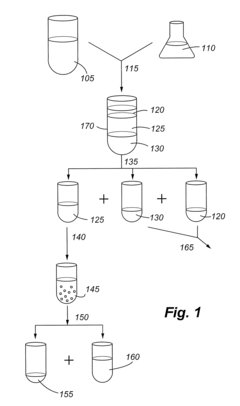
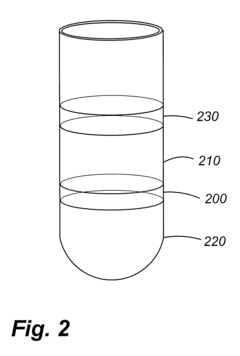
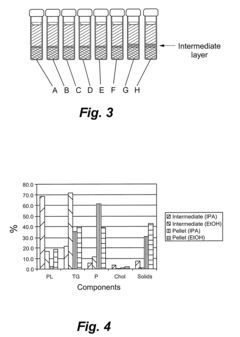
How to Optimize Phospholipid Extraction Techniques?
JUL 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Phospholipid Extraction Background and Objectives
Phospholipid extraction techniques have been a crucial area of research in biochemistry and analytical chemistry for decades. The journey of these techniques began in the early 20th century with simple solvent-based extractions and has evolved significantly over time. The primary goal of phospholipid extraction is to efficiently isolate and purify these essential biomolecules from various biological matrices, including cell membranes, tissues, and complex biological fluids.
The development of phospholipid extraction methods has been driven by the increasing recognition of their importance in cellular function, signaling, and disease processes. As our understanding of lipid biology has grown, so too has the need for more sophisticated and precise extraction techniques. The evolution of these methods has been marked by a continuous effort to improve yield, purity, and reproducibility while minimizing sample degradation and artifact formation.
Current research in phospholipid extraction is focused on addressing several key challenges. These include the need for methods that can effectively isolate specific phospholipid classes, techniques that are compatible with downstream analytical processes such as mass spectrometry, and approaches that can handle complex biological samples with minimal interference from other cellular components. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on developing extraction methods that are more environmentally friendly, less time-consuming, and amenable to high-throughput analysis.
The optimization of phospholipid extraction techniques is driven by several objectives. Firstly, there is a need to improve the overall efficiency of extraction, ensuring that a higher percentage of phospholipids are recovered from the sample. Secondly, researchers aim to enhance the selectivity of extraction methods, allowing for the isolation of specific phospholipid classes or molecular species. Thirdly, there is a push towards developing methods that preserve the native state of phospholipids, avoiding oxidation or structural changes during the extraction process.
Another critical objective is the development of extraction techniques that are compatible with a wide range of sample types and volumes. This includes methods suitable for both large-scale preparative extractions and small-scale analytical procedures. Furthermore, there is a growing interest in techniques that can be easily integrated into automated workflows, supporting high-throughput analysis in both research and clinical settings.
As we look to the future, the field of phospholipid extraction is likely to see further advancements driven by emerging technologies and interdisciplinary approaches. The integration of microfluidic devices, novel materials for solid-phase extraction, and the application of artificial intelligence in method optimization are just a few areas that hold promise for revolutionizing phospholipid extraction techniques.
The development of phospholipid extraction methods has been driven by the increasing recognition of their importance in cellular function, signaling, and disease processes. As our understanding of lipid biology has grown, so too has the need for more sophisticated and precise extraction techniques. The evolution of these methods has been marked by a continuous effort to improve yield, purity, and reproducibility while minimizing sample degradation and artifact formation.
Current research in phospholipid extraction is focused on addressing several key challenges. These include the need for methods that can effectively isolate specific phospholipid classes, techniques that are compatible with downstream analytical processes such as mass spectrometry, and approaches that can handle complex biological samples with minimal interference from other cellular components. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on developing extraction methods that are more environmentally friendly, less time-consuming, and amenable to high-throughput analysis.
The optimization of phospholipid extraction techniques is driven by several objectives. Firstly, there is a need to improve the overall efficiency of extraction, ensuring that a higher percentage of phospholipids are recovered from the sample. Secondly, researchers aim to enhance the selectivity of extraction methods, allowing for the isolation of specific phospholipid classes or molecular species. Thirdly, there is a push towards developing methods that preserve the native state of phospholipids, avoiding oxidation or structural changes during the extraction process.
