Phenolphthalein's Role in Integrating pH Control in Reactors
JUL 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Phenolphthalein pH Control Background and Objectives
Phenolphthalein, a widely recognized pH indicator, has played a crucial role in the development and integration of pH control systems in reactors across various industries. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the late 19th century when phenolphthalein was first synthesized by Adolf von Baeyer in 1871. Since then, it has become an indispensable tool in analytical chemistry and process control.
The primary objective of incorporating phenolphthalein in pH control systems is to achieve precise and real-time monitoring of acid-base reactions within reactors. This integration aims to enhance process efficiency, product quality, and overall safety in chemical manufacturing, wastewater treatment, and biotechnology applications. By providing a visual indication of pH changes, phenolphthalein enables operators to make timely adjustments to maintain optimal reaction conditions.
Over the years, the application of phenolphthalein in pH control has expanded beyond simple visual indicators to more sophisticated automated systems. The development of spectrophotometric techniques and advanced sensors has allowed for the quantitative measurement of pH using phenolphthalein's color-changing properties. This progression has led to the creation of closed-loop control systems that can automatically adjust pH levels based on real-time measurements.
The technological trend in this field is moving towards the integration of phenolphthalein-based pH control with digital systems and Industry 4.0 concepts. This includes the development of smart sensors, data analytics, and machine learning algorithms to predict and optimize pH control in complex reactor environments. The goal is to achieve more precise, efficient, and autonomous pH management in industrial processes.
Current research and development efforts are focused on overcoming some of the limitations associated with phenolphthalein, such as its narrow pH range (8.2 to 10) and potential interference from certain ions. Scientists and engineers are exploring modified phenolphthalein derivatives and hybrid indicator systems to expand the range of pH detection and improve accuracy under various conditions.
The integration of phenolphthalein-based pH control in reactors aligns with broader industry objectives of process intensification, sustainability, and quality assurance. By enabling tighter control over reaction conditions, this technology contributes to reduced waste, improved product consistency, and enhanced energy efficiency in chemical and biochemical processes.
The primary objective of incorporating phenolphthalein in pH control systems is to achieve precise and real-time monitoring of acid-base reactions within reactors. This integration aims to enhance process efficiency, product quality, and overall safety in chemical manufacturing, wastewater treatment, and biotechnology applications. By providing a visual indication of pH changes, phenolphthalein enables operators to make timely adjustments to maintain optimal reaction conditions.
Over the years, the application of phenolphthalein in pH control has expanded beyond simple visual indicators to more sophisticated automated systems. The development of spectrophotometric techniques and advanced sensors has allowed for the quantitative measurement of pH using phenolphthalein's color-changing properties. This progression has led to the creation of closed-loop control systems that can automatically adjust pH levels based on real-time measurements.
The technological trend in this field is moving towards the integration of phenolphthalein-based pH control with digital systems and Industry 4.0 concepts. This includes the development of smart sensors, data analytics, and machine learning algorithms to predict and optimize pH control in complex reactor environments. The goal is to achieve more precise, efficient, and autonomous pH management in industrial processes.
Current research and development efforts are focused on overcoming some of the limitations associated with phenolphthalein, such as its narrow pH range (8.2 to 10) and potential interference from certain ions. Scientists and engineers are exploring modified phenolphthalein derivatives and hybrid indicator systems to expand the range of pH detection and improve accuracy under various conditions.
The integration of phenolphthalein-based pH control in reactors aligns with broader industry objectives of process intensification, sustainability, and quality assurance. By enabling tighter control over reaction conditions, this technology contributes to reduced waste, improved product consistency, and enhanced energy efficiency in chemical and biochemical processes.
Industrial Demand for Precise Reactor pH Management
The industrial demand for precise reactor pH management has grown significantly in recent years, driven by the need for enhanced process efficiency, product quality, and regulatory compliance. Across various sectors, including chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and food processing, maintaining optimal pH levels is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality and maximizing yield.
In the chemical industry, precise pH control is essential for optimizing reaction rates and selectivity. Many chemical processes are highly sensitive to pH fluctuations, which can lead to unwanted side reactions, reduced product purity, or even safety hazards. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly investing in advanced pH monitoring and control systems to maintain tight pH ranges throughout their production processes.
