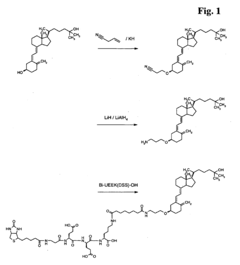
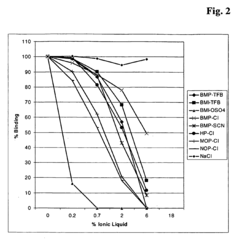
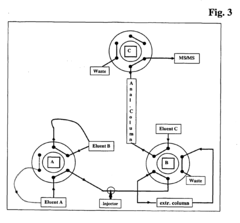
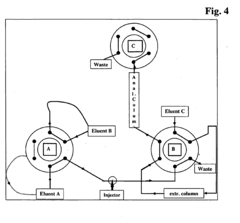
How to Test Fulvic Acid Quality Using HPLC — Standards
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HPLC Testing Background and Objectives
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) has emerged as a cornerstone analytical technique in the assessment of fulvic acid quality since its development in the late 1960s. The evolution of HPLC technology has paralleled the growing scientific interest in humic substances, particularly fulvic acids, which play crucial roles in soil fertility, plant growth, and environmental remediation. Initially, the characterization of these complex organic compounds relied on rudimentary methods that provided limited insights into their molecular composition and functional properties.
The technological trajectory of HPLC has witnessed significant advancements, transitioning from conventional systems to ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC), which offers enhanced resolution, sensitivity, and analytical speed. These improvements have been instrumental in addressing the inherent challenges associated with fulvic acid analysis, including their heterogeneous nature, polydispersity, and variable molecular weights ranging from 500 to 2000 Daltons.
Current HPLC methodologies for fulvic acid quality assessment primarily focus on molecular weight distribution, functional group characterization, and the identification of specific bioactive components. The integration of HPLC with mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (LC-NMR) has further expanded analytical capabilities, enabling more comprehensive structural elucidation of these complex molecules.
The primary objective of developing standardized HPLC testing protocols for fulvic acid quality is to establish reliable, reproducible, and internationally recognized methods that can accurately quantify key quality parameters. These parameters include concentration, purity, molecular weight distribution, functional group composition, and the presence of specific bioactive compounds that contribute to the beneficial properties of fulvic acids in agricultural, environmental, and health applications.
Additionally, standardized testing aims to differentiate authentic fulvic acids from counterfeit or adulterated products that have proliferated in the market due to increasing commercial interest. The absence of universally accepted quality standards has created significant challenges for manufacturers, regulators, and consumers in evaluating product efficacy and safety.
The development of reference standards for HPLC analysis represents a critical milestone in fulvic acid quality assessment. These standards serve as benchmarks against which commercial products can be evaluated, ensuring consistency across different laboratories and analytical platforms. Current efforts focus on isolating and characterizing representative fulvic acid fractions from various sources, including soil, peat, leonardite, and aquatic environments, to establish a comprehensive reference library.
Future technological trends in this field point toward the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to interpret complex chromatographic data, potentially revolutionizing how we understand and evaluate fulvic acid quality. The ultimate goal is to establish a standardized HPLC testing framework that balances analytical rigor with practical applicability across diverse industrial sectors.
The technological trajectory of HPLC has witnessed significant advancements, transitioning from conventional systems to ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC), which offers enhanced resolution, sensitivity, and analytical speed. These improvements have been instrumental in addressing the inherent challenges associated with fulvic acid analysis, including their heterogeneous nature, polydispersity, and variable molecular weights ranging from 500 to 2000 Daltons.
Current HPLC methodologies for fulvic acid quality assessment primarily focus on molecular weight distribution, functional group characterization, and the identification of specific bioactive components. The integration of HPLC with mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (LC-NMR) has further expanded analytical capabilities, enabling more comprehensive structural elucidation of these complex molecules.
The primary objective of developing standardized HPLC testing protocols for fulvic acid quality is to establish reliable, reproducible, and internationally recognized methods that can accurately quantify key quality parameters. These parameters include concentration, purity, molecular weight distribution, functional group composition, and the presence of specific bioactive compounds that contribute to the beneficial properties of fulvic acids in agricultural, environmental, and health applications.
