Steering Wheel Design in Future Mobility Solutions
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Future Steering Tech Evolution and Objectives
The evolution of steering wheel design in future mobility solutions is closely tied to the broader trends in automotive technology and changing consumer expectations. Historically, steering wheels have been the primary interface between driver and vehicle, but this relationship is undergoing a significant transformation.
The automotive industry is moving towards increased automation and electrification, which is reshaping the role of the steering wheel. As vehicles become more autonomous, the traditional steering wheel may become obsolete in certain scenarios, leading to the exploration of alternative control interfaces.
One of the key objectives in future steering technology is to enhance safety while maintaining or improving driver engagement. This includes the integration of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) directly into the steering wheel, providing haptic feedback and visual cues to alert drivers of potential hazards or lane departures.
Another important goal is to create more adaptable and customizable steering interfaces. Future steering wheels may incorporate shape-shifting technologies, allowing them to retract or transform based on the level of autonomous driving engaged. This adaptability aims to optimize the use of cabin space and improve the overall user experience.
Connectivity is also a crucial aspect of future steering wheel design. The integration of touch-sensitive surfaces and gesture controls on the steering wheel is expected to increase, allowing drivers to manage various vehicle functions without taking their hands off the wheel. This aligns with the broader trend of creating more intuitive and less distracting user interfaces in vehicles.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in the automotive industry, steering wheel design is also focusing on the use of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes. This includes exploring alternatives to traditional leather wraps and investigating the potential of recycled or bio-based materials.
The ultimate objective of future steering technology is to seamlessly blend human control with autonomous capabilities, creating a fluid and intuitive driving experience. This may involve the development of steer-by-wire systems that eliminate the physical connection between the steering wheel and the wheels, allowing for more flexible cabin designs and improved vehicle dynamics.
In conclusion, the evolution of steering wheel design in future mobility solutions is driven by the need to adapt to autonomous driving technologies, enhance safety and connectivity, improve sustainability, and create more engaging and customizable user experiences. The steering wheel of the future will likely be a multifunctional interface that goes far beyond its traditional role, serving as a central hub for vehicle control and information display in the evolving landscape of automotive technology.
The automotive industry is moving towards increased automation and electrification, which is reshaping the role of the steering wheel. As vehicles become more autonomous, the traditional steering wheel may become obsolete in certain scenarios, leading to the exploration of alternative control interfaces.
One of the key objectives in future steering technology is to enhance safety while maintaining or improving driver engagement. This includes the integration of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) directly into the steering wheel, providing haptic feedback and visual cues to alert drivers of potential hazards or lane departures.
Another important goal is to create more adaptable and customizable steering interfaces. Future steering wheels may incorporate shape-shifting technologies, allowing them to retract or transform based on the level of autonomous driving engaged. This adaptability aims to optimize the use of cabin space and improve the overall user experience.
Connectivity is also a crucial aspect of future steering wheel design. The integration of touch-sensitive surfaces and gesture controls on the steering wheel is expected to increase, allowing drivers to manage various vehicle functions without taking their hands off the wheel. This aligns with the broader trend of creating more intuitive and less distracting user interfaces in vehicles.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in the automotive industry, steering wheel design is also focusing on the use of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes. This includes exploring alternatives to traditional leather wraps and investigating the potential of recycled or bio-based materials.
The ultimate objective of future steering technology is to seamlessly blend human control with autonomous capabilities, creating a fluid and intuitive driving experience. This may involve the development of steer-by-wire systems that eliminate the physical connection between the steering wheel and the wheels, allowing for more flexible cabin designs and improved vehicle dynamics.
In conclusion, the evolution of steering wheel design in future mobility solutions is driven by the need to adapt to autonomous driving technologies, enhance safety and connectivity, improve sustainability, and create more engaging and customizable user experiences. The steering wheel of the future will likely be a multifunctional interface that goes far beyond its traditional role, serving as a central hub for vehicle control and information display in the evolving landscape of automotive technology.