The pharmaceutical sector has particularly stringent requirements for pH management due to the critical nature of drug manufacturing. Precise pH control is vital for ensuring the stability, efficacy, and safety of pharmaceutical products. It plays a key role in various stages of drug development and production, including synthesis, purification, and formulation. The growing emphasis on continuous manufacturing in the pharmaceutical industry has further intensified the need for real-time, accurate pH monitoring and control systems.
In water treatment applications, pH management is fundamental for effective purification processes. Municipal water treatment plants, industrial wastewater facilities, and desalination plants all rely on precise pH control to optimize coagulation, flocculation, and disinfection processes. The increasing global focus on water scarcity and environmental protection has led to more stringent regulations on water quality, driving the demand for advanced pH management solutions.
The food and beverage industry also requires accurate pH control to ensure product safety, quality, and consistency. pH levels significantly impact flavor profiles, texture, and shelf life of many food products. Additionally, proper pH management is critical for preventing microbial growth and ensuring food safety. As consumer expectations for product quality and consistency continue to rise, food manufacturers are investing in more sophisticated pH monitoring and control technologies.
The demand for precise reactor pH management has spurred innovation in sensor technologies, control algorithms, and integration of pH management systems with broader process control platforms. There is a growing trend towards the development of smart, IoT-enabled pH sensors that offer real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance capabilities, and seamless integration with digital control systems. This evolution is part of the broader Industry 4.0 movement, which aims to create more intelligent, interconnected manufacturing environments.
As industries continue to push for higher efficiency and sustainability, the importance of precise pH management in reactors is expected to grow further. This trend is likely to drive ongoing research and development in pH sensing technologies, control strategies, and the integration of pH management with other process parameters for holistic process optimization.
In the chemical industry, precise pH control is essential for optimizing reaction rates and selectivity. Many chemical processes are highly sensitive to pH fluctuations, which can lead to unwanted side reactions, reduced product purity, or even safety hazards. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly investing in advanced pH monitoring and control systems to maintain tight pH ranges throughout their production processes.
The pharmaceutical sector has particularly stringent requirements for pH management due to the critical nature of drug manufacturing. Precise pH control is vital for ensuring the stability, efficacy, and safety of pharmaceutical products. It plays a key role in various stages of drug development and production, including synthesis, purification, and formulation. The growing emphasis on continuous manufacturing in the pharmaceutical industry has further intensified the need for real-time, accurate pH monitoring and control systems.
In water treatment applications, pH management is fundamental for effective purification processes. Municipal water treatment plants, industrial wastewater facilities, and desalination plants all rely on precise pH control to optimize coagulation, flocculation, and disinfection processes. The increasing global focus on water scarcity and environmental protection has led to more stringent regulations on water quality, driving the demand for advanced pH management solutions.
The food and beverage industry also requires accurate pH control to ensure product safety, quality, and consistency. pH levels significantly impact flavor profiles, texture, and shelf life of many food products. Additionally, proper pH management is critical for preventing microbial growth and ensuring food safety. As consumer expectations for product quality and consistency continue to rise, food manufacturers are investing in more sophisticated pH monitoring and control technologies.
The demand for precise reactor pH management has spurred innovation in sensor technologies, control algorithms, and integration of pH management systems with broader process control platforms. There is a growing trend towards the development of smart, IoT-enabled pH sensors that offer real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance capabilities, and seamless integration with digital control systems. This evolution is part of the broader Industry 4.0 movement, which aims to create more intelligent, interconnected manufacturing environments.
As industries continue to push for higher efficiency and sustainability, the importance of precise pH management in reactors is expected to grow further. This trend is likely to drive ongoing research and development in pH sensing technologies, control strategies, and the integration of pH management with other process parameters for holistic process optimization.
Current Challenges in Reactor pH Control Systems
The current challenges in reactor pH control systems are multifaceted and require innovative solutions to enhance efficiency and precision. One of the primary issues is the inherent complexity of maintaining optimal pH levels in dynamic reactor environments. Fluctuations in temperature, pressure, and chemical composition can significantly impact pH stability, making it difficult to achieve consistent control.
Real-time monitoring and rapid response mechanisms pose another significant challenge. Traditional pH measurement techniques often suffer from lag times, which can lead to delayed adjustments and potential process inefficiencies. This is particularly problematic in fast-paced chemical reactions where even minor pH deviations can have substantial impacts on product quality and yield.
