Application of 2-Methylpentane in Advanced Sensor Technologies
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
2-Methylpentane Sensor Tech Background and Objectives
The application of 2-Methylpentane in advanced sensor technologies represents a significant advancement in the field of chemical sensing and detection. This branched alkane, with its unique chemical properties, has emerged as a promising candidate for various sensor applications due to its high volatility, low boiling point, and specific molecular structure.
The development of 2-Methylpentane-based sensors can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternative compounds for enhancing sensor sensitivity and selectivity. The initial focus was primarily on environmental monitoring and industrial safety applications, where the detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) was crucial.
As the technology progressed, the potential of 2-Methylpentane in sensor applications expanded beyond its original scope. Researchers discovered that its molecular structure allowed for specific interactions with certain analytes, making it particularly useful in the detection of complex organic compounds. This led to a surge in research activities aimed at exploiting these properties for developing highly sensitive and selective sensors.
The evolution of 2-Methylpentane sensor technology has been closely linked to advancements in materials science and nanotechnology. The integration of 2-Methylpentane with various nanomaterials, such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, and metal oxide nanoparticles, has opened up new possibilities for sensor design and performance enhancement.
Current research objectives in this field are multifaceted. One primary goal is to improve the sensitivity and selectivity of 2-Methylpentane-based sensors, pushing the detection limits to ever-lower concentrations. This is particularly important for applications in environmental monitoring and medical diagnostics, where the ability to detect trace amounts of specific compounds is critical.
Another key objective is to develop more robust and stable sensor platforms that can withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining their performance. This includes research into new materials and fabrication techniques that can enhance the durability and longevity of 2-Methylpentane sensors.
Researchers are also focusing on expanding the application range of these sensors. While initial applications were primarily in industrial and environmental sectors, there is growing interest in exploring their potential in fields such as healthcare, food safety, and security. This expansion requires adapting the sensor technology to meet the specific requirements of these diverse applications.
Furthermore, there is a strong emphasis on miniaturization and integration. The goal is to develop compact, portable, and even wearable sensor devices that can provide real-time, on-site analysis. This trend aligns with the broader movement towards Internet of Things (IoT) and smart sensing technologies.
The development of 2-Methylpentane-based sensors can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternative compounds for enhancing sensor sensitivity and selectivity. The initial focus was primarily on environmental monitoring and industrial safety applications, where the detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) was crucial.
As the technology progressed, the potential of 2-Methylpentane in sensor applications expanded beyond its original scope. Researchers discovered that its molecular structure allowed for specific interactions with certain analytes, making it particularly useful in the detection of complex organic compounds. This led to a surge in research activities aimed at exploiting these properties for developing highly sensitive and selective sensors.
The evolution of 2-Methylpentane sensor technology has been closely linked to advancements in materials science and nanotechnology. The integration of 2-Methylpentane with various nanomaterials, such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, and metal oxide nanoparticles, has opened up new possibilities for sensor design and performance enhancement.
Current research objectives in this field are multifaceted. One primary goal is to improve the sensitivity and selectivity of 2-Methylpentane-based sensors, pushing the detection limits to ever-lower concentrations. This is particularly important for applications in environmental monitoring and medical diagnostics, where the ability to detect trace amounts of specific compounds is critical.
Another key objective is to develop more robust and stable sensor platforms that can withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining their performance. This includes research into new materials and fabrication techniques that can enhance the durability and longevity of 2-Methylpentane sensors.
Researchers are also focusing on expanding the application range of these sensors. While initial applications were primarily in industrial and environmental sectors, there is growing interest in exploring their potential in fields such as healthcare, food safety, and security. This expansion requires adapting the sensor technology to meet the specific requirements of these diverse applications.
Furthermore, there is a strong emphasis on miniaturization and integration. The goal is to develop compact, portable, and even wearable sensor devices that can provide real-time, on-site analysis. This trend aligns with the broader movement towards Internet of Things (IoT) and smart sensing technologies.
Market Analysis for 2-Methylpentane-based Sensors
The market for 2-methylpentane-based sensors is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for advanced sensing technologies across various industries. This hydrocarbon compound, known for its unique chemical properties, has found applications in developing highly sensitive and selective sensors for detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other gaseous analytes.