Market Trends in Autonomous Vehicle Controls
The autonomous vehicle market is experiencing rapid growth and transformation, driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer preferences. This shift is significantly impacting the design and functionality of vehicle controls, particularly steering wheels. As autonomous driving capabilities progress, the role of the steering wheel is evolving from a primary control interface to a more nuanced and multifunctional component.
Market research indicates a growing demand for vehicles with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous features. Consumers are increasingly prioritizing safety, convenience, and connectivity in their vehicle purchases. This trend is reflected in the rising adoption of semi-autonomous vehicles and the development of fully autonomous vehicles by major automotive manufacturers and technology companies.
The steering wheel, as a central element of vehicle control, is undergoing substantial redesign to accommodate these market trends. Traditional circular steering wheels are being reimagined to incorporate touch-sensitive surfaces, haptic feedback, and integrated displays. These features allow for seamless interaction with vehicle systems and provide real-time information to the driver or occupant.
In the context of autonomous vehicles, the market is seeing a shift towards retractable or stowable steering wheels. This design approach allows for a more flexible interior space when the vehicle is operating in fully autonomous mode. Some concept vehicles have even explored the idea of removable steering wheels or alternative control interfaces that can be deployed only when needed.
The integration of advanced sensors and cameras into steering wheels is another significant market trend. These technologies enable driver monitoring systems, which are becoming increasingly important for ensuring safe transitions between autonomous and manual driving modes. The market for these integrated systems is expected to grow substantially as regulations around driver monitoring become more stringent.
Customization and personalization of steering wheel interfaces are also gaining traction in the market. Automakers are exploring ways to allow drivers to customize the layout and functionality of steering wheel controls to suit their preferences. This trend aligns with the broader movement towards more personalized and user-centric vehicle experiences.
As the automotive industry moves towards higher levels of autonomy, there is a growing market for steering systems that can seamlessly transition between manual and autonomous control. This includes the development of steer-by-wire systems, which eliminate the need for mechanical linkages and offer greater flexibility in steering wheel design and placement.
The market for steering wheel alternatives is also emerging, particularly for fully autonomous vehicles. This includes the exploration of joysticks, touchpads, and voice-controlled systems as potential replacements for traditional steering wheels in certain vehicle types or use cases.
Market research indicates a growing demand for vehicles with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous features. Consumers are increasingly prioritizing safety, convenience, and connectivity in their vehicle purchases. This trend is reflected in the rising adoption of semi-autonomous vehicles and the development of fully autonomous vehicles by major automotive manufacturers and technology companies.
The steering wheel, as a central element of vehicle control, is undergoing substantial redesign to accommodate these market trends. Traditional circular steering wheels are being reimagined to incorporate touch-sensitive surfaces, haptic feedback, and integrated displays. These features allow for seamless interaction with vehicle systems and provide real-time information to the driver or occupant.
In the context of autonomous vehicles, the market is seeing a shift towards retractable or stowable steering wheels. This design approach allows for a more flexible interior space when the vehicle is operating in fully autonomous mode. Some concept vehicles have even explored the idea of removable steering wheels or alternative control interfaces that can be deployed only when needed.
The integration of advanced sensors and cameras into steering wheels is another significant market trend. These technologies enable driver monitoring systems, which are becoming increasingly important for ensuring safe transitions between autonomous and manual driving modes. The market for these integrated systems is expected to grow substantially as regulations around driver monitoring become more stringent.
Customization and personalization of steering wheel interfaces are also gaining traction in the market. Automakers are exploring ways to allow drivers to customize the layout and functionality of steering wheel controls to suit their preferences. This trend aligns with the broader movement towards more personalized and user-centric vehicle experiences.
As the automotive industry moves towards higher levels of autonomy, there is a growing market for steering systems that can seamlessly transition between manual and autonomous control. This includes the development of steer-by-wire systems, which eliminate the need for mechanical linkages and offer greater flexibility in steering wheel design and placement.
