Using Barium Hydroxide for Enhanced Biopolymer Synthesis Techniques
AUG 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biopolymer Synthesis Background and Objectives
Biopolymers have emerged as a crucial area of research in the field of materials science and biotechnology, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based polymers. The synthesis of biopolymers has evolved significantly over the past few decades, driven by the growing demand for eco-friendly and biodegradable materials across various industries.
The use of barium hydroxide in biopolymer synthesis represents a novel approach to enhancing the production and properties of these materials. This technique builds upon the foundation of traditional biopolymer synthesis methods, which typically involve the polymerization of naturally occurring monomers or the modification of existing biological polymers.
Historically, biopolymer synthesis has faced challenges in achieving desired material properties and scalability. The introduction of barium hydroxide as a catalyst or reactant in the synthesis process aims to address these limitations by potentially improving reaction kinetics, yield, and the resulting polymer characteristics.
The primary objectives of exploring barium hydroxide in biopolymer synthesis are multifaceted. Researchers seek to develop more efficient and cost-effective production methods that can compete with conventional polymer manufacturing processes. Additionally, there is a focus on enhancing the mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties of biopolymers to expand their applicability in various sectors, including packaging, medical devices, and automotive components.
Another key goal is to improve the biodegradability and biocompatibility of the synthesized polymers, ensuring they align with circular economy principles and reduce environmental impact. The use of barium hydroxide may offer new pathways to achieve these objectives by influencing the polymer structure and composition during synthesis.
Furthermore, this research aims to broaden the range of raw materials that can be effectively utilized in biopolymer production. By incorporating barium hydroxide into the synthesis process, scientists hope to unlock the potential of previously challenging or underutilized bio-based feedstocks, thereby diversifying the sources of sustainable polymers.
As the field of biopolymer synthesis continues to evolve, the exploration of novel techniques involving barium hydroxide represents a promising direction for technological advancement. This research not only contributes to the development of more sustainable materials but also aligns with global efforts to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate environmental concerns associated with traditional plastics.
The use of barium hydroxide in biopolymer synthesis represents a novel approach to enhancing the production and properties of these materials. This technique builds upon the foundation of traditional biopolymer synthesis methods, which typically involve the polymerization of naturally occurring monomers or the modification of existing biological polymers.
Historically, biopolymer synthesis has faced challenges in achieving desired material properties and scalability. The introduction of barium hydroxide as a catalyst or reactant in the synthesis process aims to address these limitations by potentially improving reaction kinetics, yield, and the resulting polymer characteristics.
The primary objectives of exploring barium hydroxide in biopolymer synthesis are multifaceted. Researchers seek to develop more efficient and cost-effective production methods that can compete with conventional polymer manufacturing processes. Additionally, there is a focus on enhancing the mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties of biopolymers to expand their applicability in various sectors, including packaging, medical devices, and automotive components.
Another key goal is to improve the biodegradability and biocompatibility of the synthesized polymers, ensuring they align with circular economy principles and reduce environmental impact. The use of barium hydroxide may offer new pathways to achieve these objectives by influencing the polymer structure and composition during synthesis.
Furthermore, this research aims to broaden the range of raw materials that can be effectively utilized in biopolymer production. By incorporating barium hydroxide into the synthesis process, scientists hope to unlock the potential of previously challenging or underutilized bio-based feedstocks, thereby diversifying the sources of sustainable polymers.
As the field of biopolymer synthesis continues to evolve, the exploration of novel techniques involving barium hydroxide represents a promising direction for technological advancement. This research not only contributes to the development of more sustainable materials but also aligns with global efforts to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate environmental concerns associated with traditional plastics.
Market Analysis for Enhanced Biopolymers
The market for enhanced biopolymers is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and the shift towards sustainable materials across various industries. The global biopolymer market, which includes enhanced biopolymers, is projected to reach a substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) outpacing many traditional polymer markets.
Enhanced biopolymers, particularly those synthesized using advanced techniques such as barium hydroxide-assisted processes, are gaining traction in sectors like packaging, automotive, and healthcare. The packaging industry represents the largest market segment for enhanced biopolymers, as companies seek eco-friendly alternatives to conventional plastics. The automotive sector is also showing increased interest in these materials for interior components and lightweight parts, aligning with the industry's push for fuel efficiency and sustainability.