Additionally, standardized testing aims to differentiate authentic fulvic acids from counterfeit or adulterated products that have proliferated in the market due to increasing commercial interest. The absence of universally accepted quality standards has created significant challenges for manufacturers, regulators, and consumers in evaluating product efficacy and safety.
The development of reference standards for HPLC analysis represents a critical milestone in fulvic acid quality assessment. These standards serve as benchmarks against which commercial products can be evaluated, ensuring consistency across different laboratories and analytical platforms. Current efforts focus on isolating and characterizing representative fulvic acid fractions from various sources, including soil, peat, leonardite, and aquatic environments, to establish a comprehensive reference library.
Future technological trends in this field point toward the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to interpret complex chromatographic data, potentially revolutionizing how we understand and evaluate fulvic acid quality. The ultimate goal is to establish a standardized HPLC testing framework that balances analytical rigor with practical applicability across diverse industrial sectors.
Market Demand for Fulvic Acid Quality Analysis
The global market for fulvic acid quality analysis has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by expanding applications across multiple industries. The agricultural sector represents the largest market segment, where fulvic acid is increasingly utilized as a soil amendment and plant growth stimulant. This has created substantial demand for reliable quality testing methods, with the global agricultural biologicals market projected to reach $21.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 13.6% from 2021.
Pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries have emerged as rapidly growing segments for fulvic acid applications, particularly in supplements and therapeutic formulations. These industries demand exceptionally high standards for purity and consistency, creating a premium market for advanced analytical methods like HPLC. The global dietary supplements market, where fulvic acid products are gaining prominence, was valued at $151.9 billion in 2021 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 8.9% through 2030.
Environmental remediation represents another significant market driver, as fulvic acid's metal-binding properties make it valuable for soil and water treatment applications. The environmental testing market specifically related to humic substances is growing at approximately 7.2% annually, with particular strength in regions facing industrial contamination challenges.
Geographically, North America currently dominates the market for fulvic acid quality analysis technologies, accounting for approximately 35% of global demand. This is attributed to the region's advanced agricultural practices and robust regulatory frameworks. Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, represents the fastest-growing regional market, expanding at over 12% annually due to rapidly modernizing agricultural sectors and increasing environmental concerns.
The regulatory landscape is significantly influencing market dynamics, with stricter quality control requirements being implemented across multiple jurisdictions. The European Union's regulations on soil amendments and the FDA's oversight of dietary supplements have both created substantial demand for standardized testing protocols. This regulatory pressure has accelerated the adoption of sophisticated analytical methods like HPLC.
Consumer awareness regarding product quality and authenticity has further intensified market demand. The growing preference for natural and organic products has created a premium segment where verified quality commands significant price premiums. Manufacturers are increasingly investing in quality testing capabilities as a competitive differentiator, with certified quality becoming a key marketing advantage in consumer-facing products containing fulvic acid.
Pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries have emerged as rapidly growing segments for fulvic acid applications, particularly in supplements and therapeutic formulations. These industries demand exceptionally high standards for purity and consistency, creating a premium market for advanced analytical methods like HPLC. The global dietary supplements market, where fulvic acid products are gaining prominence, was valued at $151.9 billion in 2021 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 8.9% through 2030.
Environmental remediation represents another significant market driver, as fulvic acid's metal-binding properties make it valuable for soil and water treatment applications. The environmental testing market specifically related to humic substances is growing at approximately 7.2% annually, with particular strength in regions facing industrial contamination challenges.
Geographically, North America currently dominates the market for fulvic acid quality analysis technologies, accounting for approximately 35% of global demand. This is attributed to the region's advanced agricultural practices and robust regulatory frameworks. Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, represents the fastest-growing regional market, expanding at over 12% annually due to rapidly modernizing agricultural sectors and increasing environmental concerns.
The regulatory landscape is significantly influencing market dynamics, with stricter quality control requirements being implemented across multiple jurisdictions. The European Union's regulations on soil amendments and the FDA's oversight of dietary supplements have both created substantial demand for standardized testing protocols. This regulatory pressure has accelerated the adoption of sophisticated analytical methods like HPLC.