The market for steering wheel alternatives is also emerging, particularly for fully autonomous vehicles. This includes the exploration of joysticks, touchpads, and voice-controlled systems as potential replacements for traditional steering wheels in certain vehicle types or use cases.
Current Steering Systems and Limitations
Current steering systems in vehicles predominantly rely on mechanical linkages and hydraulic or electric power assistance. These systems have evolved significantly over the years, offering improved control, comfort, and safety. However, they still face several limitations in the context of future mobility solutions.
Traditional mechanical steering systems consist of a steering wheel connected to a steering column, which transfers the driver's input to the steering gear and ultimately to the wheels. While reliable and cost-effective, these systems lack the flexibility and adaptability required for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies.
Hydraulic power steering systems, which use fluid pressure to assist in turning the wheels, have been widely adopted for their smooth operation and reduced driver effort. However, they are energy-intensive, contributing to increased fuel consumption and emissions. Additionally, the complexity of hydraulic systems makes them prone to leaks and requires regular maintenance.
Electric power steering (EPS) systems have gained popularity in recent years due to their improved efficiency and compatibility with modern vehicle electronics. EPS uses an electric motor to assist steering, offering better fuel economy and the ability to integrate with various driver assistance features. Despite these advantages, current EPS systems still have limitations in terms of feedback and precision, particularly in high-performance driving scenarios.
One significant limitation of current steering systems is their fixed steering ratio. This means that the relationship between steering wheel movement and wheel angle remains constant, regardless of driving conditions or vehicle speed. This can result in suboptimal steering response in different scenarios, such as low-speed maneuvering or high-speed highway driving.
Another challenge is the physical connection between the steering wheel and the wheels, which limits the potential for innovative interior designs and space utilization in future vehicles. This constraint becomes particularly relevant as we move towards autonomous vehicles, where traditional steering wheels may become obsolete or require significant redesign.
Current steering systems also face limitations in terms of personalization and adaptability. They typically offer limited adjustability in terms of steering feel, feedback, and responsiveness, which may not cater to individual driver preferences or varying driving conditions.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced driver assistance systems and autonomous driving technologies with traditional steering systems presents challenges. These systems often require precise control over steering inputs, which can be difficult to achieve with conventional mechanical linkages.
As we look towards future mobility solutions, there is a growing need for steering systems that can overcome these limitations. This includes the development of steer-by-wire technologies, which eliminate the physical connection between the steering wheel and wheels, offering greater design flexibility and improved integration with autonomous systems. Additionally, adaptive steering systems that can adjust their characteristics based on driving conditions and driver preferences are becoming increasingly important.
Traditional mechanical steering systems consist of a steering wheel connected to a steering column, which transfers the driver's input to the steering gear and ultimately to the wheels. While reliable and cost-effective, these systems lack the flexibility and adaptability required for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies.
Hydraulic power steering systems, which use fluid pressure to assist in turning the wheels, have been widely adopted for their smooth operation and reduced driver effort. However, they are energy-intensive, contributing to increased fuel consumption and emissions. Additionally, the complexity of hydraulic systems makes them prone to leaks and requires regular maintenance.
Electric power steering (EPS) systems have gained popularity in recent years due to their improved efficiency and compatibility with modern vehicle electronics. EPS uses an electric motor to assist steering, offering better fuel economy and the ability to integrate with various driver assistance features. Despite these advantages, current EPS systems still have limitations in terms of feedback and precision, particularly in high-performance driving scenarios.
One significant limitation of current steering systems is their fixed steering ratio. This means that the relationship between steering wheel movement and wheel angle remains constant, regardless of driving conditions or vehicle speed. This can result in suboptimal steering response in different scenarios, such as low-speed maneuvering or high-speed highway driving.
Another challenge is the physical connection between the steering wheel and the wheels, which limits the potential for innovative interior designs and space utilization in future vehicles. This constraint becomes particularly relevant as we move towards autonomous vehicles, where traditional steering wheels may become obsolete or require significant redesign.
