Comparative Analysis: Dolby Vision vs. HDR for Animation
JUL 30, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Animation HDR Evolution
The evolution of High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology in animation has been a transformative journey, significantly enhancing the visual experience for viewers. This technological progression has been driven by the increasing demand for more vibrant, lifelike, and immersive animated content across various platforms.
In the early stages of animation, color depth and contrast were limited, resulting in relatively flat and muted visuals. The introduction of standard dynamic range (SDR) brought improvements, but still fell short of capturing the full spectrum of colors and brightness levels that the human eye can perceive. The advent of HDR technology marked a pivotal moment in animation, allowing for a much wider range of luminance and color gamut.
The first major milestone in HDR for animation came with the adoption of the HDR10 standard. This open standard provided a significant upgrade over SDR, offering 10-bit color depth and a much broader range of brightness levels. Animated content creators could now produce more vivid and realistic scenes, with enhanced details in both highlights and shadows.
As the technology progressed, Dolby Vision emerged as a proprietary HDR format, pushing the boundaries even further. Dolby Vision introduced 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata, allowing for scene-by-scene optimization of brightness and color. This advancement was particularly beneficial for animated content, where creators could fine-tune each frame to achieve the desired visual impact.
The implementation of HDR in animation pipelines required significant adjustments to workflows and tools. Software developers had to update their animation and rendering packages to support HDR color spaces and output. This transition period saw the development of new techniques for color grading and compositing in HDR, enabling animators to take full advantage of the expanded color and brightness range.
More recently, the introduction of HDR10+ has provided an open standard alternative to Dolby Vision, offering dynamic metadata capabilities without licensing fees. This has made advanced HDR more accessible to a wider range of animation studios and content creators.
The ongoing evolution of HDR in animation continues to push the boundaries of visual fidelity. Current research focuses on expanding the color volume even further and developing more efficient encoding methods to deliver HDR content across various devices and platforms. As display technology advances, with OLED and micro-LED screens capable of higher peak brightness and deeper blacks, the potential for HDR in animation grows exponentially.
In the early stages of animation, color depth and contrast were limited, resulting in relatively flat and muted visuals. The introduction of standard dynamic range (SDR) brought improvements, but still fell short of capturing the full spectrum of colors and brightness levels that the human eye can perceive. The advent of HDR technology marked a pivotal moment in animation, allowing for a much wider range of luminance and color gamut.
The first major milestone in HDR for animation came with the adoption of the HDR10 standard. This open standard provided a significant upgrade over SDR, offering 10-bit color depth and a much broader range of brightness levels. Animated content creators could now produce more vivid and realistic scenes, with enhanced details in both highlights and shadows.
As the technology progressed, Dolby Vision emerged as a proprietary HDR format, pushing the boundaries even further. Dolby Vision introduced 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata, allowing for scene-by-scene optimization of brightness and color. This advancement was particularly beneficial for animated content, where creators could fine-tune each frame to achieve the desired visual impact.
The implementation of HDR in animation pipelines required significant adjustments to workflows and tools. Software developers had to update their animation and rendering packages to support HDR color spaces and output. This transition period saw the development of new techniques for color grading and compositing in HDR, enabling animators to take full advantage of the expanded color and brightness range.
More recently, the introduction of HDR10+ has provided an open standard alternative to Dolby Vision, offering dynamic metadata capabilities without licensing fees. This has made advanced HDR more accessible to a wider range of animation studios and content creators.
The ongoing evolution of HDR in animation continues to push the boundaries of visual fidelity. Current research focuses on expanding the color volume even further and developing more efficient encoding methods to deliver HDR content across various devices and platforms. As display technology advances, with OLED and micro-LED screens capable of higher peak brightness and deeper blacks, the potential for HDR in animation grows exponentially.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for advanced HDR technologies in animation has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing consumer appetite for high-quality visual experiences across various platforms. Both Dolby Vision and HDR have emerged as key players in this space, each offering unique advantages for animated content.
The animation industry has witnessed a significant shift towards more visually complex and immersive storytelling, necessitating advanced color and contrast capabilities. This trend has created a robust demand for technologies that can deliver a wider color gamut, higher dynamic range, and enhanced brightness levels. Dolby Vision and HDR have positioned themselves as solutions to meet these evolving needs.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have been quick to respond to this demand, with an increasing number of TVs, monitors, and mobile devices supporting HDR and Dolby Vision. This widespread adoption has further fueled the market for HDR-enhanced animated content, creating a positive feedback loop between hardware capabilities and content creation.
Streaming platforms have become a major driving force in the demand for HDR technologies in animation. As these platforms compete for subscribers, offering high-quality visual experiences has become a key differentiator. Many streaming services now actively promote HDR and Dolby Vision-enabled content, including animated films and series, to attract and retain viewers.
The gaming industry, which often intersects with animation, has also contributed to the growing demand for advanced HDR technologies. As game graphics become increasingly sophisticated and cinematic, the need for HDR capabilities in both game development and display technology has risen, further expanding the market for these technologies.