Consumer awareness regarding product quality and authenticity has further intensified market demand. The growing preference for natural and organic products has created a premium segment where verified quality commands significant price premiums. Manufacturers are increasingly investing in quality testing capabilities as a competitive differentiator, with certified quality becoming a key marketing advantage in consumer-facing products containing fulvic acid.
Current HPLC Methods and Technical Limitations
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has emerged as a primary analytical technique for fulvic acid quality assessment due to its precision, reliability, and versatility. Current HPLC methods for fulvic acid analysis typically employ reversed-phase chromatography with C18 columns, which separate compounds based on hydrophobicity. These methods generally utilize gradient elution with mobile phases consisting of water, methanol, or acetonitrile, often acidified with formic or acetic acid to maintain consistent ionization states of fulvic acid molecules.
UV detection at wavelengths between 254-280 nm represents the most common detection method, as fulvic acids exhibit strong absorption in this range due to their aromatic structures. More advanced systems incorporate diode array detectors (DAD) that capture full spectral information, providing additional structural insights. Fluorescence detection offers enhanced sensitivity for specific fulvic acid components, while mass spectrometry coupling (HPLC-MS) enables more detailed molecular characterization.
Despite these capabilities, significant technical limitations persist in fulvic acid analysis. The extreme heterogeneity of fulvic acid samples presents a fundamental challenge, as these substances comprise thousands of different molecular structures with varying functional groups. This complexity results in broad, poorly resolved chromatographic peaks rather than the sharp, discrete peaks typical of pure compound analysis.
The lack of universally accepted reference standards represents another critical limitation. Unlike pharmaceutical compounds with established reference materials, fulvic acids lack standardized calibration materials, complicating quantitative analysis and inter-laboratory comparisons. Some researchers utilize commercially available humic substances from the International Humic Substances Society (IHSS) as surrogate standards, but these do not fully represent the diversity of natural fulvic acids.
Method validation challenges further complicate analysis. Recovery rates can be inconsistent due to irreversible adsorption of some fulvic acid components to stationary phases. Matrix effects from co-extracted compounds in environmental or product samples often interfere with accurate quantification. Additionally, sample preparation techniques vary widely across laboratories, affecting extraction efficiency and potentially altering the native structure of fulvic acid compounds.
Instrumental limitations also impact analysis quality. Traditional HPLC systems may lack sufficient resolution to separate the complex mixture of fulvic acid components effectively. Column degradation occurs more rapidly when analyzing these complex mixtures, leading to inconsistent retention times and reduced separation efficiency over time. The diverse functional groups in fulvic acids also create challenges in developing universal detection methods that respond proportionally to all components.
UV detection at wavelengths between 254-280 nm represents the most common detection method, as fulvic acids exhibit strong absorption in this range due to their aromatic structures. More advanced systems incorporate diode array detectors (DAD) that capture full spectral information, providing additional structural insights. Fluorescence detection offers enhanced sensitivity for specific fulvic acid components, while mass spectrometry coupling (HPLC-MS) enables more detailed molecular characterization.
Despite these capabilities, significant technical limitations persist in fulvic acid analysis. The extreme heterogeneity of fulvic acid samples presents a fundamental challenge, as these substances comprise thousands of different molecular structures with varying functional groups. This complexity results in broad, poorly resolved chromatographic peaks rather than the sharp, discrete peaks typical of pure compound analysis.
The lack of universally accepted reference standards represents another critical limitation. Unlike pharmaceutical compounds with established reference materials, fulvic acids lack standardized calibration materials, complicating quantitative analysis and inter-laboratory comparisons. Some researchers utilize commercially available humic substances from the International Humic Substances Society (IHSS) as surrogate standards, but these do not fully represent the diversity of natural fulvic acids.
Method validation challenges further complicate analysis. Recovery rates can be inconsistent due to irreversible adsorption of some fulvic acid components to stationary phases. Matrix effects from co-extracted compounds in environmental or product samples often interfere with accurate quantification. Additionally, sample preparation techniques vary widely across laboratories, affecting extraction efficiency and potentially altering the native structure of fulvic acid compounds.
Instrumental limitations also impact analysis quality. Traditional HPLC systems may lack sufficient resolution to separate the complex mixture of fulvic acid components effectively. Column degradation occurs more rapidly when analyzing these complex mixtures, leading to inconsistent retention times and reduced separation efficiency over time. The diverse functional groups in fulvic acids also create challenges in developing universal detection methods that respond proportionally to all components.
