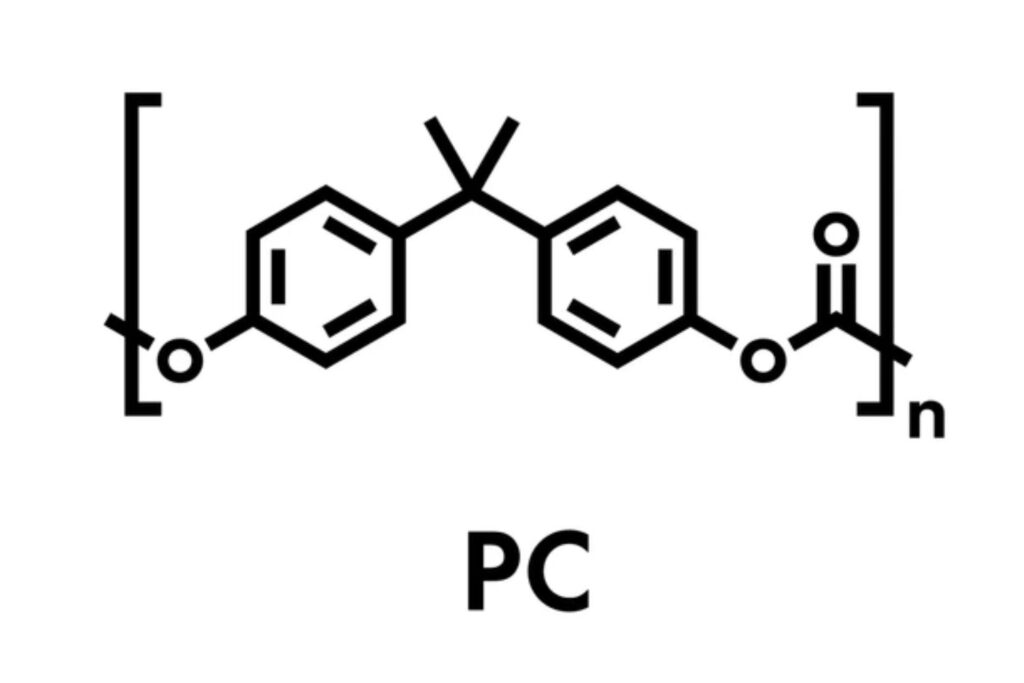
Polycarbonate (PC) is a durable, transparent thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance, optical clarity, and thermal stability. As industries face pressure to combine strength, sustainability, and lightweight performance in their materials, polycarbonate emerges as a reliable solution. It bridges performance gaps in everything from medical device housing and automotive components to optical lenses and smart electronics.
This article explores the structure, processing, and key performance traits of polycarbonate, followed by its applications across sectors such as electronics, aerospace, healthcare, energy, and construction. Each application domain is backed by curated reports from PatSnap Eureka AI Agent to help you stay ahead of material innovations.
Material Composition & Key Properties
● Polycarbonate is synthesized from bisphenol A (BPA) and phosgene (COCl₂) through an interfacial or melt polymerization process.
● It features an amorphous, high-molecular-weight polymer backbone that imparts exceptional optical and mechanical properties.
● Key properties include:
- High impact strength, even at low temperatures
- Optical transparency and UV resistance
- Dimensional stability and heat resistance
- Excellent flame retardancy and electrical insulation
- Moldability and processability into films, sheets, or complex parts
Application Domains
Advanced Electronics & Consumer Devices
With the miniaturization of devices and growing demand for thermally stable, impact-resistant components, polycarbonate offers ideal material properties for electronics casings, lenses, and transparent interfaces.
Research Frontlines: Enhanced flame-retardant grades and polycarbonate blends are being developed for telecom enclosures, LED optics, and wearable devices.
Related Reports:
- Polycarbonate in Electronics: A Material Evolution
- How to Enhance Electrical Properties of Polycarbonate?
- Polycarbonate’s Role in Smart Grid Technology
- How to Utilize Polycarbonate in Flexible Electronics?
- Polycarbonate in Telecommunication Sector
- Polycarbonate for Advanced Display Technologies
- How to Boost Polycarbonate’s Marketability?
Automotive & Aerospace Engineering
Lightweight design is vital for fuel efficiency and emissions reduction. Polycarbonate enables weight reduction while maintaining impact protection for components such as glazing, lighting covers, and interior structures.
Research Frontlines: PC-blends are being adapted for UV-stable, scratch-resistant panels and sensor-integrated automotive exteriors.