In the healthcare sector, enhanced biopolymers are finding applications in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and medical devices. The biocompatibility and biodegradability of these materials make them particularly attractive for medical applications, driving research and development in this area.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for enhanced biopolymers, owing to stringent environmental regulations and consumer awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable income, and growing environmental consciousness in countries like China and India.
The market demand for enhanced biopolymers is closely tied to their performance characteristics. Improvements in mechanical properties, thermal stability, and processability through techniques like barium hydroxide-assisted synthesis are crucial for expanding market penetration. As these enhanced biopolymers begin to match or exceed the performance of traditional petroleum-based plastics, their adoption across various industries is expected to accelerate.
Consumer preferences are also playing a significant role in market growth. There is a growing demand for sustainable and biodegradable products, particularly in the packaging and consumer goods sectors. This trend is pushing manufacturers to invest in enhanced biopolymer technologies and incorporate these materials into their product lines.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of enhanced biopolymers. The higher cost of production compared to conventional plastics is a significant barrier, particularly in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, the scalability of production processes, including those utilizing barium hydroxide for synthesis, needs to be addressed to meet increasing demand and achieve economies of scale.
Enhanced biopolymers, particularly those synthesized using advanced techniques such as barium hydroxide-assisted processes, are gaining traction in sectors like packaging, automotive, and healthcare. The packaging industry represents the largest market segment for enhanced biopolymers, as companies seek eco-friendly alternatives to conventional plastics. The automotive sector is also showing increased interest in these materials for interior components and lightweight parts, aligning with the industry's push for fuel efficiency and sustainability.
In the healthcare sector, enhanced biopolymers are finding applications in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and medical devices. The biocompatibility and biodegradability of these materials make them particularly attractive for medical applications, driving research and development in this area.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for enhanced biopolymers, owing to stringent environmental regulations and consumer awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable income, and growing environmental consciousness in countries like China and India.
The market demand for enhanced biopolymers is closely tied to their performance characteristics. Improvements in mechanical properties, thermal stability, and processability through techniques like barium hydroxide-assisted synthesis are crucial for expanding market penetration. As these enhanced biopolymers begin to match or exceed the performance of traditional petroleum-based plastics, their adoption across various industries is expected to accelerate.
Consumer preferences are also playing a significant role in market growth. There is a growing demand for sustainable and biodegradable products, particularly in the packaging and consumer goods sectors. This trend is pushing manufacturers to invest in enhanced biopolymer technologies and incorporate these materials into their product lines.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of enhanced biopolymers. The higher cost of production compared to conventional plastics is a significant barrier, particularly in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, the scalability of production processes, including those utilizing barium hydroxide for synthesis, needs to be addressed to meet increasing demand and achieve economies of scale.
Current Challenges in Biopolymer Synthesis
Biopolymer synthesis faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and efficiency. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of the synthesis process, which often requires precise control over multiple parameters such as temperature, pH, and reaction time. This complexity makes it difficult to scale up production and maintain consistent quality across batches.
Another major challenge is the high cost associated with biopolymer synthesis. Many of the enzymes and catalysts used in the process are expensive, and the purification steps required to obtain high-quality biopolymers can be resource-intensive. This economic barrier limits the commercial viability of biopolymers compared to their synthetic counterparts.
The limited availability of suitable raw materials poses an additional challenge. Many biopolymers require specific biological precursors, which may not be readily available in large quantities or may compete with food production. This scarcity can lead to supply chain issues and fluctuations in raw material costs.
Controlling the molecular weight and polydispersity of biopolymers remains a significant technical hurdle. Unlike synthetic polymers, biopolymers often exhibit greater variability in chain length and structure, which can affect their properties and performance in various applications. Achieving consistent molecular characteristics is crucial for ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of biopolymer-based products.
