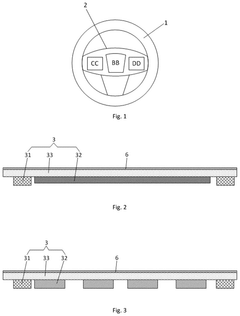
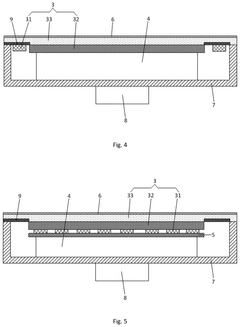
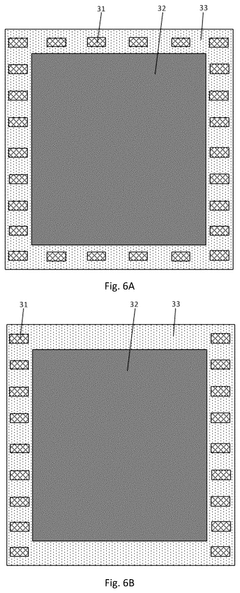
How to Utilize Digital Displays in Steering Wheel Design?
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Steering Wheel Display Evolution and Objectives
The evolution of steering wheel displays represents a significant advancement in automotive technology, reflecting the broader trend of digitalization in vehicle interfaces. Initially, steering wheels were purely mechanical devices designed for vehicle control. However, as automotive technology progressed, the steering wheel began to incorporate various controls and information displays.
The first major step in this evolution was the integration of basic controls such as horn buttons and cruise control switches. This was followed by the introduction of audio and communication controls, allowing drivers to manage these systems without removing their hands from the wheel. The next significant leap came with the incorporation of small LCD screens, typically positioned in the center of the wheel, displaying basic vehicle information such as speed and fuel levels.
As display technology advanced, these screens became larger and more sophisticated, capable of showing more complex information such as navigation instructions and vehicle diagnostics. The advent of digital instrument clusters further expanded the potential for information display, leading to the development of head-up displays (HUDs) that project information onto the windshield.
The current objective in steering wheel display technology is to create a seamless, intuitive interface that enhances driver awareness and control without causing distraction. This involves integrating touch-sensitive surfaces, haptic feedback, and customizable displays that can adapt to different driving modes and personal preferences.
One of the primary goals is to improve safety by minimizing the need for drivers to look away from the road. This is being achieved through the development of more advanced HUDs and augmented reality (AR) displays that overlay information directly onto the driver's view of the road. Another objective is to enhance the overall driving experience by providing personalized information and controls that are easily accessible and customizable.
The future of steering wheel displays is likely to involve even more advanced technologies, such as flexible OLED screens that can wrap around the wheel's contours, providing a larger display area without compromising ergonomics. There is also a focus on developing displays that can seamlessly integrate with autonomous driving systems, providing clear information about the vehicle's status and allowing for smooth transitions between manual and autonomous modes.
As vehicles become more connected, steering wheel displays are expected to play a crucial role in presenting information from various sources, including vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications. This will require displays that can prioritize and present complex information in a clear, concise manner, further enhancing driver awareness and decision-making capabilities.
The first major step in this evolution was the integration of basic controls such as horn buttons and cruise control switches. This was followed by the introduction of audio and communication controls, allowing drivers to manage these systems without removing their hands from the wheel. The next significant leap came with the incorporation of small LCD screens, typically positioned in the center of the wheel, displaying basic vehicle information such as speed and fuel levels.
As display technology advanced, these screens became larger and more sophisticated, capable of showing more complex information such as navigation instructions and vehicle diagnostics. The advent of digital instrument clusters further expanded the potential for information display, leading to the development of head-up displays (HUDs) that project information onto the windshield.
The current objective in steering wheel display technology is to create a seamless, intuitive interface that enhances driver awareness and control without causing distraction. This involves integrating touch-sensitive surfaces, haptic feedback, and customizable displays that can adapt to different driving modes and personal preferences.
One of the primary goals is to improve safety by minimizing the need for drivers to look away from the road. This is being achieved through the development of more advanced HUDs and augmented reality (AR) displays that overlay information directly onto the driver's view of the road. Another objective is to enhance the overall driving experience by providing personalized information and controls that are easily accessible and customizable.
