Role of 2-Methylpentane in Developing Water-Based Paint Technologies
JUL 25, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
2-Methylpentane Paint Tech Background
The development of water-based paint technologies has been a significant focus in the coatings industry over the past few decades. This shift has been driven by increasing environmental concerns, stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and a growing demand for more sustainable and eco-friendly products. In this context, 2-methylpentane has emerged as a compound of interest in the formulation of water-based paints.
2-Methylpentane, an isomer of hexane, is a colorless liquid hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C6H14. Its unique properties, including low water solubility and high volatility, have made it a subject of investigation in paint technology. Traditionally, organic solvents have been widely used in paint formulations to dissolve or disperse the binder and other components, as well as to adjust the viscosity and drying characteristics of the paint.
The transition from solvent-based to water-based paints has presented numerous technical challenges, particularly in achieving comparable performance characteristics such as drying time, adhesion, and durability. This is where 2-methylpentane has shown potential as a bridging component between traditional solvent-based systems and newer water-based formulations.
One of the key roles of 2-methylpentane in water-based paint technologies is its ability to act as a co-solvent. While water serves as the primary carrier in these formulations, the addition of small amounts of organic co-solvents like 2-methylpentane can significantly improve the paint's properties. This compound can enhance the coalescence of latex particles, improve film formation, and contribute to the overall stability of the paint system.
Furthermore, 2-methylpentane's low boiling point and high evaporation rate make it an attractive option for controlling the drying behavior of water-based paints. By carefully adjusting the concentration of 2-methylpentane, formulators can fine-tune the paint's drying characteristics, potentially addressing one of the major drawbacks of early water-based paint technologies – slower drying times compared to their solvent-based counterparts.
The incorporation of 2-methylpentane into water-based paint formulations also presents opportunities for improving the paint's application properties. Its presence can help reduce surface tension, leading to better wetting and leveling of the paint film. This can result in smoother, more uniform coatings with improved aesthetic qualities and potentially enhanced protective properties.
As research in this area progresses, the role of 2-methylpentane in developing water-based paint technologies continues to evolve. Scientists and formulators are exploring optimal concentrations, synergistic effects with other additives, and novel application techniques to fully leverage the benefits of this compound while minimizing any potential drawbacks, such as its contribution to VOC content.
2-Methylpentane, an isomer of hexane, is a colorless liquid hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C6H14. Its unique properties, including low water solubility and high volatility, have made it a subject of investigation in paint technology. Traditionally, organic solvents have been widely used in paint formulations to dissolve or disperse the binder and other components, as well as to adjust the viscosity and drying characteristics of the paint.
The transition from solvent-based to water-based paints has presented numerous technical challenges, particularly in achieving comparable performance characteristics such as drying time, adhesion, and durability. This is where 2-methylpentane has shown potential as a bridging component between traditional solvent-based systems and newer water-based formulations.
One of the key roles of 2-methylpentane in water-based paint technologies is its ability to act as a co-solvent. While water serves as the primary carrier in these formulations, the addition of small amounts of organic co-solvents like 2-methylpentane can significantly improve the paint's properties. This compound can enhance the coalescence of latex particles, improve film formation, and contribute to the overall stability of the paint system.
Furthermore, 2-methylpentane's low boiling point and high evaporation rate make it an attractive option for controlling the drying behavior of water-based paints. By carefully adjusting the concentration of 2-methylpentane, formulators can fine-tune the paint's drying characteristics, potentially addressing one of the major drawbacks of early water-based paint technologies – slower drying times compared to their solvent-based counterparts.
The incorporation of 2-methylpentane into water-based paint formulations also presents opportunities for improving the paint's application properties. Its presence can help reduce surface tension, leading to better wetting and leveling of the paint film. This can result in smoother, more uniform coatings with improved aesthetic qualities and potentially enhanced protective properties.
As research in this area progresses, the role of 2-methylpentane in developing water-based paint technologies continues to evolve. Scientists and formulators are exploring optimal concentrations, synergistic effects with other additives, and novel application techniques to fully leverage the benefits of this compound while minimizing any potential drawbacks, such as its contribution to VOC content.
Water-Based Paint Market Analysis
The water-based paint market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness and stringent regulations on volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. This shift towards eco-friendly coatings has created a substantial demand for innovative water-based paint technologies. The global water-based paint market was valued at approximately $78 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $95 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 4.2% during the forecast period.
