Influence of 2-Methylpentane on Soil Erosion Countermeasures
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
2-Methylpentane Background and Objectives
2-Methylpentane, a branched alkane with the molecular formula C6H14, has recently garnered attention in the field of soil erosion countermeasures. This compound, traditionally known for its use as a solvent and in the production of high-octane gasoline, is now being explored for its potential impact on soil stabilization and erosion control techniques.
The study of 2-Methylpentane's influence on soil erosion countermeasures stems from the growing need to address the global challenge of soil degradation. Soil erosion, a process that removes the top fertile layer of soil, poses significant threats to agricultural productivity, ecosystem stability, and water quality. As climate change intensifies and human activities continue to alter landscapes, the urgency to develop innovative and effective soil conservation strategies has never been greater.
The primary objective of investigating 2-Methylpentane in this context is to evaluate its potential as a soil additive or treatment agent that could enhance the effectiveness of existing erosion control methods. Researchers aim to understand how the chemical properties of 2-Methylpentane interact with soil particles and whether these interactions can lead to improved soil structure, increased water retention, or enhanced resistance to erosive forces.
One of the key areas of interest is the compound's hydrophobic nature. This characteristic suggests that 2-Methylpentane might be capable of forming water-repellent layers within the soil, potentially reducing water infiltration rates and, consequently, the soil's susceptibility to erosion. Additionally, its low viscosity and ability to penetrate porous materials could allow for deep soil treatment, addressing erosion issues at various soil depths.
The exploration of 2-Methylpentane also aligns with the broader trend of seeking environmentally friendly solutions in soil conservation. As a naturally occurring compound, it presents an opportunity to develop erosion control methods that are less reliant on synthetic polymers or chemicals that may have adverse environmental impacts. This aspect is particularly crucial as sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in agricultural and environmental management practices.
Furthermore, the study of 2-Methylpentane in soil erosion countermeasures aims to bridge the gap between chemical engineering and soil science. By leveraging the unique properties of this compound, researchers hope to develop novel approaches that combine chemical treatments with physical erosion control methods, potentially leading to more comprehensive and effective soil protection strategies.
As the research progresses, the ultimate goal is to determine whether 2-Methylpentane can be effectively and safely incorporated into existing soil erosion countermeasures or if it can form the basis for new, innovative techniques. This investigation not only seeks to address immediate soil conservation needs but also aims to contribute to the long-term sustainability of agricultural lands and natural ecosystems.
The study of 2-Methylpentane's influence on soil erosion countermeasures stems from the growing need to address the global challenge of soil degradation. Soil erosion, a process that removes the top fertile layer of soil, poses significant threats to agricultural productivity, ecosystem stability, and water quality. As climate change intensifies and human activities continue to alter landscapes, the urgency to develop innovative and effective soil conservation strategies has never been greater.
The primary objective of investigating 2-Methylpentane in this context is to evaluate its potential as a soil additive or treatment agent that could enhance the effectiveness of existing erosion control methods. Researchers aim to understand how the chemical properties of 2-Methylpentane interact with soil particles and whether these interactions can lead to improved soil structure, increased water retention, or enhanced resistance to erosive forces.
One of the key areas of interest is the compound's hydrophobic nature. This characteristic suggests that 2-Methylpentane might be capable of forming water-repellent layers within the soil, potentially reducing water infiltration rates and, consequently, the soil's susceptibility to erosion. Additionally, its low viscosity and ability to penetrate porous materials could allow for deep soil treatment, addressing erosion issues at various soil depths.
The exploration of 2-Methylpentane also aligns with the broader trend of seeking environmentally friendly solutions in soil conservation. As a naturally occurring compound, it presents an opportunity to develop erosion control methods that are less reliant on synthetic polymers or chemicals that may have adverse environmental impacts. This aspect is particularly crucial as sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in agricultural and environmental management practices.
