How Steering Wheel Smart Systems Improve Navigation?
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Smart Steering Evolution
The evolution of smart steering systems has been a significant driver in improving navigation and overall driving experience. This technological progression can be traced back to the early 2000s when electronic power steering (EPS) began replacing traditional hydraulic systems. EPS marked the first step towards integrating intelligent features into steering mechanisms, offering variable assistance based on vehicle speed and driving conditions.
As automotive technology advanced, the integration of sensors and microprocessors into steering systems became more sophisticated. By the mid-2000s, adaptive steering systems emerged, capable of adjusting steering ratios based on vehicle speed and driver input. This innovation enhanced maneuverability at low speeds while providing stability at higher speeds, significantly improving overall vehicle control and safety.
The next major leap came with the introduction of steer-by-wire technology in the late 2000s. This system eliminated the physical connection between the steering wheel and the wheels, replacing it with electronic controls and actuators. While initially met with skepticism due to safety concerns, steer-by-wire systems have since proven their reliability and opened up new possibilities for steering wheel design and functionality.
In the 2010s, the focus shifted towards integrating steering systems with other vehicle technologies. Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) began to utilize steering inputs as part of their functionality. Features like lane keeping assist and automated parking relied on smart steering systems to execute precise maneuvers, marking a significant step towards semi-autonomous driving capabilities.
The most recent developments in smart steering evolution have centered on enhancing the human-machine interface. Haptic feedback systems have been incorporated into steering wheels, providing tactile alerts to drivers for various navigation and safety functions. Additionally, the integration of touchscreens and gesture controls directly into the steering wheel has allowed for more intuitive interaction with navigation systems and other vehicle functions without taking hands off the wheel.
Looking towards the future, the evolution of smart steering systems is closely tied to the development of fully autonomous vehicles. While traditional steering wheels may eventually become obsolete in such vehicles, the interim period is likely to see further advancements in adaptive steering technologies. These systems will need to seamlessly transition between human and computer control, ensuring safety and comfort in all driving scenarios.
The ongoing evolution of smart steering systems continues to push the boundaries of what's possible in vehicle navigation and control. From its humble beginnings with EPS to the current state of integrated, multi-functional systems, smart steering has become a crucial component in the broader ecosystem of intelligent vehicle technologies, paving the way for safer, more efficient, and more enjoyable driving experiences.
As automotive technology advanced, the integration of sensors and microprocessors into steering systems became more sophisticated. By the mid-2000s, adaptive steering systems emerged, capable of adjusting steering ratios based on vehicle speed and driver input. This innovation enhanced maneuverability at low speeds while providing stability at higher speeds, significantly improving overall vehicle control and safety.
The next major leap came with the introduction of steer-by-wire technology in the late 2000s. This system eliminated the physical connection between the steering wheel and the wheels, replacing it with electronic controls and actuators. While initially met with skepticism due to safety concerns, steer-by-wire systems have since proven their reliability and opened up new possibilities for steering wheel design and functionality.
In the 2010s, the focus shifted towards integrating steering systems with other vehicle technologies. Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) began to utilize steering inputs as part of their functionality. Features like lane keeping assist and automated parking relied on smart steering systems to execute precise maneuvers, marking a significant step towards semi-autonomous driving capabilities.
The most recent developments in smart steering evolution have centered on enhancing the human-machine interface. Haptic feedback systems have been incorporated into steering wheels, providing tactile alerts to drivers for various navigation and safety functions. Additionally, the integration of touchscreens and gesture controls directly into the steering wheel has allowed for more intuitive interaction with navigation systems and other vehicle functions without taking hands off the wheel.
Looking towards the future, the evolution of smart steering systems is closely tied to the development of fully autonomous vehicles. While traditional steering wheels may eventually become obsolete in such vehicles, the interim period is likely to see further advancements in adaptive steering technologies. These systems will need to seamlessly transition between human and computer control, ensuring safety and comfort in all driving scenarios.
The ongoing evolution of smart steering systems continues to push the boundaries of what's possible in vehicle navigation and control. From its humble beginnings with EPS to the current state of integrated, multi-functional systems, smart steering has become a crucial component in the broader ecosystem of intelligent vehicle technologies, paving the way for safer, more efficient, and more enjoyable driving experiences.
