Steering Wheel Innovations: Supporting Vehicle Intelligence Systems
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Steering Wheel Evolution
The steering wheel has undergone a remarkable evolution since its inception, transforming from a simple mechanical device to a sophisticated interface for vehicle control and intelligence systems. In the early days of automobiles, steering wheels were purely functional, designed to provide directional control through mechanical linkages. As automotive technology advanced, power steering systems were introduced in the 1950s, reducing the physical effort required to maneuver vehicles.
The 1980s and 1990s saw the integration of additional controls into steering wheels, such as audio system buttons and cruise control switches. This marked the beginning of the steering wheel's transformation into a multifunctional interface. With the rise of digital technologies in the 2000s, steering wheels began incorporating more advanced features, including voice control activation and display screens for vehicle information.
In recent years, the steering wheel has become a critical component in the development of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies. Modern steering wheels are equipped with sensors to detect driver grip and attentiveness, playing a crucial role in semi-autonomous driving modes. Some designs now include haptic feedback systems to alert drivers of potential hazards or lane departures.
The advent of drive-by-wire technology has further revolutionized steering wheel design, allowing for more flexible layouts and enhanced ergonomics. This has paved the way for innovative concepts such as retractable steering wheels in autonomous vehicles and steer-by-wire systems that can adjust steering ratios based on driving conditions.
As vehicles become increasingly connected and intelligent, steering wheels are evolving into comprehensive human-machine interfaces. They now serve as hubs for accessing a wide range of vehicle functions, from navigation and infotainment to advanced driver assistance features. Some cutting-edge designs incorporate touch-sensitive surfaces and gesture recognition capabilities, further blurring the line between traditional vehicle controls and modern digital interfaces.
Looking ahead, the future of steering wheel design is closely tied to the development of autonomous driving technologies. While fully autonomous vehicles may eventually render traditional steering wheels obsolete, the transition period is likely to see highly adaptive designs that can seamlessly switch between manual and autonomous modes. These next-generation steering wheels will likely incorporate advanced haptic systems, augmented reality displays, and biometric sensors to enhance both safety and user experience in increasingly intelligent vehicles.
The 1980s and 1990s saw the integration of additional controls into steering wheels, such as audio system buttons and cruise control switches. This marked the beginning of the steering wheel's transformation into a multifunctional interface. With the rise of digital technologies in the 2000s, steering wheels began incorporating more advanced features, including voice control activation and display screens for vehicle information.
In recent years, the steering wheel has become a critical component in the development of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies. Modern steering wheels are equipped with sensors to detect driver grip and attentiveness, playing a crucial role in semi-autonomous driving modes. Some designs now include haptic feedback systems to alert drivers of potential hazards or lane departures.
The advent of drive-by-wire technology has further revolutionized steering wheel design, allowing for more flexible layouts and enhanced ergonomics. This has paved the way for innovative concepts such as retractable steering wheels in autonomous vehicles and steer-by-wire systems that can adjust steering ratios based on driving conditions.
As vehicles become increasingly connected and intelligent, steering wheels are evolving into comprehensive human-machine interfaces. They now serve as hubs for accessing a wide range of vehicle functions, from navigation and infotainment to advanced driver assistance features. Some cutting-edge designs incorporate touch-sensitive surfaces and gesture recognition capabilities, further blurring the line between traditional vehicle controls and modern digital interfaces.
Looking ahead, the future of steering wheel design is closely tied to the development of autonomous driving technologies. While fully autonomous vehicles may eventually render traditional steering wheels obsolete, the transition period is likely to see highly adaptive designs that can seamlessly switch between manual and autonomous modes. These next-generation steering wheels will likely incorporate advanced haptic systems, augmented reality displays, and biometric sensors to enhance both safety and user experience in increasingly intelligent vehicles.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for innovative steering wheel technologies supporting vehicle intelligence systems has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. This surge is primarily driven by the increasing integration of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving capabilities in modern vehicles. As vehicles become more intelligent and connected, the steering wheel has evolved from a simple control device to a sophisticated interface between the driver and the vehicle's complex systems.