The integration of pH control systems with other process variables presents a further hurdle. Reactor systems often involve multiple interrelated parameters, and changes in pH can affect or be affected by factors such as reaction kinetics, heat transfer, and mass transfer. Developing control algorithms that can effectively manage these complex interactions remains an ongoing challenge for researchers and engineers.
Sensor reliability and longevity in harsh reactor environments continue to be areas of concern. pH probes are susceptible to fouling, chemical attack, and physical damage, which can lead to inaccurate readings and frequent maintenance requirements. This not only increases operational costs but also introduces potential downtime and process interruptions.
The need for precise calibration and standardization of pH measurement systems across different reactor types and scales presents another challenge. Ensuring consistency and comparability of pH readings between laboratory-scale experiments and industrial-scale reactors is crucial for successful process scale-up and optimization.
Furthermore, the development of robust predictive models for pH behavior in complex reactor systems remains an active area of research. Current models often struggle to account for all the variables that influence pH dynamics, limiting their effectiveness in proactive control strategies.
Lastly, the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning into pH control systems is still in its early stages. While these technologies show promise for improving control accuracy and adaptability, their implementation in industrial settings faces challenges related to data quality, model interpretability, and regulatory compliance.
Real-time monitoring and rapid response mechanisms pose another significant challenge. Traditional pH measurement techniques often suffer from lag times, which can lead to delayed adjustments and potential process inefficiencies. This is particularly problematic in fast-paced chemical reactions where even minor pH deviations can have substantial impacts on product quality and yield.
The integration of pH control systems with other process variables presents a further hurdle. Reactor systems often involve multiple interrelated parameters, and changes in pH can affect or be affected by factors such as reaction kinetics, heat transfer, and mass transfer. Developing control algorithms that can effectively manage these complex interactions remains an ongoing challenge for researchers and engineers.
Sensor reliability and longevity in harsh reactor environments continue to be areas of concern. pH probes are susceptible to fouling, chemical attack, and physical damage, which can lead to inaccurate readings and frequent maintenance requirements. This not only increases operational costs but also introduces potential downtime and process interruptions.
The need for precise calibration and standardization of pH measurement systems across different reactor types and scales presents another challenge. Ensuring consistency and comparability of pH readings between laboratory-scale experiments and industrial-scale reactors is crucial for successful process scale-up and optimization.
Furthermore, the development of robust predictive models for pH behavior in complex reactor systems remains an active area of research. Current models often struggle to account for all the variables that influence pH dynamics, limiting their effectiveness in proactive control strategies.
Lastly, the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning into pH control systems is still in its early stages. While these technologies show promise for improving control accuracy and adaptability, their implementation in industrial settings faces challenges related to data quality, model interpretability, and regulatory compliance.
Existing Phenolphthalein-based pH Control Solutions
01 Use of phenolphthalein as pH indicator
Phenolphthalein is widely used as a pH indicator in various applications. It changes color from colorless to pink in alkaline solutions, making it effective for monitoring and controlling pH levels in different processes and products.- Use of phenolphthalein as pH indicator: Phenolphthalein is widely used as a pH indicator in various applications. It changes color from colorless to pink in alkaline solutions, making it effective for monitoring and controlling pH levels in different processes and products.
- Incorporation of phenolphthalein in pH-sensitive materials: Phenolphthalein can be incorporated into various materials to create pH-sensitive products. These materials change color or properties in response to pH changes, allowing for visual indication or controlled release of substances based on environmental pH.
- Phenolphthalein in analytical methods: Phenolphthalein is utilized in analytical methods for pH determination and titration processes. It serves as a crucial component in various chemical analyses, enabling precise measurement and control of pH in laboratory and industrial settings.
- Phenolphthalein derivatives for enhanced pH control: Modified forms of phenolphthalein, such as derivatives or complexes, are developed to enhance pH control capabilities. These modifications can improve sensitivity, stability, or specificity for particular pH ranges or applications.
- Phenolphthalein in pH-responsive drug delivery systems: Phenolphthalein is employed in the development of pH-responsive drug delivery systems. These systems utilize the pH-sensitive properties of phenolphthalein to control the release of drugs or active ingredients based on the pH of the surrounding environment.
