How Phenolphthalein Contributes to Smart Polymer Design
JUL 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Phenolphthalein in Smart Polymers: Background and Objectives
Phenolphthalein, a compound traditionally known for its use as a pH indicator, has emerged as a key player in the development of smart polymers. This fascinating journey from a simple chemical indicator to a crucial component in advanced materials exemplifies the innovative spirit driving modern polymer science.
The concept of smart polymers, materials that can respond to environmental stimuli, has gained significant traction in recent decades. These polymers exhibit changes in their properties when exposed to external factors such as temperature, pH, light, or electrical fields. Phenolphthalein's unique color-changing properties in response to pH variations make it an ideal candidate for incorporation into smart polymer systems.
The evolution of phenolphthalein's role in polymer science can be traced back to the early 20th century when its pH-sensitive characteristics were first discovered. However, it wasn't until the late 1980s and early 1990s that researchers began to explore its potential in polymer applications. This shift in focus coincided with the growing interest in developing materials that could mimic biological systems' adaptive behaviors.
The primary objective of incorporating phenolphthalein into smart polymer design is to create materials with controllable and reversible color changes. These color transitions can serve as visual indicators of environmental conditions, making them valuable in various fields such as biosensors, drug delivery systems, and smart packaging.
Another crucial goal is to harness phenolphthalein's structural changes in response to pH variations to induce physical or chemical alterations in the polymer matrix. This property can be exploited to develop materials with switchable mechanical properties, self-healing capabilities, or controlled release mechanisms.
Researchers also aim to enhance the sensitivity and specificity of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers. By fine-tuning the polymer composition and structure, scientists seek to create materials that respond to minute changes in pH or other stimuli, expanding their potential applications in areas like environmental monitoring and medical diagnostics.
The integration of phenolphthalein into smart polymers opens up possibilities for multifunctional materials. For instance, combining pH-sensitivity with other responsive elements could lead to polymers that react to multiple stimuli simultaneously, offering unprecedented control over material properties and behaviors.
As we delve deeper into the world of smart polymers, the role of phenolphthalein continues to evolve. From its humble beginnings as a simple pH indicator, it has become a cornerstone in the development of advanced, responsive materials. The ongoing research in this field promises to unlock new applications and push the boundaries of what's possible in materials science, paving the way for innovative solutions to complex challenges across various industries.
The concept of smart polymers, materials that can respond to environmental stimuli, has gained significant traction in recent decades. These polymers exhibit changes in their properties when exposed to external factors such as temperature, pH, light, or electrical fields. Phenolphthalein's unique color-changing properties in response to pH variations make it an ideal candidate for incorporation into smart polymer systems.
The evolution of phenolphthalein's role in polymer science can be traced back to the early 20th century when its pH-sensitive characteristics were first discovered. However, it wasn't until the late 1980s and early 1990s that researchers began to explore its potential in polymer applications. This shift in focus coincided with the growing interest in developing materials that could mimic biological systems' adaptive behaviors.
The primary objective of incorporating phenolphthalein into smart polymer design is to create materials with controllable and reversible color changes. These color transitions can serve as visual indicators of environmental conditions, making them valuable in various fields such as biosensors, drug delivery systems, and smart packaging.
Another crucial goal is to harness phenolphthalein's structural changes in response to pH variations to induce physical or chemical alterations in the polymer matrix. This property can be exploited to develop materials with switchable mechanical properties, self-healing capabilities, or controlled release mechanisms.
Researchers also aim to enhance the sensitivity and specificity of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers. By fine-tuning the polymer composition and structure, scientists seek to create materials that respond to minute changes in pH or other stimuli, expanding their potential applications in areas like environmental monitoring and medical diagnostics.
The integration of phenolphthalein into smart polymers opens up possibilities for multifunctional materials. For instance, combining pH-sensitivity with other responsive elements could lead to polymers that react to multiple stimuli simultaneously, offering unprecedented control over material properties and behaviors.
