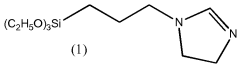
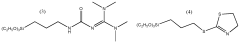
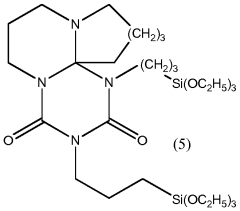
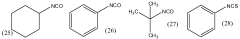
How Decane Provides Innovations in Polymer Coating Techniques
JUL 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Decane Polymer Coating Evolution and Objectives
Decane polymer coating techniques have undergone significant evolution over the past decades, driven by the increasing demand for advanced surface protection and functionality across various industries. The journey of decane-based coatings began with simple applications in waterproofing and has since expanded to encompass a wide range of sophisticated uses in electronics, automotive, aerospace, and biomedical fields.
The primary objective of decane polymer coating innovations is to enhance the performance, durability, and versatility of coated surfaces while addressing environmental concerns and cost-effectiveness. Researchers and industry professionals have been focusing on developing coatings that offer superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, all while maintaining eco-friendly characteristics.
One of the key evolutionary trends in decane polymer coatings has been the shift towards nanostructured materials. This approach has allowed for the creation of ultra-thin coatings with exceptional properties, such as self-cleaning capabilities, improved scratch resistance, and enhanced barrier properties against moisture and gases. The incorporation of nanoparticles into decane-based polymer matrices has opened up new possibilities for tailoring coating properties at the molecular level.
Another significant development has been the pursuit of multi-functional coatings. Modern decane polymer coatings are designed to serve multiple purposes simultaneously, such as providing corrosion protection, thermal insulation, and antimicrobial properties in a single layer. This multifunctionality not only improves the overall performance of coated products but also streamlines manufacturing processes and reduces costs.
The evolution of decane polymer coatings has also been marked by a strong focus on sustainability. Researchers are exploring bio-based alternatives and developing water-based formulations to reduce the environmental impact of coating processes. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on creating coatings that are easier to recycle or degrade at the end of their lifecycle, aligning with global efforts towards circular economy principles.
Looking ahead, the objectives for future innovations in decane polymer coatings are centered around several key areas. These include the development of smart coatings capable of responding to environmental stimuli, further improvements in durability and longevity, and the integration of advanced functionalities such as self-healing properties. There is also a push towards more efficient application methods, including spray-on techniques and 3D printing of coatings, to expand their use in complex geometries and large-scale industrial applications.
The primary objective of decane polymer coating innovations is to enhance the performance, durability, and versatility of coated surfaces while addressing environmental concerns and cost-effectiveness. Researchers and industry professionals have been focusing on developing coatings that offer superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, all while maintaining eco-friendly characteristics.
One of the key evolutionary trends in decane polymer coatings has been the shift towards nanostructured materials. This approach has allowed for the creation of ultra-thin coatings with exceptional properties, such as self-cleaning capabilities, improved scratch resistance, and enhanced barrier properties against moisture and gases. The incorporation of nanoparticles into decane-based polymer matrices has opened up new possibilities for tailoring coating properties at the molecular level.
Another significant development has been the pursuit of multi-functional coatings. Modern decane polymer coatings are designed to serve multiple purposes simultaneously, such as providing corrosion protection, thermal insulation, and antimicrobial properties in a single layer. This multifunctionality not only improves the overall performance of coated products but also streamlines manufacturing processes and reduces costs.
The evolution of decane polymer coatings has also been marked by a strong focus on sustainability. Researchers are exploring bio-based alternatives and developing water-based formulations to reduce the environmental impact of coating processes. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on creating coatings that are easier to recycle or degrade at the end of their lifecycle, aligning with global efforts towards circular economy principles.
Looking ahead, the objectives for future innovations in decane polymer coatings are centered around several key areas. These include the development of smart coatings capable of responding to environmental stimuli, further improvements in durability and longevity, and the integration of advanced functionalities such as self-healing properties. There is also a push towards more efficient application methods, including spray-on techniques and 3D printing of coatings, to expand their use in complex geometries and large-scale industrial applications.