Consumer expectations for safer, more comfortable, and technologically advanced vehicles are fueling this demand. The steering wheel, being the primary point of contact between the driver and the vehicle, is seen as a crucial component for enhancing the overall driving experience. Market research indicates that consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for vehicles equipped with intelligent steering systems that offer enhanced safety features, improved handling, and seamless integration with other vehicle systems.
The automotive industry's shift towards electric and autonomous vehicles is another key factor driving the demand for innovative steering wheel technologies. As traditional mechanical linkages are replaced by electronic systems in these vehicles, there is a growing need for steering wheels that can effectively interface with these new technologies. This transition is opening up new opportunities for steering wheel innovations that can support drive-by-wire systems, adaptive steering, and even steer-by-wire technologies.
Furthermore, the increasing focus on reducing driver distraction and improving safety has led to a rising demand for steering wheels with integrated controls and displays. These advanced steering wheels allow drivers to access various vehicle functions and information without taking their hands off the wheel, thereby enhancing safety and convenience. The market for such multifunctional steering wheels is expected to grow substantially in the coming years.
The commercial vehicle sector is also contributing to the market demand for intelligent steering systems. Fleet operators are increasingly looking for technologies that can improve driver performance, reduce fatigue, and enhance overall fleet efficiency. Steering wheel innovations that can provide real-time feedback on driving behavior, integrate with fleet management systems, and support semi-autonomous driving features are gaining traction in this segment.
Regulatory pressures and safety standards are further propelling the market for advanced steering technologies. As governments worldwide implement stricter safety regulations, automakers are compelled to incorporate more sophisticated steering systems that can support features like lane-keeping assistance, collision avoidance, and adaptive cruise control. This regulatory environment is creating a sustained demand for steering wheel innovations that can meet these evolving safety requirements.
Consumer expectations for safer, more comfortable, and technologically advanced vehicles are fueling this demand. The steering wheel, being the primary point of contact between the driver and the vehicle, is seen as a crucial component for enhancing the overall driving experience. Market research indicates that consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for vehicles equipped with intelligent steering systems that offer enhanced safety features, improved handling, and seamless integration with other vehicle systems.
The automotive industry's shift towards electric and autonomous vehicles is another key factor driving the demand for innovative steering wheel technologies. As traditional mechanical linkages are replaced by electronic systems in these vehicles, there is a growing need for steering wheels that can effectively interface with these new technologies. This transition is opening up new opportunities for steering wheel innovations that can support drive-by-wire systems, adaptive steering, and even steer-by-wire technologies.
Furthermore, the increasing focus on reducing driver distraction and improving safety has led to a rising demand for steering wheels with integrated controls and displays. These advanced steering wheels allow drivers to access various vehicle functions and information without taking their hands off the wheel, thereby enhancing safety and convenience. The market for such multifunctional steering wheels is expected to grow substantially in the coming years.
The commercial vehicle sector is also contributing to the market demand for intelligent steering systems. Fleet operators are increasingly looking for technologies that can improve driver performance, reduce fatigue, and enhance overall fleet efficiency. Steering wheel innovations that can provide real-time feedback on driving behavior, integrate with fleet management systems, and support semi-autonomous driving features are gaining traction in this segment.
Regulatory pressures and safety standards are further propelling the market for advanced steering technologies. As governments worldwide implement stricter safety regulations, automakers are compelled to incorporate more sophisticated steering systems that can support features like lane-keeping assistance, collision avoidance, and adaptive cruise control. This regulatory environment is creating a sustained demand for steering wheel innovations that can meet these evolving safety requirements.
Technical Challenges
The development of steering wheel innovations to support vehicle intelligence systems faces several significant technical challenges. These challenges stem from the need to integrate advanced technologies into a traditionally mechanical component while ensuring safety, reliability, and user acceptance.
One of the primary challenges is the seamless integration of sensors and electronic components into the steering wheel without compromising its structural integrity or ergonomics. Engineers must design steering wheels that can accommodate a variety of sensors, such as touch-sensitive surfaces, biometric sensors, and gesture recognition systems, while maintaining the wheel's primary function and comfort for the driver.