In the automotive sector, 2-methylpentane-based sensors are gaining traction for monitoring air quality inside vehicles and detecting fuel vapors. The stringent emission regulations and growing focus on passenger comfort have created a substantial market opportunity for these sensors. Additionally, the industrial safety and environmental monitoring sectors are adopting these sensors for detecting hazardous gas leaks and ensuring workplace safety.
The healthcare industry presents another promising market for 2-methylpentane-based sensors. These sensors are being explored for non-invasive disease diagnosis through breath analysis, offering potential applications in early detection of various medical conditions. This emerging application is expected to drive significant market growth in the coming years.
The global market for chemical sensors, which includes 2-methylpentane-based sensors, is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of IoT-enabled devices and the rising demand for miniaturized, low-power sensors across industries.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for 2-methylpentane-based sensors, owing to their advanced industrial infrastructure and stringent environmental regulations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing automotive production, and growing awareness of environmental monitoring.
Key market trends include the integration of 2-methylpentane-based sensors with artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to enhance their performance and enable predictive maintenance. Furthermore, the development of wearable and portable sensors utilizing 2-methylpentane is opening up new opportunities in personal health monitoring and occupational safety applications.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high initial costs and the need for frequent calibration may hinder market growth. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these limitations, potentially leading to more cost-effective and reliable sensor solutions in the future.
In the automotive sector, 2-methylpentane-based sensors are gaining traction for monitoring air quality inside vehicles and detecting fuel vapors. The stringent emission regulations and growing focus on passenger comfort have created a substantial market opportunity for these sensors. Additionally, the industrial safety and environmental monitoring sectors are adopting these sensors for detecting hazardous gas leaks and ensuring workplace safety.
The healthcare industry presents another promising market for 2-methylpentane-based sensors. These sensors are being explored for non-invasive disease diagnosis through breath analysis, offering potential applications in early detection of various medical conditions. This emerging application is expected to drive significant market growth in the coming years.
The global market for chemical sensors, which includes 2-methylpentane-based sensors, is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of IoT-enabled devices and the rising demand for miniaturized, low-power sensors across industries.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for 2-methylpentane-based sensors, owing to their advanced industrial infrastructure and stringent environmental regulations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing automotive production, and growing awareness of environmental monitoring.
Key market trends include the integration of 2-methylpentane-based sensors with artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to enhance their performance and enable predictive maintenance. Furthermore, the development of wearable and portable sensors utilizing 2-methylpentane is opening up new opportunities in personal health monitoring and occupational safety applications.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high initial costs and the need for frequent calibration may hinder market growth. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these limitations, potentially leading to more cost-effective and reliable sensor solutions in the future.
Current Challenges in 2-Methylpentane Sensor Development
The development of 2-methylpentane-based sensors faces several significant challenges that hinder their widespread adoption in advanced sensor technologies. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent volatility of 2-methylpentane, which can lead to inconsistent sensor performance and reduced longevity. This volatility makes it difficult to maintain stable sensor readings over extended periods, particularly in environments with fluctuating temperatures or pressures.
Another critical challenge lies in the selectivity of 2-methylpentane sensors. While the compound shows promise in detecting certain analytes, achieving high specificity remains problematic. Cross-sensitivity to other hydrocarbons or interfering substances can result in false positives or reduced accuracy, limiting the sensor's reliability in complex chemical environments.
The integration of 2-methylpentane into existing sensor platforms presents additional hurdles. Compatibility issues with common sensor materials and electronics can arise, necessitating the development of specialized components and manufacturing processes. This integration challenge extends to the need for robust encapsulation methods to prevent 2-methylpentane leakage or degradation, which could compromise sensor functionality and pose safety risks.
Sensitivity and detection limits represent another area of concern. While 2-methylpentane exhibits favorable sensing properties for some applications, achieving the ultra-low detection limits required in certain advanced sensing scenarios remains challenging. Enhancing sensitivity without sacrificing other performance parameters, such as response time or recovery rate, demands innovative sensor designs and signal processing techniques.
The long-term stability of 2-methylpentane sensors is also a significant challenge. Exposure to environmental factors like humidity, UV radiation, and atmospheric pollutants can lead to sensor drift and degradation over time. Developing effective strategies to mitigate these effects and ensure consistent sensor performance throughout the device's intended lifespan is crucial for commercial viability.