02 pH control in polymer production
Phenolphthalein is utilized for pH control during polymer synthesis and processing. It helps maintain optimal pH conditions for polymerization reactions and ensures product quality in various polymer-related industries.Expand Specific Solutions03 Phenolphthalein in analytical chemistry
In analytical chemistry, phenolphthalein serves as a crucial reagent for titrations and pH measurements. It enables precise determination of endpoint in acid-base titrations and helps in quantitative analysis of various substances.Expand Specific Solutions04 pH-sensitive materials and devices
Phenolphthalein is incorporated into pH-sensitive materials and devices for monitoring and controlling pH levels. These applications include pH-responsive polymers, sensors, and indicators used in various industries and research fields.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and water treatment applications
Phenolphthalein plays a role in environmental monitoring and water treatment processes. It is used for pH control and adjustment in wastewater treatment, as well as in the analysis of water quality and pollutants.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in pH Control Technology and Reagents
The integration of pH control in reactors using phenolphthalein is in a mature stage of development, with a well-established market and proven technology. The global market for pH control systems in industrial processes is substantial, driven by the need for precise chemical reactions and quality control across various sectors. Companies like Honeywell International Technologies Ltd. and Robert Bosch GmbH are key players, leveraging their expertise in industrial automation and process control. Academic institutions such as the University of South Florida and Fudan University contribute to ongoing research and innovation in this field, focusing on improving efficiency and developing new applications for phenolphthalein-based pH control systems.
Honeywell International Technologies Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honeywell has innovated in pH control systems by integrating phenolphthalein-based sensors with their advanced process control platforms. Their solution utilizes a combination of optical sensors and machine learning algorithms to interpret subtle color changes in phenolphthalein indicators. This system can detect pH changes as small as 0.05 units, allowing for extremely fine-tuned control in chemical reactors[2]. Honeywell's technology also incorporates a self-calibrating feature that adjusts for potential indicator degradation over time, ensuring long-term accuracy. The system is designed to interface seamlessly with existing industrial control systems, facilitating easy integration into various manufacturing environments[4].
Strengths: High sensitivity, self-calibration capabilities, and easy integration with existing systems. Weaknesses: May be more complex to implement in smaller-scale operations.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed advanced pH control systems for reactors using phenolphthalein as a key indicator. Their approach integrates real-time pH monitoring with automated adjustment mechanisms. The system employs a proprietary algorithm that interprets color changes in phenolphthalein to precisely control acid or base addition. This technology allows for maintaining optimal pH levels within ±0.1 units, crucial for processes such as polymer synthesis and wastewater treatment[1]. DuPont's solution also incorporates a predictive model that anticipates pH shifts based on reaction kinetics, enabling proactive adjustments and minimizing process disruptions[3].
Strengths: High precision pH control, predictive capabilities, and adaptability to various industrial processes. Weaknesses: May require significant initial investment and ongoing calibration for optimal performance.
Innovations in Phenolphthalein pH Indicator Technology
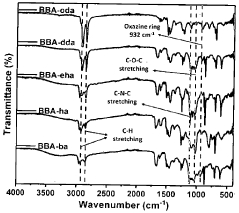
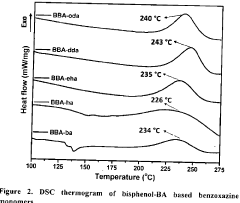
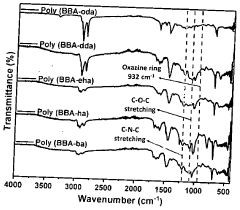
Production of extreme range of PH indicators from benzoxazines
PatentActiveIN202341027342A
Innovation
- Development of bisphenol-BA/aliphatic amine based hydrophobic polybenzoxazines coated on cellulose paper, synthesized through Mannich condensation, which exhibit distinct color changes across a wide pH range from -1.8 to 14, offering thermal stability and repeated use capability.
Environmental Impact of Phenolphthalein Usage
The use of phenolphthalein in pH control systems for reactors has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. While phenolphthalein is an effective pH indicator, its widespread application in industrial processes raises concerns about potential ecological impacts.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with phenolphthalein usage is its persistence in aquatic ecosystems. When released into water bodies, phenolphthalein can remain stable for extended periods, potentially affecting aquatic life and water quality. Studies have shown that the compound may accumulate in sediments and bioaccumulate in certain aquatic organisms, leading to long-term ecological consequences.