Another critical challenge lies in developing robust and reliable communication protocols between the steering wheel and the vehicle's central intelligence system. This requires low-latency, high-bandwidth data transmission to ensure real-time responsiveness to driver inputs and system feedback. The challenge is compounded by the need for electromagnetic compatibility to prevent interference with other vehicle systems.
The integration of haptic feedback mechanisms presents another technical hurdle. Engineers must develop systems that can provide nuanced tactile information to the driver without causing distraction or fatigue. This involves precise control of vibration patterns, force feedback, and temperature changes within the steering wheel, all of which must be carefully calibrated to enhance the driving experience without overwhelming the user.
Power management and energy efficiency pose significant challenges, particularly in the context of electric and hybrid vehicles. The steering wheel's intelligent systems must operate with minimal power consumption to avoid draining the vehicle's battery or impacting its range. This necessitates the development of ultra-low-power electronics and efficient power distribution systems within the steering wheel assembly.
Durability and longevity of the integrated technologies are also major concerns. The steering wheel must withstand years of use under various environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, humidity, and physical stress. Ensuring that the embedded electronics and sensors can maintain their functionality over the vehicle's lifetime requires advanced materials science and robust design principles.
Safety considerations present perhaps the most critical challenge. The steering wheel must maintain its primary function as a critical safety component while incorporating new technologies. This includes ensuring that the additional features do not interfere with airbag deployment or compromise the wheel's structural integrity in the event of a collision. Additionally, fail-safe mechanisms must be implemented to prevent system malfunctions from affecting steering control.
Human-machine interface (HMI) design presents a unique challenge in steering wheel innovations. Creating intuitive, non-distracting interfaces that allow drivers to access advanced features while maintaining focus on the road requires extensive research in ergonomics, cognitive psychology, and user experience design. The challenge lies in balancing functionality with simplicity to enhance rather than complicate the driving experience.
One of the primary challenges is the seamless integration of sensors and electronic components into the steering wheel without compromising its structural integrity or ergonomics. Engineers must design steering wheels that can accommodate a variety of sensors, such as touch-sensitive surfaces, biometric sensors, and gesture recognition systems, while maintaining the wheel's primary function and comfort for the driver.
Another critical challenge lies in developing robust and reliable communication protocols between the steering wheel and the vehicle's central intelligence system. This requires low-latency, high-bandwidth data transmission to ensure real-time responsiveness to driver inputs and system feedback. The challenge is compounded by the need for electromagnetic compatibility to prevent interference with other vehicle systems.
The integration of haptic feedback mechanisms presents another technical hurdle. Engineers must develop systems that can provide nuanced tactile information to the driver without causing distraction or fatigue. This involves precise control of vibration patterns, force feedback, and temperature changes within the steering wheel, all of which must be carefully calibrated to enhance the driving experience without overwhelming the user.
Power management and energy efficiency pose significant challenges, particularly in the context of electric and hybrid vehicles. The steering wheel's intelligent systems must operate with minimal power consumption to avoid draining the vehicle's battery or impacting its range. This necessitates the development of ultra-low-power electronics and efficient power distribution systems within the steering wheel assembly.
Durability and longevity of the integrated technologies are also major concerns. The steering wheel must withstand years of use under various environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, humidity, and physical stress. Ensuring that the embedded electronics and sensors can maintain their functionality over the vehicle's lifetime requires advanced materials science and robust design principles.
Safety considerations present perhaps the most critical challenge. The steering wheel must maintain its primary function as a critical safety component while incorporating new technologies. This includes ensuring that the additional features do not interfere with airbag deployment or compromise the wheel's structural integrity in the event of a collision. Additionally, fail-safe mechanisms must be implemented to prevent system malfunctions from affecting steering control.
Human-machine interface (HMI) design presents a unique challenge in steering wheel innovations. Creating intuitive, non-distracting interfaces that allow drivers to access advanced features while maintaining focus on the road requires extensive research in ergonomics, cognitive psychology, and user experience design. The challenge lies in balancing functionality with simplicity to enhance rather than complicate the driving experience.