The future of steering wheel displays is likely to involve even more advanced technologies, such as flexible OLED screens that can wrap around the wheel's contours, providing a larger display area without compromising ergonomics. There is also a focus on developing displays that can seamlessly integrate with autonomous driving systems, providing clear information about the vehicle's status and allowing for smooth transitions between manual and autonomous modes.
As vehicles become more connected, steering wheel displays are expected to play a crucial role in presenting information from various sources, including vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications. This will require displays that can prioritize and present complex information in a clear, concise manner, further enhancing driver awareness and decision-making capabilities.
Market Demand for Smart Steering Wheels
The market demand for smart steering wheels with integrated digital displays has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by the increasing consumer appetite for advanced in-vehicle technology and the automotive industry's push towards more connected and intelligent vehicles. This trend is particularly evident in the luxury and high-end vehicle segments, where consumers are willing to pay a premium for cutting-edge features that enhance both safety and convenience.
One of the primary drivers of this demand is the growing emphasis on driver safety. Digital displays integrated into steering wheels can provide crucial information directly in the driver's line of sight, reducing the need to look away from the road. This feature is especially valuable for displaying navigation instructions, speed limits, and other critical driving data, which can significantly improve driver awareness and reaction times.
The rise of autonomous and semi-autonomous driving technologies has also contributed to the increased demand for smart steering wheels. As vehicles become more capable of self-driving, the steering wheel is evolving into a multifunctional interface that can seamlessly transition between manual and autonomous modes. Digital displays play a crucial role in this transition, providing real-time feedback on the vehicle's autonomous status and allowing for intuitive control handovers.
Consumer expectations for seamless connectivity and infotainment experiences in vehicles are another significant factor driving the market for smart steering wheels. The integration of digital displays allows for easy access to smartphone applications, media controls, and vehicle settings without the need to interact with a separate center console display. This level of integration appeals to tech-savvy consumers who value convenience and connectivity in their driving experience.
The automotive industry's focus on personalization and customization has further fueled the demand for digital displays in steering wheels. These displays offer the flexibility to adapt the steering wheel interface to individual driver preferences, potentially changing the layout, information displayed, or even the visual theme to suit different drivers or driving modes.
Market research indicates that the global smart steering wheel market is expected to grow significantly over the next decade. While precise figures vary depending on the source, industry analysts consistently project double-digit compound annual growth rates. This growth is attributed not only to the increasing adoption in luxury vehicles but also to the gradual penetration into mid-range and entry-level vehicle segments as technology costs decrease and consumer expectations evolve.
One of the primary drivers of this demand is the growing emphasis on driver safety. Digital displays integrated into steering wheels can provide crucial information directly in the driver's line of sight, reducing the need to look away from the road. This feature is especially valuable for displaying navigation instructions, speed limits, and other critical driving data, which can significantly improve driver awareness and reaction times.
The rise of autonomous and semi-autonomous driving technologies has also contributed to the increased demand for smart steering wheels. As vehicles become more capable of self-driving, the steering wheel is evolving into a multifunctional interface that can seamlessly transition between manual and autonomous modes. Digital displays play a crucial role in this transition, providing real-time feedback on the vehicle's autonomous status and allowing for intuitive control handovers.
Consumer expectations for seamless connectivity and infotainment experiences in vehicles are another significant factor driving the market for smart steering wheels. The integration of digital displays allows for easy access to smartphone applications, media controls, and vehicle settings without the need to interact with a separate center console display. This level of integration appeals to tech-savvy consumers who value convenience and connectivity in their driving experience.
The automotive industry's focus on personalization and customization has further fueled the demand for digital displays in steering wheels. These displays offer the flexibility to adapt the steering wheel interface to individual driver preferences, potentially changing the layout, information displayed, or even the visual theme to suit different drivers or driving modes.
Market research indicates that the global smart steering wheel market is expected to grow significantly over the next decade. While precise figures vary depending on the source, industry analysts consistently project double-digit compound annual growth rates. This growth is attributed not only to the increasing adoption in luxury vehicles but also to the gradual penetration into mid-range and entry-level vehicle segments as technology costs decrease and consumer expectations evolve.