Navigation Market Trends
The navigation market has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer preferences. The global navigation market size was valued at approximately $150 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $300 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15%. This growth is primarily attributed to the increasing adoption of smart navigation systems across various industries, including automotive, marine, and aviation.
In the automotive sector, the integration of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies has been a major catalyst for the navigation market's expansion. The demand for real-time traffic information, route optimization, and location-based services has surged, leading to the development of more sophisticated navigation solutions. Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles has created new opportunities for navigation systems that can provide accurate range estimates and locate charging stations.
The proliferation of smartphones and mobile devices has also played a crucial role in shaping navigation market trends. Mobile navigation apps have become increasingly popular, offering users convenient and cost-effective alternatives to traditional in-car navigation systems. This shift has prompted established navigation companies to adapt their strategies and develop cross-platform solutions that seamlessly integrate with mobile devices.
Another significant trend in the navigation market is the growing emphasis on personalization and user experience. Navigation systems are now incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to provide more accurate predictions, personalized recommendations, and adaptive routing based on individual preferences and historical data. This trend is expected to continue as consumers demand more intuitive and tailored navigation experiences.
The emergence of smart cities and the Internet of Things (IoT) has also influenced navigation market trends. Cities are investing in connected infrastructure and intelligent transportation systems, creating new opportunities for navigation providers to offer enhanced services such as real-time parking availability, public transportation integration, and multi-modal routing options.
In terms of regional trends, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the navigation market, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing vehicle sales, and government initiatives to improve transportation infrastructure. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on innovation and the adoption of advanced navigation technologies.
Looking ahead, the navigation market is poised for further evolution with the advent of 5G technology, which will enable faster data transmission and more precise location services. Additionally, the integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies in navigation systems is expected to revolutionize the way users interact with navigation information, providing more immersive and intuitive guidance experiences.
In the automotive sector, the integration of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies has been a major catalyst for the navigation market's expansion. The demand for real-time traffic information, route optimization, and location-based services has surged, leading to the development of more sophisticated navigation solutions. Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles has created new opportunities for navigation systems that can provide accurate range estimates and locate charging stations.
The proliferation of smartphones and mobile devices has also played a crucial role in shaping navigation market trends. Mobile navigation apps have become increasingly popular, offering users convenient and cost-effective alternatives to traditional in-car navigation systems. This shift has prompted established navigation companies to adapt their strategies and develop cross-platform solutions that seamlessly integrate with mobile devices.
Another significant trend in the navigation market is the growing emphasis on personalization and user experience. Navigation systems are now incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to provide more accurate predictions, personalized recommendations, and adaptive routing based on individual preferences and historical data. This trend is expected to continue as consumers demand more intuitive and tailored navigation experiences.
The emergence of smart cities and the Internet of Things (IoT) has also influenced navigation market trends. Cities are investing in connected infrastructure and intelligent transportation systems, creating new opportunities for navigation providers to offer enhanced services such as real-time parking availability, public transportation integration, and multi-modal routing options.
In terms of regional trends, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the navigation market, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing vehicle sales, and government initiatives to improve transportation infrastructure. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on innovation and the adoption of advanced navigation technologies.
Looking ahead, the navigation market is poised for further evolution with the advent of 5G technology, which will enable faster data transmission and more precise location services. Additionally, the integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies in navigation systems is expected to revolutionize the way users interact with navigation information, providing more immersive and intuitive guidance experiences.
Steering Tech Challenges
The development of steering wheel smart systems for improved navigation faces several significant challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the integration of complex technologies within the limited space of a steering wheel. Engineers must balance the need for advanced features with ergonomic considerations and driver comfort, ensuring that the added functionality does not compromise the wheel's primary purpose of vehicle control.
Data processing and real-time responsiveness present another hurdle. Smart steering systems require rapid analysis of vast amounts of information from various sensors and external sources. Achieving low-latency performance while maintaining accuracy in navigation suggestions and alerts is crucial for driver safety and system reliability.