Current Solutions
01 Intelligent steering control systems
Advanced steering control systems that incorporate sensors, processors, and actuators to enhance vehicle handling, stability, and safety. These systems can adjust steering response based on driving conditions, vehicle speed, and driver input, providing a more intelligent and adaptive steering experience.- Intelligent steering control systems: Advanced steering control systems that incorporate sensors, processors, and actuators to enhance vehicle handling, stability, and safety. These systems can adjust steering response based on driving conditions, vehicle speed, and driver input, providing a more intelligent and adaptive steering experience.
- Haptic feedback and force-feedback steering wheels: Steering wheels equipped with haptic feedback mechanisms to provide tactile information to the driver. These systems can communicate road conditions, potential hazards, or navigation cues through vibrations or resistance in the steering wheel, enhancing driver awareness and safety.
- Steering wheel-mounted controls and displays: Integration of various controls and display systems directly into the steering wheel. This can include touchscreens, buttons, or gesture recognition systems that allow drivers to control vehicle functions, infotainment systems, or access important information without taking their hands off the wheel.
- Autonomous and semi-autonomous steering systems: Intelligent steering systems capable of partially or fully controlling the vehicle's steering in certain situations. These systems can assist with parking, lane keeping, or even take full control during autonomous driving modes, integrating with other vehicle systems to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Adaptive steering geometry and variable ratio steering: Intelligent steering systems that can dynamically adjust the steering ratio or geometry based on driving conditions and vehicle speed. These systems can provide more responsive steering at low speeds for improved maneuverability, while offering more stable steering at higher speeds for enhanced comfort and control.
02 Haptic feedback and force-feedback steering wheels
Steering wheels equipped with haptic feedback mechanisms to provide tactile information to the driver. These systems can alert the driver to potential hazards, lane departures, or other important information through vibrations or resistance in the steering wheel, enhancing driver awareness and safety.Expand Specific Solutions03 Steering wheel-mounted controls and displays
Integration of various controls and display systems directly into the steering wheel. This can include touchscreens, buttons, switches, and small displays that allow the driver to control vehicle functions, access information, and interact with infotainment systems without taking their hands off the wheel.Expand Specific Solutions04 Autonomous and semi-autonomous steering systems
Steering systems designed for autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicles, capable of controlling the vehicle's direction with minimal or no human input. These systems often integrate with other vehicle sensors and navigation systems to guide the vehicle safely and efficiently.Expand Specific Solutions05 Adaptive steering geometry and variable ratio steering
Intelligent steering systems that can adjust the steering ratio or geometry based on driving conditions and vehicle speed. These systems can provide more responsive steering at low speeds for improved maneuverability, while offering more stable steering at higher speeds for enhanced comfort and safety.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The steering wheel innovation market supporting vehicle intelligence systems is in a dynamic growth phase, driven by increasing demand for advanced driver assistance systems and autonomous vehicles. The market size is expanding rapidly, with major automotive players like BMW, Volkswagen, and Hyundai investing heavily in this technology. Companies such as Bosch, Continental, and ZF are at the forefront of developing sophisticated steering systems, indicating a high level of technological maturity. However, emerging players like BYD and Xiaomi are also entering the space, potentially disrupting traditional market dynamics. The competition is fierce, with established automotive suppliers and tech companies vying for market share in this critical component of future mobility.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has developed an innovative steering wheel system that integrates advanced sensors and haptic feedback technology to support vehicle intelligence systems. Their solution includes a capacitive sensing layer embedded within the steering wheel rim, capable of detecting hand position and grip strength[1]. This data is used to enhance driver monitoring systems and improve the accuracy of semi-autonomous driving features. Additionally, Bosch has implemented a sophisticated haptic feedback mechanism that can provide subtle vibrations and resistance changes to communicate important information to the driver, such as lane departure warnings or upcoming navigation instructions[2]. The system also incorporates LED lighting elements around the steering wheel rim, which can be used to provide visual cues and alerts to the driver, further enhancing the human-machine interface in intelligent vehicles[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive integration of multiple technologies (capacitive sensing, haptic feedback, visual cues) enhances driver-vehicle interaction. Weaknesses: May require significant changes to existing steering wheel manufacturing processes, potentially increasing costs.
