Optimization of Controlled Release Systems Using Phenolphthalein
JUL 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Background and Objectives
Controlled release systems have been a cornerstone of pharmaceutical and materials science for decades, offering precise control over the delivery of active compounds. The optimization of these systems has been an ongoing challenge, with researchers constantly seeking innovative approaches to enhance efficacy and efficiency. In recent years, the use of phenolphthalein as a model compound has gained traction in the field, providing a unique opportunity to study and refine controlled release mechanisms.
The evolution of controlled release technology can be traced back to the 1950s, with significant advancements occurring in the 1970s and 1980s. These systems have since found applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and consumer products. The primary goal has always been to achieve a sustained and predictable release profile of active ingredients, maximizing their effectiveness while minimizing side effects or waste.
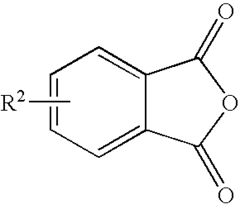
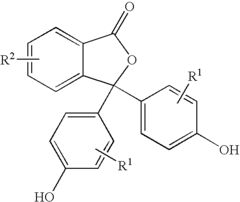
Phenolphthalein, traditionally known for its use as a pH indicator, has emerged as an ideal candidate for studying controlled release systems due to its well-characterized properties and easily detectable color changes. Its molecular structure and behavior under different pH conditions make it an excellent model for understanding the intricacies of release kinetics and diffusion processes.
The objectives of optimizing controlled release systems using phenolphthalein are multifaceted. Firstly, researchers aim to develop more precise and tunable release profiles, allowing for greater control over the timing and rate of compound delivery. This could lead to improved drug delivery systems with reduced side effects and enhanced therapeutic outcomes. Secondly, there is a focus on creating more environmentally friendly and sustainable release systems, addressing concerns about the long-term impact of synthetic materials used in traditional formulations.
Another key objective is to enhance the stability and longevity of controlled release systems. By studying the interactions between phenolphthalein and various carrier materials, researchers hope to design more robust systems that maintain their efficacy over extended periods. This is particularly crucial for applications in harsh environments or those requiring long-term storage.
Furthermore, the optimization process seeks to improve the cost-effectiveness and scalability of controlled release technologies. By refining manufacturing processes and exploring novel materials, researchers aim to make these systems more accessible and applicable across a broader range of industries and applications.
The use of phenolphthalein in this context also serves as a stepping stone towards developing more complex and responsive controlled release systems. The insights gained from these studies could pave the way for smart delivery systems capable of responding to environmental cues or physiological changes, opening up new possibilities in personalized medicine and adaptive materials.
The evolution of controlled release technology can be traced back to the 1950s, with significant advancements occurring in the 1970s and 1980s. These systems have since found applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and consumer products. The primary goal has always been to achieve a sustained and predictable release profile of active ingredients, maximizing their effectiveness while minimizing side effects or waste.
Phenolphthalein, traditionally known for its use as a pH indicator, has emerged as an ideal candidate for studying controlled release systems due to its well-characterized properties and easily detectable color changes. Its molecular structure and behavior under different pH conditions make it an excellent model for understanding the intricacies of release kinetics and diffusion processes.
The objectives of optimizing controlled release systems using phenolphthalein are multifaceted. Firstly, researchers aim to develop more precise and tunable release profiles, allowing for greater control over the timing and rate of compound delivery. This could lead to improved drug delivery systems with reduced side effects and enhanced therapeutic outcomes. Secondly, there is a focus on creating more environmentally friendly and sustainable release systems, addressing concerns about the long-term impact of synthetic materials used in traditional formulations.
Another key objective is to enhance the stability and longevity of controlled release systems. By studying the interactions between phenolphthalein and various carrier materials, researchers hope to design more robust systems that maintain their efficacy over extended periods. This is particularly crucial for applications in harsh environments or those requiring long-term storage.
Furthermore, the optimization process seeks to improve the cost-effectiveness and scalability of controlled release technologies. By refining manufacturing processes and exploring novel materials, researchers aim to make these systems more accessible and applicable across a broader range of industries and applications.