The human-machine interface (HMI) design poses a considerable challenge. Creating an intuitive and non-distracting interface that allows drivers to access navigation information without taking their hands off the wheel or eyes off the road requires innovative approaches to user experience design. This includes developing haptic feedback systems, voice control mechanisms, and easily readable displays that do not obstruct the driver's view.
Power management and energy efficiency are also significant concerns. Integrating smart systems into the steering wheel increases power consumption, which can impact the vehicle's overall energy efficiency, particularly in electric vehicles where power conservation is critical.
Durability and reliability under various environmental conditions present another set of challenges. Smart steering systems must withstand temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and potential impacts while maintaining consistent performance over the vehicle's lifetime.
Cybersecurity is an increasingly important concern as steering wheel smart systems become more connected. Protecting these systems from potential hacking attempts or malicious interference is crucial to ensure driver safety and maintain consumer trust.
Regulatory compliance and standardization pose additional challenges. As smart steering technologies evolve, manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of safety regulations and industry standards that may vary across different regions and markets.
Cost-effectiveness is another significant hurdle. Developing and implementing advanced steering wheel smart systems while keeping vehicle prices competitive requires careful balancing of feature sets and production costs.
Lastly, ensuring compatibility and integration with various vehicle models and existing navigation systems presents a challenge. Manufacturers must develop solutions that can be easily adapted to different vehicle architectures and software platforms, allowing for seamless integration and updates across diverse product lines.
Data processing and real-time responsiveness present another hurdle. Smart steering systems require rapid analysis of vast amounts of information from various sensors and external sources. Achieving low-latency performance while maintaining accuracy in navigation suggestions and alerts is crucial for driver safety and system reliability.
The human-machine interface (HMI) design poses a considerable challenge. Creating an intuitive and non-distracting interface that allows drivers to access navigation information without taking their hands off the wheel or eyes off the road requires innovative approaches to user experience design. This includes developing haptic feedback systems, voice control mechanisms, and easily readable displays that do not obstruct the driver's view.
Power management and energy efficiency are also significant concerns. Integrating smart systems into the steering wheel increases power consumption, which can impact the vehicle's overall energy efficiency, particularly in electric vehicles where power conservation is critical.
Durability and reliability under various environmental conditions present another set of challenges. Smart steering systems must withstand temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and potential impacts while maintaining consistent performance over the vehicle's lifetime.
Cybersecurity is an increasingly important concern as steering wheel smart systems become more connected. Protecting these systems from potential hacking attempts or malicious interference is crucial to ensure driver safety and maintain consumer trust.
Regulatory compliance and standardization pose additional challenges. As smart steering technologies evolve, manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of safety regulations and industry standards that may vary across different regions and markets.
Cost-effectiveness is another significant hurdle. Developing and implementing advanced steering wheel smart systems while keeping vehicle prices competitive requires careful balancing of feature sets and production costs.
Lastly, ensuring compatibility and integration with various vehicle models and existing navigation systems presents a challenge. Manufacturers must develop solutions that can be easily adapted to different vehicle architectures and software platforms, allowing for seamless integration and updates across diverse product lines.
Current Smart Solutions
01 Integration of navigation systems in steering wheels
Smart steering wheels are being developed with integrated navigation systems, allowing drivers to access and control navigation features directly from the wheel. This integration enhances driver convenience and safety by minimizing distractions and keeping hands on the wheel while navigating.- Integration of navigation systems in steering wheels: Smart steering wheels are being developed with integrated navigation systems, allowing drivers to access and control navigation features directly from the wheel. This integration enhances driver convenience and safety by minimizing distractions and keeping hands on the wheel while navigating.
- Gesture and touch-based controls for navigation: Advanced steering wheels incorporate gesture recognition and touch-sensitive surfaces to control navigation functions. These features allow drivers to interact with the navigation system through intuitive gestures or touch inputs on the steering wheel, reducing the need for physical buttons or touchscreens elsewhere in the vehicle.
- Heads-up display integration with steering wheel controls: Steering wheel smart systems are being designed to work in conjunction with heads-up displays, projecting navigation information onto the windshield. The steering wheel controls allow drivers to interact with the projected navigation data, providing a seamless and less distracting navigation experience.