Standard HPLC Protocols for Fulvic Acid Analysis
01 HPLC methods for fulvic acid quantification
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) techniques can be used to quantify fulvic acid content in various samples. These methods typically involve specific column selection, mobile phase optimization, and detection parameters tailored for humic substances. The techniques allow for precise measurement of fulvic acid concentration, which is essential for quality control in products containing this compound. HPLC analysis provides reproducible results and can distinguish fulvic acid from other similar organic compounds.- HPLC methods for fulvic acid analysis: High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) techniques are widely used for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of fulvic acid. These methods typically involve specific column selections, mobile phase compositions, and detection systems optimized for humic substances. The techniques allow for precise separation of fulvic acid from other organic compounds and can determine molecular weight distribution and concentration with high accuracy. Various detection methods including UV-Vis, fluorescence, and mass spectrometry can be coupled with HPLC for enhanced sensitivity and specificity.
- Quality control standards for fulvic acid testing: Standardized protocols have been developed for ensuring the quality and consistency of fulvic acid analysis. These standards include reference materials, calibration procedures, and validation methods specific to humic substances. Quality control measures involve system suitability tests, precision assessments, and recovery studies to ensure reliable and reproducible results. International standards organizations have established guidelines for fulvic acid testing that specify acceptable purity levels, contaminant thresholds, and analytical performance criteria.
- Sample preparation techniques for fulvic acid HPLC analysis: Effective sample preparation is crucial for accurate HPLC analysis of fulvic acid. Techniques include extraction methods optimized for different source materials, purification steps to remove interfering compounds, and concentration procedures to enhance detection sensitivity. Solid-phase extraction, liquid-liquid extraction, and filtration are commonly employed to isolate fulvic acid from complex matrices. pH adjustment and buffer selection play important roles in maintaining the stability and solubility of fulvic acid during preparation and analysis.
- Specialized HPLC equipment for fulvic acid detection: Custom-designed HPLC systems have been developed specifically for fulvic acid analysis. These systems feature specialized components such as size-exclusion columns, ion-exchange resins, and advanced detectors tailored to the unique properties of humic substances. Automated sample handling systems, temperature-controlled compartments, and gradient elution capabilities enhance the precision and throughput of fulvic acid testing. Some systems incorporate multiple detection methods in series to provide comprehensive characterization of fulvic acid samples.
- Applications of HPLC fulvic acid testing in various industries: HPLC-based fulvic acid testing has important applications across multiple industries. In agriculture, it's used to assess soil amendments and fertilizer quality. Pharmaceutical applications include quality control of fulvic acid-containing supplements and medicines. Environmental monitoring utilizes these methods to track humic substances in water systems and assess remediation efforts. The food and beverage industry employs fulvic acid testing to evaluate certain natural ingredients and additives. Cosmetic manufacturers use these techniques to verify the composition and purity of fulvic acid in skincare products.
02 Sample preparation techniques for fulvic acid analysis
Proper sample preparation is crucial for accurate HPLC analysis of fulvic acid. This includes extraction methods from soil, water, or commercial products, followed by filtration and sometimes pre-concentration steps. Techniques may involve solid-phase extraction, liquid-liquid extraction, or specialized dissolution procedures depending on the sample matrix. The pH adjustment of samples is often necessary to optimize fulvic acid extraction and subsequent chromatographic separation. These preparation methods significantly impact the quality and reliability of the analytical results.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quality control standards for fulvic acid products
Quality control standards for fulvic acid products involve establishing acceptable ranges for purity, concentration, and potential contaminants. These standards typically include specifications for heavy metal content, microbial limits, and minimum fulvic acid concentration. HPLC testing is a key component in verifying compliance with these quality parameters. Standardized testing protocols ensure consistency across different batches and manufacturers, providing reliable quality assurance for fulvic acid products used in agricultural, pharmaceutical, or nutritional applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Detection and characterization of fulvic acid components