Another critical objective is the development of extraction techniques that are compatible with a wide range of sample types and volumes. This includes methods suitable for both large-scale preparative extractions and small-scale analytical procedures. Furthermore, there is a growing interest in techniques that can be easily integrated into automated workflows, supporting high-throughput analysis in both research and clinical settings.
As we look to the future, the field of phospholipid extraction is likely to see further advancements driven by emerging technologies and interdisciplinary approaches. The integration of microfluidic devices, novel materials for solid-phase extraction, and the application of artificial intelligence in method optimization are just a few areas that hold promise for revolutionizing phospholipid extraction techniques.
Market Analysis for Phospholipid Products
The global phospholipid market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries, particularly in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic sectors. Phospholipids, essential components of cell membranes, have gained significant attention due to their versatile applications and health benefits. The market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6% over the next five years.
In the food and beverage industry, phospholipids are widely used as emulsifiers, stabilizers, and nutritional supplements. The growing consumer awareness of health and wellness has led to increased demand for functional foods and nutraceuticals, where phospholipids play a crucial role. This trend is particularly evident in developed markets such as North America and Europe, where consumers are willing to pay premium prices for products with added health benefits.
The pharmaceutical sector represents another significant market for phospholipids, with applications in drug delivery systems, liposomal formulations, and parenteral nutrition. The rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing elderly population are driving the demand for advanced drug delivery technologies, further boosting the phospholipid market in this sector.
Cosmetics and personal care products have also emerged as a promising application area for phospholipids. Their moisturizing and skin-repairing properties make them valuable ingredients in anti-aging creams, hair care products, and other cosmetic formulations. The natural and organic cosmetics trend has further accelerated the adoption of phospholipids as plant-derived alternatives to synthetic ingredients.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the phospholipid market, owing to their well-established food and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and growing health awareness among consumers.
The market landscape is characterized by the presence of several key players, including major chemical and ingredient companies. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve extraction techniques and develop novel phospholipid formulations. The optimization of phospholipid extraction techniques is crucial for meeting the growing market demand and ensuring cost-effective production.
As the demand for high-purity phospholipids continues to rise, there is a growing need for more efficient and sustainable extraction methods. This presents both challenges and opportunities for companies involved in phospholipid production and research. Innovations in extraction technologies could potentially lead to increased market share and competitive advantage in this rapidly evolving industry.
In the food and beverage industry, phospholipids are widely used as emulsifiers, stabilizers, and nutritional supplements. The growing consumer awareness of health and wellness has led to increased demand for functional foods and nutraceuticals, where phospholipids play a crucial role. This trend is particularly evident in developed markets such as North America and Europe, where consumers are willing to pay premium prices for products with added health benefits.
The pharmaceutical sector represents another significant market for phospholipids, with applications in drug delivery systems, liposomal formulations, and parenteral nutrition. The rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing elderly population are driving the demand for advanced drug delivery technologies, further boosting the phospholipid market in this sector.
Cosmetics and personal care products have also emerged as a promising application area for phospholipids. Their moisturizing and skin-repairing properties make them valuable ingredients in anti-aging creams, hair care products, and other cosmetic formulations. The natural and organic cosmetics trend has further accelerated the adoption of phospholipids as plant-derived alternatives to synthetic ingredients.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the phospholipid market, owing to their well-established food and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and growing health awareness among consumers.
The market landscape is characterized by the presence of several key players, including major chemical and ingredient companies. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve extraction techniques and develop novel phospholipid formulations. The optimization of phospholipid extraction techniques is crucial for meeting the growing market demand and ensuring cost-effective production.
As the demand for high-purity phospholipids continues to rise, there is a growing need for more efficient and sustainable extraction methods. This presents both challenges and opportunities for companies involved in phospholipid production and research. Innovations in extraction technologies could potentially lead to increased market share and competitive advantage in this rapidly evolving industry.
Current Extraction Techniques and Challenges
Phospholipid extraction techniques have evolved significantly over the years, with several methods currently in use. The most common techniques include Folch extraction, Bligh and Dyer method, and solid-phase extraction (SPE). Each of these methods has its strengths and limitations, presenting unique challenges in the quest for optimal phospholipid extraction.