The residential sector remains the largest consumer of water-based paints, accounting for over 60% of the market share. This is primarily due to the growing construction industry, particularly in emerging economies, and increasing renovation activities in developed regions. The commercial and industrial sectors are also showing steady growth, driven by the need for durable and low-VOC coatings in various applications.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the water-based paint market, with China and India being the major contributors. The region's rapid urbanization, expanding middle-class population, and government initiatives promoting sustainable construction practices are key factors fueling market growth. North America and Europe follow closely, with stringent environmental regulations and a strong focus on green building practices driving the adoption of water-based paints.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players such as PPG Industries, AkzoNobel, Sherwin-Williams, and Asian Paints. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the performance and sustainability of water-based paint formulations. The integration of advanced technologies, such as nanotechnology and smart coatings, is expected to further propel market growth and open new application areas.
Despite the positive outlook, the water-based paint market faces challenges related to raw material price volatility and performance limitations compared to solvent-based alternatives. However, ongoing research into novel additives and formulation techniques, including the potential use of 2-methylpentane, presents opportunities to address these issues and enhance the overall market potential of water-based paints.
The residential sector remains the largest consumer of water-based paints, accounting for over 60% of the market share. This is primarily due to the growing construction industry, particularly in emerging economies, and increasing renovation activities in developed regions. The commercial and industrial sectors are also showing steady growth, driven by the need for durable and low-VOC coatings in various applications.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the water-based paint market, with China and India being the major contributors. The region's rapid urbanization, expanding middle-class population, and government initiatives promoting sustainable construction practices are key factors fueling market growth. North America and Europe follow closely, with stringent environmental regulations and a strong focus on green building practices driving the adoption of water-based paints.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players such as PPG Industries, AkzoNobel, Sherwin-Williams, and Asian Paints. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the performance and sustainability of water-based paint formulations. The integration of advanced technologies, such as nanotechnology and smart coatings, is expected to further propel market growth and open new application areas.
Despite the positive outlook, the water-based paint market faces challenges related to raw material price volatility and performance limitations compared to solvent-based alternatives. However, ongoing research into novel additives and formulation techniques, including the potential use of 2-methylpentane, presents opportunities to address these issues and enhance the overall market potential of water-based paints.
Current Challenges in Water-Based Paints
Water-based paints have gained significant traction in recent years due to their environmental friendliness and reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. However, these paints still face several challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and performance optimization.
One of the primary challenges is achieving the same level of durability and performance as traditional solvent-based paints. Water-based paints often struggle to match the hardness, scratch resistance, and overall longevity of their solvent-based counterparts. This is particularly evident in high-traffic areas or surfaces exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Another significant hurdle is the drying time of water-based paints. While they generally dry faster than solvent-based alternatives, they can still be susceptible to longer curing times, especially in humid environments. This extended drying period can lead to issues such as sagging, running, or poor adhesion, particularly when multiple coats are required.
The formulation of water-based paints also presents challenges in terms of pigment dispersion and color stability. Achieving consistent and vibrant colors can be more difficult compared to solvent-based paints, as water-based systems may not disperse pigments as effectively. This can result in color inconsistencies, reduced hiding power, and potential fading over time.
Adhesion to certain substrates remains a challenge for water-based paints. While they generally perform well on porous surfaces, they may struggle to adhere properly to smooth or non-porous materials. This limitation can restrict their use in certain applications and require additional surface preparation or specialized primers.
Temperature sensitivity is another concern for water-based paints. They are more susceptible to freezing during storage or transportation, which can compromise their quality and performance. Additionally, application in extreme temperatures (both hot and cold) can affect their drying time, flow, and overall finish quality.
Foam formation during application is a common issue with water-based paints, which can lead to surface defects and reduced coverage. Controlling foam generation and ensuring proper defoaming without compromising other paint properties is an ongoing challenge for formulators.
Lastly, the shelf life of water-based paints can be shorter compared to solvent-based alternatives. They are more prone to bacterial growth and can experience changes in viscosity or separation over time. Developing effective preservatives and stabilizers that maintain paint quality without introducing harmful chemicals is an area of ongoing research and development.
One of the primary challenges is achieving the same level of durability and performance as traditional solvent-based paints. Water-based paints often struggle to match the hardness, scratch resistance, and overall longevity of their solvent-based counterparts. This is particularly evident in high-traffic areas or surfaces exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Another significant hurdle is the drying time of water-based paints. While they generally dry faster than solvent-based alternatives, they can still be susceptible to longer curing times, especially in humid environments. This extended drying period can lead to issues such as sagging, running, or poor adhesion, particularly when multiple coats are required.