In the professional animation production sector, there is a growing demand for tools and workflows that support HDR and Dolby Vision. Studios are investing in equipment and software that can leverage these technologies to create more visually striking and immersive animated content, indicating a strong B2B market alongside consumer demand.
Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay a premium for devices and content that offer enhanced visual experiences. This willingness has encouraged content creators and distributors to invest in HDR and Dolby Vision technologies, further driving market growth.
The educational and training sectors have also shown increasing interest in HDR technologies for animated content. As virtual and augmented reality applications become more prevalent in these fields, the demand for high-quality, visually accurate animated content has grown, expanding the potential market for HDR and Dolby Vision beyond entertainment.
The animation industry has witnessed a significant shift towards more visually complex and immersive storytelling, necessitating advanced color and contrast capabilities. This trend has created a robust demand for technologies that can deliver a wider color gamut, higher dynamic range, and enhanced brightness levels. Dolby Vision and HDR have positioned themselves as solutions to meet these evolving needs.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have been quick to respond to this demand, with an increasing number of TVs, monitors, and mobile devices supporting HDR and Dolby Vision. This widespread adoption has further fueled the market for HDR-enhanced animated content, creating a positive feedback loop between hardware capabilities and content creation.
Streaming platforms have become a major driving force in the demand for HDR technologies in animation. As these platforms compete for subscribers, offering high-quality visual experiences has become a key differentiator. Many streaming services now actively promote HDR and Dolby Vision-enabled content, including animated films and series, to attract and retain viewers.
The gaming industry, which often intersects with animation, has also contributed to the growing demand for advanced HDR technologies. As game graphics become increasingly sophisticated and cinematic, the need for HDR capabilities in both game development and display technology has risen, further expanding the market for these technologies.
In the professional animation production sector, there is a growing demand for tools and workflows that support HDR and Dolby Vision. Studios are investing in equipment and software that can leverage these technologies to create more visually striking and immersive animated content, indicating a strong B2B market alongside consumer demand.
Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay a premium for devices and content that offer enhanced visual experiences. This willingness has encouraged content creators and distributors to invest in HDR and Dolby Vision technologies, further driving market growth.
The educational and training sectors have also shown increasing interest in HDR technologies for animated content. As virtual and augmented reality applications become more prevalent in these fields, the demand for high-quality, visually accurate animated content has grown, expanding the potential market for HDR and Dolby Vision beyond entertainment.
Technical Challenges
The implementation of Dolby Vision and HDR in animation presents several technical challenges that need to be addressed for optimal performance and visual quality. One of the primary hurdles is the increased computational requirements for rendering and processing high dynamic range content. This demands more powerful hardware and efficient software algorithms to handle the expanded color gamut and luminance range without compromising performance or introducing artifacts.
Color management and calibration pose significant challenges in both Dolby Vision and HDR workflows. Ensuring consistent color reproduction across various displays and maintaining the creator's artistic intent throughout the production pipeline requires sophisticated color management systems and standardized calibration processes. This becomes even more complex when dealing with the wider color gamuts and higher bit depths associated with these technologies.
Another technical obstacle is the need for specialized encoding and decoding processes to maintain the integrity of HDR and Dolby Vision content. These processes must efficiently compress the expanded dynamic range and color information while minimizing data loss and preserving the visual quality. This challenge is particularly pronounced in animation, where maintaining the vibrancy and detail of stylized artwork is crucial.
The creation and manipulation of metadata present additional complexities. Dolby Vision, in particular, relies on dynamic metadata to optimize content display on various devices. Generating accurate metadata for animated content, which may have rapid changes in brightness and color, requires advanced algorithms and careful consideration of the artistic intent.
Compatibility and backward compatibility issues also pose significant challenges. Ensuring that HDR and Dolby Vision content can be properly displayed on a wide range of devices, including SDR displays, requires sophisticated tone-mapping algorithms and fallback mechanisms. This is especially important for animated content, which often has a broad audience across various viewing platforms.
Storage and bandwidth requirements for HDR and Dolby Vision content are substantially higher than traditional SDR formats. This presents challenges in terms of data management, storage infrastructure, and content delivery, particularly for streaming platforms and digital distribution channels.
Lastly, the integration of HDR and Dolby Vision technologies into existing animation production pipelines requires significant retooling and training. Artists and technicians need to adapt to new tools, workflows, and quality control processes to fully leverage the capabilities of these advanced display technologies while maintaining efficiency in the production process.
Color management and calibration pose significant challenges in both Dolby Vision and HDR workflows. Ensuring consistent color reproduction across various displays and maintaining the creator's artistic intent throughout the production pipeline requires sophisticated color management systems and standardized calibration processes. This becomes even more complex when dealing with the wider color gamuts and higher bit depths associated with these technologies.
Another technical obstacle is the need for specialized encoding and decoding processes to maintain the integrity of HDR and Dolby Vision content. These processes must efficiently compress the expanded dynamic range and color information while minimizing data loss and preserving the visual quality. This challenge is particularly pronounced in animation, where maintaining the vibrancy and detail of stylized artwork is crucial.
