of personnel and the integrity of equipment during multi-phase chemical separation operations. Decane, being a hydrocarbon, presents specific hazards that require careful management and mitigation strategies.
One of the primary safety concerns in decane-based processes is its flammability. Decane has a relatively low flash point, making it susceptible to ignition under certain conditions. To address this risk, proper ventilation systems must be installed and maintained in all areas where decane is handled or stored. These systems should be designed to prevent the accumulation of vapors and reduce the likelihood of reaching explosive concentrations.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a vital role in safeguarding workers involved in decane-based separation processes. Appropriate PPE includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and flame-resistant clothing. In areas with potential for splashes or spills, face shields and chemical-resistant aprons should also be worn. Regular training on the proper use and maintenance of PPE is essential to ensure its effectiveness.
Proper storage and handling procedures are critical for minimizing risks associated with decane. Storage tanks and containers should be properly labeled, grounded, and equipped with pressure relief valves to prevent the buildup of dangerous pressures. Transfer operations should be conducted using closed systems whenever possible to reduce the potential for spills and vapor releases.
Emergency response planning is another crucial aspect of safety protocols in decane-based processes. This includes the development and regular updating of spill response procedures, evacuation plans, and firefighting strategies specific to decane-related incidents. Emergency showers and eyewash stations should be readily accessible in all areas where decane is handled.
Monitoring and detection systems play a key role in maintaining a safe working environment. Gas detectors should be installed to provide early warning of potential leaks or vapor accumulations. Regular calibration and maintenance of these systems are essential to ensure their reliability and effectiveness.
Process safety management (PSM) principles should be applied to decane-based separation processes. This includes conducting thorough hazard and operability (HAZOP) studies, implementing management of change procedures, and performing regular process safety audits. These practices help identify potential hazards and ensure that appropriate controls are in place to mitigate risks.
Training and education are fundamental components of safety protocols in decane-based processes. All personnel involved in these operations should receive comprehensive training on the properties of decane, associated hazards, safe handling procedures, and emergency response protocols. Regular refresher courses and safety drills should be conducted to maintain a high level of awareness and preparedness among the workforce.
One of the primary safety concerns in decane-based processes is its flammability. Decane has a relatively low flash point, making it susceptible to ignition under certain conditions. To address this risk, proper ventilation systems must be installed and maintained in all areas where decane is handled or stored. These systems should be designed to prevent the accumulation of vapors and reduce the likelihood of reaching explosive concentrations.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a vital role in safeguarding workers involved in decane-based separation processes. Appropriate PPE includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and flame-resistant clothing. In areas with potential for splashes or spills, face shields and chemical-resistant aprons should also be worn. Regular training on the proper use and maintenance of PPE is essential to ensure its effectiveness.
Proper storage and handling procedures are critical for minimizing risks associated with decane. Storage tanks and containers should be properly labeled, grounded, and equipped with pressure relief valves to prevent the buildup of dangerous pressures. Transfer operations should be conducted using closed systems whenever possible to reduce the potential for spills and vapor releases.
Emergency response planning is another crucial aspect of safety protocols in decane-based processes. This includes the development and regular updating of spill response procedures, evacuation plans, and firefighting strategies specific to decane-related incidents. Emergency showers and eyewash stations should be readily accessible in all areas where decane is handled.
Monitoring and detection systems play a key role in maintaining a safe working environment. Gas detectors should be installed to provide early warning of potential leaks or vapor accumulations. Regular calibration and maintenance of these systems are essential to ensure their reliability and effectiveness.
Process safety management (PSM) principles should be applied to decane-based separation processes. This includes conducting thorough hazard and operability (HAZOP) studies, implementing management of change procedures, and performing regular process safety audits. These practices help identify potential hazards and ensure that appropriate controls are in place to mitigate risks.
Training and education are fundamental components of safety protocols in decane-based processes. All personnel involved in these operations should receive comprehensive training on the properties of decane, associated hazards, safe handling procedures, and emergency response protocols. Regular refresher courses and safety drills should be conducted to maintain a high level of awareness and preparedness among the workforce.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!