Volkswagen AG
Technical Solution: Volkswagen has introduced a revolutionary steering wheel concept for their intelligent vehicles, focusing on adaptability and enhanced user interaction. Their system features a shape-shifting steering wheel that can transform between traditional circular and flattened rectangular configurations[4]. This morphing capability allows for improved visibility of the instrument cluster in autonomous driving modes and provides a more ergonomic interface for manual control. The steering wheel is equipped with touch-sensitive controls that can adapt their functionality based on the driving mode, offering context-aware interfaces[5]. Volkswagen has also integrated advanced gesture recognition technology, allowing drivers to perform certain vehicle functions with simple hand movements near the steering wheel, reducing the need for physical buttons and enhancing the futuristic feel of the cockpit[6].
Strengths: Highly adaptable design supports both manual and autonomous driving modes seamlessly. Weaknesses: Complex mechanical systems in the morphing steering wheel may lead to higher maintenance requirements and potential reliability issues.
Core Technologies
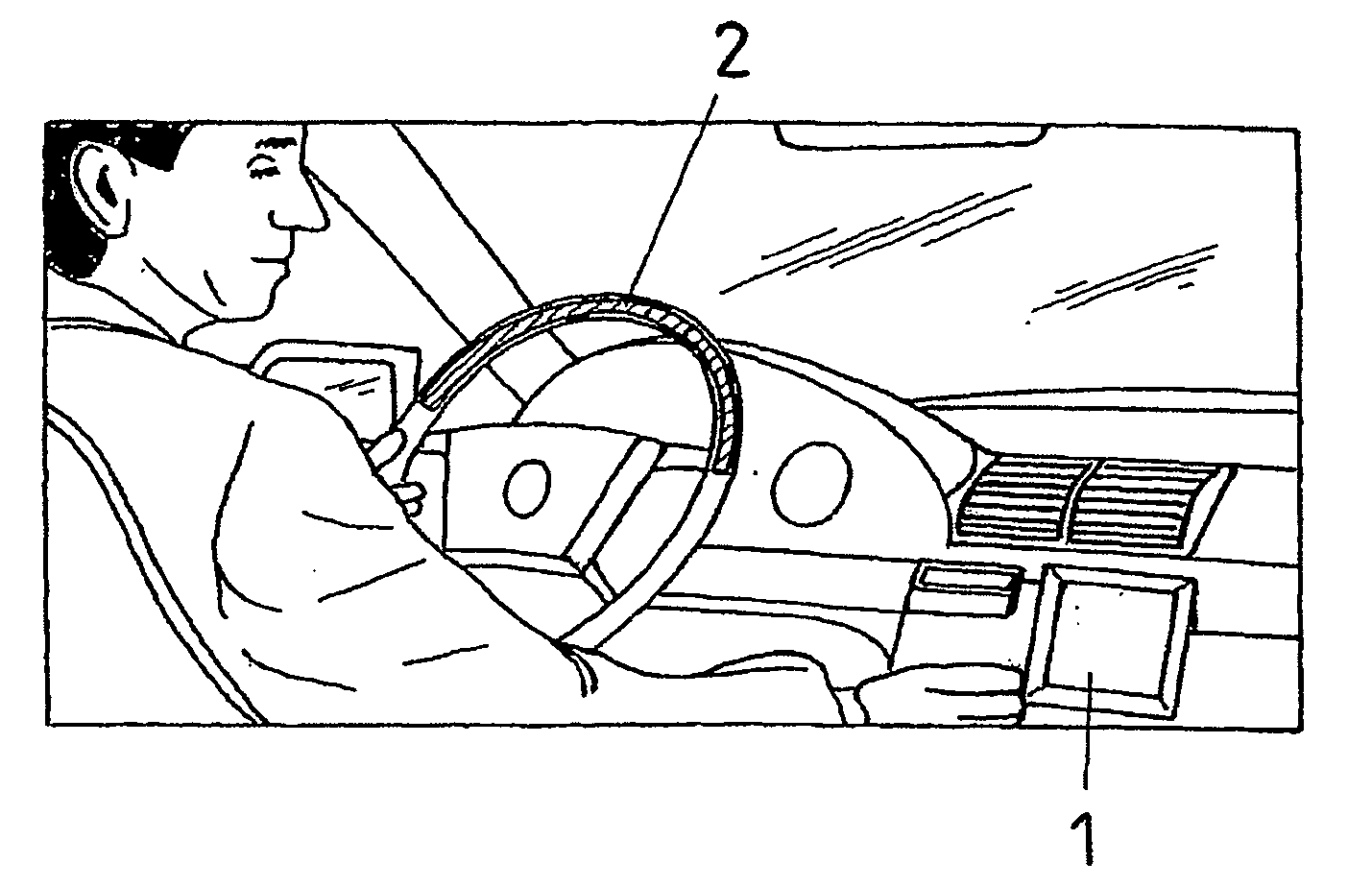
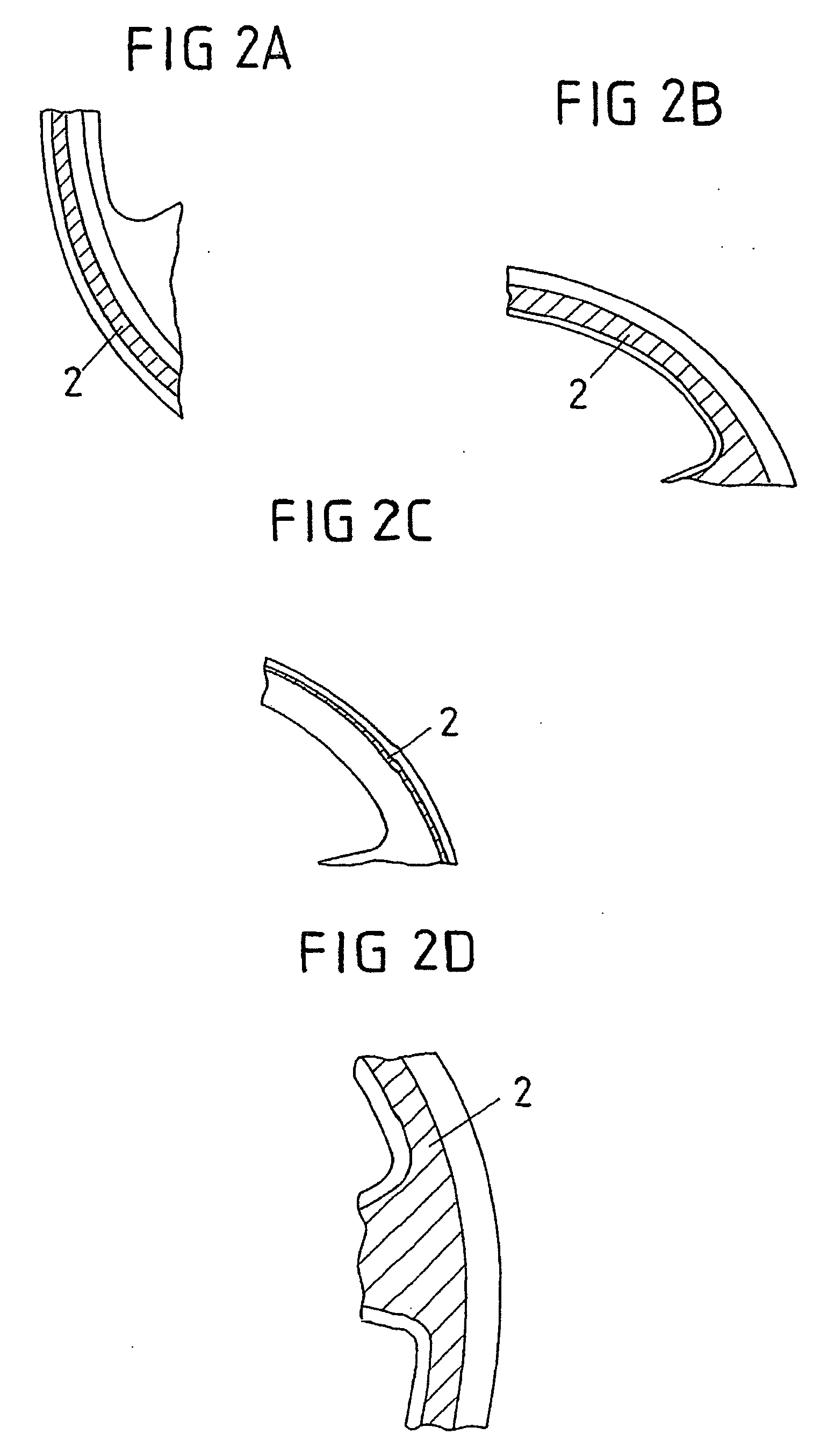
Steering wheel for motor vehicles
PatentWO2004091994A1
Innovation
- The steering wheel is designed as a communication interface with integrated light, display, and vibration elements that provide information from sensors and systems without diverting the driver's attention from the road, allowing for hands-free operation and intuitive feedback on traffic conditions and system alerts.