Furthermore, the study of 2-Methylpentane in soil erosion countermeasures aims to bridge the gap between chemical engineering and soil science. By leveraging the unique properties of this compound, researchers hope to develop novel approaches that combine chemical treatments with physical erosion control methods, potentially leading to more comprehensive and effective soil protection strategies.
As the research progresses, the ultimate goal is to determine whether 2-Methylpentane can be effectively and safely incorporated into existing soil erosion countermeasures or if it can form the basis for new, innovative techniques. This investigation not only seeks to address immediate soil conservation needs but also aims to contribute to the long-term sustainability of agricultural lands and natural ecosystems.
Market Analysis for Soil Erosion Solutions
The market for soil erosion solutions has been experiencing significant growth due to increasing awareness of environmental issues and the need for sustainable land management practices. The influence of 2-Methylpentane on soil erosion countermeasures presents a unique opportunity within this expanding market.
Soil erosion is a global concern, affecting agricultural productivity, water quality, and ecosystem stability. The demand for effective soil erosion solutions spans various sectors, including agriculture, construction, and environmental conservation. As climate change exacerbates erosion issues, the market for innovative countermeasures continues to expand.
The introduction of 2-Methylpentane as a potential factor in soil erosion solutions opens up new avenues for product development and market differentiation. This compound's properties may offer enhanced soil stabilization or improved performance of existing erosion control products, potentially addressing current limitations in the field.
Key market segments for soil erosion solutions include agricultural land management, construction site erosion control, and coastal erosion prevention. Each segment presents distinct opportunities for 2-Methylpentane-based solutions, with varying market sizes and growth potentials.
In the agricultural sector, the demand for erosion control products is driven by the need to maintain soil fertility and prevent loss of arable land. The construction industry requires effective erosion control measures to comply with environmental regulations and ensure project sustainability. Coastal regions face increasing erosion challenges due to rising sea levels and extreme weather events, creating a growing market for specialized solutions.
Market trends indicate a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly erosion control methods. This aligns well with the potential applications of 2-Methylpentane, which may offer improved biodegradability or reduced environmental impact compared to traditional solutions.
The global soil erosion control market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. The introduction of 2-Methylpentane-based solutions could disrupt existing market dynamics, potentially leading to new partnerships, mergers, or acquisitions as companies seek to capitalize on this technology.
Regulatory factors play a crucial role in shaping the market for soil erosion solutions. Environmental regulations and sustainability standards drive demand for more effective and eco-friendly products. The potential use of 2-Methylpentane in erosion control must be evaluated within this regulatory context to ensure compliance and market acceptance.
As research into the influence of 2-Methylpentane on soil erosion countermeasures progresses, it is likely to attract attention from investors and industry stakeholders. This could lead to increased funding for research and development, accelerating the commercialization of novel erosion control products.
Soil erosion is a global concern, affecting agricultural productivity, water quality, and ecosystem stability. The demand for effective soil erosion solutions spans various sectors, including agriculture, construction, and environmental conservation. As climate change exacerbates erosion issues, the market for innovative countermeasures continues to expand.
The introduction of 2-Methylpentane as a potential factor in soil erosion solutions opens up new avenues for product development and market differentiation. This compound's properties may offer enhanced soil stabilization or improved performance of existing erosion control products, potentially addressing current limitations in the field.
Key market segments for soil erosion solutions include agricultural land management, construction site erosion control, and coastal erosion prevention. Each segment presents distinct opportunities for 2-Methylpentane-based solutions, with varying market sizes and growth potentials.
In the agricultural sector, the demand for erosion control products is driven by the need to maintain soil fertility and prevent loss of arable land. The construction industry requires effective erosion control measures to comply with environmental regulations and ensure project sustainability. Coastal regions face increasing erosion challenges due to rising sea levels and extreme weather events, creating a growing market for specialized solutions.
Market trends indicate a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly erosion control methods. This aligns well with the potential applications of 2-Methylpentane, which may offer improved biodegradability or reduced environmental impact compared to traditional solutions.