Advanced HPLC techniques coupled with various detection methods allow for detailed characterization of fulvic acid components. These may include UV-Vis detection, fluorescence detection, mass spectrometry, or diode array detection to identify specific molecular structures within fulvic acid complexes. Fractionation techniques can separate different molecular weight components for more detailed analysis. These methods help in understanding the composition and functional properties of fulvic acid, which is important for both research purposes and quality assessment of commercial products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Automated systems for fulvic acid testing
Automated HPLC systems have been developed specifically for routine testing of fulvic acid quality. These systems incorporate automated sample preparation, injection, and analysis with minimal human intervention. Software solutions for data processing and interpretation help standardize results and reduce operator-dependent variations. Such automated approaches are particularly valuable for high-throughput quality control in industrial settings where numerous samples need to be analyzed consistently. These systems often include calibration protocols and quality assurance measures to ensure reliable and reproducible results.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The fulvic acid quality testing market using HPLC standards is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across pharmaceutical and agricultural sectors. The competitive landscape features established pharmaceutical companies like Novartis AG and Lupin Ltd alongside specialized players such as Chengdu Push-Bio Technology and Hubei Hongyuan Pharmaceutical Technology. The market is characterized by varying levels of technical maturity, with companies like Chia Tai Tianqing and Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals demonstrating advanced capabilities in analytical chemistry and standardization. Academic institutions like Chongqing University and research centers such as Shanghai Institute of Pharmaceutical Industry are contributing to methodology development, indicating a collaborative ecosystem focused on improving testing precision and reliability.
Chongqing University
Technical Solution: Chongqing University has pioneered an advanced HPLC methodology specifically for fulvic acid quality determination. Their approach employs size exclusion chromatography (SEC) combined with diode array detection (DAD) to characterize fulvic acid fractions based on molecular weight distribution and spectral properties. The university's research team has developed a unique sample preparation protocol involving sequential extraction with alkaline solutions followed by acid precipitation to isolate fulvic acid components with minimal interference. Their method utilizes a specialized mobile phase composition (phosphate buffer with controlled ionic strength) that enhances separation of fulvic acid components while minimizing secondary interactions with the stationary phase. The university has established a library of spectral fingerprints from authenticated fulvic acid sources, enabling comparative analysis of unknown samples against verified standards. Their analytical protocol includes determination of E4/E6 ratios (absorbance ratios at 465nm and 665nm) via the HPLC-DAD system, providing insights into humification degree and aromaticity of fulvic acid samples. The method has been validated through interlaboratory studies showing excellent reproducibility (RSD < 3%) and has been successfully applied to environmental, agricultural, and pharmaceutical grade fulvic acid samples.
Strengths: The method provides comprehensive characterization of fulvic acid quality through molecular weight distribution and spectral properties, offering deeper insights than conventional single-parameter approaches. Their spectral library enables rapid identification of authentic fulvic acid sources. Weaknesses: The equipment requirements (SEC-HPLC with DAD) represent significant capital investment. The method requires specialized knowledge for data interpretation, particularly for molecular weight distribution analysis.
Jiangxi Institute of Drug Inspection and Testing
Technical Solution: The Jiangxi Institute of Drug Inspection and Testing has developed a comprehensive HPLC methodology for fulvic acid quality assessment. Their approach utilizes reversed-phase HPLC with UV detection at multiple wavelengths (254nm and 280nm) to identify characteristic peaks in fulvic acid samples. The institute has established a standardized extraction protocol using phosphate buffer solutions at controlled pH levels to ensure consistent sample preparation. Their method incorporates reference standards derived from well-characterized fulvic acid sources to create calibration curves for quantitative analysis. The institute has validated this method according to ICH guidelines, demonstrating linearity (r² > 0.998), precision (RSD < 2%), and accuracy (recovery rates between 98-102%) across multiple laboratories. Their approach also includes specific parameters for column selection (typically C18, 5μm, 250 × 4.6mm) and mobile phase composition (acetonitrile/phosphate buffer gradients) optimized for fulvic acid separation.
Strengths: Highly standardized methodology with validated parameters across multiple laboratories, ensuring reproducible results. Their approach offers excellent sensitivity for detecting trace components in complex fulvic acid matrices. Weaknesses: The method requires sophisticated HPLC equipment and trained personnel, making it less accessible for routine field testing. The extraction process is time-consuming, potentially limiting throughput for large sample volumes.