The use of phenolphthalein in this context also serves as a stepping stone towards developing more complex and responsive controlled release systems. The insights gained from these studies could pave the way for smart delivery systems capable of responding to environmental cues or physiological changes, opening up new possibilities in personalized medicine and adaptive materials.
Market Analysis
The market for controlled release systems utilizing phenolphthalein has shown significant growth potential in recent years, driven by increasing demand for advanced drug delivery mechanisms and innovative pharmaceutical formulations. This technology finds applications across various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, healthcare, and personal care products.
In the pharmaceutical industry, controlled release systems using phenolphthalein have gained traction due to their ability to enhance drug efficacy and patient compliance. These systems allow for precise dosage control and sustained release of active ingredients, reducing the frequency of drug administration and minimizing side effects. The global market for controlled release drug delivery systems is expected to expand substantially, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be in the high single digits over the next five years.
The healthcare sector has also shown keen interest in phenolphthalein-based controlled release systems for diagnostic applications. These systems offer improved sensitivity and specificity in various medical tests, particularly in colorimetric assays. The growing emphasis on point-of-care diagnostics and personalized medicine is likely to further boost the demand for such advanced release systems.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, controlled release systems incorporating phenolphthalein have found applications in color-changing products and pH-sensitive formulations. This niche market segment is experiencing rapid growth, driven by consumer demand for innovative and interactive beauty products.
Market trends indicate a shift towards more sophisticated and tailored controlled release systems. Manufacturers are focusing on developing smart release mechanisms that can respond to specific physiological conditions or external stimuli. This trend aligns well with the unique properties of phenolphthalein, which can change color based on pH levels, making it an attractive component for intelligent delivery systems.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for controlled release systems, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and robust pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a lucrative market, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure, growing awareness of advanced drug delivery systems, and rising investments in research and development.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials may impact the growth rate of phenolphthalein-based controlled release systems. Additionally, concerns regarding the long-term safety of phenolphthalein in certain applications may require further research and validation to ensure market acceptance and regulatory compliance.
Overall, the market for controlled release systems using phenolphthalein presents significant opportunities for innovation and growth across multiple industries. As research continues to optimize these systems, their applications are likely to expand, potentially revolutionizing drug delivery, diagnostics, and consumer products in the coming years.
In the pharmaceutical industry, controlled release systems using phenolphthalein have gained traction due to their ability to enhance drug efficacy and patient compliance. These systems allow for precise dosage control and sustained release of active ingredients, reducing the frequency of drug administration and minimizing side effects. The global market for controlled release drug delivery systems is expected to expand substantially, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be in the high single digits over the next five years.
The healthcare sector has also shown keen interest in phenolphthalein-based controlled release systems for diagnostic applications. These systems offer improved sensitivity and specificity in various medical tests, particularly in colorimetric assays. The growing emphasis on point-of-care diagnostics and personalized medicine is likely to further boost the demand for such advanced release systems.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, controlled release systems incorporating phenolphthalein have found applications in color-changing products and pH-sensitive formulations. This niche market segment is experiencing rapid growth, driven by consumer demand for innovative and interactive beauty products.
Market trends indicate a shift towards more sophisticated and tailored controlled release systems. Manufacturers are focusing on developing smart release mechanisms that can respond to specific physiological conditions or external stimuli. This trend aligns well with the unique properties of phenolphthalein, which can change color based on pH levels, making it an attractive component for intelligent delivery systems.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for controlled release systems, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and robust pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a lucrative market, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure, growing awareness of advanced drug delivery systems, and rising investments in research and development.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials may impact the growth rate of phenolphthalein-based controlled release systems. Additionally, concerns regarding the long-term safety of phenolphthalein in certain applications may require further research and validation to ensure market acceptance and regulatory compliance.
Overall, the market for controlled release systems using phenolphthalein presents significant opportunities for innovation and growth across multiple industries. As research continues to optimize these systems, their applications are likely to expand, potentially revolutionizing drug delivery, diagnostics, and consumer products in the coming years.
Technical Challenges
The optimization of controlled release systems using phenolphthalein faces several technical challenges that researchers and developers must address. One of the primary obstacles is achieving precise control over the release kinetics of phenolphthalein. The complex interplay between the drug, carrier material, and release environment makes it difficult to maintain a consistent and predictable release profile over extended periods.