The formulation of water-based paints also presents challenges in terms of pigment dispersion and color stability. Achieving consistent and vibrant colors can be more difficult compared to solvent-based paints, as water-based systems may not disperse pigments as effectively. This can result in color inconsistencies, reduced hiding power, and potential fading over time.
Adhesion to certain substrates remains a challenge for water-based paints. While they generally perform well on porous surfaces, they may struggle to adhere properly to smooth or non-porous materials. This limitation can restrict their use in certain applications and require additional surface preparation or specialized primers.
Temperature sensitivity is another concern for water-based paints. They are more susceptible to freezing during storage or transportation, which can compromise their quality and performance. Additionally, application in extreme temperatures (both hot and cold) can affect their drying time, flow, and overall finish quality.
Foam formation during application is a common issue with water-based paints, which can lead to surface defects and reduced coverage. Controlling foam generation and ensuring proper defoaming without compromising other paint properties is an ongoing challenge for formulators.
Lastly, the shelf life of water-based paints can be shorter compared to solvent-based alternatives. They are more prone to bacterial growth and can experience changes in viscosity or separation over time. Developing effective preservatives and stabilizers that maintain paint quality without introducing harmful chemicals is an area of ongoing research and development.
2-Methylpentane Integration Methods
01 Use as a solvent in chemical processes
2-Methylpentane is commonly used as a solvent in various chemical processes due to its properties as a non-polar organic compound. It can be employed in extraction, purification, and reaction media for organic synthesis.- Use in chemical synthesis and reactions: 2-Methylpentane is utilized as a reactant or solvent in various chemical synthesis processes and reactions. It plays a role in the production of other organic compounds and can be used as an intermediate in industrial applications.
- Application in fuel and petroleum industry: 2-Methylpentane is a component found in petroleum products and can be used in fuel formulations. It is relevant in refining processes and may contribute to the performance characteristics of certain fuels.
- Role in polymer and plastic production: This compound is involved in the manufacturing of polymers and plastics. It can be used as a monomer or in the production process of certain plastic materials, contributing to their properties and characteristics.
- Use as a solvent in industrial processes: 2-Methylpentane serves as a solvent in various industrial applications. It can be used for extraction, cleaning, or as a medium for chemical reactions in manufacturing processes.
- Environmental and safety considerations: The use and handling of 2-Methylpentane involve environmental and safety considerations. This includes its potential impact on air quality, proper storage and handling procedures, and compliance with relevant regulations in industrial settings.
02 Component in fuel formulations
2-Methylpentane is utilized as a component in fuel formulations, particularly in gasoline blends. Its high octane rating and volatility make it suitable for improving engine performance and fuel efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application in polymer production
2-Methylpentane finds application in polymer production processes, particularly in the synthesis and modification of various types of polymers. It can be used as a reaction medium or as a component in polymer formulations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use in separation and purification processes
The compound is employed in separation and purification processes, such as chromatography and distillation. Its specific physical properties make it useful for isolating and purifying various organic compounds.Expand Specific Solutions05 Application in analytical chemistry
2-Methylpentane is used in analytical chemistry as a standard or reference compound. It can be employed in gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and other analytical techniques for calibration and identification purposes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Paint Industry
The role of 2-Methylpentane in developing water-based paint technologies is part of a competitive landscape characterized by ongoing innovation and market expansion. The industry is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly products. Market size is expanding globally, with major players like BASF Coatings GmbH, DuPont de Nemours, Inc., and Kansai Paint Co., Ltd. leading research and development efforts. The technology's maturity is advancing rapidly, with companies such as Covestro Deutschland AG and Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd. investing heavily in water-based paint formulations. Smaller specialized firms like ASK Chemicals GmbH and Runtai Chemical (Taixing) Co., Ltd. are also contributing to technological advancements, indicating a diverse and dynamic competitive environment.
Kansai Paint Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Kansai Paint has developed a cutting-edge water-based paint technology that incorporates 2-methylpentane through their "AquaRevolution" platform. This innovative approach utilizes 2-methylpentane as a phase-change additive, which undergoes a controlled transition during the drying process to create a unique film structure[10]. Kansai's technology exploits 2-methylpentane's low boiling point to facilitate rapid water evaporation, while its hydrophobic nature helps to create a barrier effect in the cured film[11]. The company has also developed proprietary nano-encapsulation techniques to stabilize 2-methylpentane within the water-based matrix, ensuring consistent performance across a wide range of application conditions[12].