Key Chromatographic Parameters and Reference Standards
Improved measurement of vitamin d
PatentActiveEP2030026B1
Innovation
- A method using a vitamin D releasing reagent based on a salt with a quaternary N-heterocycle cation to release vitamin D metabolites from binding proteins without causing protein precipitation, allowing for direct online chromatographic separation and measurement.
Crystal form and amorphous form of dezocine analogue hydrochloride
PatentActiveUS11897830B2
Innovation
- The development of a crystal form and an amorphous form of dezocine hydrochloride with specific X-ray powder diffraction patterns and thermal stability characteristics, including characteristic peaks and thermal gravimetric analysis data, to create stable and easily preparable pharmaceutical forms.
Method Validation and Quality Control Procedures
Method validation for HPLC analysis of fulvic acid quality requires a systematic approach to ensure reliable and reproducible results. The validation process should begin with establishing system suitability parameters, including retention time stability, peak resolution, and detector response. These parameters must be verified before each analytical run to confirm that the chromatographic system is functioning properly.
Linearity assessment is crucial and should be performed using fulvic acid standards at a minimum of five concentration levels, covering the expected range of sample concentrations. The correlation coefficient (r²) should exceed 0.995 to demonstrate acceptable linearity. Precision evaluation must include both repeatability (intra-day) and intermediate precision (inter-day) measurements, with relative standard deviation (RSD) values below 2% for retention times and below 5% for peak areas.
Accuracy determination requires recovery studies using spiked samples at low, medium, and high concentration levels, with acceptable recovery rates typically between 95-105%. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) should be established using signal-to-noise ratios of 3:1 and 10:1, respectively, or through statistical methods based on the standard deviation of the response and the slope of the calibration curve.
Robustness testing is essential to evaluate the method's reliability under varying conditions. Parameters to be tested include mobile phase composition (±2%), flow rate (±0.1 mL/min), column temperature (±5°C), and pH of buffer solutions (±0.2 units). The method should demonstrate stability under these variations with minimal impact on chromatographic performance.
Quality control procedures must include regular analysis of certified reference materials (CRMs) of fulvic acid to verify accuracy. Control charts should be maintained to monitor system performance over time, with warning and action limits set at ±2SD and ±3SD, respectively. Blank samples should be analyzed with each batch to detect potential contamination, and duplicate samples (minimum 10% of total samples) should be processed to assess method reproducibility.
Internal quality control samples at known concentrations should be included at the beginning and end of each analytical sequence, with acceptance criteria of ±10% of the target value. Proficiency testing participation is recommended at least annually to verify laboratory performance against peer laboratories. All analytical data should undergo thorough review by qualified personnel before release, with comprehensive documentation maintained according to good laboratory practice (GLP) principles.
Linearity assessment is crucial and should be performed using fulvic acid standards at a minimum of five concentration levels, covering the expected range of sample concentrations. The correlation coefficient (r²) should exceed 0.995 to demonstrate acceptable linearity. Precision evaluation must include both repeatability (intra-day) and intermediate precision (inter-day) measurements, with relative standard deviation (RSD) values below 2% for retention times and below 5% for peak areas.
Accuracy determination requires recovery studies using spiked samples at low, medium, and high concentration levels, with acceptable recovery rates typically between 95-105%. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) should be established using signal-to-noise ratios of 3:1 and 10:1, respectively, or through statistical methods based on the standard deviation of the response and the slope of the calibration curve.
Robustness testing is essential to evaluate the method's reliability under varying conditions. Parameters to be tested include mobile phase composition (±2%), flow rate (±0.1 mL/min), column temperature (±5°C), and pH of buffer solutions (±0.2 units). The method should demonstrate stability under these variations with minimal impact on chromatographic performance.
Quality control procedures must include regular analysis of certified reference materials (CRMs) of fulvic acid to verify accuracy. Control charts should be maintained to monitor system performance over time, with warning and action limits set at ±2SD and ±3SD, respectively. Blank samples should be analyzed with each batch to detect potential contamination, and duplicate samples (minimum 10% of total samples) should be processed to assess method reproducibility.
Internal quality control samples at known concentrations should be included at the beginning and end of each analytical sequence, with acceptance criteria of ±10% of the target value. Proficiency testing participation is recommended at least annually to verify laboratory performance against peer laboratories. All analytical data should undergo thorough review by qualified personnel before release, with comprehensive documentation maintained according to good laboratory practice (GLP) principles.