Current Challenges in Steering Wheel Displays
The integration of digital displays into steering wheel design presents several significant challenges that manufacturers and engineers must address. One of the primary obstacles is the limited space available within the steering wheel structure. Traditional steering wheels are compact by necessity, and incorporating a display without compromising the wheel's ergonomics or safety features requires innovative design solutions.
Another critical challenge is ensuring driver safety while implementing digital displays. The steering wheel is a crucial control interface, and any additions must not distract the driver or impede their ability to maintain control of the vehicle. Balancing the provision of useful information with minimizing cognitive load is a complex task that requires careful consideration of human-machine interface principles.
Durability and reliability pose additional hurdles in steering wheel display integration. The steering wheel is subject to constant movement and vibration, which can potentially damage sensitive electronic components. Manufacturers must develop robust display technologies and mounting solutions that can withstand the rigors of daily use and maintain functionality over the vehicle's lifespan.
Power management and connectivity present further challenges. Steering wheel displays require a reliable power source and data connection, which must be seamlessly integrated into the wheel's rotating structure. This necessitates the development of advanced slip ring technologies or wireless power and data transfer solutions that can operate consistently in the automotive environment.
Environmental factors also play a significant role in the challenges faced by steering wheel displays. These displays must function effectively across a wide range of temperatures and lighting conditions, from bright sunlight to nighttime driving. Ensuring readability and touch responsiveness in all scenarios is crucial for the technology's practicality and user acceptance.
Cost considerations present another obstacle in the widespread adoption of digital displays in steering wheels. Integrating advanced display technology and the necessary supporting systems can significantly increase the overall cost of the steering wheel and, by extension, the vehicle. Manufacturers must find ways to balance the added functionality with cost-effectiveness to make the technology viable for mass-market adoption.
Lastly, regulatory compliance and standardization pose challenges in the development and implementation of steering wheel displays. As this technology is relatively new, regulatory frameworks may need to be updated to address safety and performance standards specific to steering wheel-integrated displays. Manufacturers must navigate these evolving regulations while also working towards industry-wide standardization to ensure compatibility and consistency across different vehicle models and brands.
Another critical challenge is ensuring driver safety while implementing digital displays. The steering wheel is a crucial control interface, and any additions must not distract the driver or impede their ability to maintain control of the vehicle. Balancing the provision of useful information with minimizing cognitive load is a complex task that requires careful consideration of human-machine interface principles.
Durability and reliability pose additional hurdles in steering wheel display integration. The steering wheel is subject to constant movement and vibration, which can potentially damage sensitive electronic components. Manufacturers must develop robust display technologies and mounting solutions that can withstand the rigors of daily use and maintain functionality over the vehicle's lifespan.
Power management and connectivity present further challenges. Steering wheel displays require a reliable power source and data connection, which must be seamlessly integrated into the wheel's rotating structure. This necessitates the development of advanced slip ring technologies or wireless power and data transfer solutions that can operate consistently in the automotive environment.
Environmental factors also play a significant role in the challenges faced by steering wheel displays. These displays must function effectively across a wide range of temperatures and lighting conditions, from bright sunlight to nighttime driving. Ensuring readability and touch responsiveness in all scenarios is crucial for the technology's practicality and user acceptance.
Cost considerations present another obstacle in the widespread adoption of digital displays in steering wheels. Integrating advanced display technology and the necessary supporting systems can significantly increase the overall cost of the steering wheel and, by extension, the vehicle. Manufacturers must find ways to balance the added functionality with cost-effectiveness to make the technology viable for mass-market adoption.
Lastly, regulatory compliance and standardization pose challenges in the development and implementation of steering wheel displays. As this technology is relatively new, regulatory frameworks may need to be updated to address safety and performance standards specific to steering wheel-integrated displays. Manufacturers must navigate these evolving regulations while also working towards industry-wide standardization to ensure compatibility and consistency across different vehicle models and brands.
Existing Digital Steering Wheel Solutions
01 Display technology advancements
Digital displays have evolved significantly, incorporating various technologies to enhance visual quality and user experience. These advancements include improved resolution, color reproduction, and refresh rates, as well as the development of flexible and transparent displays for diverse applications.- Digital display technologies and improvements: Various technologies and improvements in digital displays, including advancements in display resolution, color reproduction, and energy efficiency. These innovations enhance the overall quality and performance of digital displays for diverse applications.