- AI-powered navigation assistance through steering wheel interface: Artificial intelligence is being incorporated into steering wheel smart systems to provide intelligent navigation assistance. These systems can learn driver preferences, predict destinations, and offer personalized route suggestions, all accessible through the steering wheel interface.
- Integration of voice commands for navigation control: Voice recognition technology is being integrated into steering wheel systems, allowing drivers to control navigation features through voice commands. This hands-free approach enables drivers to input destinations, change routes, or access navigation information without taking their hands off the wheel or eyes off the road.
02 Gesture and touch-based controls for navigation
Advanced steering wheels incorporate gesture recognition and touch-sensitive surfaces to control navigation functions. These features allow drivers to interact with the navigation system through intuitive gestures or touch inputs on the steering wheel, reducing the need for physical buttons or touchscreens elsewhere in the vehicle.Expand Specific Solutions03 Heads-up display integration with steering wheel controls
Steering wheel smart systems are being designed to work in conjunction with heads-up displays, projecting navigation information onto the windshield. The steering wheel controls allow drivers to interact with the projected navigation data, providing a seamless and less distracting navigation experience.Expand Specific Solutions04 AI-powered navigation assistance through steering wheel interface
Artificial intelligence is being incorporated into steering wheel smart systems to provide intelligent navigation assistance. These systems can learn driver preferences, predict destinations, and offer personalized route suggestions, all accessible through the steering wheel interface.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of voice commands for navigation control
Voice recognition technology is being integrated into steering wheel systems, allowing drivers to control navigation features through voice commands. This hands-free approach enables drivers to input destinations, change routes, or access navigation information without taking their hands off the wheel or eyes off the road.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The steering wheel smart systems market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for advanced navigation and driver assistance features. Major players like Mercedes-Benz, BMW, and Continental are leading innovation in this space, leveraging their automotive expertise to develop sophisticated solutions. The market size is expanding rapidly as more vehicles incorporate smart steering technologies. While established automakers have a head start, tech companies like Xiaomi are also entering the field, potentially disrupting traditional dynamics. The technology is maturing quickly, with companies like Bosch and Valeo pushing boundaries in sensor integration and user interface design. However, there's still room for significant advancements in areas such as haptic feedback and AI-driven personalization.
Mercedes-Benz Group AG
Technical Solution: Mercedes-Benz has developed a sophisticated steering wheel smart system as part of its MBUX (Mercedes-Benz User Experience) platform. The system features capacitive touch controls on the steering wheel spokes that respond to swipe gestures, allowing drivers to control navigation functions without taking their hands off the wheel. It incorporates a high-resolution display in the instrument cluster that shows 3D map views and augmented reality navigation overlays[5]. The system also utilizes AI to predict frequent destinations and suggest optimal routes based on traffic patterns and driver preferences[6].
Strengths: Seamless integration with luxury vehicle features, advanced visualization capabilities. Weaknesses: Steep learning curve for new users, potentially high replacement costs.
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG
Technical Solution: BMW has developed a steering wheel smart system that enhances navigation through its iDrive operating system. The system features a multifunctional steering wheel with touch-sensitive buttons and scroll wheels that allow drivers to control navigation functions intuitively. It incorporates BMW's Intelligent Personal Assistant, which uses natural language processing for voice-controlled navigation commands[9]. The system also integrates with BMW's Live Cockpit Professional, providing 3D map views and real-time traffic information on both the central display and the instrument cluster[10]. Additionally, it offers augmented reality navigation features that overlay directional arrows and other guidance information onto live video feeds of the road ahead.
Strengths: Intuitive controls, advanced voice command capabilities, integration with augmented reality features. Weaknesses: Potential for driver distraction, reliance on complex electronic systems.
Steering Innovations
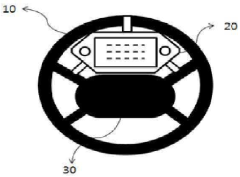
Car steering wheel of the integrated smart navigation
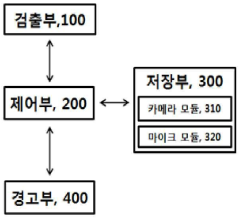
PatentActiveKR1020150137264A
Innovation
- A smart navigation device is integrated into the steering wheel, positioned between its center and upper surface, with a spring mechanism and airbag detection, allowing safe detachment during emergencies.