Environmental and Agricultural Applications
Fulvic acid applications in environmental science and agriculture represent significant areas where HPLC quality testing delivers substantial benefits. In environmental remediation, fulvic acids play a crucial role in binding heavy metals and organic pollutants, facilitating their removal from contaminated soils and water bodies. The precise determination of fulvic acid quality through HPLC analysis enables environmental scientists to select optimal fulvic acid products for specific remediation projects, maximizing contaminant sequestration efficiency while minimizing treatment costs.
Agricultural applications of fulvic acids have expanded dramatically in recent years, particularly in sustainable and organic farming systems. When applied as soil amendments or foliar sprays, high-quality fulvic acids enhance nutrient uptake, improve soil structure, and stimulate beneficial microbial activity. HPLC testing provides farmers and agricultural input manufacturers with critical quality assurance data, ensuring consistent product performance across varying field conditions and crop types.
The chelation properties of fulvic acids make them particularly valuable in areas with nutrient-deficient or contaminated soils. By forming stable complexes with micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese, fulvic acids increase nutrient bioavailability to plants. HPLC analysis can quantify the chelation capacity of different fulvic acid products, allowing for targeted application rates based on specific soil conditions and crop requirements.
Water treatment represents another significant environmental application where fulvic acid quality assessment proves essential. Municipal water facilities increasingly utilize fulvic acids in advanced filtration systems to remove pharmaceutical residues, pesticides, and other emerging contaminants. HPLC testing ensures that the fulvic acid products used maintain consistent molecular weight distributions and functional group compositions necessary for effective contaminant removal.
Climate-smart agriculture initiatives have also begun incorporating fulvic acids as carbon sequestration enhancers. By stabilizing organic matter in soils, high-quality fulvic acids contribute to long-term carbon storage while simultaneously improving soil health. HPLC analysis helps researchers and carbon credit programs verify the structural characteristics of fulvic acids that correlate with superior carbon sequestration potential, supporting the development of standardized protocols for climate mitigation projects.
Precision agriculture technologies increasingly integrate fulvic acid applications with site-specific management practices. HPLC quality testing enables the development of specialized fulvic acid formulations tailored to different crop growth stages, soil types, and environmental stressors. This targeted approach maximizes agricultural productivity while minimizing environmental impacts through optimized input efficiency.
Agricultural applications of fulvic acids have expanded dramatically in recent years, particularly in sustainable and organic farming systems. When applied as soil amendments or foliar sprays, high-quality fulvic acids enhance nutrient uptake, improve soil structure, and stimulate beneficial microbial activity. HPLC testing provides farmers and agricultural input manufacturers with critical quality assurance data, ensuring consistent product performance across varying field conditions and crop types.
The chelation properties of fulvic acids make them particularly valuable in areas with nutrient-deficient or contaminated soils. By forming stable complexes with micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese, fulvic acids increase nutrient bioavailability to plants. HPLC analysis can quantify the chelation capacity of different fulvic acid products, allowing for targeted application rates based on specific soil conditions and crop requirements.
Water treatment represents another significant environmental application where fulvic acid quality assessment proves essential. Municipal water facilities increasingly utilize fulvic acids in advanced filtration systems to remove pharmaceutical residues, pesticides, and other emerging contaminants. HPLC testing ensures that the fulvic acid products used maintain consistent molecular weight distributions and functional group compositions necessary for effective contaminant removal.
Climate-smart agriculture initiatives have also begun incorporating fulvic acids as carbon sequestration enhancers. By stabilizing organic matter in soils, high-quality fulvic acids contribute to long-term carbon storage while simultaneously improving soil health. HPLC analysis helps researchers and carbon credit programs verify the structural characteristics of fulvic acids that correlate with superior carbon sequestration potential, supporting the development of standardized protocols for climate mitigation projects.
Precision agriculture technologies increasingly integrate fulvic acid applications with site-specific management practices. HPLC quality testing enables the development of specialized fulvic acid formulations tailored to different crop growth stages, soil types, and environmental stressors. This targeted approach maximizes agricultural productivity while minimizing environmental impacts through optimized input efficiency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!