As we delve deeper into the world of smart polymers, the role of phenolphthalein continues to evolve. From its humble beginnings as a simple pH indicator, it has become a cornerstone in the development of advanced, responsive materials. The ongoing research in this field promises to unlock new applications and push the boundaries of what's possible in materials science, paving the way for innovative solutions to complex challenges across various industries.
Market Analysis for Smart Polymer Applications
The smart polymer market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for advanced materials in various industries. Smart polymers, also known as stimuli-responsive polymers, have the ability to change their properties in response to external stimuli such as temperature, pH, light, or electric fields. This unique characteristic makes them highly valuable in applications ranging from biomedical devices to environmental sensors.
The global smart polymer market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% in the coming years. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising adoption of smart polymers in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and self-healing materials. The healthcare sector, in particular, is expected to be a major contributor to market growth, with smart polymers being utilized in controlled drug release systems and biosensors.
In the context of phenolphthalein's contribution to smart polymer design, there is a growing interest in pH-responsive polymers. Phenolphthalein, traditionally known as a pH indicator, is being incorporated into polymer structures to create materials that can change their properties based on the surrounding pH environment. This has opened up new possibilities in areas such as targeted drug delivery and environmental monitoring.
The automotive and aerospace industries are also showing increased interest in smart polymers, particularly for their potential in developing self-healing materials and shape-memory polymers. These applications could lead to more durable and efficient components, reducing maintenance costs and improving overall performance.
Environmental applications of smart polymers are gaining traction as well. Water treatment and pollution control are areas where pH-responsive polymers, including those incorporating phenolphthalein, could play a crucial role. The ability of these materials to selectively remove contaminants or change their properties in response to environmental conditions makes them valuable tools in addressing water quality issues.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the smart polymer market, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing research and development activities, and growing investments in advanced materials. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront of this regional growth, with numerous research institutions and companies focusing on smart polymer development.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of smart polymers. These include high production costs, scalability issues, and the need for further research to fully understand and control the behavior of these materials in complex environments. However, ongoing advancements in polymer science and nanotechnology are expected to address many of these challenges in the coming years.
The global smart polymer market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% in the coming years. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising adoption of smart polymers in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and self-healing materials. The healthcare sector, in particular, is expected to be a major contributor to market growth, with smart polymers being utilized in controlled drug release systems and biosensors.
In the context of phenolphthalein's contribution to smart polymer design, there is a growing interest in pH-responsive polymers. Phenolphthalein, traditionally known as a pH indicator, is being incorporated into polymer structures to create materials that can change their properties based on the surrounding pH environment. This has opened up new possibilities in areas such as targeted drug delivery and environmental monitoring.
The automotive and aerospace industries are also showing increased interest in smart polymers, particularly for their potential in developing self-healing materials and shape-memory polymers. These applications could lead to more durable and efficient components, reducing maintenance costs and improving overall performance.
Environmental applications of smart polymers are gaining traction as well. Water treatment and pollution control are areas where pH-responsive polymers, including those incorporating phenolphthalein, could play a crucial role. The ability of these materials to selectively remove contaminants or change their properties in response to environmental conditions makes them valuable tools in addressing water quality issues.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the smart polymer market, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing research and development activities, and growing investments in advanced materials. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront of this regional growth, with numerous research institutions and companies focusing on smart polymer development.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of smart polymers. These include high production costs, scalability issues, and the need for further research to fully understand and control the behavior of these materials in complex environments. However, ongoing advancements in polymer science and nanotechnology are expected to address many of these challenges in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Smart Polymer Design
Smart polymer design faces several significant challenges that hinder the full realization of their potential in various applications. One of the primary obstacles is achieving precise control over the polymer's response to external stimuli. While smart polymers are designed to react to specific environmental changes, fine-tuning the sensitivity and specificity of these responses remains a complex task. This challenge is particularly evident when attempting to create polymers that can respond to multiple stimuli simultaneously or in a predetermined sequence.
Another critical challenge lies in the scalability and reproducibility of smart polymer production. Laboratory-scale successes often encounter difficulties when transitioning to industrial-scale manufacturing. Ensuring consistent performance and properties across large batches of smart polymers is crucial for their commercial viability but remains a significant hurdle. This issue is compounded by the intricate molecular structures and precise chemical compositions required for many smart polymer designs.