- User interface and interaction methods: Development of innovative user interface designs and interaction methods for digital displays, focusing on improving user experience and accessibility. This includes touch-based interfaces, gesture recognition, and adaptive display layouts.
- Integration of digital displays in vehicles: Incorporation of digital displays in automotive applications, including dashboard displays, infotainment systems, and heads-up displays. These integrations aim to enhance driver information, safety, and entertainment features in vehicles.
- Digital signage and advertising applications: Utilization of digital displays for signage and advertising purposes, including interactive billboards, dynamic content delivery systems, and targeted advertising solutions. These applications leverage digital display technology to create engaging and personalized experiences for viewers.
- Security and privacy features for digital displays: Implementation of security and privacy measures for digital displays, including data encryption, secure content delivery, and privacy screens. These features aim to protect sensitive information displayed on digital screens and ensure user privacy in various environments.
02 Interactive and touch-based interfaces
Modern digital displays often feature interactive capabilities, such as touch screens and gesture recognition. These interfaces allow for more intuitive user interactions, enabling applications in areas like education, entertainment, and information kiosks.Expand Specific Solutions03 Mobile device display integration
Digital displays are increasingly integrated into mobile devices, offering compact yet high-quality visual outputs. This integration has led to innovations in power efficiency, display durability, and adaptability to various lighting conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Digital signage and advertising
Digital displays are widely used in signage and advertising, allowing for dynamic content delivery and real-time updates. These systems can be networked for centralized management and can incorporate features like audience analytics and interactive elements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy-efficient display technologies
Advancements in digital display technology have focused on improving energy efficiency without compromising visual quality. This includes the development of low-power display modes, adaptive brightness controls, and more efficient backlighting systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Automotive HMI
The digital display steering wheel technology market is in its early growth stage, with increasing adoption across luxury and mid-range vehicle segments. The market size is expanding rapidly, driven by growing consumer demand for advanced in-vehicle interfaces and connectivity. While the technology is maturing, there is still room for innovation and refinement. Key players like BMW, Volkswagen, and Toyota are leading development efforts, with suppliers such as Bosch and Valeo providing critical components. Emerging companies like Preh and HiRain Technologies are also making significant contributions to advancing the technology. As the market evolves, we can expect increased competition and further technological advancements to enhance driver experience and safety.
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG
Technical Solution: BMW has developed an innovative steering wheel design incorporating digital displays. Their solution integrates a curved display seamlessly into the steering wheel rim, providing drivers with essential information without obstructing their view of the road. The display uses OLED technology for high contrast and visibility in various lighting conditions [1]. BMW's system allows for customizable information display, including navigation directions, vehicle status, and media controls. The company has also implemented haptic feedback technology in conjunction with the display, enhancing the user interface and reducing driver distraction [3]. BMW's digital steering wheel is designed to work in harmony with their larger dashboard displays, creating a cohesive and intuitive cockpit environment.
Strengths: Seamless integration, customizable interface, and enhanced driver information without compromising safety. Weaknesses: Potential for information overload and higher production costs compared to traditional steering wheels.
Volkswagen AG
Technical Solution: Volkswagen has introduced a revolutionary steering wheel design featuring integrated touch-sensitive controls and digital displays. Their system, known as the "Smart Steering Wheel," incorporates small OLED screens within the steering wheel spokes. These displays are programmable and context-sensitive, changing their function based on the driving mode or user preferences [2]. Volkswagen's approach includes haptic feedback for improved tactile response and minimized driver distraction. The company has also developed an AI-assisted interface that learns driver habits and adjusts the displayed information accordingly [4]. Additionally, Volkswagen's digital steering wheel integrates with their larger infotainment system, allowing for seamless information flow between different vehicle interfaces.
Strengths: Adaptive interface, integration with vehicle systems, and improved ergonomics. Weaknesses: Learning curve for users and potential for system complexity leading to reliability issues.