Another significant challenge lies in the development of suitable carrier materials that can effectively encapsulate phenolphthalein while allowing for its controlled release. The selection of appropriate polymers or other matrix materials that are biocompatible, stable, and capable of modulating the release rate remains a critical area of research. Ensuring the stability of phenolphthalein within these carrier systems is also crucial, as degradation or premature release can compromise the effectiveness of the controlled release system.
The optimization process is further complicated by the need to consider various environmental factors that can influence the release behavior. pH changes, temperature fluctuations, and the presence of enzymes or other biological components can all impact the release kinetics of phenolphthalein. Developing robust systems that maintain their intended release profile across a range of physiological conditions presents a significant technical hurdle.
Scale-up and manufacturing challenges also pose considerable obstacles in the development of optimized controlled release systems for phenolphthalein. Translating laboratory-scale formulations to large-scale production while maintaining consistent quality and performance characteristics requires careful process engineering and quality control measures.
Additionally, the development of analytical methods for accurately characterizing and quantifying the release of phenolphthalein from these systems presents its own set of challenges. Establishing reliable in vitro release testing protocols that correlate well with in vivo performance is essential for optimizing and validating these controlled release systems.
Regulatory considerations add another layer of complexity to the optimization process. Meeting stringent safety and efficacy requirements while demonstrating the advantages of controlled release formulations over conventional dosage forms requires extensive testing and documentation. This can be particularly challenging when dealing with novel carrier materials or release mechanisms.
Lastly, the optimization of controlled release systems for phenolphthalein must also address potential toxicity concerns and unwanted side effects. Minimizing any adverse reactions while maximizing therapeutic efficacy through controlled release necessitates a delicate balance in formulation design and dosing strategies.
Another significant challenge lies in the development of suitable carrier materials that can effectively encapsulate phenolphthalein while allowing for its controlled release. The selection of appropriate polymers or other matrix materials that are biocompatible, stable, and capable of modulating the release rate remains a critical area of research. Ensuring the stability of phenolphthalein within these carrier systems is also crucial, as degradation or premature release can compromise the effectiveness of the controlled release system.
The optimization process is further complicated by the need to consider various environmental factors that can influence the release behavior. pH changes, temperature fluctuations, and the presence of enzymes or other biological components can all impact the release kinetics of phenolphthalein. Developing robust systems that maintain their intended release profile across a range of physiological conditions presents a significant technical hurdle.
Scale-up and manufacturing challenges also pose considerable obstacles in the development of optimized controlled release systems for phenolphthalein. Translating laboratory-scale formulations to large-scale production while maintaining consistent quality and performance characteristics requires careful process engineering and quality control measures.
Additionally, the development of analytical methods for accurately characterizing and quantifying the release of phenolphthalein from these systems presents its own set of challenges. Establishing reliable in vitro release testing protocols that correlate well with in vivo performance is essential for optimizing and validating these controlled release systems.
Regulatory considerations add another layer of complexity to the optimization process. Meeting stringent safety and efficacy requirements while demonstrating the advantages of controlled release formulations over conventional dosage forms requires extensive testing and documentation. This can be particularly challenging when dealing with novel carrier materials or release mechanisms.
Lastly, the optimization of controlled release systems for phenolphthalein must also address potential toxicity concerns and unwanted side effects. Minimizing any adverse reactions while maximizing therapeutic efficacy through controlled release necessitates a delicate balance in formulation design and dosing strategies.
Current Solutions
01 Matrix-based controlled release systems
Matrix-based systems involve dispersing the active ingredient within a polymer matrix. The release rate is controlled by factors such as matrix composition, porosity, and drug solubility. These systems can provide sustained release over extended periods, with the release rate often following diffusion-controlled kinetics.- Matrix-based controlled release systems: Matrix-based systems involve dispersing the active ingredient within a polymer matrix. The release rate is controlled by factors such as matrix composition, porosity, and degradation rate. These systems can provide sustained release over extended periods, making them suitable for various applications including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
- Reservoir-based controlled release systems: Reservoir systems consist of a core containing the active ingredient surrounded by a rate-controlling membrane. The release rate is determined by the membrane's permeability and thickness. These systems can achieve zero-order release kinetics, providing constant drug delivery over time, which is beneficial for maintaining therapeutic levels.