Current steering systems also face limitations in terms of personalization and adaptability. They typically offer limited adjustability in terms of steering feel, feedback, and responsiveness, which may not cater to individual driver preferences or varying driving conditions.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced driver assistance systems and autonomous driving technologies with traditional steering systems presents challenges. These systems often require precise control over steering inputs, which can be difficult to achieve with conventional mechanical linkages.
As we look towards future mobility solutions, there is a growing need for steering systems that can overcome these limitations. This includes the development of steer-by-wire technologies, which eliminate the physical connection between the steering wheel and wheels, offering greater design flexibility and improved integration with autonomous systems. Additionally, adaptive steering systems that can adjust their characteristics based on driving conditions and driver preferences are becoming increasingly important.
Existing Advanced Steering Wheel Solutions
01 Ergonomic design for improved comfort and control
Steering wheel designs focus on ergonomic features to enhance driver comfort and control. This includes optimizing the shape, size, and grip of the wheel to reduce fatigue during long drives and improve handling in various driving conditions.- Ergonomic design for improved comfort and control: Steering wheel designs focus on ergonomic features to enhance driver comfort and control. This includes optimizing the shape, size, and grip of the wheel to reduce fatigue during long drives and improve handling. Ergonomic designs may incorporate contoured surfaces, textured materials, and adjustable elements to accommodate different hand sizes and driving preferences.
- Integration of advanced controls and displays: Modern steering wheel designs incorporate various controls and displays to enhance functionality and reduce driver distraction. This includes integrating buttons, switches, and touch-sensitive surfaces for controlling vehicle systems, as well as embedding small displays or head-up projections to provide essential information without requiring the driver to look away from the road.
- Adaptive steering systems for improved maneuverability: Steering wheel designs are evolving to incorporate adaptive steering systems that adjust the steering ratio based on vehicle speed and driving conditions. These systems can provide easier maneuverability at low speeds while offering more stability at higher speeds. Some designs also include features for automatic parking assistance or lane-keeping functions.
- Safety enhancements and airbag integration: Steering wheel designs prioritize safety features, including improved airbag integration and deployment systems. This involves optimizing the wheel's structure to accommodate airbags while maintaining aesthetic appeal and functionality. Some designs also incorporate energy-absorbing materials or collapsible structures to reduce injury risks in the event of a collision.
- Customizable and modular steering wheel designs: Innovative steering wheel designs offer customization options to cater to individual preferences and vehicle types. This includes modular components that allow for easy replacement or upgrading of specific parts, as well as adjustable elements that can be personalized for different drivers or driving modes. Some designs also incorporate removable steering wheels for enhanced security or to facilitate entry and exit in tight spaces.
02 Integration of advanced controls and displays
Modern steering wheel designs incorporate various controls and displays directly on the wheel. This integration allows drivers to access vehicle functions, infotainment systems, and driver assistance features without taking their hands off the wheel, improving safety and convenience.Expand Specific Solutions03 Adjustable steering wheel mechanisms
Steering wheels are designed with adjustable mechanisms to accommodate different driver preferences and body types. These mechanisms allow for tilt, telescoping, and sometimes memory functions to ensure optimal positioning for each driver.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety features in steering wheel design
Safety is a crucial aspect of steering wheel design, incorporating features such as airbag integration, energy-absorbing materials, and collapsible structures. These elements are designed to protect the driver in the event of a collision while maintaining the wheel's primary function.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovative materials and manufacturing techniques
Steering wheel designs utilize advanced materials and manufacturing techniques to improve durability, reduce weight, and enhance aesthetics. This includes the use of lightweight alloys, composite materials, and advanced coatings to create wheels that are both functional and visually appealing.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Automotive and Tech Companies in Steering Innovation
The steering wheel design landscape in future mobility solutions is evolving rapidly, with the market in a growth phase characterized by increasing technological sophistication and expanding applications. The global market size for advanced steering systems is projected to grow significantly, driven by the shift towards autonomous and electric vehicles. Technologically, the field is progressing from traditional mechanical systems to advanced electronic and steer-by-wire solutions. Companies like Autoliv, Honda, Audi, and Hyundai are at the forefront, investing heavily in R&D to develop innovative steering technologies that integrate with autonomous driving systems and enhance user experience. Emerging players such as NIO and Polestar are also making significant contributions, particularly in the electric vehicle segment.