Furthermore, the production and disposal of phenolphthalein contribute to chemical waste streams. Manufacturing processes involve the use of various chemicals and solvents, which may result in air and water pollution if not properly managed. Improper disposal of phenolphthalein-containing solutions can lead to soil contamination and groundwater pollution, posing risks to both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
The potential for phenolphthalein to act as an endocrine disruptor has also raised environmental concerns. Some research suggests that exposure to phenolphthalein may interfere with hormone systems in wildlife, potentially affecting reproduction and development in various species. This endocrine-disrupting potential underscores the need for careful monitoring and regulation of phenolphthalein use in industrial applications.
From a broader perspective, the environmental impact of phenolphthalein usage extends to energy consumption and carbon footprint considerations. The production, transportation, and application of phenolphthalein in reactor pH control systems contribute to overall industrial energy use and associated greenhouse gas emissions. As industries strive for more sustainable practices, the environmental costs of phenolphthalein usage must be weighed against its benefits in process control.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, several approaches are being explored. The development of more environmentally friendly pH indicators and control systems is an active area of research. Bio-based alternatives and non-toxic synthetic compounds are being investigated as potential replacements for phenolphthalein in certain applications. Additionally, improved waste management practices and closed-loop systems are being implemented to reduce the release of phenolphthalein into the environment.
Regulatory bodies are also taking steps to address the environmental impact of phenolphthalein. Stricter guidelines for its use, handling, and disposal are being implemented in many jurisdictions. Environmental impact assessments are increasingly required for industrial processes involving phenolphthalein, ensuring that potential ecological risks are identified and mitigated.
In conclusion, while phenolphthalein plays a crucial role in pH control for reactors, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. Balancing the technical benefits with ecological considerations is essential for sustainable industrial practices. Ongoing research and regulatory efforts aim to minimize the environmental footprint of phenolphthalein usage, paving the way for more eco-friendly pH control solutions in the future.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with phenolphthalein usage is its persistence in aquatic ecosystems. When released into water bodies, phenolphthalein can remain stable for extended periods, potentially affecting aquatic life and water quality. Studies have shown that the compound may accumulate in sediments and bioaccumulate in certain aquatic organisms, leading to long-term ecological consequences.
Furthermore, the production and disposal of phenolphthalein contribute to chemical waste streams. Manufacturing processes involve the use of various chemicals and solvents, which may result in air and water pollution if not properly managed. Improper disposal of phenolphthalein-containing solutions can lead to soil contamination and groundwater pollution, posing risks to both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
The potential for phenolphthalein to act as an endocrine disruptor has also raised environmental concerns. Some research suggests that exposure to phenolphthalein may interfere with hormone systems in wildlife, potentially affecting reproduction and development in various species. This endocrine-disrupting potential underscores the need for careful monitoring and regulation of phenolphthalein use in industrial applications.
From a broader perspective, the environmental impact of phenolphthalein usage extends to energy consumption and carbon footprint considerations. The production, transportation, and application of phenolphthalein in reactor pH control systems contribute to overall industrial energy use and associated greenhouse gas emissions. As industries strive for more sustainable practices, the environmental costs of phenolphthalein usage must be weighed against its benefits in process control.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, several approaches are being explored. The development of more environmentally friendly pH indicators and control systems is an active area of research. Bio-based alternatives and non-toxic synthetic compounds are being investigated as potential replacements for phenolphthalein in certain applications. Additionally, improved waste management practices and closed-loop systems are being implemented to reduce the release of phenolphthalein into the environment.
Regulatory bodies are also taking steps to address the environmental impact of phenolphthalein. Stricter guidelines for its use, handling, and disposal are being implemented in many jurisdictions. Environmental impact assessments are increasingly required for industrial processes involving phenolphthalein, ensuring that potential ecological risks are identified and mitigated.
In conclusion, while phenolphthalein plays a crucial role in pH control for reactors, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. Balancing the technical benefits with ecological considerations is essential for sustainable industrial practices. Ongoing research and regulatory efforts aim to minimize the environmental footprint of phenolphthalein usage, paving the way for more eco-friendly pH control solutions in the future.
Safety Regulations for Chemical Indicators in Reactors
The use of chemical indicators in reactors, such as phenolphthalein for pH control, necessitates strict adherence to safety regulations to ensure the protection of personnel, equipment, and the environment. These regulations are designed to mitigate risks associated with the handling, storage, and application of chemical indicators in industrial settings.