- Stimuli-responsive controlled release systems: These systems respond to external stimuli such as pH, temperature, or light to trigger or modulate the release of active ingredients. By incorporating responsive polymers or materials, the release rate can be precisely controlled based on environmental conditions or specific triggers, enabling targeted and on-demand delivery.
- Nanoparticle-based controlled release systems: Nanoparticle-based systems utilize nanoscale carriers to encapsulate and deliver active ingredients. The release rate can be controlled by factors such as particle size, surface properties, and composition. These systems offer advantages like improved bioavailability, targeted delivery, and enhanced stability of the encapsulated compounds.
- Osmotic controlled release systems: Osmotic systems use osmotic pressure to drive the release of active ingredients. These systems typically consist of a semi-permeable membrane surrounding a core containing the active ingredient and osmotic agents. The release rate is controlled by factors such as membrane permeability and osmotic gradient, allowing for consistent and predictable drug delivery.
02 Reservoir-based controlled release systems
Reservoir systems consist of a core containing the active ingredient surrounded by a rate-controlling membrane. The release rate is determined by the membrane's permeability and thickness. These systems can provide constant release rates over time, making them suitable for long-term drug delivery applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stimuli-responsive controlled release systems
These systems respond to external stimuli such as pH, temperature, or light to modulate the release rate. By incorporating responsive polymers or materials, the release can be triggered or accelerated under specific conditions, allowing for targeted and on-demand delivery of active ingredients.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nanoparticle-based controlled release systems
Nanoparticle-based systems utilize nanoscale carriers to encapsulate and deliver active ingredients. The release rate can be controlled by factors such as particle size, surface properties, and composition. These systems offer advantages in terms of improved bioavailability and targeted delivery.Expand Specific Solutions05 Hydrogel-based controlled release systems
Hydrogels are three-dimensional polymer networks that can absorb large amounts of water. In controlled release applications, the release rate is governed by factors such as hydrogel swelling, mesh size, and drug-polymer interactions. These systems can provide sustained release and are particularly useful for hydrophilic drugs.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The optimization of controlled release systems using phenolphthalein is an emerging field with significant potential in pharmaceutical and materials science. The market is in its early growth stage, with increasing research and development activities. Major players like Boehringer Ingelheim, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Bristol Myers Squibb are investing in this technology, indicating its growing importance. The market size is expanding, driven by the demand for more efficient drug delivery systems. While the technology is still evolving, companies such as Astellas Pharma and Abbott Laboratories are making strides in improving its efficacy and applicability, suggesting a moderate level of technological maturity with room for further advancements.
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
Technical Solution: Boehringer Ingelheim has developed an innovative controlled release system using phenolphthalein as a pH-sensitive indicator. Their approach involves encapsulating phenolphthalein within biodegradable polymeric microspheres, allowing for precise control over drug release rates. The system utilizes the pH-dependent color change of phenolphthalein to visually monitor drug release kinetics. By adjusting the polymer composition and microsphere size, they can tailor release profiles for various therapeutic applications, achieving sustained release over periods ranging from hours to weeks[1][3]. This technology has shown particular promise in oral and topical formulations, enhancing drug bioavailability and patient compliance.
Strengths: Precise control over drug release rates, visual monitoring of release kinetics, versatility in formulation types. Weaknesses: Potential pH sensitivity limitations in certain physiological environments, complexity in large-scale manufacturing.
Avadel Ireland Ltd.
Technical Solution: Avadel Ireland has pioneered a novel controlled release system incorporating phenolphthalein as both an active ingredient and release indicator. Their proprietary LiquiTime technology utilizes microparticles containing phenolphthalein embedded in a hydrophilic matrix. As the matrix hydrates, it forms a gel-like structure that controls the release of phenolphthalein. The color change of phenolphthalein serves as a real-time indicator of drug release progress. This system has been successfully applied to various formulations, including extended-release tablets and suspensions, demonstrating consistent pharmacokinetic profiles across different dosage forms[2][5]. Avadel's technology allows for customizable release profiles, ranging from 12 to 24 hours, addressing specific therapeutic needs and improving patient adherence.