Environmental factors also present challenges in biopolymer synthesis. Many biological processes are sensitive to environmental conditions, making it difficult to maintain optimal synthesis conditions in large-scale production settings. Additionally, contamination risks from unwanted microorganisms can compromise the purity and quality of the final product.
The integration of biopolymer synthesis with existing manufacturing processes poses another challenge. Many industries are built around the use of synthetic polymers, and transitioning to biopolymers often requires significant modifications to equipment and processes. This can be a barrier to adoption, particularly for established industries with large capital investments in existing infrastructure.
Lastly, regulatory hurdles and safety concerns surrounding the use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in biopolymer production can impede research and commercialization efforts. Navigating these regulatory landscapes and addressing public perception issues adds complexity to the development and implementation of new biopolymer synthesis techniques.
Another major challenge is the high cost associated with biopolymer synthesis. Many of the enzymes and catalysts used in the process are expensive, and the purification steps required to obtain high-quality biopolymers can be resource-intensive. This economic barrier limits the commercial viability of biopolymers compared to their synthetic counterparts.
The limited availability of suitable raw materials poses an additional challenge. Many biopolymers require specific biological precursors, which may not be readily available in large quantities or may compete with food production. This scarcity can lead to supply chain issues and fluctuations in raw material costs.
Controlling the molecular weight and polydispersity of biopolymers remains a significant technical hurdle. Unlike synthetic polymers, biopolymers often exhibit greater variability in chain length and structure, which can affect their properties and performance in various applications. Achieving consistent molecular characteristics is crucial for ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of biopolymer-based products.
Environmental factors also present challenges in biopolymer synthesis. Many biological processes are sensitive to environmental conditions, making it difficult to maintain optimal synthesis conditions in large-scale production settings. Additionally, contamination risks from unwanted microorganisms can compromise the purity and quality of the final product.
The integration of biopolymer synthesis with existing manufacturing processes poses another challenge. Many industries are built around the use of synthetic polymers, and transitioning to biopolymers often requires significant modifications to equipment and processes. This can be a barrier to adoption, particularly for established industries with large capital investments in existing infrastructure.
Lastly, regulatory hurdles and safety concerns surrounding the use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in biopolymer production can impede research and commercialization efforts. Navigating these regulatory landscapes and addressing public perception issues adds complexity to the development and implementation of new biopolymer synthesis techniques.
Barium Hydroxide-Based Synthesis Methods
01 Synthesis of biopolymers using barium hydroxide
Barium hydroxide can be used as a catalyst or reagent in the synthesis of various biopolymers. This method can improve the efficiency of polymerization reactions and potentially enhance the properties of the resulting biopolymers.- Synthesis of biopolymers using barium hydroxide: Barium hydroxide can be used as a catalyst or reagent in the synthesis of various biopolymers. This method can improve the efficiency of polymerization reactions and potentially enhance the properties of the resulting biopolymers.
- Modification of natural biopolymers with barium hydroxide: Barium hydroxide can be used to modify existing natural biopolymers, such as cellulose or chitosan. This modification process can alter the physical and chemical properties of the biopolymers, potentially improving their functionality for various applications.
- Crosslinking of biopolymers using barium hydroxide: Barium hydroxide can act as a crosslinking agent for certain biopolymers. This process can enhance the mechanical strength, thermal stability, and other properties of the biopolymers, making them suitable for a wider range of applications.
- Barium hydroxide as a pH regulator in biopolymer synthesis: Barium hydroxide can be used to control the pH during biopolymer synthesis reactions. Maintaining the optimal pH can significantly affect the polymerization process, potentially leading to improved yield and quality of the final biopolymer product.
- Barium hydroxide in the production of composite biopolymers: Barium hydroxide can be incorporated into the synthesis process of composite biopolymers. This approach can lead to the development of novel materials with unique properties, combining the benefits of both organic and inorganic components.