The Folch method, developed in 1957, remains a gold standard for lipid extraction. It utilizes a mixture of chloroform and methanol to extract lipids from biological samples. While effective, this method is time-consuming and requires large volumes of organic solvents, raising environmental and safety concerns. Additionally, the use of chloroform can lead to oxidation of unsaturated lipids, potentially compromising the integrity of the extracted phospholipids.
The Bligh and Dyer method, a modification of the Folch technique, aims to reduce solvent usage and improve efficiency. It employs a ternary mixture of chloroform, methanol, and water. Although this method is widely used due to its simplicity and reduced solvent consumption, it may not be as effective for samples with high lipid content. Furthermore, the presence of water in the extraction mixture can lead to the formation of emulsions, complicating the separation process.
Solid-phase extraction has gained popularity as a more environmentally friendly alternative. This technique uses specialized sorbents to selectively retain phospholipids while allowing other compounds to pass through. SPE offers advantages in terms of reduced solvent usage and potential for automation. However, it can be less effective for complex biological matrices and may result in lower recovery rates for certain phospholipid classes.
A significant challenge across all extraction techniques is the potential for oxidation and degradation of phospholipids during the extraction process. This is particularly problematic for polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are highly susceptible to oxidation. Maintaining sample integrity throughout the extraction procedure remains a critical concern for researchers.
Another challenge lies in the selective extraction of specific phospholipid classes. Current methods often co-extract other lipid classes, necessitating additional separation steps. This not only increases processing time but can also lead to sample loss and reduced overall yield.
The scalability of extraction techniques presents another hurdle. While methods like Folch and Bligh and Dyer work well for small-scale laboratory extractions, they become impractical and cost-prohibitive at industrial scales. Developing extraction techniques that are both efficient and scalable remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
Furthermore, the increasing demand for green chemistry solutions has put pressure on researchers to develop more environmentally friendly extraction methods. This includes finding alternatives to chlorinated solvents and reducing overall solvent consumption. Balancing these environmental considerations with extraction efficiency and phospholipid yield is a complex challenge that continues to drive innovation in the field.
The Folch method, developed in 1957, remains a gold standard for lipid extraction. It utilizes a mixture of chloroform and methanol to extract lipids from biological samples. While effective, this method is time-consuming and requires large volumes of organic solvents, raising environmental and safety concerns. Additionally, the use of chloroform can lead to oxidation of unsaturated lipids, potentially compromising the integrity of the extracted phospholipids.
The Bligh and Dyer method, a modification of the Folch technique, aims to reduce solvent usage and improve efficiency. It employs a ternary mixture of chloroform, methanol, and water. Although this method is widely used due to its simplicity and reduced solvent consumption, it may not be as effective for samples with high lipid content. Furthermore, the presence of water in the extraction mixture can lead to the formation of emulsions, complicating the separation process.
Solid-phase extraction has gained popularity as a more environmentally friendly alternative. This technique uses specialized sorbents to selectively retain phospholipids while allowing other compounds to pass through. SPE offers advantages in terms of reduced solvent usage and potential for automation. However, it can be less effective for complex biological matrices and may result in lower recovery rates for certain phospholipid classes.
A significant challenge across all extraction techniques is the potential for oxidation and degradation of phospholipids during the extraction process. This is particularly problematic for polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are highly susceptible to oxidation. Maintaining sample integrity throughout the extraction procedure remains a critical concern for researchers.
Another challenge lies in the selective extraction of specific phospholipid classes. Current methods often co-extract other lipid classes, necessitating additional separation steps. This not only increases processing time but can also lead to sample loss and reduced overall yield.
The scalability of extraction techniques presents another hurdle. While methods like Folch and Bligh and Dyer work well for small-scale laboratory extractions, they become impractical and cost-prohibitive at industrial scales. Developing extraction techniques that are both efficient and scalable remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
Furthermore, the increasing demand for green chemistry solutions has put pressure on researchers to develop more environmentally friendly extraction methods. This includes finding alternatives to chlorinated solvents and reducing overall solvent consumption. Balancing these environmental considerations with extraction efficiency and phospholipid yield is a complex challenge that continues to drive innovation in the field.
Existing Optimization Strategies for Extraction
01 Solvent-based extraction methods
Various solvent-based techniques are employed for phospholipid extraction, including the use of organic solvents like chloroform, methanol, or hexane. These methods can be optimized by adjusting solvent ratios, extraction time, and temperature to improve yield and purity of extracted phospholipids.- Solvent-based extraction methods: Various solvents can be used for phospholipid extraction, including chloroform, methanol, and ethanol. The choice of solvent and optimization of extraction conditions such as temperature, time, and solvent-to-sample ratio can significantly improve the efficiency and yield of phospholipid extraction.