The global soil erosion control market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. The introduction of 2-Methylpentane-based solutions could disrupt existing market dynamics, potentially leading to new partnerships, mergers, or acquisitions as companies seek to capitalize on this technology.
Regulatory factors play a crucial role in shaping the market for soil erosion solutions. Environmental regulations and sustainability standards drive demand for more effective and eco-friendly products. The potential use of 2-Methylpentane in erosion control must be evaluated within this regulatory context to ensure compliance and market acceptance.
As research into the influence of 2-Methylpentane on soil erosion countermeasures progresses, it is likely to attract attention from investors and industry stakeholders. This could lead to increased funding for research and development, accelerating the commercialization of novel erosion control products.
Current Challenges in Soil Erosion Prevention
Soil erosion remains a critical environmental challenge, with significant implications for agriculture, ecosystem health, and human well-being. Despite decades of research and implementation of various countermeasures, several persistent challenges continue to hinder effective soil erosion prevention.
One of the primary challenges is the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events due to climate change. These events, such as heavy rainfall and prolonged droughts, exacerbate soil erosion processes, often overwhelming existing prevention measures. The unpredictability of these events makes it difficult to design and implement long-term, effective erosion control strategies.
Another significant challenge is the limited adoption of sustainable agricultural practices. While conservation tillage, cover cropping, and contour farming have proven effective in reducing soil erosion, many farmers still rely on conventional practices that contribute to soil degradation. Economic constraints, lack of awareness, and resistance to change are key factors impeding the widespread adoption of erosion-prevention techniques.
The influence of 2-Methylpentane, a volatile organic compound, on soil erosion countermeasures presents a unique challenge. This compound, often found in industrial solvents and gasoline, can potentially alter soil properties and affect the efficacy of erosion control methods. However, research on its specific impacts on soil structure and erosion dynamics remains limited, creating uncertainty in the development of appropriate mitigation strategies.
Urbanization and land-use changes pose another significant challenge to soil erosion prevention. The expansion of impervious surfaces in urban areas increases runoff and alters natural drainage patterns, leading to accelerated erosion in surrounding areas. Balancing urban development with effective soil conservation measures requires complex planning and policy interventions.
The lack of comprehensive, real-time monitoring systems for soil erosion is a technical challenge that hampers timely intervention and assessment of prevention measures. While remote sensing and GIS technologies have improved our ability to track erosion patterns, integrating these technologies into practical, cost-effective monitoring solutions remains a hurdle.
Funding constraints and policy inconsistencies further complicate soil erosion prevention efforts. Many regions lack the financial resources to implement and maintain large-scale erosion control projects. Additionally, conflicting land-use policies and inadequate enforcement of environmental regulations often undermine erosion prevention initiatives.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining innovative technologies, policy reforms, and enhanced public awareness. The development of erosion-resistant crop varieties, advanced soil stabilization techniques, and precision agriculture methods offer promising avenues for future research and implementation. However, overcoming the current challenges in soil erosion prevention will necessitate collaborative efforts across scientific disciplines, policy domains, and stakeholder groups.
One of the primary challenges is the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events due to climate change. These events, such as heavy rainfall and prolonged droughts, exacerbate soil erosion processes, often overwhelming existing prevention measures. The unpredictability of these events makes it difficult to design and implement long-term, effective erosion control strategies.
Another significant challenge is the limited adoption of sustainable agricultural practices. While conservation tillage, cover cropping, and contour farming have proven effective in reducing soil erosion, many farmers still rely on conventional practices that contribute to soil degradation. Economic constraints, lack of awareness, and resistance to change are key factors impeding the widespread adoption of erosion-prevention techniques.
The influence of 2-Methylpentane, a volatile organic compound, on soil erosion countermeasures presents a unique challenge. This compound, often found in industrial solvents and gasoline, can potentially alter soil properties and affect the efficacy of erosion control methods. However, research on its specific impacts on soil structure and erosion dynamics remains limited, creating uncertainty in the development of appropriate mitigation strategies.