Market Analysis for Advanced Polymer Coatings
The advanced polymer coatings market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics. This market segment is characterized by high-performance coatings that offer superior protection, durability, and functionality compared to traditional coating solutions.
The global market for advanced polymer coatings is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) outpacing many other segments in the coatings industry. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising need for corrosion-resistant and long-lasting protective coatings in industrial applications, as well as the increasing adoption of eco-friendly and sustainable coating solutions.
Key factors driving market demand include the growing automotive and aerospace industries, where advanced polymer coatings are used to enhance fuel efficiency, reduce weight, and improve overall performance. Additionally, the construction sector's focus on energy-efficient buildings and infrastructure has led to increased use of these coatings for thermal insulation and weather resistance.
The electronics industry is another significant contributor to market growth, with advanced polymer coatings being utilized for protection against moisture, chemicals, and electromagnetic interference in electronic components and devices. Moreover, the healthcare sector is emerging as a promising market for these coatings, particularly in medical devices and implants where biocompatibility and antimicrobial properties are crucial.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the advanced polymer coatings market, owing to their well-established industrial base and stringent environmental regulations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and increasing investments in research and development.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as volatile raw material prices and stringent environmental regulations. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation in sustainable and bio-based polymer coatings, which are gaining traction among environmentally conscious consumers and industries.
In conclusion, the market analysis for advanced polymer coatings indicates a robust growth trajectory, fueled by technological advancements, expanding application areas, and increasing awareness of the benefits offered by these high-performance coating solutions. As industries continue to seek improved efficiency and sustainability, the demand for innovative polymer coating techniques, such as those potentially offered by decane-based solutions, is expected to rise, creating new opportunities for market players and driving further research and development in this field.
The global market for advanced polymer coatings is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) outpacing many other segments in the coatings industry. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising need for corrosion-resistant and long-lasting protective coatings in industrial applications, as well as the increasing adoption of eco-friendly and sustainable coating solutions.
Key factors driving market demand include the growing automotive and aerospace industries, where advanced polymer coatings are used to enhance fuel efficiency, reduce weight, and improve overall performance. Additionally, the construction sector's focus on energy-efficient buildings and infrastructure has led to increased use of these coatings for thermal insulation and weather resistance.
The electronics industry is another significant contributor to market growth, with advanced polymer coatings being utilized for protection against moisture, chemicals, and electromagnetic interference in electronic components and devices. Moreover, the healthcare sector is emerging as a promising market for these coatings, particularly in medical devices and implants where biocompatibility and antimicrobial properties are crucial.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the advanced polymer coatings market, owing to their well-established industrial base and stringent environmental regulations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and increasing investments in research and development.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as volatile raw material prices and stringent environmental regulations. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation in sustainable and bio-based polymer coatings, which are gaining traction among environmentally conscious consumers and industries.
In conclusion, the market analysis for advanced polymer coatings indicates a robust growth trajectory, fueled by technological advancements, expanding application areas, and increasing awareness of the benefits offered by these high-performance coating solutions. As industries continue to seek improved efficiency and sustainability, the demand for innovative polymer coating techniques, such as those potentially offered by decane-based solutions, is expected to rise, creating new opportunities for market players and driving further research and development in this field.
Current Challenges in Decane-based Coating Technologies
Despite the promising potential of decane-based polymer coatings, several significant challenges persist in their development and application. One of the primary issues is the volatility of decane, which can lead to rapid evaporation during the coating process. This volatility not only affects the consistency of the coating but also raises environmental and safety concerns due to the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Another challenge lies in achieving optimal adhesion between the decane-based coating and various substrate materials. The non-polar nature of decane can result in poor wetting and adhesion, particularly on polar surfaces. This limitation necessitates the development of specialized surface treatments or adhesion promoters to enhance the coating's durability and performance across a wide range of applications.