Durability and long-term stability present additional challenges in smart polymer development. Many smart polymers exhibit degradation or loss of responsiveness over time, especially when subjected to repeated stimuli cycles. This limitation restricts their applicability in scenarios requiring prolonged or frequent use. Enhancing the resilience of smart polymers without compromising their responsive properties is an ongoing area of research and development.
The integration of smart polymers with other materials and systems also poses significant challenges. Creating effective interfaces between smart polymers and electronic components, for instance, is crucial for developing advanced sensors and actuators. However, achieving seamless integration while maintaining the functionality of both the polymer and the coupled system remains a complex task.
Furthermore, the biocompatibility and environmental impact of smart polymers are growing concerns, particularly for applications in medicine and environmental sensing. Developing smart polymers that are both functional and safe for biological systems, as well as environmentally friendly, is a multifaceted challenge that requires balancing performance with safety and sustainability.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of smart polymer production and application remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Many current smart polymer designs rely on expensive materials or complex synthesis processes, limiting their commercial viability. Finding ways to reduce production costs while maintaining or enhancing performance is crucial for expanding the use of smart polymers across various industries.
Another critical challenge lies in the scalability and reproducibility of smart polymer production. Laboratory-scale successes often encounter difficulties when transitioning to industrial-scale manufacturing. Ensuring consistent performance and properties across large batches of smart polymers is crucial for their commercial viability but remains a significant hurdle. This issue is compounded by the intricate molecular structures and precise chemical compositions required for many smart polymer designs.
Durability and long-term stability present additional challenges in smart polymer development. Many smart polymers exhibit degradation or loss of responsiveness over time, especially when subjected to repeated stimuli cycles. This limitation restricts their applicability in scenarios requiring prolonged or frequent use. Enhancing the resilience of smart polymers without compromising their responsive properties is an ongoing area of research and development.
The integration of smart polymers with other materials and systems also poses significant challenges. Creating effective interfaces between smart polymers and electronic components, for instance, is crucial for developing advanced sensors and actuators. However, achieving seamless integration while maintaining the functionality of both the polymer and the coupled system remains a complex task.
Furthermore, the biocompatibility and environmental impact of smart polymers are growing concerns, particularly for applications in medicine and environmental sensing. Developing smart polymers that are both functional and safe for biological systems, as well as environmentally friendly, is a multifaceted challenge that requires balancing performance with safety and sustainability.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of smart polymer production and application remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Many current smart polymer designs rely on expensive materials or complex synthesis processes, limiting their commercial viability. Finding ways to reduce production costs while maintaining or enhancing performance is crucial for expanding the use of smart polymers across various industries.
Existing Phenolphthalein-Polymer Integration Methods
01 Synthesis of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers
Smart polymers incorporating phenolphthalein are synthesized through various polymerization techniques. These polymers exhibit responsive behavior to environmental stimuli such as pH changes, making them suitable for applications in sensors and controlled release systems.- Phenolphthalein-based smart polymer synthesis: Smart polymers incorporating phenolphthalein are synthesized to create materials with color-changing properties in response to environmental stimuli. These polymers can be designed to change color based on pH, temperature, or other factors, making them useful for various applications in sensing and indicator systems.
- pH-responsive phenolphthalein polymer applications: Phenolphthalein-based smart polymers are developed for pH-sensitive applications. These materials can be used in various fields such as drug delivery systems, environmental monitoring, and biomedical devices. The polymers change color or properties in response to pH changes, allowing for visual or measurable detection of pH variations.
- Thermochromic phenolphthalein polymer design: Smart polymers incorporating phenolphthalein are designed to exhibit thermochromic properties. These materials change color in response to temperature variations, making them suitable for temperature-sensitive indicators, packaging, and thermal monitoring applications. The polymer structure is engineered to control the temperature range for color change.