- Supercritical fluid extraction: Supercritical fluid extraction, particularly using carbon dioxide, is an environmentally friendly and efficient method for phospholipid extraction. This technique can be optimized by adjusting pressure, temperature, and co-solvent addition to enhance selectivity and yield.
- Microwave-assisted extraction: Microwave-assisted extraction can significantly reduce extraction time and solvent consumption while improving phospholipid yield. Optimization involves adjusting microwave power, irradiation time, and solvent selection to maximize extraction efficiency.
- Ultrasound-assisted extraction: Ultrasound-assisted extraction enhances phospholipid extraction by increasing mass transfer and cell disruption. Optimization parameters include ultrasound frequency, power, and duration, as well as solvent selection and sample-to-solvent ratio.
- Enzymatic extraction methods: Enzymatic extraction uses specific enzymes to break down cell walls and release phospholipids. This method can be optimized by selecting appropriate enzymes, adjusting pH, temperature, and reaction time, and combining with other extraction techniques for improved efficiency.
02 Supercritical fluid extraction
Supercritical fluid extraction, particularly using carbon dioxide, is an emerging technique for phospholipid extraction. This method offers advantages such as high selectivity, low environmental impact, and the ability to operate at lower temperatures, which can be beneficial for heat-sensitive phospholipids.Expand Specific Solutions03 Microwave-assisted extraction
Microwave-assisted extraction techniques can be used to optimize phospholipid extraction. This method can reduce extraction time and solvent consumption while improving yield. The process can be further optimized by adjusting microwave power, irradiation time, and solvent selection.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ultrasound-assisted extraction
Ultrasound-assisted extraction is another technique for optimizing phospholipid extraction. This method uses acoustic cavitation to enhance mass transfer and cell disruption, potentially increasing extraction efficiency. Parameters such as ultrasound frequency, power, and duration can be optimized for better results.Expand Specific Solutions05 Enzymatic extraction methods
Enzymatic extraction techniques can be used to selectively isolate phospholipids from complex matrices. This approach involves the use of specific enzymes to break down cell walls or hydrolyze unwanted components, allowing for more efficient phospholipid extraction. Optimization can involve selecting appropriate enzymes, adjusting pH, temperature, and reaction time.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Phospholipid Extraction Industry
The optimization of phospholipid extraction techniques is currently in a mature stage of development, with a growing market driven by increasing applications in pharmaceuticals, food, and biotechnology. The global market size for phospholipids is expected to reach several billion dollars by 2025, reflecting the importance of efficient extraction methods. Technologically, the field is characterized by ongoing refinements rather than revolutionary breakthroughs. Key players in this space include Agilent Technologies, known for analytical instruments, and DSM IP Assets BV, a leader in nutrition and materials science. Academic institutions like Cornell University and Zhejiang Gongshang University contribute significantly to research advancements, while companies such as NOF Corp. and Nippon Fine Chemical Co., Ltd. focus on specialized phospholipid products and applications.
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Agilent Technologies has developed advanced phospholipid extraction techniques using their Captiva EMR-Lipid technology. This method employs a unique sorbent that selectively removes phospholipids and other lipids from biological samples while allowing target analytes to pass through[1]. The process involves a simple pass-through extraction, which can be automated for high-throughput applications. Agilent's approach significantly reduces ion suppression in LC-MS/MS analysis, improving sensitivity and reproducibility. Their method has been optimized for various biological matrices, including plasma, serum, and whole blood, demonstrating up to 99% removal of phospholipids[2][3].
Strengths: High selectivity for phospholipid removal, improved LC-MS/MS sensitivity, automation-friendly. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment, potential loss of some target analytes.
Waters Technology Corp.
Technical Solution: Waters Technology has innovated phospholipid extraction optimization through their Oasis PRiME HLB technology. This solid-phase extraction (SPE) method utilizes a novel sorbent that combines hydrophilic-lipophilic balance properties with a unique pore structure. The technique allows for efficient removal of phospholipids and proteins from biological samples while maintaining high recovery of target analytes[4]. Waters' approach includes a simplified workflow that eliminates conditioning and equilibration steps, reducing processing time and solvent consumption. Their method has shown to remove >99% of phospholipids across various biological matrices, including plasma and whole blood, while providing excellent recovery for a wide range of analytes[5][6].