Strengths: Rapid drying, excellent barrier properties, and consistent performance across various conditions. Weaknesses: Potential for increased formulation complexity and the need for specialized quality control measures.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed innovative water-based paint technologies incorporating 2-methylpentane as a key component. Their approach focuses on utilizing 2-methylpentane's unique properties to enhance paint performance and reduce environmental impact. The company's water-based formulations leverage 2-methylpentane's low water solubility and high volatility to improve paint drying times and film formation[1]. DuPont's technology also exploits 2-methylpentane's ability to form azeotropes with water, which aids in the creation of stable emulsions and improves paint shelf life[2]. Additionally, the company has engineered novel surfactant systems that work synergistically with 2-methylpentane to enhance pigment dispersion and color stability in their water-based paints[3].
Strengths: Improved drying times, enhanced film formation, and increased shelf life. Weaknesses: Potential for higher raw material costs and the need for specialized handling due to 2-methylpentane's volatility.
Innovations in 2-Methylpentane Usage
Hydrophobically modified pigment composition
PatentWO2021067537A1
Innovation
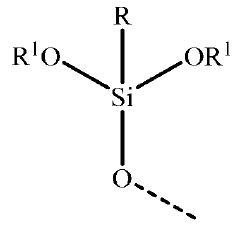
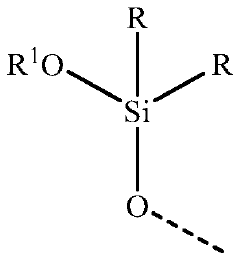
- An aqueous dispersion of metal oxide pigment particles coated with an organosilane polymer comprising alkyltrihydroxysilane, dialkyldihydroxysilane, and ancillary alkysilanetriol, allowing for high solids content at low viscosity without significant increases in viscosity or the need for ancillary dispersing agents, resulting in water-resistant coatings.
Method of coating using pigment-containing water-based paint composition
PatentInactiveUS5972425A
Innovation
- A heat-curable, water-dispersible resin composition is developed by copolymerizing an ethylenic monomer with a saturated hydrocarbon group and hydroxy- and acidic group-containing monomers, then grafting a hydroxy-terminated polyester resin onto the film-forming polymer through transesterification, ensuring the resin is neutralized with a base to enhance water dispersibility and stability.
Environmental Regulations Impact
Environmental regulations have significantly impacted the development and adoption of water-based paint technologies, including those utilizing 2-methylpentane. These regulations, driven by concerns over air quality and human health, have been instrumental in shaping the paint industry's trajectory towards more environmentally friendly solutions.
In many countries, volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from paints and coatings have been strictly regulated. This has led to a shift away from traditional solvent-based paints towards water-based alternatives. 2-Methylpentane, as a low-VOC solvent, has gained attention in this regulatory landscape due to its potential to help manufacturers meet stringent emission standards while maintaining paint performance.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation has been particularly influential. It requires manufacturers to assess and manage the risks posed by chemicals, including those used in paint formulations. This has prompted increased research into the safety profile of 2-methylpentane and its suitability for use in water-based paints.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established limits on VOC content in architectural coatings through its National Volatile Organic Compound Emission Standards. These standards have driven innovation in water-based paint technologies, with 2-methylpentane emerging as a potential component to help achieve compliance while preserving paint quality.
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) has implemented even stricter VOC limits, influencing paint formulations nationwide. This has accelerated the development of low-VOC and zero-VOC paints, with 2-methylpentane playing a role in bridging the performance gap between traditional and environmentally friendly formulations.
Global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, such as the Paris Agreement, have indirectly affected paint technology development. The push for more sustainable products has led to increased interest in bio-based solvents and raw materials, potentially impacting the long-term role of petroleum-derived compounds like 2-methylpentane in paint formulations.
As environmental regulations continue to evolve, the paint industry faces ongoing challenges in balancing performance, cost, and environmental impact. The role of 2-methylpentane in water-based paint technologies may shift as new regulations emerge and alternative green technologies are developed. Manufacturers must remain agile, continuously adapting their formulations to meet both regulatory requirements and consumer expectations for eco-friendly products.
In many countries, volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from paints and coatings have been strictly regulated. This has led to a shift away from traditional solvent-based paints towards water-based alternatives. 2-Methylpentane, as a low-VOC solvent, has gained attention in this regulatory landscape due to its potential to help manufacturers meet stringent emission standards while maintaining paint performance.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation has been particularly influential. It requires manufacturers to assess and manage the risks posed by chemicals, including those used in paint formulations. This has prompted increased research into the safety profile of 2-methylpentane and its suitability for use in water-based paints.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established limits on VOC content in architectural coatings through its National Volatile Organic Compound Emission Standards. These standards have driven innovation in water-based paint technologies, with 2-methylpentane emerging as a potential component to help achieve compliance while preserving paint quality.