- Phenolphthalein polymer composites for sensing: Composite materials combining phenolphthalein-based smart polymers with other functional components are developed for advanced sensing applications. These composites can integrate multiple responsive elements to detect various environmental changes simultaneously, enhancing their versatility in fields such as environmental monitoring and smart packaging.
- Encapsulation techniques for phenolphthalein polymers: Encapsulation methods are developed to protect and control the release of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers. These techniques aim to improve the stability, longevity, and performance of the polymers in various applications. Encapsulation can also be used to create multi-functional materials with controlled release properties.
02 pH-responsive color-changing properties
Phenolphthalein-based smart polymers demonstrate color-changing properties in response to pH variations. This characteristic is utilized in developing visual indicators for pH monitoring in various fields, including environmental sensing and biomedical applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Controlled release mechanisms
Smart polymers containing phenolphthalein are designed to enable controlled release of active compounds. The pH-sensitive nature of these polymers allows for targeted delivery in specific environments, such as drug delivery systems responding to physiological pH changes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Incorporation into sensing devices
Phenolphthalein-based smart polymers are integrated into various sensing devices. These materials enable the development of advanced sensors for detecting pH changes, chemical species, or environmental conditions, with applications in water quality monitoring and industrial process control.Expand Specific Solutions05 Modification techniques for enhanced functionality
Various modification techniques are employed to enhance the functionality of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers. These include copolymerization with other monomers, surface modifications, and incorporation of additional functional groups to improve sensitivity, selectivity, or mechanical properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Smart Polymer Industry
The field of smart polymer design utilizing phenolphthalein is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The competitive landscape is diverse, involving academic institutions, research organizations, and industrial players. Universities like Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Jilin University, and the University of Washington are at the forefront of research, while companies such as SHPP Global Technologies BV and Solvay SA are driving commercial applications. The technology is maturing rapidly, with collaborations between academia and industry accelerating development. Key players like the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology and the Chinese Academy of Science Institute of Chemistry are contributing significantly to technological progress, indicating a promising future for phenolphthalein-based smart polymers across various sectors.
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
Technical Solution: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute has made notable advancements in using phenolphthalein for smart polymer design. Their research team has developed a novel class of shape-memory polymers incorporating phenolphthalein as a molecular switch[7]. These polymers can change shape and color in response to multiple stimuli, including pH, temperature, and light. The institute has also explored the use of phenolphthalein-based polymers in creating smart hydrogels for controlled drug release applications[8]. Additionally, they have investigated the potential of phenolphthalein-modified polymers in creating self-reporting materials that can indicate mechanical stress or damage through color changes[9].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research in multi-responsive smart polymers, strong focus on biomedical applications. Weaknesses: May face challenges in scaling up laboratory discoveries to practical, commercial products.
Dalian University of Technology
Technical Solution: Dalian University of Technology has made significant strides in incorporating phenolphthalein into smart polymer designs. Their research team has developed a series of phenolphthalein-based polymeric nanoparticles with pH-responsive properties for targeted drug delivery[10]. These nanoparticles exhibit controlled release behavior in different pH environments, making them promising for cancer therapy. The university has also explored the use of phenolphthalein-modified polymers in creating smart coatings with self-cleaning and anti-fouling properties[11]. Furthermore, they have investigated the potential of phenolphthalein-containing polymers in developing colorimetric sensors for detecting heavy metal ions in environmental samples[12].
Strengths: Strong focus on nanotechnology and environmental applications, innovative approaches to drug delivery systems. Weaknesses: May face regulatory challenges in bringing advanced drug delivery systems to market.
Innovative Phenolphthalein-Polymer Interactions
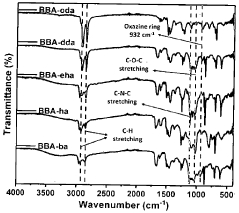
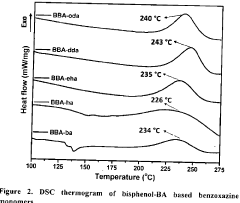
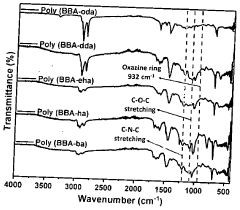
Production of extreme range of PH indicators from benzoxazines
PatentActiveIN202341027342A
Innovation
- Development of bisphenol-BA/aliphatic amine based hydrophobic polybenzoxazines coated on cellulose paper, synthesized through Mannich condensation, which exhibit distinct color changes across a wide pH range from -1.8 to 14, offering thermal stability and repeated use capability.