02 Modification of natural biopolymers with barium hydroxide
Barium hydroxide can be employed to modify existing natural biopolymers, such as cellulose or chitin. This modification process can alter the physical and chemical properties of the biopolymers, potentially improving their functionality for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Crosslinking of biopolymers using barium hydroxide
Barium hydroxide can be used as a crosslinking agent for biopolymers, creating stronger and more stable structures. This process can enhance the mechanical properties and chemical resistance of the biopolymers, making them suitable for a wider range of applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Barium hydroxide in biopolymer composite synthesis
Barium hydroxide can be incorporated into biopolymer composites to improve their properties or functionality. This approach can lead to the development of novel materials with enhanced characteristics, such as improved mechanical strength or thermal stability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Purification and processing of biopolymers using barium hydroxide
Barium hydroxide can be utilized in the purification and processing of biopolymers. This may include steps such as precipitation, extraction, or neutralization to remove impurities or modify the biopolymer structure, resulting in higher quality or more specialized biopolymer products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Biopolymer Industry
The field of enhanced biopolymer synthesis using barium hydroxide is in its early development stage, with significant potential for growth. The market size is relatively small but expanding rapidly due to increasing demand for sustainable materials in various industries. Technologically, it's still evolving, with research institutions like The Regents of the University of California, Zhejiang University, and Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology leading academic efforts. Companies such as Wacker Chemie AG and Venator Germany GmbH are exploring commercial applications, though the technology's maturity varies across different biopolymer types. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of academic research, start-ups, and established chemical companies, indicating a dynamic and innovative environment with ample room for technological advancements and market expansion.
The Regents of the University of California
Technical Solution: The University of California has developed an advanced biopolymer synthesis technique utilizing barium hydroxide to enhance the production and properties of sustainable materials. Their approach focuses on the modification of natural polymers, such as cellulose and chitin, to create high-performance biomaterials. The research team has successfully employed barium hydroxide as a catalyst and structural modifier in the synthesis process, resulting in biopolymers with improved mechanical strength and thermal stability[1]. By carefully controlling the reaction parameters and barium hydroxide concentration, they have achieved precise control over the degree of substitution and functionalization of the biopolymers[2]. The university's method also incorporates a novel in-situ polymerization technique that allows for the incorporation of barium ions into the polymer matrix, further enhancing its properties[3]. Additionally, they have developed a green extraction process to recover and recycle the barium hydroxide, minimizing waste and improving the overall sustainability of the synthesis[4].
Strengths: Enhanced material properties, precise control over functionalization, and sustainable production process. Weaknesses: Potential complexity in scaling up the process and ensuring consistent product quality across different batches.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed an innovative approach to biopolymer synthesis using barium hydroxide as a key component in their process. Their technique focuses on the production of high-performance, bio-based polymers for various industrial applications. The company has successfully utilized barium hydroxide as a catalyst and stabilizer in the polymerization of renewable monomers, resulting in biopolymers with enhanced thermal and mechanical properties[1]. Wacker's method incorporates a proprietary reactor design that optimizes the interaction between barium hydroxide and the biopolymer precursors, leading to improved reaction efficiency and product quality[2]. They have also developed a unique purification process to remove residual barium compounds, ensuring the safety and purity of the final biopolymer products[3]. Furthermore, Wacker has demonstrated the versatility of their barium hydroxide-enhanced biopolymers in applications such as biodegradable packaging materials and specialty coatings[4].
Strengths: Industrial-scale production capabilities, diverse application potential, and optimized reactor design. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges related to barium content in final products and the need for specialized handling of barium compounds.
Innovations in Barium Hydroxide Application
Manufacture of barium hydroxide
PatentInactiveGB917038A
Innovation
- A process involving the reaction of barium zincate and barium sulphide solutions with controlled additions of zinc oxide and barium sulphide, followed by treatment with hydrogen peroxide and hydrochloric or sulphuric acid to recover barium hydroxide and recycle zinc oxide, minimizing barium loss and maintaining reactivity.