Autoliv Development AB
Technical Solution: Autoliv has developed an innovative steering wheel design that integrates advanced safety features and intuitive controls. Their solution incorporates a dual-stage airbag system that adapts deployment force based on crash severity and occupant position[1]. The steering wheel also features capacitive touch sensors for hands-on detection and seamless integration of driver assistance controls[2]. Autoliv's design includes a modular structure that allows for easy customization and integration of additional features such as heating elements and biometric sensors for driver monitoring[3]. The company has also implemented sustainable materials in their steering wheel construction, reducing environmental impact while maintaining durability[4].
Strengths: Advanced safety features, intuitive controls, customizable design. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to advanced technology integration, may require additional driver training for optimal use.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honda has developed a next-generation steering wheel design focused on enhancing driver comfort and control in autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles. Their solution features a shape-shifting capability that allows the steering wheel to retract and transform into a more compact form during autonomous driving modes[1]. The design incorporates haptic feedback systems to provide tactile alerts and information to the driver[2]. Honda's steering wheel also integrates advanced gesture recognition technology, enabling drivers to control various vehicle functions with simple hand movements[3]. Additionally, the company has implemented a novel material that can change texture and temperature, providing a more personalized and comfortable driving experience[4].
Strengths: Adaptable design for various driving modes, advanced haptic and gesture controls. Weaknesses: Complex technology may lead to higher maintenance costs, potential reliability concerns with shape-shifting mechanism.
Breakthrough Steering Technologies Analysis
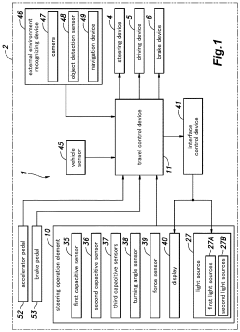
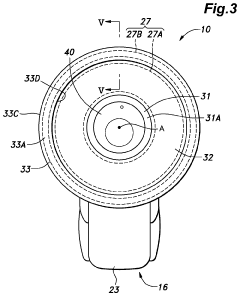
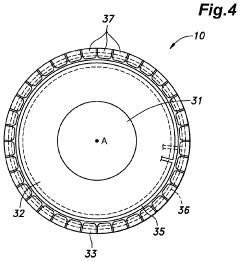
Steering wheel with display and light source
PatentActiveUS11952032B2
Innovation
- A steering operation element with a hub part, extending part, and outer edge part, featuring a display and strategically placed light sources that are controlled to provide vehicle and environmental information without constant illumination, adjusting based on driving mode and occupant input to prevent annoyance.
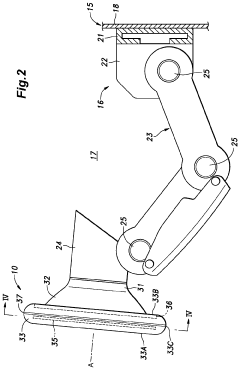
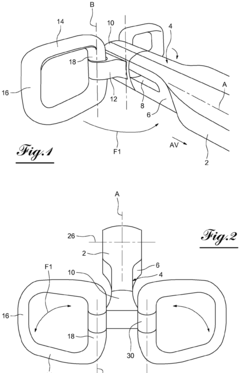
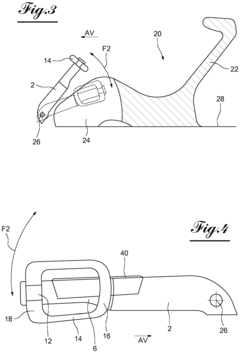
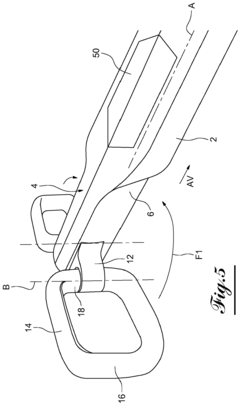
Steering system for an autonomous vehicle including a collapsible wheel fitted with an airbag
PatentInactiveEP3415785A1
Innovation
- A steering system with a longitudinally elongated steering column and a steering wheel featuring two lateral branches connected by pivots, allowing the branches to fold closely around the column, and a rear cowl that accommodates an airbag, reducing lateral bulk and freeing up space for driver comfort.