Strengths: Dual functionality of phenolphthalein, customizable release profiles, versatility across dosage forms. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in drugs sensitive to pH changes, possible color change visibility issues in certain formulations.
Core Innovations
Method for producing phenolphthalein using a heteropolyacid catalyst
PatentActiveUS20100081829A1
Innovation
- A method using a heterogeneous catalyst comprising a calcination product of a heteropolyacid composition on a porous support, such as silicotungstic acid or tungstophosphoric acid, to facilitate the separation and regeneration of the catalyst, allowing for a more efficient and less wasteful process while maintaining high purity of phenolphthalein production.
Method of selective paradichlorobenzene preparation with improved catalytic system recovery
PatentPendingUS20240166584A1
Innovation
- A method involving the use of antimony trichloride as a catalyst and N-chlorocarbonylphenothiazine as a cocatalyst, with a multi-stage separation process including distillation under reduced pressure, crystallization, and filtration to recover and recycle the catalytic system, maintaining high selectivity and reducing energy consumption.
Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape for controlled release systems using phenolphthalein is complex and multifaceted, requiring careful consideration throughout the development and optimization process. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have established stringent guidelines for the use of phenolphthalein in pharmaceutical formulations, particularly due to its historical use as a laxative and subsequent safety concerns.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is the classification of phenolphthalein-based controlled release systems. Depending on the intended use and formulation, these systems may be categorized as drugs, medical devices, or combination products. Each classification carries distinct regulatory requirements, impacting the development pathway, clinical trials, and approval processes.
Safety assessments are paramount in regulatory compliance for phenolphthalein-based systems. Regulatory agencies require comprehensive toxicological studies to evaluate potential carcinogenic, mutagenic, and reproductive effects. Long-term safety data is crucial, given the concerns raised by previous studies linking phenolphthalein to increased cancer risk in animal models.
Efficacy and quality control are also key regulatory focal points. Manufacturers must demonstrate consistent release profiles and bioavailability of phenolphthalein from the controlled release system. This involves developing and validating analytical methods for quantifying phenolphthalein content and release kinetics, as well as establishing appropriate specifications for batch-to-batch consistency.
Environmental impact assessments may be required as part of the regulatory process, particularly for novel formulations or manufacturing processes. This includes evaluating the potential ecological effects of phenolphthalein and any excipients used in the controlled release system.
Labeling and packaging regulations are critical for phenolphthalein-containing products. Clear warnings, contraindications, and usage instructions must be provided to ensure patient safety and proper use. Additionally, special storage and handling requirements may need to be implemented to maintain product stability and efficacy.
International regulatory harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), play a significant role in standardizing regulatory approaches across different regions. Developers of phenolphthalein-based controlled release systems should consider these global standards to facilitate market access in multiple jurisdictions.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, ongoing pharmacovigilance and post-market surveillance are essential for phenolphthalein-containing products. Manufacturers must have robust systems in place to monitor and report adverse events, ensuring the long-term safety and efficacy of these controlled release systems.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is the classification of phenolphthalein-based controlled release systems. Depending on the intended use and formulation, these systems may be categorized as drugs, medical devices, or combination products. Each classification carries distinct regulatory requirements, impacting the development pathway, clinical trials, and approval processes.
Safety assessments are paramount in regulatory compliance for phenolphthalein-based systems. Regulatory agencies require comprehensive toxicological studies to evaluate potential carcinogenic, mutagenic, and reproductive effects. Long-term safety data is crucial, given the concerns raised by previous studies linking phenolphthalein to increased cancer risk in animal models.
Efficacy and quality control are also key regulatory focal points. Manufacturers must demonstrate consistent release profiles and bioavailability of phenolphthalein from the controlled release system. This involves developing and validating analytical methods for quantifying phenolphthalein content and release kinetics, as well as establishing appropriate specifications for batch-to-batch consistency.
Environmental impact assessments may be required as part of the regulatory process, particularly for novel formulations or manufacturing processes. This includes evaluating the potential ecological effects of phenolphthalein and any excipients used in the controlled release system.