Related Reports:
- Polycarbonate Contributions to Automotive Light Weighting
- Polycarbonate for Aerospace: Reducing Weight and Cost
- How to Optimize Polycarbonate for Automotive Interiors?
- Polycarbonate in Advanced Aerospace Solutions
- Polycarbonate’s Impact on Modern Transportation
- Polycarbonate for Revolutionary Automotive Design
- How to Enhance Polycarbonate’s Load-Bearing Capacity?
Biomedical & Pharmaceutical Applications
In medical devices, polycarbonate provides a balance between transparency, biocompatibility, and sterilizability—ideal for surgical instruments, drug delivery systems, and dialysis components.
Research Frontlines: Emerging research focuses on PC formulations for wearables, implants, and MRI-safe components.
Related Reports:
- Polycarbonate Applications in Medical Devices
- Polycarbonate in Pharmaceutical Packaging: Trends and Techniques
- Polycarbonate in Medical Implant Innovations
- Polycarbonate for Advanced Medical Imaging
- Polycarbonate in High-Performance Sports Gear
- Polycarbonate for Enhanced Personal Protective Equipment
- Polycarbonate in Advanced Health Monitoring Devices
Sustainable Construction & Infrastructure
Architectural panels, glazing, and insulation materials demand both strength and UV protection. Polycarbonate provides thermal insulation and weather resistance while being easier to mold than glass.
Research Frontlines: Multi-wall PC sheets and anti-yellowing coatings are pushing sustainability and durability in smart building applications.
Related Reports:
- Polycarbonate Innovations for Sustainable Construction
- Polycarbonate Sheet Applications in Architecture
- Polycarbonate’s Role in Smart Building Technologies
- Polycarbonate for Eco-Friendly Building Materials
- Polycarbonate in Future-Ready Infrastructure Developments
- Polycarbonate’s Role in Elite Space Technology
- Polycarbonate for Innovative Building Solutions
Energy & Environmental Applications
Polycarbonate’s transparency and electrical insulation make it a fit for energy-efficient devices, renewable energy modules, and environmental sensors.
Research Frontlines: Work is expanding in hydrogen fuel cell enclosures, solar panel protective layers, and polycarbonate composites in wind energy.
Related Reports:
- Polycarbonate Use in Renewable Energy Innovations
- Polycarbonate for Hydrogen Fuel Storage Systems
- Polycarbonate in Water Filtration Systems: The Future
- Polycarbonate for Next-Generation Energy Solutions
- Polycarbonate in High-Capacity Energy Solutions
- Polycarbonate for Water Purification Technologies
- How to Enhance Polycarbonate’s Eco-Friendliness?
Comparative Advantages & Limitations
Advantages:
● High impact resistance and toughness
● Lightweight compared to glass and metals
● Good optical clarity and dimensional stability
● Thermal resistance and flame retardancy
● Easily moldable for complex geometries
Limitations:
● Susceptible to scratching without coatings
● Yellowing and UV degradation over time (without additives)
● Potential BPA-related health concerns
● Costlier than commodity plastics like polyethylene
● Requires optimization for recycling efficiency
Future Outlook & Research Frontiers
Over the next 5–10 years, polycarbonate is poised to empower high-value applications such as:
- Transparent armor and blast-resistant glazing
- Biocompatible polycarbonate alternatives (BPA-free)
- Energy-efficient smart lighting and heat management
- Recyclable and bio-based PC composites
- Hybrid structures for aerospace and automotive interiors
- Nanostructured PC for optics and sensor networks
Key trends include low-carbon synthesis, polycarbonate foams for energy efficiency, and smart coatings that adapt to environmental conditions.
Conclusion & Strategic Takeaways
Polycarbonate continues to be a high-performance material that balances mechanical strength, optical clarity, and design flexibility. Its versatility makes it indispensable across a wide range of sectors—from high-tech electronics and aerospace to healthcare and construction. As industries seek materials that align with both performance and sustainability goals, polycarbonate will remain a critical enabler of next-generation innovation.
Accelerate Innovation with PatSnap Eureka AI Agent
Polycarbonate’s research and application space is expanding rapidly—and keeping up requires more than scattered reports or outdated whitepapers. With PatSnap Eureka AI Agent, you can:
- Track global innovation across thousands of patents
- Benchmark polycarbonate technologies and market leaders
- Identify white space and R&D opportunities
👉 Discover how Eureka can revolutionize your material strategy—[Request a Demo]