Steering wheel for motor vehicles
PatentInactiveUS20060070795A1
Innovation
- The steering wheel is transformed into a communications interface by integrating light, display, and vibration elements that provide information directly to the driver, allowing them to receive and input data without significant distraction, with elements arranged on the rim to maintain the driver's focus on the road.
Safety Regulations
Safety regulations play a crucial role in the development and implementation of steering wheel innovations that support vehicle intelligence systems. As automotive technology advances, regulatory bodies must adapt to ensure that new features enhance safety without compromising driver control or introducing new risks.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States and the European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) are at the forefront of establishing safety standards for intelligent vehicle systems. These organizations continuously update their guidelines to address emerging technologies, including those related to steering wheel innovations.
One key area of focus is the integration of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) with steering controls. Regulations mandate that these systems must not interfere with the driver's ability to maintain control of the vehicle at all times. This includes requirements for clear feedback mechanisms and the ability for drivers to override automated steering inputs easily.
Cybersecurity has become a significant concern as steering systems become more connected and software-dependent. Regulatory bodies are developing standards to protect against potential hacking or malicious interference with steering controls. These regulations often require manufacturers to implement robust security measures and provide regular software updates to address vulnerabilities.
Human-machine interface (HMI) design is another critical aspect of safety regulations for intelligent steering systems. Guidelines specify the need for intuitive controls and clear, non-distracting visual and haptic feedback. This ensures that drivers can quickly understand and respond to information provided by the vehicle's intelligence systems through the steering wheel.
Regulations also address the transition between different levels of automation. As vehicles move towards higher levels of autonomy, safety standards require smooth and predictable handovers between automated and manual control. This includes specific protocols for alerting drivers when they need to take control and ensuring that steering systems can operate safely in various modes.
Durability and reliability testing requirements have been expanded to account for the increased complexity of intelligent steering systems. Manufacturers must demonstrate that these systems can withstand long-term use and maintain consistent performance under various environmental conditions.
As the automotive industry continues to innovate, regulatory bodies are working to strike a balance between encouraging technological advancement and maintaining stringent safety standards. This involves ongoing collaboration with manufacturers, technology providers, and safety experts to develop forward-looking regulations that can accommodate future steering wheel innovations while prioritizing vehicle and occupant safety.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States and the European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) are at the forefront of establishing safety standards for intelligent vehicle systems. These organizations continuously update their guidelines to address emerging technologies, including those related to steering wheel innovations.
One key area of focus is the integration of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) with steering controls. Regulations mandate that these systems must not interfere with the driver's ability to maintain control of the vehicle at all times. This includes requirements for clear feedback mechanisms and the ability for drivers to override automated steering inputs easily.
Cybersecurity has become a significant concern as steering systems become more connected and software-dependent. Regulatory bodies are developing standards to protect against potential hacking or malicious interference with steering controls. These regulations often require manufacturers to implement robust security measures and provide regular software updates to address vulnerabilities.
Human-machine interface (HMI) design is another critical aspect of safety regulations for intelligent steering systems. Guidelines specify the need for intuitive controls and clear, non-distracting visual and haptic feedback. This ensures that drivers can quickly understand and respond to information provided by the vehicle's intelligence systems through the steering wheel.
Regulations also address the transition between different levels of automation. As vehicles move towards higher levels of autonomy, safety standards require smooth and predictable handovers between automated and manual control. This includes specific protocols for alerting drivers when they need to take control and ensuring that steering systems can operate safely in various modes.