Safety Regulations for Next-Gen Steering Systems
As the automotive industry evolves towards autonomous and connected vehicles, safety regulations for next-generation steering systems are becoming increasingly critical. These regulations aim to ensure that innovative steering technologies maintain or enhance the safety standards established for traditional steering wheels.
One of the primary focuses of safety regulations is the reliability and redundancy of steer-by-wire systems. These systems, which replace mechanical linkages with electronic controls, must demonstrate fail-safe mechanisms to prevent loss of steering control. Regulatory bodies are developing stringent testing protocols to verify the robustness of these systems under various conditions, including electromagnetic interference and cybersecurity threats.
Haptic feedback in steering systems is another area of regulatory interest. As traditional steering wheels may be replaced by joysticks or other control interfaces, regulations are being developed to ensure that drivers receive adequate tactile information about road conditions and vehicle dynamics. This is crucial for maintaining situational awareness, especially in semi-autonomous driving modes.
The integration of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) with steering controls is also subject to new safety regulations. These regulations address the handover process between automated and manual driving, ensuring that drivers can quickly and safely resume control when necessary. Clear guidelines are being established for the design of human-machine interfaces to minimize driver confusion and error.
For vehicles equipped with retractable or stowable steering wheels, regulations are being formulated to address deployment speed and reliability. These systems must demonstrate the ability to quickly present a fully functional steering interface when transitioning from autonomous to manual mode, with stringent requirements for response times and failure rates.
Ergonomic considerations are also being incorporated into safety regulations for next-generation steering systems. This includes guidelines for the placement and design of steering controls to accommodate a wide range of driver physiques and abilities, as well as requirements for adjustability and customization to ensure optimal driver positioning and comfort.
Lastly, regulatory bodies are addressing the need for standardization in emergency override systems. These regulations aim to ensure that, regardless of the steering system design, drivers can always take manual control in critical situations. This includes requirements for intuitive emergency controls that can be easily accessed and operated under stress.
One of the primary focuses of safety regulations is the reliability and redundancy of steer-by-wire systems. These systems, which replace mechanical linkages with electronic controls, must demonstrate fail-safe mechanisms to prevent loss of steering control. Regulatory bodies are developing stringent testing protocols to verify the robustness of these systems under various conditions, including electromagnetic interference and cybersecurity threats.
Haptic feedback in steering systems is another area of regulatory interest. As traditional steering wheels may be replaced by joysticks or other control interfaces, regulations are being developed to ensure that drivers receive adequate tactile information about road conditions and vehicle dynamics. This is crucial for maintaining situational awareness, especially in semi-autonomous driving modes.
The integration of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) with steering controls is also subject to new safety regulations. These regulations address the handover process between automated and manual driving, ensuring that drivers can quickly and safely resume control when necessary. Clear guidelines are being established for the design of human-machine interfaces to minimize driver confusion and error.
For vehicles equipped with retractable or stowable steering wheels, regulations are being formulated to address deployment speed and reliability. These systems must demonstrate the ability to quickly present a fully functional steering interface when transitioning from autonomous to manual mode, with stringent requirements for response times and failure rates.
Ergonomic considerations are also being incorporated into safety regulations for next-generation steering systems. This includes guidelines for the placement and design of steering controls to accommodate a wide range of driver physiques and abilities, as well as requirements for adjustability and customization to ensure optimal driver positioning and comfort.