Innovative Display Technologies for Steering Wheels
Display unit and method for displaying a steering angle of the steering wheel of a vehicle
PatentInactiveEP1633620A1
Innovation
- A display unit with adjacent, controllable display elements that illuminate to indicate the required steering direction, allowing drivers to easily recognize steering corrections and changes, with options for color and spatial control to simplify orientation, and integration into the instrument panel or rearview mirror for enhanced visibility.
Steering assembly and automobile
PatentPendingUS20240359724A1
Innovation
- A steering assembly incorporating a flexible touch display screen with a piezoelectric device, arranged to avoid overlap with the airbag, providing haptic feedback and integrated visual and auditory functions while ensuring safety by non-interfering positional arrangement and adhesive bonding to prevent ejection during airbag deployment.
Safety Regulations for In-Vehicle Displays
The integration of digital displays in steering wheel design necessitates strict adherence to safety regulations to ensure driver safety and minimize distractions. Regulatory bodies such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States and the European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) have established guidelines for in-vehicle displays, including those incorporated into steering wheels.
These regulations primarily focus on minimizing driver distraction and ensuring that essential vehicle information remains easily accessible. The NHTSA's Visual-Manual NHTSA Driver Distraction Guidelines for In-Vehicle Electronic Devices emphasize that any non-driving-related tasks should not require more than 2 seconds of eye-off-road time per glance and a total of 12 seconds to complete the entire task.
For steering wheel-mounted displays, regulations stipulate that the information presented must be directly related to driving tasks or vehicle status. This includes data such as speed, navigation instructions, and critical warnings. The placement of these displays must not obstruct the driver's view of the road or interfere with airbag deployment zones.
Size and brightness regulations are also crucial for steering wheel displays. The display size must be optimized to provide clear visibility without being overly large or distracting. Brightness levels must be adjustable to accommodate various lighting conditions, with automatic dimming capabilities for nighttime driving.
Touch sensitivity and haptic feedback in steering wheel displays are subject to regulations ensuring that interactions can be performed without compromising steering control. These systems must be designed to minimize accidental inputs and provide clear tactile feedback to confirm user actions without requiring visual confirmation.
Durability and crash safety standards apply to steering wheel displays, mandating that they must withstand impact forces and not pose additional risks to the driver in the event of a collision. This includes requirements for shatter-resistant materials and secure mounting to prevent detachment during accidents.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations are also applicable, ensuring that the digital displays do not interfere with other vehicle electronic systems or external communications. This is particularly important given the proximity of the steering wheel to various vehicle control modules.
As technology evolves, regulatory bodies continue to update their guidelines to address emerging trends in automotive display technology. Manufacturers must stay abreast of these changes and design their steering wheel displays to comply with the latest safety standards while also anticipating future regulatory developments.
These regulations primarily focus on minimizing driver distraction and ensuring that essential vehicle information remains easily accessible. The NHTSA's Visual-Manual NHTSA Driver Distraction Guidelines for In-Vehicle Electronic Devices emphasize that any non-driving-related tasks should not require more than 2 seconds of eye-off-road time per glance and a total of 12 seconds to complete the entire task.
For steering wheel-mounted displays, regulations stipulate that the information presented must be directly related to driving tasks or vehicle status. This includes data such as speed, navigation instructions, and critical warnings. The placement of these displays must not obstruct the driver's view of the road or interfere with airbag deployment zones.
Size and brightness regulations are also crucial for steering wheel displays. The display size must be optimized to provide clear visibility without being overly large or distracting. Brightness levels must be adjustable to accommodate various lighting conditions, with automatic dimming capabilities for nighttime driving.
Touch sensitivity and haptic feedback in steering wheel displays are subject to regulations ensuring that interactions can be performed without compromising steering control. These systems must be designed to minimize accidental inputs and provide clear tactile feedback to confirm user actions without requiring visual confirmation.
Durability and crash safety standards apply to steering wheel displays, mandating that they must withstand impact forces and not pose additional risks to the driver in the event of a collision. This includes requirements for shatter-resistant materials and secure mounting to prevent detachment during accidents.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations are also applicable, ensuring that the digital displays do not interfere with other vehicle electronic systems or external communications. This is particularly important given the proximity of the steering wheel to various vehicle control modules.
As technology evolves, regulatory bodies continue to update their guidelines to address emerging trends in automotive display technology. Manufacturers must stay abreast of these changes and design their steering wheel displays to comply with the latest safety standards while also anticipating future regulatory developments.