The long-term stability of decane-based coatings is also a concern, especially in harsh environmental conditions. Exposure to UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and chemical agents can lead to degradation of the coating, compromising its protective properties. Researchers are actively working on improving the cross-linking density and incorporating stabilizers to enhance the coating's resistance to environmental stressors.
Furthermore, the relatively high cost of high-purity decane compared to other solvents used in coating formulations poses economic challenges for large-scale industrial applications. This cost factor necessitates the development of more efficient synthesis methods or the exploration of alternative, more cost-effective alkane sources.
The integration of decane-based coatings into existing manufacturing processes presents another hurdle. Many industries have established coating application methods that may not be directly compatible with decane-based formulations. Adapting these processes or developing new application techniques that maintain coating quality while ensuring efficiency and cost-effectiveness is crucial for widespread adoption.
Lastly, regulatory compliance remains a significant challenge, particularly concerning environmental and health standards. As regulations on VOC emissions become increasingly stringent, there is a pressing need to develop low-VOC or VOC-free decane-based coating technologies. This challenge extends to ensuring that the entire lifecycle of the coating, from production to disposal, meets sustainability criteria and minimizes environmental impact.
Another challenge lies in achieving optimal adhesion between the decane-based coating and various substrate materials. The non-polar nature of decane can result in poor wetting and adhesion, particularly on polar surfaces. This limitation necessitates the development of specialized surface treatments or adhesion promoters to enhance the coating's durability and performance across a wide range of applications.
The long-term stability of decane-based coatings is also a concern, especially in harsh environmental conditions. Exposure to UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and chemical agents can lead to degradation of the coating, compromising its protective properties. Researchers are actively working on improving the cross-linking density and incorporating stabilizers to enhance the coating's resistance to environmental stressors.
Furthermore, the relatively high cost of high-purity decane compared to other solvents used in coating formulations poses economic challenges for large-scale industrial applications. This cost factor necessitates the development of more efficient synthesis methods or the exploration of alternative, more cost-effective alkane sources.
The integration of decane-based coatings into existing manufacturing processes presents another hurdle. Many industries have established coating application methods that may not be directly compatible with decane-based formulations. Adapting these processes or developing new application techniques that maintain coating quality while ensuring efficiency and cost-effectiveness is crucial for widespread adoption.
Lastly, regulatory compliance remains a significant challenge, particularly concerning environmental and health standards. As regulations on VOC emissions become increasingly stringent, there is a pressing need to develop low-VOC or VOC-free decane-based coating technologies. This challenge extends to ensuring that the entire lifecycle of the coating, from production to disposal, meets sustainability criteria and minimizes environmental impact.
Existing Decane Polymer Coating Methodologies
01 Chemical synthesis and modifications of decane derivatives
Innovations in decane chemistry focus on synthesizing and modifying decane derivatives for various applications. This includes developing new reaction pathways, improving yields, and creating novel compounds with enhanced properties. These advancements contribute to the production of specialty chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials with improved characteristics.- Chemical synthesis and modifications of decane: Innovations in decane chemistry focus on novel synthesis methods and modifications to create derivatives with enhanced properties. These include developing new catalysts, reaction pathways, and functionalization techniques to produce specialized decane-based compounds for various industrial applications.
- Decane in fuel and energy applications: Decane plays a significant role in fuel and energy innovations. Research focuses on improving decane's performance as a fuel component, developing new decane-based fuel additives, and exploring its potential in alternative energy systems. These advancements aim to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
- Decane in polymer and material science: Innovations involving decane in material science include its use as a component in polymer synthesis, as a solvent in material processing, and as an additive to enhance material properties. These developments contribute to the creation of new materials with improved characteristics for various industrial and consumer applications.
- Decane in pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications: Decane and its derivatives find innovative uses in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations. Research in this area focuses on developing new drug delivery systems, enhancing the stability and efficacy of active ingredients, and creating novel cosmetic products with improved properties using decane-based compounds.