Strengths: Simplified workflow, reduced solvent use, broad applicability across analytes. Weaknesses: May require specific SPE cartridges, potential for higher initial costs.
Innovative Approaches in Phospholipid Extraction
Process for releasing and extracting phosphatides from a phosphatide-containing matrix
PatentInactiveUS20060068041A1
Innovation
- A process involving contacting a phosphatide-containing matrix with a solvent and a metal salt to release phosphatides, forming a phosphatide-enriched solvent portion and a depleted matrix portion, followed by separation and recovery of phosphatides, using C1-3 alcohols or their combination with water to produce a hexane-free product.
Method for the separation of phospholipids from phospholipid-containing materials
PatentInactiveUS20100145085A1
Innovation
- A process involving the use of a water-soluble aliphatic alcohol, such as propanol, at slightly elevated temperatures to form a true solution of phospholipids, which can then be cooled to precipitate out, allowing for easier separation through centrifugation or filtration, reducing the need for high solvent concentrations and drying steps.
Environmental Impact of Extraction Processes
The environmental impact of phospholipid extraction processes is a critical consideration in the optimization of these techniques. Traditional extraction methods often rely on large volumes of organic solvents, which can pose significant environmental risks. These solvents, such as chloroform and methanol, are known for their toxicity and potential to contaminate soil and water systems if not properly managed.
Recent advancements in extraction techniques have focused on reducing the environmental footprint of these processes. Supercritical fluid extraction, particularly using carbon dioxide, has emerged as a more environmentally friendly alternative. This method eliminates the need for toxic organic solvents and produces minimal waste. However, the high-pressure equipment required for this process can be energy-intensive, potentially offsetting some of its environmental benefits.
Green extraction techniques, such as those utilizing ionic liquids or deep eutectic solvents, have shown promise in reducing the environmental impact of phospholipid extraction. These solvents are generally less toxic and more biodegradable than traditional organic solvents. However, their production and disposal still require careful consideration to ensure overall environmental sustainability.
The use of enzyme-assisted extraction methods has also gained attention for its potential to reduce environmental impact. These techniques often operate under milder conditions and require fewer harsh chemicals. However, the production and disposal of enzymes must be factored into the overall environmental assessment.
Water consumption is another significant environmental concern in phospholipid extraction processes. Some techniques, particularly those involving multiple washing steps, can be water-intensive. Optimizing water use through recycling and implementing closed-loop systems can significantly reduce the environmental impact of these processes.
Energy consumption is a key factor in assessing the environmental impact of extraction techniques. Methods that require high temperatures or pressures, such as microwave-assisted extraction or pressurized liquid extraction, may have higher energy demands. Balancing the efficiency of extraction with energy consumption is crucial for developing environmentally sustainable processes.
Waste management is an essential aspect of minimizing the environmental impact of phospholipid extraction. Proper disposal or recycling of solvents, byproducts, and other waste materials is necessary to prevent environmental contamination. Implementing waste reduction strategies and exploring ways to valorize byproducts can further improve the environmental profile of these processes.
Recent advancements in extraction techniques have focused on reducing the environmental footprint of these processes. Supercritical fluid extraction, particularly using carbon dioxide, has emerged as a more environmentally friendly alternative. This method eliminates the need for toxic organic solvents and produces minimal waste. However, the high-pressure equipment required for this process can be energy-intensive, potentially offsetting some of its environmental benefits.
Green extraction techniques, such as those utilizing ionic liquids or deep eutectic solvents, have shown promise in reducing the environmental impact of phospholipid extraction. These solvents are generally less toxic and more biodegradable than traditional organic solvents. However, their production and disposal still require careful consideration to ensure overall environmental sustainability.
The use of enzyme-assisted extraction methods has also gained attention for its potential to reduce environmental impact. These techniques often operate under milder conditions and require fewer harsh chemicals. However, the production and disposal of enzymes must be factored into the overall environmental assessment.
Water consumption is another significant environmental concern in phospholipid extraction processes. Some techniques, particularly those involving multiple washing steps, can be water-intensive. Optimizing water use through recycling and implementing closed-loop systems can significantly reduce the environmental impact of these processes.