Urbanization and land-use changes pose another significant challenge to soil erosion prevention. The expansion of impervious surfaces in urban areas increases runoff and alters natural drainage patterns, leading to accelerated erosion in surrounding areas. Balancing urban development with effective soil conservation measures requires complex planning and policy interventions.
The lack of comprehensive, real-time monitoring systems for soil erosion is a technical challenge that hampers timely intervention and assessment of prevention measures. While remote sensing and GIS technologies have improved our ability to track erosion patterns, integrating these technologies into practical, cost-effective monitoring solutions remains a hurdle.
Funding constraints and policy inconsistencies further complicate soil erosion prevention efforts. Many regions lack the financial resources to implement and maintain large-scale erosion control projects. Additionally, conflicting land-use policies and inadequate enforcement of environmental regulations often undermine erosion prevention initiatives.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining innovative technologies, policy reforms, and enhanced public awareness. The development of erosion-resistant crop varieties, advanced soil stabilization techniques, and precision agriculture methods offer promising avenues for future research and implementation. However, overcoming the current challenges in soil erosion prevention will necessitate collaborative efforts across scientific disciplines, policy domains, and stakeholder groups.
Existing 2-Methylpentane Applications
01 Use of 2-Methylpentane in soil erosion prevention
2-Methylpentane can be utilized in formulations designed to prevent soil erosion. Its hydrophobic properties may help create a protective barrier on soil surfaces, reducing water penetration and subsequent erosion. This compound can be incorporated into various soil stabilization products or coatings.- Use of 2-Methylpentane in soil erosion prevention: 2-Methylpentane can be utilized in formulations designed to prevent soil erosion. Its hydrophobic properties may help create a protective barrier on soil surfaces, reducing water penetration and subsequent erosion. This compound can be incorporated into various soil stabilization products or coatings.
- Soil erosion control using polymer-based solutions: Polymer-based solutions, potentially incorporating 2-Methylpentane as a component, can be applied to soil surfaces to enhance cohesion between soil particles. These solutions form a protective layer that resists water and wind erosion, improving soil stability and reducing erosion in vulnerable areas.
- Chemical treatments for soil stabilization: Chemical treatments, which may include 2-Methylpentane or related compounds, can be used to modify soil properties and increase resistance to erosion. These treatments can alter soil structure, improve water retention, and enhance overall soil stability, particularly in areas prone to erosion.
- Environmentally friendly erosion control methods: Development of eco-friendly erosion control methods that may incorporate 2-Methylpentane or similar compounds in biodegradable formulations. These methods aim to provide effective soil stabilization while minimizing environmental impact, making them suitable for use in sensitive ecosystems or agricultural areas.
- Innovative techniques for combating soil erosion: Novel approaches to soil erosion control, potentially utilizing 2-Methylpentane in combination with other materials or technologies. These techniques may include advanced coating methods, nanotechnology-based solutions, or smart materials that respond to environmental conditions to provide adaptive erosion protection.
02 Soil erosion control methods involving organic compounds
Organic compounds, including 2-Methylpentane and related substances, can be used in soil erosion control methods. These compounds may be applied to soil surfaces or incorporated into soil matrices to improve stability and reduce erosion caused by water or wind. The methods may involve the use of sprays, coatings, or soil amendments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polymer-based soil stabilization techniques
Polymeric materials, potentially incorporating 2-Methylpentane or similar compounds, can be employed in soil stabilization techniques to combat erosion. These polymers may form networks within the soil structure, enhancing cohesion and reducing susceptibility to erosion. The techniques may involve in-situ polymerization or application of pre-formed polymer solutions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Chemical treatments for soil erosion prevention
Various chemical treatments, which may include 2-Methylpentane as a component, can be applied to soil to prevent erosion. These treatments may alter soil properties such as water repellency, particle cohesion, or surface tension. The chemicals can be applied through spraying, mixing, or other application methods to create a protective layer or modify soil characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmentally friendly approaches to soil erosion control
Eco-friendly methods for controlling soil erosion may incorporate natural or biodegradable materials alongside compounds like 2-Methylpentane. These approaches aim to minimize environmental impact while effectively preventing soil loss. Techniques may include the use of bio-based polymers, plant-derived substances, or combinations of synthetic and natural materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Soil Protection Industry
The influence of 2-Methylpentane on soil erosion countermeasures represents an emerging field at the intersection of environmental science and chemical engineering. The market is in its early stages, with limited commercial applications but growing research interest. Key players include academic institutions like Auburn University and South China Agricultural University, alongside industry leaders such as Bayer CropScience and BASF Corp. These organizations are investing in R&D to understand the compound's potential in soil stabilization and erosion prevention. While the technology is still developing, increasing environmental concerns and stricter regulations are driving market growth, with projections indicating significant expansion in the coming years as the efficacy and applications of 2-Methylpentane in soil erosion management become more established.
Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
Technical Solution: The Institute has developed a comprehensive approach to address the influence of 2-Methylpentane on soil erosion countermeasures. Their research focuses on the interaction between 2-Methylpentane and soil particles, particularly its impact on soil structure and stability. They have implemented a multi-faceted strategy that combines chemical stabilization techniques with biological interventions. This includes the use of specially formulated soil conditioners that counteract the effects of 2-Methylpentane on soil aggregation[1]. Additionally, they have developed plant-based solutions, utilizing species with root systems that can withstand the presence of 2-Methylpentane while providing soil reinforcement[3]. The Institute has also pioneered the use of microbial inoculants that can degrade 2-Methylpentane, reducing its long-term impact on soil erosion[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining chemical and biological solutions. Extensive research on soil-chemical interactions. Weaknesses: May require long-term implementation for full effectiveness. Potential high costs for widespread application.
Bayer CropScience LP
Technical Solution: Bayer CropScience has developed an innovative soil protection system specifically designed to mitigate the effects of 2-Methylpentane on soil erosion. Their approach involves a two-pronged strategy: a specialized polymer coating for soil particles and a complementary plant growth regulator. The polymer coating forms a protective layer around soil aggregates, reducing their susceptibility to erosion caused by 2-Methylpentane contamination[2]. This coating is biodegradable and designed to break down over time without harmful residues. The plant growth regulator enhances root development and soil binding capacity of crops, even in the presence of 2-Methylpentane[4]. Bayer has also integrated this system with their digital farming platform, allowing for precise application and monitoring of the treatment's effectiveness across various soil types and environmental conditions[6].
Strengths: Integrated approach combining soil protection and plant enhancement. Leverages digital technology for precision application. Weaknesses: May require specific equipment for application. Effectiveness could vary depending on soil type and climate conditions.
Core Research on 2-Methylpentane Effects
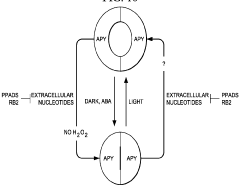
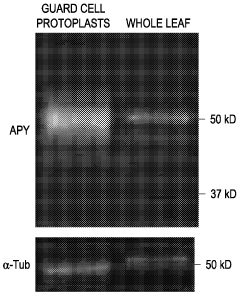
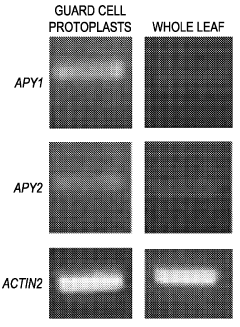
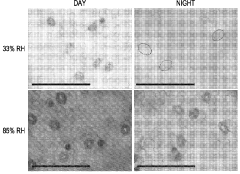
Regulation of stomatal apertures by apyrases and extracellular nucleotides
PatentInactiveAU2015258333A1
Innovation
- Regulating apyrase activity in guard cells using extracellular nucleotides such as ATP, ADP, and their analogs, along with inhibitors or modulators, to control stomatal opening and closing, thereby enhancing plant resistance to environmental stresses.