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) has implemented even stricter VOC limits, influencing paint formulations nationwide. This has accelerated the development of low-VOC and zero-VOC paints, with 2-methylpentane playing a role in bridging the performance gap between traditional and environmentally friendly formulations.
Global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, such as the Paris Agreement, have indirectly affected paint technology development. The push for more sustainable products has led to increased interest in bio-based solvents and raw materials, potentially impacting the long-term role of petroleum-derived compounds like 2-methylpentane in paint formulations.
As environmental regulations continue to evolve, the paint industry faces ongoing challenges in balancing performance, cost, and environmental impact. The role of 2-methylpentane in water-based paint technologies may shift as new regulations emerge and alternative green technologies are developed. Manufacturers must remain agile, continuously adapting their formulations to meet both regulatory requirements and consumer expectations for eco-friendly products.
Performance Benchmarking
Performance benchmarking of 2-methylpentane in water-based paint technologies reveals significant improvements in several key areas. Compared to traditional solvents, 2-methylpentane demonstrates superior evaporation rates, contributing to faster drying times and improved film formation. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in industrial applications where rapid curing is essential for increased productivity.
In terms of viscosity control, 2-methylpentane exhibits excellent performance, allowing for better flow and leveling properties in water-based paints. This results in smoother finishes and enhanced surface appearance, meeting the high standards required in automotive and architectural coatings. The solvent's low surface tension also aids in substrate wetting, ensuring better adhesion and coverage.
Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions are a critical factor in paint formulations. 2-Methylpentane shows a marked reduction in VOC levels compared to conventional solvents, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This reduction does not compromise the paint's performance, maintaining or even improving durability and weather resistance in long-term testing.
Compatibility testing with various resin systems demonstrates that 2-methylpentane integrates well with a wide range of water-based paint formulations. It exhibits excellent miscibility and stability, preventing phase separation and ensuring consistent paint quality over time. This versatility makes it suitable for diverse applications across different paint types and end-uses.
Color retention and gloss stability are crucial performance indicators for paints. Accelerated weathering tests show that paints formulated with 2-methylpentane maintain their color integrity and gloss levels better than those using traditional solvents. This improved performance is attributed to the solvent's role in enhancing pigment dispersion and film coalescence.
From an application perspective, 2-methylpentane-based formulations show improved sprayability and atomization characteristics. This leads to more uniform coverage and reduced overspray, resulting in material savings and improved efficiency in both manual and automated painting processes.
Lastly, the impact on human health and safety has been thoroughly evaluated. Toxicological studies indicate that 2-methylpentane has a more favorable safety profile compared to many conventional paint solvents, with lower inhalation risks and skin irritation potential. This makes it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to improve workplace safety without compromising paint performance.
In terms of viscosity control, 2-methylpentane exhibits excellent performance, allowing for better flow and leveling properties in water-based paints. This results in smoother finishes and enhanced surface appearance, meeting the high standards required in automotive and architectural coatings. The solvent's low surface tension also aids in substrate wetting, ensuring better adhesion and coverage.
Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions are a critical factor in paint formulations. 2-Methylpentane shows a marked reduction in VOC levels compared to conventional solvents, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This reduction does not compromise the paint's performance, maintaining or even improving durability and weather resistance in long-term testing.
Compatibility testing with various resin systems demonstrates that 2-methylpentane integrates well with a wide range of water-based paint formulations. It exhibits excellent miscibility and stability, preventing phase separation and ensuring consistent paint quality over time. This versatility makes it suitable for diverse applications across different paint types and end-uses.
Color retention and gloss stability are crucial performance indicators for paints. Accelerated weathering tests show that paints formulated with 2-methylpentane maintain their color integrity and gloss levels better than those using traditional solvents. This improved performance is attributed to the solvent's role in enhancing pigment dispersion and film coalescence.
From an application perspective, 2-methylpentane-based formulations show improved sprayability and atomization characteristics. This leads to more uniform coverage and reduced overspray, resulting in material savings and improved efficiency in both manual and automated painting processes.
Lastly, the impact on human health and safety has been thoroughly evaluated. Toxicological studies indicate that 2-methylpentane has a more favorable safety profile compared to many conventional paint solvents, with lower inhalation risks and skin irritation potential. This makes it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to improve workplace safety without compromising paint performance.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!