User Experience and Ergonomics in Steering Wheel Design
The integration of digital displays in steering wheel design represents a significant advancement in automotive user interface technology. This innovation aims to enhance driver interaction, improve safety, and provide a more intuitive driving experience. When considering user experience and ergonomics in steering wheel design with digital displays, several key factors come into play.
Firstly, the placement and size of digital displays on the steering wheel must be carefully considered to ensure optimal visibility without obstructing the driver's view of the road. The displays should be positioned within the driver's natural line of sight, typically at the center or upper portion of the steering wheel. The size of the display must strike a balance between providing sufficient information and maintaining the steering wheel's primary function as a control device.
Ergonomic considerations are crucial in integrating digital displays into steering wheels. The design must account for various hand positions and grip styles to ensure that the display does not interfere with comfortable and safe steering. Touch-sensitive areas or physical buttons adjacent to the display should be easily accessible without requiring the driver to remove their hands from the wheel or compromise their grip.
The user interface of the digital display must be designed with simplicity and clarity in mind. Information presented should be concise, easily readable at a glance, and prioritized based on importance. The use of customizable layouts and themes can cater to individual preferences and driving styles, enhancing the overall user experience.
Haptic feedback and tactile elements play a significant role in improving the ergonomics of digital steering wheel displays. Incorporating subtle vibrations or texture changes can provide confirmation of input without requiring visual attention, allowing drivers to keep their eyes on the road. This tactile feedback can also help drivers distinguish between different controls and functions without looking at the display.
The integration of voice commands and gesture controls can further enhance the user experience and ergonomics of digital steering wheel displays. These features allow drivers to interact with the system while maintaining proper hand position on the wheel, reducing distractions and improving safety.
Consideration must also be given to the adaptability of the display under various lighting conditions. The brightness and contrast of the display should automatically adjust to ensure readability in bright sunlight or during nighttime driving. Anti-glare coatings and adjustable viewing angles can further improve visibility and reduce eye strain.
Lastly, the durability and reliability of the digital display system are crucial ergonomic factors. The display and associated electronics must withstand the rigors of daily use, temperature fluctuations, and potential impacts. A robust design ensures long-term functionality and maintains the integrity of the steering wheel as a critical safety component.
Firstly, the placement and size of digital displays on the steering wheel must be carefully considered to ensure optimal visibility without obstructing the driver's view of the road. The displays should be positioned within the driver's natural line of sight, typically at the center or upper portion of the steering wheel. The size of the display must strike a balance between providing sufficient information and maintaining the steering wheel's primary function as a control device.
Ergonomic considerations are crucial in integrating digital displays into steering wheels. The design must account for various hand positions and grip styles to ensure that the display does not interfere with comfortable and safe steering. Touch-sensitive areas or physical buttons adjacent to the display should be easily accessible without requiring the driver to remove their hands from the wheel or compromise their grip.
The user interface of the digital display must be designed with simplicity and clarity in mind. Information presented should be concise, easily readable at a glance, and prioritized based on importance. The use of customizable layouts and themes can cater to individual preferences and driving styles, enhancing the overall user experience.
Haptic feedback and tactile elements play a significant role in improving the ergonomics of digital steering wheel displays. Incorporating subtle vibrations or texture changes can provide confirmation of input without requiring visual attention, allowing drivers to keep their eyes on the road. This tactile feedback can also help drivers distinguish between different controls and functions without looking at the display.
The integration of voice commands and gesture controls can further enhance the user experience and ergonomics of digital steering wheel displays. These features allow drivers to interact with the system while maintaining proper hand position on the wheel, reducing distractions and improving safety.
Consideration must also be given to the adaptability of the display under various lighting conditions. The brightness and contrast of the display should automatically adjust to ensure readability in bright sunlight or during nighttime driving. Anti-glare coatings and adjustable viewing angles can further improve visibility and reduce eye strain.
Lastly, the durability and reliability of the digital display system are crucial ergonomic factors. The display and associated electronics must withstand the rigors of daily use, temperature fluctuations, and potential impacts. A robust design ensures long-term functionality and maintains the integrity of the steering wheel as a critical safety component.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!