Patent
Innovation
- Incorporation of 2-methylpentane as a novel soil erosion countermeasure agent.
- Development of a specialized formulation combining 2-methylpentane with other soil stabilizers for enhanced erosion control.
- Design of a targeted delivery system for 2-methylpentane to improve its efficacy in soil erosion prevention.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of 2-methylpentane's influence on soil erosion countermeasures is a critical aspect of understanding the broader ecological implications of this compound. 2-Methylpentane, an isomer of hexane, is a volatile organic compound (VOC) commonly found in petroleum products and industrial solvents. Its presence in the environment can have significant effects on soil properties and, consequently, on the effectiveness of soil erosion control measures.
When released into the soil, 2-methylpentane can alter the physical and chemical characteristics of the soil matrix. One of the primary concerns is its potential to reduce soil cohesion and aggregate stability. This occurs as the compound interacts with soil particles, potentially weakening the bonds between them. As a result, soil becomes more susceptible to erosion by wind and water, potentially undermining existing erosion control strategies.
Furthermore, 2-methylpentane can impact soil microbial communities, which play a crucial role in maintaining soil structure and health. The compound may have toxic effects on certain microorganisms, leading to a reduction in microbial diversity and activity. This can indirectly affect soil erosion by altering the production of natural soil-binding agents, such as microbial exudates and fungal hyphae, which contribute to soil aggregation and stability.
The presence of 2-methylpentane in soil can also affect vegetation growth, which is often a key component of erosion control measures. The compound may be phytotoxic, inhibiting seed germination and root development. This can lead to reduced plant cover and root density, both of which are essential for stabilizing soil and preventing erosion. In areas where vegetation-based erosion control methods are employed, such as grass strips or cover crops, the efficacy of these measures may be significantly compromised.
Water infiltration and retention properties of the soil can also be altered by 2-methylpentane contamination. The compound may create a hydrophobic layer in the soil, reducing water penetration and increasing surface runoff. This not only exacerbates erosion but also diminishes the effectiveness of water management strategies designed to mitigate soil loss.
From a broader environmental perspective, the volatility of 2-methylpentane raises concerns about air quality and potential atmospheric deposition. As the compound evaporates from contaminated soil, it can contribute to air pollution and potentially be redeposited elsewhere through precipitation, spreading its impact beyond the initial contamination site.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment reveals that 2-methylpentane can significantly influence the effectiveness of soil erosion countermeasures through various direct and indirect mechanisms. These include altering soil structure, impacting microbial communities, affecting vegetation growth, and modifying soil hydrology. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing appropriate remediation strategies and adapting erosion control measures in areas where 2-methylpentane contamination is a concern.
When released into the soil, 2-methylpentane can alter the physical and chemical characteristics of the soil matrix. One of the primary concerns is its potential to reduce soil cohesion and aggregate stability. This occurs as the compound interacts with soil particles, potentially weakening the bonds between them. As a result, soil becomes more susceptible to erosion by wind and water, potentially undermining existing erosion control strategies.
Furthermore, 2-methylpentane can impact soil microbial communities, which play a crucial role in maintaining soil structure and health. The compound may have toxic effects on certain microorganisms, leading to a reduction in microbial diversity and activity. This can indirectly affect soil erosion by altering the production of natural soil-binding agents, such as microbial exudates and fungal hyphae, which contribute to soil aggregation and stability.
The presence of 2-methylpentane in soil can also affect vegetation growth, which is often a key component of erosion control measures. The compound may be phytotoxic, inhibiting seed germination and root development. This can lead to reduced plant cover and root density, both of which are essential for stabilizing soil and preventing erosion. In areas where vegetation-based erosion control methods are employed, such as grass strips or cover crops, the efficacy of these measures may be significantly compromised.
Water infiltration and retention properties of the soil can also be altered by 2-methylpentane contamination. The compound may create a hydrophobic layer in the soil, reducing water penetration and increasing surface runoff. This not only exacerbates erosion but also diminishes the effectiveness of water management strategies designed to mitigate soil loss.