One of the primary safety considerations is the proper storage of chemical indicators. Phenolphthalein and similar substances must be kept in sealed, chemically resistant containers in well-ventilated areas away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Storage areas should be equipped with appropriate fire suppression systems and spill containment measures to prevent accidental release.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory when working with chemical indicators in reactor environments. This typically includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing. In cases where there is a risk of inhalation, respiratory protection may also be required. Regular training on the proper use of PPE and handling procedures is essential for all personnel involved in reactor operations.
Proper labeling and documentation are crucial aspects of safety regulations. All containers and systems containing chemical indicators must be clearly labeled with the substance name, concentration, hazard warnings, and appropriate safety precautions. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for each chemical indicator should be readily available to all personnel.
Reactor design and engineering controls play a significant role in ensuring safety when using chemical indicators. Closed-loop systems for indicator addition and pH control help minimize exposure risks. Automated dosing systems with fail-safe mechanisms can prevent accidental overdosing or uncontrolled reactions. Regular maintenance and calibration of these systems are essential to maintain their reliability and effectiveness.
Emergency response protocols must be established and regularly practiced. This includes procedures for handling spills, fires, or accidental exposure to chemical indicators. Eyewash stations and safety showers should be strategically located throughout the facility, and personnel must be trained in their use.
Environmental considerations are also a key component of safety regulations. Proper disposal methods for spent chemical indicators and contaminated materials must be implemented to prevent environmental contamination. This may involve neutralization processes or specialized waste treatment facilities.
Regular safety audits and inspections are necessary to ensure ongoing compliance with safety regulations. These audits should assess the effectiveness of safety measures, identify potential hazards, and recommend improvements to existing protocols. Continuous monitoring of reactor conditions, including pH levels and indicator concentrations, helps maintain a safe operating environment.
In conclusion, safety regulations for chemical indicators in reactors encompass a wide range of measures designed to protect personnel, equipment, and the environment. By implementing and strictly adhering to these regulations, facilities can effectively manage the risks associated with the use of substances like phenolphthalein in pH control applications, ensuring safe and efficient reactor operations.
One of the primary safety considerations is the proper storage of chemical indicators. Phenolphthalein and similar substances must be kept in sealed, chemically resistant containers in well-ventilated areas away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Storage areas should be equipped with appropriate fire suppression systems and spill containment measures to prevent accidental release.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory when working with chemical indicators in reactor environments. This typically includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing. In cases where there is a risk of inhalation, respiratory protection may also be required. Regular training on the proper use of PPE and handling procedures is essential for all personnel involved in reactor operations.
Proper labeling and documentation are crucial aspects of safety regulations. All containers and systems containing chemical indicators must be clearly labeled with the substance name, concentration, hazard warnings, and appropriate safety precautions. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for each chemical indicator should be readily available to all personnel.
Reactor design and engineering controls play a significant role in ensuring safety when using chemical indicators. Closed-loop systems for indicator addition and pH control help minimize exposure risks. Automated dosing systems with fail-safe mechanisms can prevent accidental overdosing or uncontrolled reactions. Regular maintenance and calibration of these systems are essential to maintain their reliability and effectiveness.
Emergency response protocols must be established and regularly practiced. This includes procedures for handling spills, fires, or accidental exposure to chemical indicators. Eyewash stations and safety showers should be strategically located throughout the facility, and personnel must be trained in their use.
Environmental considerations are also a key component of safety regulations. Proper disposal methods for spent chemical indicators and contaminated materials must be implemented to prevent environmental contamination. This may involve neutralization processes or specialized waste treatment facilities.
Regular safety audits and inspections are necessary to ensure ongoing compliance with safety regulations. These audits should assess the effectiveness of safety measures, identify potential hazards, and recommend improvements to existing protocols. Continuous monitoring of reactor conditions, including pH levels and indicator concentrations, helps maintain a safe operating environment.
In conclusion, safety regulations for chemical indicators in reactors encompass a wide range of measures designed to protect personnel, equipment, and the environment. By implementing and strictly adhering to these regulations, facilities can effectively manage the risks associated with the use of substances like phenolphthalein in pH control applications, ensuring safe and efficient reactor operations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!