Miniaturization presents yet another obstacle in the advancement of 2-methylpentane sensor technologies. As the demand for compact, portable sensing devices grows, reducing sensor size while maintaining or improving performance becomes increasingly challenging. This miniaturization effort must address issues such as reduced signal strength, increased noise, and thermal management in confined spaces.
Lastly, the environmental and health implications of using 2-methylpentane in sensors raise concerns. As a volatile organic compound, its potential impact on air quality and human health necessitates careful consideration in sensor design and application. Developing eco-friendly alternatives or implementing effective containment strategies is essential for the sustainable development of this technology.
Another critical challenge lies in the selectivity of 2-methylpentane sensors. While the compound shows promise in detecting certain analytes, achieving high specificity remains problematic. Cross-sensitivity to other hydrocarbons or interfering substances can result in false positives or reduced accuracy, limiting the sensor's reliability in complex chemical environments.
The integration of 2-methylpentane into existing sensor platforms presents additional hurdles. Compatibility issues with common sensor materials and electronics can arise, necessitating the development of specialized components and manufacturing processes. This integration challenge extends to the need for robust encapsulation methods to prevent 2-methylpentane leakage or degradation, which could compromise sensor functionality and pose safety risks.
Sensitivity and detection limits represent another area of concern. While 2-methylpentane exhibits favorable sensing properties for some applications, achieving the ultra-low detection limits required in certain advanced sensing scenarios remains challenging. Enhancing sensitivity without sacrificing other performance parameters, such as response time or recovery rate, demands innovative sensor designs and signal processing techniques.
The long-term stability of 2-methylpentane sensors is also a significant challenge. Exposure to environmental factors like humidity, UV radiation, and atmospheric pollutants can lead to sensor drift and degradation over time. Developing effective strategies to mitigate these effects and ensure consistent sensor performance throughout the device's intended lifespan is crucial for commercial viability.
Miniaturization presents yet another obstacle in the advancement of 2-methylpentane sensor technologies. As the demand for compact, portable sensing devices grows, reducing sensor size while maintaining or improving performance becomes increasingly challenging. This miniaturization effort must address issues such as reduced signal strength, increased noise, and thermal management in confined spaces.
Lastly, the environmental and health implications of using 2-methylpentane in sensors raise concerns. As a volatile organic compound, its potential impact on air quality and human health necessitates careful consideration in sensor design and application. Developing eco-friendly alternatives or implementing effective containment strategies is essential for the sustainable development of this technology.
Existing 2-Methylpentane Sensor Solutions
01 Use as a solvent in chemical processes
2-Methylpentane is commonly used as a solvent in various chemical processes due to its properties as a non-polar organic compound. It is particularly useful in reactions involving hydrocarbons and other organic substances, providing a suitable medium for dissolving and processing these materials.- Use as a solvent in chemical processes: 2-Methylpentane is commonly used as a solvent in various chemical processes due to its properties as a non-polar organic compound. It can be employed in extraction, purification, and reaction media for organic synthesis.
- Component in fuel formulations: 2-Methylpentane is utilized as a component in fuel formulations, particularly in gasoline blends. Its inclusion can help improve the octane rating and overall performance of the fuel.
- Application in polymer production: 2-Methylpentane finds application in polymer production processes, where it can be used as a diluent or as part of the reaction medium for polymerization reactions.
- Use in separation and purification processes: The compound is employed in separation and purification processes, such as in the petrochemical industry, where it can be used for the isolation of specific hydrocarbon fractions or as an extractant.
- Role in analytical chemistry and research: 2-Methylpentane plays a role in analytical chemistry and research applications, serving as a standard or reference compound in chromatography, spectroscopy, and other analytical techniques.