Lastly, regulatory bodies are addressing the need for standardization in emergency override systems. These regulations aim to ensure that, regardless of the steering system design, drivers can always take manual control in critical situations. This includes requirements for intuitive emergency controls that can be easily accessed and operated under stress.
User Experience Considerations in Steering Design
User experience considerations play a crucial role in steering design for future mobility solutions. As vehicles evolve towards autonomous capabilities, the steering wheel's function and form must adapt to accommodate changing user needs and expectations.
One key aspect of user experience in steering design is the integration of haptic feedback. Advanced haptic systems can provide drivers with subtle tactile cues, enhancing their awareness of road conditions and vehicle status. This technology can simulate the feel of different road surfaces or alert drivers to potential hazards, improving safety and driver confidence.
Ergonomics remains a critical factor in steering wheel design. Future steering wheels must cater to a wide range of user preferences and physical characteristics. Adjustable steering wheels that can change shape or size to fit individual drivers may become more prevalent. This adaptability ensures comfort during both manual and semi-autonomous driving modes.
The incorporation of touch-sensitive surfaces on steering wheels is another trend shaping user experience. These interfaces allow drivers to control various vehicle functions without removing their hands from the wheel. However, designers must carefully balance functionality with simplicity to prevent cognitive overload and maintain safety.
As vehicles transition between manual and autonomous modes, steering wheel designs must adapt accordingly. Retractable or foldable steering wheels that can be stowed away during fully autonomous operation are being explored. These designs must ensure a seamless transition between driving modes while maintaining user trust and comfort.
Visual feedback integrated into the steering wheel is becoming increasingly important. Heads-up displays or LED indicators embedded in the wheel can provide critical information directly in the driver's line of sight. This reduces the need for drivers to look away from the road, enhancing safety and user experience.
Customization options are likely to become more prevalent in future steering wheel designs. Users may be able to personalize the look, feel, and functionality of their steering wheels through modular components or digital interfaces. This level of personalization can enhance the emotional connection between driver and vehicle.
Lastly, the psychological aspects of steering wheel design must be considered. As vehicles become more autonomous, the steering wheel remains a symbolic link to the act of driving. Designers must balance the need for advanced functionality with the emotional and psychological comfort that traditional steering wheels provide to many users.
One key aspect of user experience in steering design is the integration of haptic feedback. Advanced haptic systems can provide drivers with subtle tactile cues, enhancing their awareness of road conditions and vehicle status. This technology can simulate the feel of different road surfaces or alert drivers to potential hazards, improving safety and driver confidence.
Ergonomics remains a critical factor in steering wheel design. Future steering wheels must cater to a wide range of user preferences and physical characteristics. Adjustable steering wheels that can change shape or size to fit individual drivers may become more prevalent. This adaptability ensures comfort during both manual and semi-autonomous driving modes.
The incorporation of touch-sensitive surfaces on steering wheels is another trend shaping user experience. These interfaces allow drivers to control various vehicle functions without removing their hands from the wheel. However, designers must carefully balance functionality with simplicity to prevent cognitive overload and maintain safety.
As vehicles transition between manual and autonomous modes, steering wheel designs must adapt accordingly. Retractable or foldable steering wheels that can be stowed away during fully autonomous operation are being explored. These designs must ensure a seamless transition between driving modes while maintaining user trust and comfort.
Visual feedback integrated into the steering wheel is becoming increasingly important. Heads-up displays or LED indicators embedded in the wheel can provide critical information directly in the driver's line of sight. This reduces the need for drivers to look away from the road, enhancing safety and user experience.
Customization options are likely to become more prevalent in future steering wheel designs. Users may be able to personalize the look, feel, and functionality of their steering wheels through modular components or digital interfaces. This level of personalization can enhance the emotional connection between driver and vehicle.
Lastly, the psychological aspects of steering wheel design must be considered. As vehicles become more autonomous, the steering wheel remains a symbolic link to the act of driving. Designers must balance the need for advanced functionality with the emotional and psychological comfort that traditional steering wheels provide to many users.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!