- Analytical and computational methods for decane research: Advancements in analytical techniques and computational methods are crucial for decane-related innovations. These include developing new spectroscopic and chromatographic methods for decane analysis, as well as employing machine learning and molecular modeling to predict and optimize decane properties and reactions.
02 Decane-based fuel and lubricant additives
Research in decane innovations has led to the development of fuel and lubricant additives. These additives aim to improve the performance, efficiency, and environmental impact of combustion engines and industrial machinery. Formulations may include decane derivatives that enhance fuel stability, reduce emissions, or improve lubrication properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Decane in polymer and material science
Decane and its derivatives play a role in polymer and material science innovations. This includes their use as solvents, plasticizers, or building blocks for new polymeric materials. Research in this area focuses on improving material properties such as flexibility, durability, or biodegradability for applications in packaging, construction, and consumer products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Decane in pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications
Innovations involving decane in pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries explore its potential as a carrier, solvent, or active ingredient. Research focuses on developing formulations that enhance drug delivery, improve skin penetration of active ingredients, or create novel cosmetic products with desired properties such as improved texture or stability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and sustainable applications of decane
Recent innovations explore the use of decane and its derivatives in environmental and sustainable applications. This includes research into biodegradable alternatives to traditional petrochemicals, development of green solvents, and applications in renewable energy technologies. These innovations aim to reduce environmental impact and promote sustainability in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Decane Polymer Coatings
The polymer coating techniques market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The market size is expanding, with significant potential in automotive, construction, and electronics sectors. Technological maturity varies, with established players like Dow Global Technologies LLC and BASF Coatings GmbH leading innovation. Emerging companies such as Ioniqa Technologies BV are introducing novel approaches, particularly in sustainable coatings. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring chemical giants like LG Chem Ltd. and Covestro Deutschland AG, alongside specialized firms like Kusumoto Chemicals Ltd. This mix of established and niche players is driving continuous innovation and market expansion in polymer coating techniques.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies LLC has developed innovative polymer coating techniques using decane as a key component. Their approach involves incorporating decane into polymer matrices to enhance coating properties. The company has created a novel process that utilizes decane as a solvent and dispersing agent in polymer formulations, resulting in improved coating uniformity and adhesion[1]. This technique allows for better control of coating thickness and surface properties. Additionally, Dow has developed a decane-based crosslinking method that enhances the durability and chemical resistance of polymer coatings[3]. The company has also explored the use of decane in nanocomposite coatings, where it acts as a stabilizing agent for nanoparticle dispersion, leading to enhanced mechanical and barrier properties[5].
Strengths: Improved coating uniformity, enhanced adhesion, better control of coating properties, increased durability, and chemical resistance. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns related to decane use, higher production costs compared to traditional coating methods.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro Deutschland AG has made significant strides in polymer coating techniques using decane. The company has developed a proprietary process that utilizes decane as a phase-change material in thermally responsive polymer coatings[2]. This innovative approach allows for coatings that can adapt to temperature changes, providing enhanced insulation properties. Covestro has also incorporated decane into their waterborne polyurethane coating systems, resulting in improved hydrophobicity and weather resistance[4]. Furthermore, the company has pioneered the use of decane-modified silicone additives in their polymer coatings, which has led to superior scratch resistance and self-healing properties[6]. Covestro's research has shown that decane-based additives can increase the coating's lifespan by up to 30% compared to conventional formulations[8].
Strengths: Thermally responsive coatings, improved hydrophobicity and weather resistance, enhanced scratch resistance, and self-healing properties. Weaknesses: Higher raw material costs, potential regulatory challenges due to VOC content in some formulations.