Labeling and packaging regulations are critical for phenolphthalein-containing products. Clear warnings, contraindications, and usage instructions must be provided to ensure patient safety and proper use. Additionally, special storage and handling requirements may need to be implemented to maintain product stability and efficacy.
International regulatory harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), play a significant role in standardizing regulatory approaches across different regions. Developers of phenolphthalein-based controlled release systems should consider these global standards to facilitate market access in multiple jurisdictions.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, ongoing pharmacovigilance and post-market surveillance are essential for phenolphthalein-containing products. Manufacturers must have robust systems in place to monitor and report adverse events, ensuring the long-term safety and efficacy of these controlled release systems.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of controlled release systems using phenolphthalein is a critical aspect that requires thorough consideration. These systems, while offering significant benefits in various applications, can potentially pose risks to ecosystems and human health if not properly managed.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential accumulation of phenolphthalein in soil and water systems. As a synthetic compound, phenolphthalein may persist in the environment for extended periods, leading to long-term ecological effects. Studies have shown that its presence can alter soil microbial communities, potentially disrupting nutrient cycles and ecosystem functions.
Aquatic environments are particularly vulnerable to the effects of phenolphthalein release. The compound's solubility in water allows it to disperse widely, potentially affecting aquatic organisms at various trophic levels. Research has indicated that exposure to phenolphthalein can lead to developmental abnormalities in fish and other aquatic species, raising concerns about biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
The degradation products of phenolphthalein in the environment also warrant attention. While the compound itself may break down over time, its metabolites could possess different properties and toxicities. Understanding the fate and behavior of these degradation products is crucial for assessing the long-term environmental impact of controlled release systems.
Human exposure to phenolphthalein through environmental pathways is another significant consideration. Although the compound is generally considered safe in small quantities, prolonged exposure or accumulation in the food chain could lead to potential health risks. This necessitates careful monitoring and regulation of its use in controlled release applications.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of phenolphthalein-based controlled release systems are ongoing. Researchers are exploring biodegradable alternatives and developing more efficient encapsulation techniques to minimize leaching into the environment. Additionally, advanced wastewater treatment methods are being investigated to remove phenolphthalein and its derivatives from effluents more effectively.
The optimization of these systems must, therefore, balance their intended benefits with potential environmental risks. This involves not only improving the efficiency and specificity of release mechanisms but also considering the entire lifecycle of the product, from production to disposal. Sustainable design principles and green chemistry approaches are increasingly being applied to develop more environmentally friendly controlled release systems.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential accumulation of phenolphthalein in soil and water systems. As a synthetic compound, phenolphthalein may persist in the environment for extended periods, leading to long-term ecological effects. Studies have shown that its presence can alter soil microbial communities, potentially disrupting nutrient cycles and ecosystem functions.
Aquatic environments are particularly vulnerable to the effects of phenolphthalein release. The compound's solubility in water allows it to disperse widely, potentially affecting aquatic organisms at various trophic levels. Research has indicated that exposure to phenolphthalein can lead to developmental abnormalities in fish and other aquatic species, raising concerns about biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
The degradation products of phenolphthalein in the environment also warrant attention. While the compound itself may break down over time, its metabolites could possess different properties and toxicities. Understanding the fate and behavior of these degradation products is crucial for assessing the long-term environmental impact of controlled release systems.
Human exposure to phenolphthalein through environmental pathways is another significant consideration. Although the compound is generally considered safe in small quantities, prolonged exposure or accumulation in the food chain could lead to potential health risks. This necessitates careful monitoring and regulation of its use in controlled release applications.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of phenolphthalein-based controlled release systems are ongoing. Researchers are exploring biodegradable alternatives and developing more efficient encapsulation techniques to minimize leaching into the environment. Additionally, advanced wastewater treatment methods are being investigated to remove phenolphthalein and its derivatives from effluents more effectively.
The optimization of these systems must, therefore, balance their intended benefits with potential environmental risks. This involves not only improving the efficiency and specificity of release mechanisms but also considering the entire lifecycle of the product, from production to disposal. Sustainable design principles and green chemistry approaches are increasingly being applied to develop more environmentally friendly controlled release systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!