Energy consumption is a key factor in assessing the environmental impact of extraction techniques. Methods that require high temperatures or pressures, such as microwave-assisted extraction or pressurized liquid extraction, may have higher energy demands. Balancing the efficiency of extraction with energy consumption is crucial for developing environmentally sustainable processes.
Waste management is an essential aspect of minimizing the environmental impact of phospholipid extraction. Proper disposal or recycling of solvents, byproducts, and other waste materials is necessary to prevent environmental contamination. Implementing waste reduction strategies and exploring ways to valorize byproducts can further improve the environmental profile of these processes.
Quality Control in Phospholipid Extraction
Quality control is a critical aspect of phospholipid extraction techniques, ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of results. The process begins with the careful selection and preparation of samples, which should be representative of the source material and free from contaminants. Standardized protocols for sample handling, storage, and pre-treatment are essential to maintain consistency across different batches and experiments.
During the extraction process, several key parameters must be closely monitored and controlled. These include temperature, pH, solvent composition, and extraction time. Deviations in these factors can significantly impact the yield and purity of extracted phospholipids. Implementing automated systems for precise control of these parameters can greatly enhance the consistency of the extraction process.
The use of internal standards is a crucial quality control measure in phospholipid extraction. These standards, typically synthetic phospholipids with known concentrations, are added to the sample before extraction. By comparing the recovery of these standards to the extracted phospholipids, researchers can assess the efficiency and reproducibility of their extraction method.
Post-extraction, the purity and composition of the extracted phospholipids must be rigorously evaluated. Chromatographic techniques, such as thin-layer chromatography (TLC) or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), are commonly employed for this purpose. These methods allow for the separation and quantification of different phospholipid classes, providing a comprehensive profile of the extracted lipids.
Mass spectrometry has emerged as a powerful tool for quality control in phospholipid extraction. It offers high sensitivity and specificity, enabling the identification and quantification of individual phospholipid species. This technique is particularly valuable for detecting trace contaminants or unexpected lipid modifications that may occur during the extraction process.
Regular calibration and maintenance of analytical instruments are essential for ensuring accurate and reliable results. This includes periodic checks of instrument performance, validation of analytical methods, and participation in inter-laboratory comparison studies to verify the accuracy of measurements across different research facilities.
Documentation and traceability are fundamental aspects of quality control in phospholipid extraction. Detailed records of all procedures, reagents, and equipment used should be maintained. This includes lot numbers of chemicals, calibration records of instruments, and any deviations from standard protocols. Such comprehensive documentation facilitates troubleshooting and ensures the reproducibility of results.
During the extraction process, several key parameters must be closely monitored and controlled. These include temperature, pH, solvent composition, and extraction time. Deviations in these factors can significantly impact the yield and purity of extracted phospholipids. Implementing automated systems for precise control of these parameters can greatly enhance the consistency of the extraction process.
The use of internal standards is a crucial quality control measure in phospholipid extraction. These standards, typically synthetic phospholipids with known concentrations, are added to the sample before extraction. By comparing the recovery of these standards to the extracted phospholipids, researchers can assess the efficiency and reproducibility of their extraction method.
Post-extraction, the purity and composition of the extracted phospholipids must be rigorously evaluated. Chromatographic techniques, such as thin-layer chromatography (TLC) or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), are commonly employed for this purpose. These methods allow for the separation and quantification of different phospholipid classes, providing a comprehensive profile of the extracted lipids.
Mass spectrometry has emerged as a powerful tool for quality control in phospholipid extraction. It offers high sensitivity and specificity, enabling the identification and quantification of individual phospholipid species. This technique is particularly valuable for detecting trace contaminants or unexpected lipid modifications that may occur during the extraction process.
Regular calibration and maintenance of analytical instruments are essential for ensuring accurate and reliable results. This includes periodic checks of instrument performance, validation of analytical methods, and participation in inter-laboratory comparison studies to verify the accuracy of measurements across different research facilities.
Documentation and traceability are fundamental aspects of quality control in phospholipid extraction. Detailed records of all procedures, reagents, and equipment used should be maintained. This includes lot numbers of chemicals, calibration records of instruments, and any deviations from standard protocols. Such comprehensive documentation facilitates troubleshooting and ensures the reproducibility of results.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!