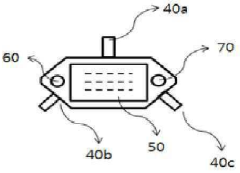
Steering wheel with improved interface to a finger navigation module
PatentActiveEP2946271A1
Innovation
- A steering wheel with a 3-wire SPI data bus for communication between the optical finger navigation module and the steering wheel electronics, eliminating the need for a separate interrupt line and utilizing cyclic polling, along with temperature compensation controlled by the steering wheel electronics, to achieve reduced installation space and improved noise immunity.
Safety Regulations
Safety regulations play a crucial role in the development and implementation of steering wheel smart systems for improved navigation. As these advanced technologies become more prevalent in modern vehicles, regulatory bodies worldwide are adapting and creating new guidelines to ensure the safety of drivers, passengers, and other road users.
One of the primary concerns addressed by safety regulations is the potential for driver distraction. Steering wheel smart systems often incorporate touch-sensitive controls, voice commands, and visual displays, which can divert a driver's attention from the road. To mitigate this risk, regulations typically mandate that these systems be designed with minimal cognitive load and physical interaction requirements. For instance, many jurisdictions limit the amount of time a driver can take their eyes off the road to interact with in-vehicle systems, often setting this threshold at two seconds or less.
Another key aspect of safety regulations for steering wheel smart systems is the integration of fail-safe mechanisms. These regulations require manufacturers to implement redundant systems and backup controls to ensure that critical vehicle functions remain operational even if the smart system experiences a malfunction. This includes maintaining basic steering and navigation capabilities in the event of a system failure.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is also a significant consideration in safety regulations. Steering wheel smart systems rely heavily on electronic components and wireless communication, which can potentially interfere with other vehicle systems or external devices. Regulatory standards mandate rigorous EMC testing to prevent such interference and ensure the reliable operation of all vehicle systems.
Data privacy and cybersecurity have emerged as critical concerns in recent years. Safety regulations now often include provisions for protecting sensitive user data collected by steering wheel smart systems, as well as safeguarding the vehicle's electronic systems against potential cyber attacks. These regulations may require manufacturers to implement robust encryption methods, secure over-the-air update processes, and regular security audits.
As autonomous driving technologies advance, safety regulations are evolving to address the transition between manual and automated control. Steering wheel smart systems that incorporate semi-autonomous features must comply with regulations governing the handover process between the vehicle and the driver. This includes clear communication of the system's status and capabilities, as well as ensuring that the driver remains sufficiently engaged to take control when necessary.
Regulatory bodies are also focusing on the standardization of user interfaces and control layouts across different vehicle makes and models. This aims to reduce confusion and potential errors when drivers switch between vehicles equipped with steering wheel smart systems. Standardization efforts extend to symbols, colors, and tactile feedback used in these systems to ensure consistent interpretation and operation.
One of the primary concerns addressed by safety regulations is the potential for driver distraction. Steering wheel smart systems often incorporate touch-sensitive controls, voice commands, and visual displays, which can divert a driver's attention from the road. To mitigate this risk, regulations typically mandate that these systems be designed with minimal cognitive load and physical interaction requirements. For instance, many jurisdictions limit the amount of time a driver can take their eyes off the road to interact with in-vehicle systems, often setting this threshold at two seconds or less.
Another key aspect of safety regulations for steering wheel smart systems is the integration of fail-safe mechanisms. These regulations require manufacturers to implement redundant systems and backup controls to ensure that critical vehicle functions remain operational even if the smart system experiences a malfunction. This includes maintaining basic steering and navigation capabilities in the event of a system failure.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is also a significant consideration in safety regulations. Steering wheel smart systems rely heavily on electronic components and wireless communication, which can potentially interfere with other vehicle systems or external devices. Regulatory standards mandate rigorous EMC testing to prevent such interference and ensure the reliable operation of all vehicle systems.
Data privacy and cybersecurity have emerged as critical concerns in recent years. Safety regulations now often include provisions for protecting sensitive user data collected by steering wheel smart systems, as well as safeguarding the vehicle's electronic systems against potential cyber attacks. These regulations may require manufacturers to implement robust encryption methods, secure over-the-air update processes, and regular security audits.