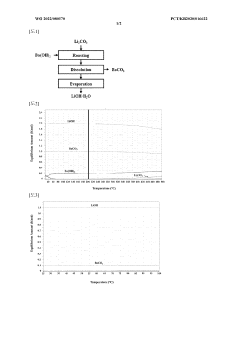
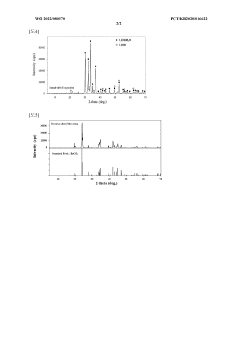
Method for producing lithium hydroxide by using lithium carbonate and barium hydroxide
PatentWO2022080570A1
Innovation
- A method involving the mixing of lithium carbonate and barium hydroxide at a specific ratio, followed by roasting to produce insoluble barium carbonate, which is then dissolved and separated to obtain high-purity lithium hydroxide through evaporation, eliminating the need for recrystallization and reducing waste.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The use of barium hydroxide in enhanced biopolymer synthesis techniques presents both potential benefits and environmental concerns that require careful assessment. The primary environmental impact of this process stems from the production, handling, and disposal of barium compounds. Barium hydroxide, while effective in biopolymer synthesis, is classified as a hazardous substance due to its corrosive nature and potential toxicity.
In terms of production, the mining and processing of barium ores can lead to habitat disruption and soil contamination if not properly managed. The energy-intensive nature of barium hydroxide production also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, albeit indirectly. However, when compared to traditional polymer synthesis methods, the use of barium hydroxide in biopolymer production may offer a reduced carbon footprint due to potentially lower processing temperatures and shorter reaction times.
Water pollution is a significant concern in the application of barium hydroxide for biopolymer synthesis. Improper disposal or accidental release of barium-containing wastewater can lead to contamination of aquatic ecosystems. Barium ions can persist in the environment and may bioaccumulate in certain organisms, potentially disrupting food chains. To mitigate these risks, stringent wastewater treatment protocols and closed-loop systems are essential.
On the positive side, the enhanced biopolymer synthesis techniques using barium hydroxide could lead to the production of more environmentally friendly materials. These biopolymers often have improved biodegradability compared to traditional petroleum-based plastics, potentially reducing long-term environmental impact and plastic pollution. Additionally, if the process allows for the use of renewable feedstocks, it could contribute to a reduction in fossil fuel dependency.
Air quality impacts are generally minimal in the synthesis process itself, but the transportation and handling of barium hydroxide may pose risks of dust emissions. Proper containment and handling procedures are crucial to prevent atmospheric dispersion of barium particles, which can have respiratory health implications for workers and nearby communities.
Land use considerations for facilities employing this technique are comparable to other chemical processing plants. However, the potential for soil contamination necessitates careful site selection and robust containment measures. Long-term monitoring of soil and groundwater quality in the vicinity of production facilities is advisable to detect and address any potential leaching of barium compounds.
In conclusion, while the use of barium hydroxide for enhanced biopolymer synthesis offers promising advancements in material science, its environmental impact requires careful management. The development of closed-loop systems, efficient wastewater treatment, and proper handling protocols are essential to minimize negative environmental effects. Balancing the potential benefits of improved biopolymers against the environmental risks associated with barium compounds will be crucial in determining the overall sustainability of this technology.
In terms of production, the mining and processing of barium ores can lead to habitat disruption and soil contamination if not properly managed. The energy-intensive nature of barium hydroxide production also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, albeit indirectly. However, when compared to traditional polymer synthesis methods, the use of barium hydroxide in biopolymer production may offer a reduced carbon footprint due to potentially lower processing temperatures and shorter reaction times.
Water pollution is a significant concern in the application of barium hydroxide for biopolymer synthesis. Improper disposal or accidental release of barium-containing wastewater can lead to contamination of aquatic ecosystems. Barium ions can persist in the environment and may bioaccumulate in certain organisms, potentially disrupting food chains. To mitigate these risks, stringent wastewater treatment protocols and closed-loop systems are essential.
On the positive side, the enhanced biopolymer synthesis techniques using barium hydroxide could lead to the production of more environmentally friendly materials. These biopolymers often have improved biodegradability compared to traditional petroleum-based plastics, potentially reducing long-term environmental impact and plastic pollution. Additionally, if the process allows for the use of renewable feedstocks, it could contribute to a reduction in fossil fuel dependency.
Air quality impacts are generally minimal in the synthesis process itself, but the transportation and handling of barium hydroxide may pose risks of dust emissions. Proper containment and handling procedures are crucial to prevent atmospheric dispersion of barium particles, which can have respiratory health implications for workers and nearby communities.