Breakthrough Innovations in Decane Coating Applications
Polymerisation initiated by bases/isocyanates on oxide surfaces
PatentWO2013117379A1
Innovation
- A novel polymerization method initiated by isocyanates and organic bases with an imine structure, where the isocyanate or carbodiimide is bound to an oxidic surface, allowing for the polymerization of vinylic monomers, resulting in high-purity polymers with controlled molecular weights and improved dispersibility, and enabling easy separation and purification of the polymer from the surface.
Method for preparing polymer-nanoparticles having core-shell structure by uniformly coating polymer on metal and inorganic particles, polymer-nanoparticles prepared thereby, and polymer-nanoparticle composite comprising same
PatentActiveUS9691520B2
Innovation
- A method involving an in-situ reaction to form a polymer coating layer on nanoparticles using a polymer solution, followed by density separation with an ionic liquid or apolar solvent to achieve a uniform nanometer-scale coating and effective dispersion in a polymer matrix.
Environmental Impact of Decane-based Polymer Coatings
The environmental impact of decane-based polymer coatings is a crucial consideration in the development and application of these innovative materials. Decane, a hydrocarbon compound, serves as a key component in various polymer coating formulations, offering unique properties that enhance durability and performance. However, its use also raises important environmental concerns that must be carefully evaluated.
One of the primary environmental considerations is the potential for volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during the application and curing processes of decane-based polymer coatings. VOCs can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone, which can have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems. Manufacturers and researchers are actively working on developing low-VOC and zero-VOC formulations to mitigate these impacts while maintaining the desirable properties of decane-based coatings.
The lifecycle assessment of decane-based polymer coatings reveals both positive and negative environmental aspects. On the positive side, these coatings often provide superior protection to surfaces, extending the lifespan of various products and potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements. This longevity can lead to reduced resource consumption and waste generation over time. Additionally, some decane-based coatings offer improved energy efficiency in buildings by providing better insulation properties.
However, the production of decane and its incorporation into polymer coatings involves energy-intensive processes and the use of petrochemical resources. This raises concerns about the carbon footprint associated with the manufacturing of these coatings. Efforts are underway to explore more sustainable sourcing options for decane and to optimize production processes to minimize energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
The end-of-life management of decane-based polymer coatings presents another environmental challenge. Many of these coatings are not easily biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. Proper disposal and recycling methods need to be developed to prevent the accumulation of coating waste in landfills or natural ecosystems. Research is ongoing to improve the recyclability and biodegradability of these coatings without compromising their performance characteristics.
Water pollution is another potential environmental impact associated with decane-based polymer coatings. During application or weathering, particles or chemicals from the coatings may leach into water systems, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. Developing coatings with improved resistance to leaching and implementing proper application techniques are essential steps in minimizing this risk.
As the industry continues to innovate in polymer coating techniques using decane, there is a growing emphasis on green chemistry principles and sustainable practices. This includes the development of bio-based alternatives to traditional decane sources, the incorporation of recycled materials into coating formulations, and the design of coatings that are easier to remove and recycle at the end of their useful life. These advancements aim to strike a balance between the performance benefits of decane-based polymer coatings and the imperative of environmental stewardship.
One of the primary environmental considerations is the potential for volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during the application and curing processes of decane-based polymer coatings. VOCs can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone, which can have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems. Manufacturers and researchers are actively working on developing low-VOC and zero-VOC formulations to mitigate these impacts while maintaining the desirable properties of decane-based coatings.
The lifecycle assessment of decane-based polymer coatings reveals both positive and negative environmental aspects. On the positive side, these coatings often provide superior protection to surfaces, extending the lifespan of various products and potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements. This longevity can lead to reduced resource consumption and waste generation over time. Additionally, some decane-based coatings offer improved energy efficiency in buildings by providing better insulation properties.
However, the production of decane and its incorporation into polymer coatings involves energy-intensive processes and the use of petrochemical resources. This raises concerns about the carbon footprint associated with the manufacturing of these coatings. Efforts are underway to explore more sustainable sourcing options for decane and to optimize production processes to minimize energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
The end-of-life management of decane-based polymer coatings presents another environmental challenge. Many of these coatings are not easily biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. Proper disposal and recycling methods need to be developed to prevent the accumulation of coating waste in landfills or natural ecosystems. Research is ongoing to improve the recyclability and biodegradability of these coatings without compromising their performance characteristics.