Environmental Impact of Phenolphthalein-based Smart Polymers
The environmental impact of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers is a critical consideration in their development and application. These innovative materials, which respond to environmental stimuli, offer potential benefits in various fields but also raise concerns about their ecological footprint.
One of the primary environmental advantages of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers is their potential to reduce waste and improve resource efficiency. These materials can be designed to change properties in response to specific environmental conditions, allowing for more targeted and efficient use in applications such as drug delivery or environmental sensing. This precision can lead to reduced material consumption and decreased environmental contamination.
However, the production and disposal of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers present environmental challenges. The synthesis of these materials often involves complex chemical processes that may require significant energy inputs and potentially harmful solvents. Additionally, the long-term environmental fate of these polymers is not yet fully understood, raising questions about their biodegradability and potential accumulation in ecosystems.
The pH-sensitive nature of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers offers opportunities for environmental monitoring and remediation. These materials can be used to detect and respond to changes in pH levels in water bodies, potentially aiding in the early detection of pollution or acidification. However, the release of phenolphthalein or its derivatives into the environment during the polymer's lifecycle could have unintended consequences on aquatic ecosystems.
Recycling and end-of-life management of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers pose unique challenges. The complex nature of these materials, often incorporating multiple components and responsive elements, can make traditional recycling methods ineffective. Developing sustainable disposal or recycling strategies for these polymers is crucial to mitigate their long-term environmental impact.
Research into more environmentally friendly alternatives and production methods for phenolphthalein-based smart polymers is ongoing. This includes exploring bio-based precursors, green synthesis techniques, and designing for easier recyclability or biodegradability. Such advancements could significantly improve the environmental profile of these materials, aligning their innovative potential with sustainability goals.
As the field of smart polymer design continues to evolve, balancing the technological benefits with environmental considerations remains a key challenge. Comprehensive lifecycle assessments and long-term environmental studies are essential to fully understand and mitigate the ecological impact of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers, ensuring their responsible development and application in various industries.
One of the primary environmental advantages of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers is their potential to reduce waste and improve resource efficiency. These materials can be designed to change properties in response to specific environmental conditions, allowing for more targeted and efficient use in applications such as drug delivery or environmental sensing. This precision can lead to reduced material consumption and decreased environmental contamination.
However, the production and disposal of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers present environmental challenges. The synthesis of these materials often involves complex chemical processes that may require significant energy inputs and potentially harmful solvents. Additionally, the long-term environmental fate of these polymers is not yet fully understood, raising questions about their biodegradability and potential accumulation in ecosystems.
The pH-sensitive nature of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers offers opportunities for environmental monitoring and remediation. These materials can be used to detect and respond to changes in pH levels in water bodies, potentially aiding in the early detection of pollution or acidification. However, the release of phenolphthalein or its derivatives into the environment during the polymer's lifecycle could have unintended consequences on aquatic ecosystems.
Recycling and end-of-life management of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers pose unique challenges. The complex nature of these materials, often incorporating multiple components and responsive elements, can make traditional recycling methods ineffective. Developing sustainable disposal or recycling strategies for these polymers is crucial to mitigate their long-term environmental impact.
Research into more environmentally friendly alternatives and production methods for phenolphthalein-based smart polymers is ongoing. This includes exploring bio-based precursors, green synthesis techniques, and designing for easier recyclability or biodegradability. Such advancements could significantly improve the environmental profile of these materials, aligning their innovative potential with sustainability goals.