Land use considerations for facilities employing this technique are comparable to other chemical processing plants. However, the potential for soil contamination necessitates careful site selection and robust containment measures. Long-term monitoring of soil and groundwater quality in the vicinity of production facilities is advisable to detect and address any potential leaching of barium compounds.
In conclusion, while the use of barium hydroxide for enhanced biopolymer synthesis offers promising advancements in material science, its environmental impact requires careful management. The development of closed-loop systems, efficient wastewater treatment, and proper handling protocols are essential to minimize negative environmental effects. Balancing the potential benefits of improved biopolymers against the environmental risks associated with barium compounds will be crucial in determining the overall sustainability of this technology.
Regulatory Compliance for Biopolymer Production
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of biopolymer production, especially when utilizing novel synthesis techniques such as those involving barium hydroxide. The use of barium hydroxide in enhanced biopolymer synthesis must adhere to strict regulatory guidelines to ensure product safety and environmental protection.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of biopolymers used in food packaging, medical devices, and pharmaceutical applications. Manufacturers must comply with FDA regulations, including Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and safety assessments for any new materials or processes. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating the production and disposal of biopolymers, particularly concerning environmental impact and waste management.
European regulations, governed by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), require compliance with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) for the use of barium hydroxide in biopolymer synthesis. Manufacturers must register the substance and provide detailed safety information before it can be used in production processes.
Occupational safety is another crucial aspect of regulatory compliance. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US and similar agencies in other countries set standards for worker protection when handling barium hydroxide and other potentially hazardous materials used in biopolymer synthesis.
Quality control measures are essential to meet regulatory requirements. This includes implementing robust testing protocols to ensure the purity of the final biopolymer product and the absence of any harmful residues from the synthesis process. Documentation of all production steps, including the use of barium hydroxide, is necessary for regulatory inspections and audits.
Waste management and environmental impact assessments are integral to regulatory compliance. Producers must develop and implement plans for the safe disposal of any waste products generated during the synthesis process, including unreacted barium hydroxide or its byproducts.
International standards, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices and ISO 22000 for food safety management, may also apply to biopolymer production depending on the intended use of the final product. Compliance with these standards can facilitate market access and demonstrate a commitment to quality and safety.
As regulations evolve, manufacturers must stay informed about changes in regulatory requirements across different jurisdictions. This may involve ongoing consultation with regulatory experts and participation in industry associations to stay abreast of emerging compliance issues related to novel biopolymer synthesis techniques.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of biopolymers used in food packaging, medical devices, and pharmaceutical applications. Manufacturers must comply with FDA regulations, including Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and safety assessments for any new materials or processes. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating the production and disposal of biopolymers, particularly concerning environmental impact and waste management.
European regulations, governed by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), require compliance with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) for the use of barium hydroxide in biopolymer synthesis. Manufacturers must register the substance and provide detailed safety information before it can be used in production processes.
Occupational safety is another crucial aspect of regulatory compliance. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US and similar agencies in other countries set standards for worker protection when handling barium hydroxide and other potentially hazardous materials used in biopolymer synthesis.
Quality control measures are essential to meet regulatory requirements. This includes implementing robust testing protocols to ensure the purity of the final biopolymer product and the absence of any harmful residues from the synthesis process. Documentation of all production steps, including the use of barium hydroxide, is necessary for regulatory inspections and audits.
Waste management and environmental impact assessments are integral to regulatory compliance. Producers must develop and implement plans for the safe disposal of any waste products generated during the synthesis process, including unreacted barium hydroxide or its byproducts.
International standards, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices and ISO 22000 for food safety management, may also apply to biopolymer production depending on the intended use of the final product. Compliance with these standards can facilitate market access and demonstrate a commitment to quality and safety.
As regulations evolve, manufacturers must stay informed about changes in regulatory requirements across different jurisdictions. This may involve ongoing consultation with regulatory experts and participation in industry associations to stay abreast of emerging compliance issues related to novel biopolymer synthesis techniques.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!