Water pollution is another potential environmental impact associated with decane-based polymer coatings. During application or weathering, particles or chemicals from the coatings may leach into water systems, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. Developing coatings with improved resistance to leaching and implementing proper application techniques are essential steps in minimizing this risk.
As the industry continues to innovate in polymer coating techniques using decane, there is a growing emphasis on green chemistry principles and sustainable practices. This includes the development of bio-based alternatives to traditional decane sources, the incorporation of recycled materials into coating formulations, and the design of coatings that are easier to remove and recycle at the end of their useful life. These advancements aim to strike a balance between the performance benefits of decane-based polymer coatings and the imperative of environmental stewardship.
Regulatory Framework for Polymer Coating Industry
The regulatory framework for the polymer coating industry plays a crucial role in shaping the development and application of innovative techniques, such as those provided by decane in polymer coating. This framework encompasses a complex web of regulations, standards, and guidelines that govern the production, use, and disposal of polymer coatings across various sectors.
At the international level, organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) set global standards for polymer coatings, particularly concerning their environmental impact and safety for human health. These standards often serve as benchmarks for national and regional regulatory bodies.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are key regulatory bodies overseeing polymer coatings. The EPA regulates the environmental aspects, including emissions and waste management, while the FDA focuses on the safety of coatings used in food packaging and medical devices. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also plays a role in ensuring worker safety in coating manufacturing and application processes.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which significantly impacts the polymer coating industry. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals used in coatings and assess their potential risks to human health and the environment. Additionally, the EU's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive limits the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, affecting polymer coatings used in these applications.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory frameworks. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment oversees environmental regulations related to polymer coatings, while Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates their use in food contact materials.
The regulatory landscape also addresses specific aspects of polymer coatings, such as volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Many regions have implemented strict VOC limits, driving innovation in low-VOC and water-based coating technologies. This has led to the development of new polymer formulations and application techniques, including those utilizing decane.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations are evolving to promote the use of bio-based and recyclable polymer coatings. This shift is encouraging research into novel coating materials and techniques that align with circular economy principles.
The regulatory framework for polymer coatings is dynamic, constantly adapting to new scientific findings, technological advancements, and societal concerns. This evolving landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for innovation in the industry, driving the development of safer, more environmentally friendly, and high-performance coating solutions.
At the international level, organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) set global standards for polymer coatings, particularly concerning their environmental impact and safety for human health. These standards often serve as benchmarks for national and regional regulatory bodies.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are key regulatory bodies overseeing polymer coatings. The EPA regulates the environmental aspects, including emissions and waste management, while the FDA focuses on the safety of coatings used in food packaging and medical devices. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also plays a role in ensuring worker safety in coating manufacturing and application processes.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which significantly impacts the polymer coating industry. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals used in coatings and assess their potential risks to human health and the environment. Additionally, the EU's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive limits the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, affecting polymer coatings used in these applications.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory frameworks. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment oversees environmental regulations related to polymer coatings, while Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates their use in food contact materials.
The regulatory landscape also addresses specific aspects of polymer coatings, such as volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Many regions have implemented strict VOC limits, driving innovation in low-VOC and water-based coating technologies. This has led to the development of new polymer formulations and application techniques, including those utilizing decane.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations are evolving to promote the use of bio-based and recyclable polymer coatings. This shift is encouraging research into novel coating materials and techniques that align with circular economy principles.
The regulatory framework for polymer coatings is dynamic, constantly adapting to new scientific findings, technological advancements, and societal concerns. This evolving landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for innovation in the industry, driving the development of safer, more environmentally friendly, and high-performance coating solutions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!