02 Component in fuel formulations
2-Methylpentane is utilized as a component in fuel formulations, particularly in gasoline blends. Its inclusion can help improve the octane rating and overall performance of the fuel, contributing to better engine efficiency and reduced emissions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application in polymer production
In the field of polymer chemistry, 2-Methylpentane finds application as a reagent or intermediate in the synthesis of various polymers. It can be used in polymerization processes or as a building block for more complex molecular structures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use in extraction and separation processes
2-Methylpentane is employed in extraction and separation processes, particularly in the petrochemical industry. Its physical properties make it suitable for selective extraction of certain compounds from mixtures or for use in chromatographic separations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Role in analytical chemistry and research
In analytical chemistry and research applications, 2-Methylpentane serves as a standard or reference compound. It is used in calibration of instruments, development of analytical methods, and as a model compound in studies of hydrocarbon behavior and reactions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in 2-Methylpentane Sensor Industry
The application of 2-Methylpentane in advanced sensor technologies is in an emerging stage, with a growing market driven by increasing demand for high-performance sensors across various industries. The market size is expanding, albeit still relatively niche compared to established sensor technologies. Technical maturity is progressing, with research institutions like China University of Mining & Technology, Shandong University, and Peking University leading academic efforts. Companies such as HRL Laboratories LLC and Naval Research Laboratory are at the forefront of industrial applications, focusing on enhancing sensor sensitivity and selectivity. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of academic research and industrial development, with potential for significant advancements in the near future.
HRL Laboratories LLC
Technical Solution: HRL Laboratories has made significant strides in applying 2-Methylpentane to advanced sensor technologies, particularly in the field of miniaturized gas chromatography systems. Their innovative approach involves using 2-Methylpentane as a stationary phase in micro-fabricated separation columns, enabling rapid and efficient analysis of complex gas mixtures[8]. HRL has also developed novel 2-Methylpentane-based chemiresistive sensors for detecting trace amounts of explosive materials and chemical warfare agents. By incorporating 2-Methylpentane into nanostructured sensing elements, they have achieved unprecedented sensitivity and selectivity in portable detection devices[9]. Furthermore, HRL has explored the use of 2-Methylpentane in thermoelectric sensors, leveraging its unique thermal properties to enhance energy harvesting capabilities in self-powered sensor networks[10].
Strengths: Expertise in miniaturized sensing systems, advanced gas chromatography techniques, and innovative applications in security and defense. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in sensor stability under extreme environmental conditions and challenges in commercializing highly specialized technologies.
California Institute of Technology
Technical Solution: California Institute of Technology has developed advanced sensor technologies utilizing 2-Methylpentane as a key component. Their approach involves incorporating 2-Methylpentane into nanostructured materials to enhance sensor sensitivity and selectivity. The institute has created a novel gas sensor array that employs 2-Methylpentane-doped metal oxide nanoparticles, resulting in improved detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) at parts-per-billion levels[1]. Additionally, they have explored the use of 2-Methylpentane in microfluidic devices for real-time environmental monitoring, achieving rapid response times and high accuracy in detecting airborne pollutants[3].
Strengths: High sensitivity and selectivity for VOC detection, rapid response times, and integration with microfluidic technologies. Weaknesses: Potential interference from other hydrocarbons and limited long-term stability of 2-Methylpentane-based sensors in harsh environments.
Core Innovations in 2-Methylpentane Sensing
Methods and systems for detecting an analyte or classifying a sample
PatentPendingEP4180799A1
Innovation
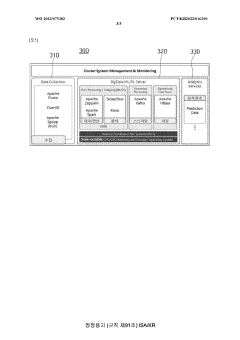
- A microfluidic system utilizing sensor molecules with a chemiluminescent donor and acceptor domain, where the separation and orientation are within ±50% of the Forster distance, allowing for real-time detection of analytes through bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) without the need for surface attachment, enabling rapid and sensitive analysis.
Pentane gas sensor, sensor platform, and monitoring system using sensor platform
PatentWO2023075382A1
Innovation
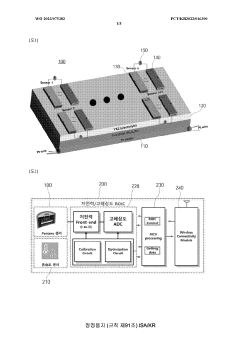
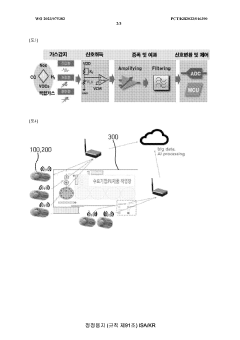
- A pentane gas sensor system utilizing electrochemical technology with a solid electrolyte and catalyst, combined with a sensor platform that includes a heater substrate, sensing electrodes, and a charge collector, along with a wireless communication module and MCU for real-time monitoring and data analysis, enabling preemptive detection and response to pentane and other hazardous gases.