As the field of smart polymer design continues to evolve, balancing the technological benefits with environmental considerations remains a key challenge. Comprehensive lifecycle assessments and long-term environmental studies are essential to fully understand and mitigate the ecological impact of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers, ensuring their responsible development and application in various industries.
Scalability and Manufacturing Considerations
The scalability and manufacturing considerations for smart polymers incorporating phenolphthalein are crucial aspects that determine the feasibility of large-scale production and commercial viability. One of the primary challenges in scaling up production is maintaining consistent quality and performance across batches. The synthesis of phenolphthalein-based smart polymers often involves complex chemical reactions that are sensitive to environmental conditions, such as temperature, pH, and pressure. Ensuring these conditions remain uniform throughout larger reaction vessels is essential for producing polymers with consistent properties.
Another important consideration is the selection of appropriate manufacturing processes that can accommodate the unique characteristics of phenolphthalein-containing polymers. Traditional polymer processing techniques may need to be modified or entirely new methods developed to handle the responsive nature of these materials. For instance, the pH-sensitive properties of phenolphthalein may require specialized equipment or handling procedures to prevent premature activation or degradation during manufacturing.
Cost-effectiveness is a critical factor in scaling up production. While phenolphthalein itself is relatively inexpensive, the additional processing steps and specialized equipment required for smart polymer synthesis can significantly increase production costs. Manufacturers must carefully evaluate the trade-offs between material performance and production expenses to ensure the final product remains economically viable in the target market.
Environmental and safety considerations also play a significant role in the manufacturing process. Phenolphthalein and its derivatives may pose health risks if not handled properly, necessitating stringent safety protocols and potentially specialized waste management procedures. Additionally, the increasing focus on sustainability in manufacturing processes may require the development of more environmentally friendly synthesis routes or the implementation of recycling strategies for these smart polymers.
The choice of raw materials and their sourcing can impact both scalability and sustainability. Ensuring a stable supply chain for high-quality phenolphthalein and other polymer components is crucial for consistent production. Furthermore, exploring bio-based alternatives or renewable sources for polymer precursors could enhance the environmental profile of the manufacturing process and align with growing market demands for sustainable materials.
Lastly, quality control and characterization methods must be adapted for large-scale production. Developing rapid, reliable testing procedures that can be integrated into the manufacturing line is essential for maintaining product consistency and meeting regulatory requirements. This may involve the use of advanced analytical techniques or the development of new quality assurance protocols specific to phenolphthalein-based smart polymers.
Another important consideration is the selection of appropriate manufacturing processes that can accommodate the unique characteristics of phenolphthalein-containing polymers. Traditional polymer processing techniques may need to be modified or entirely new methods developed to handle the responsive nature of these materials. For instance, the pH-sensitive properties of phenolphthalein may require specialized equipment or handling procedures to prevent premature activation or degradation during manufacturing.
Cost-effectiveness is a critical factor in scaling up production. While phenolphthalein itself is relatively inexpensive, the additional processing steps and specialized equipment required for smart polymer synthesis can significantly increase production costs. Manufacturers must carefully evaluate the trade-offs between material performance and production expenses to ensure the final product remains economically viable in the target market.
Environmental and safety considerations also play a significant role in the manufacturing process. Phenolphthalein and its derivatives may pose health risks if not handled properly, necessitating stringent safety protocols and potentially specialized waste management procedures. Additionally, the increasing focus on sustainability in manufacturing processes may require the development of more environmentally friendly synthesis routes or the implementation of recycling strategies for these smart polymers.
The choice of raw materials and their sourcing can impact both scalability and sustainability. Ensuring a stable supply chain for high-quality phenolphthalein and other polymer components is crucial for consistent production. Furthermore, exploring bio-based alternatives or renewable sources for polymer precursors could enhance the environmental profile of the manufacturing process and align with growing market demands for sustainable materials.
Lastly, quality control and characterization methods must be adapted for large-scale production. Developing rapid, reliable testing procedures that can be integrated into the manufacturing line is essential for maintaining product consistency and meeting regulatory requirements. This may involve the use of advanced analytical techniques or the development of new quality assurance protocols specific to phenolphthalein-based smart polymers.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!