As autonomous driving technologies advance, safety regulations are evolving to address the transition between manual and automated control. Steering wheel smart systems that incorporate semi-autonomous features must comply with regulations governing the handover process between the vehicle and the driver. This includes clear communication of the system's status and capabilities, as well as ensuring that the driver remains sufficiently engaged to take control when necessary.
Regulatory bodies are also focusing on the standardization of user interfaces and control layouts across different vehicle makes and models. This aims to reduce confusion and potential errors when drivers switch between vehicles equipped with steering wheel smart systems. Standardization efforts extend to symbols, colors, and tactile feedback used in these systems to ensure consistent interpretation and operation.
User Experience Design
User experience design plays a crucial role in the development of steering wheel smart systems for improved navigation. These systems aim to enhance the driver's interaction with navigation features while maintaining focus on the road. The design process begins with a thorough understanding of user needs and behaviors, incorporating ergonomic principles to ensure comfortable and intuitive operation.
One key aspect of user experience design for steering wheel smart systems is the integration of tactile feedback. This feature allows drivers to receive navigation cues through subtle vibrations or haptic sensations on the steering wheel, reducing the need for visual distractions. Designers carefully calibrate these tactile signals to convey different types of information, such as upcoming turns or lane changes, without overwhelming the driver.
Visual elements are also carefully considered in the user experience design. Head-up displays (HUDs) projected onto the windshield or small screens integrated into the steering wheel itself provide essential navigation information within the driver's line of sight. These displays are designed to be non-intrusive, with clear, high-contrast graphics that are easily readable in various lighting conditions.
Voice control is another critical component of the user experience design for steering wheel smart systems. Natural language processing algorithms are implemented to allow drivers to input destinations, request route changes, or access other navigation features using voice commands. The system's responses are designed to be concise and clear, minimizing cognitive load on the driver.
Customization options are incorporated into the user experience design to accommodate different driver preferences. This may include adjustable display settings, personalized voice assistant interactions, and the ability to prioritize certain types of navigation information based on individual needs.
The design process also considers the integration of steering wheel smart systems with other vehicle systems and external devices. Seamless connectivity with smartphones and in-car infotainment systems ensures a cohesive navigation experience across different interfaces. This integration extends to real-time traffic updates, points of interest, and other location-based services.
User testing and iterative design are fundamental to refining the user experience of steering wheel smart systems. Designers employ techniques such as eye-tracking studies, simulated driving scenarios, and real-world trials to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of different interface elements. This data-driven approach helps identify potential usability issues and informs continuous improvements to the system's design.
One key aspect of user experience design for steering wheel smart systems is the integration of tactile feedback. This feature allows drivers to receive navigation cues through subtle vibrations or haptic sensations on the steering wheel, reducing the need for visual distractions. Designers carefully calibrate these tactile signals to convey different types of information, such as upcoming turns or lane changes, without overwhelming the driver.
Visual elements are also carefully considered in the user experience design. Head-up displays (HUDs) projected onto the windshield or small screens integrated into the steering wheel itself provide essential navigation information within the driver's line of sight. These displays are designed to be non-intrusive, with clear, high-contrast graphics that are easily readable in various lighting conditions.
Voice control is another critical component of the user experience design for steering wheel smart systems. Natural language processing algorithms are implemented to allow drivers to input destinations, request route changes, or access other navigation features using voice commands. The system's responses are designed to be concise and clear, minimizing cognitive load on the driver.
Customization options are incorporated into the user experience design to accommodate different driver preferences. This may include adjustable display settings, personalized voice assistant interactions, and the ability to prioritize certain types of navigation information based on individual needs.
The design process also considers the integration of steering wheel smart systems with other vehicle systems and external devices. Seamless connectivity with smartphones and in-car infotainment systems ensures a cohesive navigation experience across different interfaces. This integration extends to real-time traffic updates, points of interest, and other location-based services.
User testing and iterative design are fundamental to refining the user experience of steering wheel smart systems. Designers employ techniques such as eye-tracking studies, simulated driving scenarios, and real-world trials to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of different interface elements. This data-driven approach helps identify potential usability issues and informs continuous improvements to the system's design.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!