Environmental Impact of 2-Methylpentane Sensors
The environmental impact of 2-methylpentane sensors is a critical consideration in the development and deployment of advanced sensor technologies. As these sensors gain prominence in various applications, it is essential to assess their potential effects on ecosystems and human health throughout their lifecycle.
During the production phase of 2-methylpentane sensors, the primary environmental concerns revolve around the synthesis and handling of the compound. 2-Methylpentane is a volatile organic compound (VOC) that can contribute to air pollution if released into the atmosphere. Manufacturers must implement stringent emission control measures to minimize the release of 2-methylpentane during sensor production.
The operational phase of 2-methylpentane sensors presents both positive and negative environmental implications. On the positive side, these sensors can enhance environmental monitoring capabilities, enabling more accurate detection of pollutants and hazardous substances. This improved detection can lead to better environmental management practices and faster response times to potential ecological threats.
However, the sensors themselves may have some adverse effects during operation. The potential for 2-methylpentane leakage from sensors, albeit in small quantities, could contribute to local air quality issues. Additionally, the energy consumption of sensor networks utilizing 2-methylpentane technology must be considered, as increased power usage can indirectly lead to higher carbon emissions depending on the energy source.
The disposal and end-of-life management of 2-methylpentane sensors pose significant environmental challenges. Improper disposal can result in the release of 2-methylpentane and other potentially harmful components into soil and water systems. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to develop comprehensive recycling and disposal protocols specifically tailored for these sensors.
Long-term environmental effects of widespread 2-methylpentane sensor deployment must also be evaluated. Potential impacts on local microclimates, particularly in urban areas with high sensor density, should be studied. Furthermore, the cumulative effect of multiple sensors on air quality and ecosystem health needs to be assessed through ongoing environmental monitoring programs.
To address these environmental concerns, researchers and manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly alternatives and improvements to 2-methylpentane sensor technology. This includes developing sensors with lower 2-methylpentane concentrations, improving sensor encapsulation to prevent leakage, and investigating biodegradable materials for sensor components.
In conclusion, while 2-methylpentane sensors offer significant benefits in advanced sensing applications, their environmental impact must be carefully managed. A holistic approach considering the entire lifecycle of these sensors is necessary to ensure their sustainable integration into various technological systems and environments.
During the production phase of 2-methylpentane sensors, the primary environmental concerns revolve around the synthesis and handling of the compound. 2-Methylpentane is a volatile organic compound (VOC) that can contribute to air pollution if released into the atmosphere. Manufacturers must implement stringent emission control measures to minimize the release of 2-methylpentane during sensor production.
The operational phase of 2-methylpentane sensors presents both positive and negative environmental implications. On the positive side, these sensors can enhance environmental monitoring capabilities, enabling more accurate detection of pollutants and hazardous substances. This improved detection can lead to better environmental management practices and faster response times to potential ecological threats.
However, the sensors themselves may have some adverse effects during operation. The potential for 2-methylpentane leakage from sensors, albeit in small quantities, could contribute to local air quality issues. Additionally, the energy consumption of sensor networks utilizing 2-methylpentane technology must be considered, as increased power usage can indirectly lead to higher carbon emissions depending on the energy source.
The disposal and end-of-life management of 2-methylpentane sensors pose significant environmental challenges. Improper disposal can result in the release of 2-methylpentane and other potentially harmful components into soil and water systems. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to develop comprehensive recycling and disposal protocols specifically tailored for these sensors.
Long-term environmental effects of widespread 2-methylpentane sensor deployment must also be evaluated. Potential impacts on local microclimates, particularly in urban areas with high sensor density, should be studied. Furthermore, the cumulative effect of multiple sensors on air quality and ecosystem health needs to be assessed through ongoing environmental monitoring programs.