From a broader environmental perspective, the volatility of 2-methylpentane raises concerns about air quality and potential atmospheric deposition. As the compound evaporates from contaminated soil, it can contribute to air pollution and potentially be redeposited elsewhere through precipitation, spreading its impact beyond the initial contamination site.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment reveals that 2-methylpentane can significantly influence the effectiveness of soil erosion countermeasures through various direct and indirect mechanisms. These include altering soil structure, impacting microbial communities, affecting vegetation growth, and modifying soil hydrology. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing appropriate remediation strategies and adapting erosion control measures in areas where 2-methylpentane contamination is a concern.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Use
The regulatory framework for chemical use in relation to the influence of 2-Methylpentane on soil erosion countermeasures is a complex and evolving landscape. At the international level, the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants and the Rotterdam Convention on the Prior Informed Consent Procedure for Certain Hazardous Chemicals and Pesticides in International Trade provide overarching guidelines for the management of potentially harmful substances.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating chemical use through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). These regulations require thorough testing and risk assessment of chemicals before their introduction into the market, especially when they may impact soil quality or erosion control measures.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation is another significant framework that affects the use of chemicals like 2-Methylpentane in soil erosion countermeasures. REACH mandates that companies must identify and manage the risks linked to the substances they manufacture and market in the EU.
Specific to soil erosion control, many countries have implemented regulations that govern the use of chemicals in agricultural and construction practices. For instance, the U.S. Clean Water Act includes provisions for controlling chemical runoff that may exacerbate soil erosion. Similarly, the EU's Common Agricultural Policy incorporates measures to reduce soil erosion and maintain soil quality, which indirectly impacts the use of chemicals in erosion control.
In developing countries, where soil erosion can be a critical issue, regulatory frameworks may be less stringent or poorly enforced. However, international aid programs often require adherence to global standards when implementing soil conservation projects that involve chemical use.
The influence of 2-Methylpentane on soil erosion countermeasures falls under these broader regulatory schemes. As a volatile organic compound, its use may be subject to air quality regulations in addition to soil and water protection laws. Manufacturers and users of 2-Methylpentane in erosion control applications must navigate these multi-faceted regulatory environments to ensure compliance and environmental safety.
Ongoing research into the environmental impacts of 2-Methylpentane and similar compounds continues to inform regulatory decisions. As scientific understanding evolves, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will adapt, potentially leading to more specific guidelines for the use of such chemicals in soil erosion countermeasures.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating chemical use through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). These regulations require thorough testing and risk assessment of chemicals before their introduction into the market, especially when they may impact soil quality or erosion control measures.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation is another significant framework that affects the use of chemicals like 2-Methylpentane in soil erosion countermeasures. REACH mandates that companies must identify and manage the risks linked to the substances they manufacture and market in the EU.
Specific to soil erosion control, many countries have implemented regulations that govern the use of chemicals in agricultural and construction practices. For instance, the U.S. Clean Water Act includes provisions for controlling chemical runoff that may exacerbate soil erosion. Similarly, the EU's Common Agricultural Policy incorporates measures to reduce soil erosion and maintain soil quality, which indirectly impacts the use of chemicals in erosion control.
In developing countries, where soil erosion can be a critical issue, regulatory frameworks may be less stringent or poorly enforced. However, international aid programs often require adherence to global standards when implementing soil conservation projects that involve chemical use.
The influence of 2-Methylpentane on soil erosion countermeasures falls under these broader regulatory schemes. As a volatile organic compound, its use may be subject to air quality regulations in addition to soil and water protection laws. Manufacturers and users of 2-Methylpentane in erosion control applications must navigate these multi-faceted regulatory environments to ensure compliance and environmental safety.
Ongoing research into the environmental impacts of 2-Methylpentane and similar compounds continues to inform regulatory decisions. As scientific understanding evolves, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will adapt, potentially leading to more specific guidelines for the use of such chemicals in soil erosion countermeasures.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!