Durability and reliability testing requirements have been expanded to account for the increased complexity of intelligent steering systems. Manufacturers must demonstrate that these systems can withstand long-term use and maintain consistent performance under various environmental conditions.
As the automotive industry continues to innovate, regulatory bodies are working to strike a balance between encouraging technological advancement and maintaining stringent safety standards. This involves ongoing collaboration with manufacturers, technology providers, and safety experts to develop forward-looking regulations that can accommodate future steering wheel innovations while prioritizing vehicle and occupant safety.
Human-Machine Interface
The human-machine interface (HMI) in steering wheel innovations plays a crucial role in supporting vehicle intelligence systems. As vehicles become increasingly autonomous, the steering wheel serves as a primary point of interaction between the driver and the vehicle's advanced systems. Modern steering wheels are evolving into sophisticated control centers, integrating touch-sensitive surfaces, haptic feedback mechanisms, and voice recognition capabilities.
These innovations aim to enhance driver awareness and control while minimizing distractions. For instance, touch-sensitive panels embedded in the steering wheel allow drivers to access various vehicle functions without removing their hands from the wheel. This feature improves safety by reducing the need for drivers to look away from the road or reach for dashboard controls.
Haptic feedback systems integrated into the steering wheel provide tactile cues to the driver, conveying important information about road conditions, navigation directions, or potential hazards. This technology enhances the driver's situational awareness and complements visual and auditory alerts, creating a more immersive and intuitive driving experience.
Voice recognition technology incorporated into the steering wheel enables hands-free control of various vehicle systems, including infotainment, climate control, and navigation. This feature allows drivers to maintain focus on the road while interacting with the vehicle's intelligent systems, further enhancing safety and convenience.
Advanced steering wheels also incorporate biometric sensors to monitor driver alertness and health status. These sensors can detect signs of fatigue or stress, prompting the vehicle's intelligence systems to intervene if necessary, such as suggesting a rest stop or activating driver assistance features.
As vehicles transition towards higher levels of autonomy, the steering wheel HMI is adapting to support new modes of operation. For instance, some concept designs feature retractable steering wheels that can be stowed away during fully autonomous driving, transforming the driver's area into a more versatile space. When manual control is required, the steering wheel can be quickly deployed, seamlessly transitioning between autonomous and manual driving modes.
The integration of augmented reality (AR) displays into the steering wheel HMI is another emerging trend. These displays can project relevant information directly onto the windshield or the steering wheel itself, providing real-time data about the vehicle's surroundings, navigation instructions, and system status without requiring the driver to look away from the road.
These innovations aim to enhance driver awareness and control while minimizing distractions. For instance, touch-sensitive panels embedded in the steering wheel allow drivers to access various vehicle functions without removing their hands from the wheel. This feature improves safety by reducing the need for drivers to look away from the road or reach for dashboard controls.
Haptic feedback systems integrated into the steering wheel provide tactile cues to the driver, conveying important information about road conditions, navigation directions, or potential hazards. This technology enhances the driver's situational awareness and complements visual and auditory alerts, creating a more immersive and intuitive driving experience.
Voice recognition technology incorporated into the steering wheel enables hands-free control of various vehicle systems, including infotainment, climate control, and navigation. This feature allows drivers to maintain focus on the road while interacting with the vehicle's intelligent systems, further enhancing safety and convenience.
Advanced steering wheels also incorporate biometric sensors to monitor driver alertness and health status. These sensors can detect signs of fatigue or stress, prompting the vehicle's intelligence systems to intervene if necessary, such as suggesting a rest stop or activating driver assistance features.
As vehicles transition towards higher levels of autonomy, the steering wheel HMI is adapting to support new modes of operation. For instance, some concept designs feature retractable steering wheels that can be stowed away during fully autonomous driving, transforming the driver's area into a more versatile space. When manual control is required, the steering wheel can be quickly deployed, seamlessly transitioning between autonomous and manual driving modes.
The integration of augmented reality (AR) displays into the steering wheel HMI is another emerging trend. These displays can project relevant information directly onto the windshield or the steering wheel itself, providing real-time data about the vehicle's surroundings, navigation instructions, and system status without requiring the driver to look away from the road.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!