To address these environmental concerns, researchers and manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly alternatives and improvements to 2-methylpentane sensor technology. This includes developing sensors with lower 2-methylpentane concentrations, improving sensor encapsulation to prevent leakage, and investigating biodegradable materials for sensor components.
In conclusion, while 2-methylpentane sensors offer significant benefits in advanced sensing applications, their environmental impact must be carefully managed. A holistic approach considering the entire lifecycle of these sensors is necessary to ensure their sustainable integration into various technological systems and environments.
Standardization and Calibration Challenges
The application of 2-Methylpentane in advanced sensor technologies presents significant challenges in standardization and calibration. These challenges stem from the unique properties of 2-Methylpentane and its interactions with various sensor components, necessitating the development of robust and reliable calibration methods.
One of the primary challenges lies in establishing standardized protocols for sensor calibration using 2-Methylpentane. The compound's volatility and sensitivity to environmental factors, such as temperature and pressure, require precise control during the calibration process. This necessitates the development of specialized calibration chambers and equipment capable of maintaining stable conditions throughout the procedure.
Furthermore, the potential for cross-sensitivity with other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) presents a significant hurdle in achieving accurate and reproducible calibration results. Sensors utilizing 2-Methylpentane must be rigorously tested against a wide range of potential interferents to ensure selectivity and minimize false positives or negatives in real-world applications.
The long-term stability of 2-Methylpentane-based sensors poses another challenge in standardization efforts. Drift in sensor response over time can lead to inaccurate measurements and reduced reliability. Developing standardized methods for assessing and compensating for sensor drift is crucial for maintaining consistent performance across different devices and over extended periods of use.
Calibration of multi-sensor arrays incorporating 2-Methylpentane sensors adds another layer of complexity. The interactions between different sensor elements and the potential for synergistic or antagonistic effects require sophisticated calibration algorithms and data processing techniques. Standardizing these approaches across different sensor designs and manufacturers is essential for ensuring comparability of results.
The development of reference materials and certified gas mixtures containing 2-Methylpentane at precise concentrations is another critical aspect of standardization. These materials are necessary for accurate calibration and validation of sensor performance. However, producing and maintaining such reference materials with long-term stability and traceability to international standards presents significant technical challenges.
Addressing these standardization and calibration challenges requires collaborative efforts between sensor manufacturers, research institutions, and regulatory bodies. The establishment of international standards and guidelines for 2-Methylpentane sensor calibration is crucial for advancing the field and ensuring the reliability of sensor data across different applications and geographical regions.
One of the primary challenges lies in establishing standardized protocols for sensor calibration using 2-Methylpentane. The compound's volatility and sensitivity to environmental factors, such as temperature and pressure, require precise control during the calibration process. This necessitates the development of specialized calibration chambers and equipment capable of maintaining stable conditions throughout the procedure.
Furthermore, the potential for cross-sensitivity with other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) presents a significant hurdle in achieving accurate and reproducible calibration results. Sensors utilizing 2-Methylpentane must be rigorously tested against a wide range of potential interferents to ensure selectivity and minimize false positives or negatives in real-world applications.
The long-term stability of 2-Methylpentane-based sensors poses another challenge in standardization efforts. Drift in sensor response over time can lead to inaccurate measurements and reduced reliability. Developing standardized methods for assessing and compensating for sensor drift is crucial for maintaining consistent performance across different devices and over extended periods of use.
Calibration of multi-sensor arrays incorporating 2-Methylpentane sensors adds another layer of complexity. The interactions between different sensor elements and the potential for synergistic or antagonistic effects require sophisticated calibration algorithms and data processing techniques. Standardizing these approaches across different sensor designs and manufacturers is essential for ensuring comparability of results.
The development of reference materials and certified gas mixtures containing 2-Methylpentane at precise concentrations is another critical aspect of standardization. These materials are necessary for accurate calibration and validation of sensor performance. However, producing and maintaining such reference materials with long-term stability and traceability to international standards presents significant technical challenges.
Addressing these standardization and calibration challenges requires collaborative efforts between sensor manufacturers, research institutions, and regulatory bodies. The establishment of international standards and guidelines for 2-Methylpentane sensor calibration is crucial for advancing the field and ensuring the reliability of sensor data across different applications and geographical regions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!