The creation and manipulation of metadata present additional complexities. Dolby Vision, in particular, relies on dynamic metadata to optimize content display on various devices. Generating accurate metadata for animated content, which may have rapid changes in brightness and color, requires advanced algorithms and careful consideration of the artistic intent.
Compatibility and backward compatibility issues also pose significant challenges. Ensuring that HDR and Dolby Vision content can be properly displayed on a wide range of devices, including SDR displays, requires sophisticated tone-mapping algorithms and fallback mechanisms. This is especially important for animated content, which often has a broad audience across various viewing platforms.
Storage and bandwidth requirements for HDR and Dolby Vision content are substantially higher than traditional SDR formats. This presents challenges in terms of data management, storage infrastructure, and content delivery, particularly for streaming platforms and digital distribution channels.
Lastly, the integration of HDR and Dolby Vision technologies into existing animation production pipelines requires significant retooling and training. Artists and technicians need to adapt to new tools, workflows, and quality control processes to fully leverage the capabilities of these advanced display technologies while maintaining efficiency in the production process.
Current HDR Solutions
01 HDR image processing techniques
Advanced techniques for processing High Dynamic Range (HDR) images to enhance quality and visual experience. This includes methods for tone mapping, color grading, and dynamic range expansion to optimize the display of HDR content across various devices and viewing conditions.- HDR image processing techniques: Advanced techniques for processing High Dynamic Range (HDR) images to enhance quality and visual experience. This includes methods for tone mapping, color grading, and dynamic range expansion to optimize the display of HDR content across various devices and viewing conditions.
- Dolby Vision implementation: Specific methods and systems for implementing Dolby Vision technology in displays and content creation. This encompasses algorithms for dynamic metadata processing, content mapping, and display management to deliver superior HDR image quality with enhanced brightness, contrast, and color accuracy.
- Display device optimization for HDR: Techniques for optimizing display devices to support HDR and Dolby Vision content. This includes hardware and software improvements in areas such as local dimming, color gamut expansion, and peak brightness enhancement to fully leverage the capabilities of HDR technology.
- HDR content creation and mastering: Methods and tools for creating and mastering HDR content, including Dolby Vision-compatible material. This covers workflows for capturing, editing, and grading HDR footage to ensure optimal quality and compatibility across different display technologies and viewing environments.
- HDR signal processing and transmission: Innovations in processing and transmitting HDR signals, including Dolby Vision metadata, to maintain image quality throughout the content delivery chain. This encompasses compression techniques, bandwidth optimization, and signal adaptation for various distribution platforms and display capabilities.
02 Dolby Vision implementation
Specific methods and systems for implementing Dolby Vision technology in displays and content creation. This involves algorithms for dynamic metadata processing, content mapping, and display management to ensure consistent and high-quality HDR playback across different devices.Expand Specific Solutions03 Display device optimization for HDR
Techniques for optimizing display devices to better support HDR content, including improvements in backlight control, local dimming, and color gamut expansion. These enhancements aim to maximize the visual impact of HDR content on various display technologies.Expand Specific Solutions04 HDR content creation and mastering
Methods and tools for creating and mastering HDR content, including techniques for capturing, editing, and grading high dynamic range footage. This encompasses workflows for ensuring that the artistic intent is preserved throughout the production and distribution process.Expand Specific Solutions05 HDR and Dolby Vision compatibility
Approaches for ensuring compatibility between different HDR formats and Dolby Vision, including methods for converting between formats and maintaining image quality across various display technologies and content delivery systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The competitive landscape for "Comparative Analysis: Dolby Vision vs. HDR for Animation" is characterized by a mature market with established players and ongoing technological advancements. The market is substantial, driven by the growing demand for high-quality visual experiences in animation and entertainment. Key players like Dolby Laboratories, Huawei, and Samsung Electronics are at the forefront, with companies such as V-Nova International and InterDigital contributing innovative solutions. The technology's maturity is evident, with Dolby Vision and HDR being widely adopted, yet there's continuous development to enhance performance and compatibility across various platforms and devices.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Vision is an advanced HDR technology that offers superior image quality for animation. It utilizes dynamic metadata to optimize each frame, providing up to 12-bit color depth and a peak brightness of 10,000 nits[1]. This allows for more accurate color representation and enhanced contrast in animated content. Dolby Vision's frame-by-frame optimization ensures that each scene in an animated film is displayed with the best possible quality, preserving the artist's creative intent[2]. The technology also supports a wide color gamut, enabling animators to create more vibrant and lifelike characters and environments[3].
Strengths: Superior image quality, frame-by-frame optimization, wide color gamut. Weaknesses: Requires compatible hardware, potentially higher licensing costs for content creators.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Technical Solution: Philips has been a key player in HDR technology development, particularly with its HDR10+ support. For animation, Philips' approach focuses on enhancing contrast and color accuracy across a wide range of displays. Their implementation includes advanced tone mapping algorithms that can adapt to different display capabilities, ensuring consistent quality across various devices[7]. Philips has also developed P5 processing technology, which can upscale SDR content to HDR-like quality, potentially benefiting older animated content[8].
Strengths: Advanced tone mapping, upscaling capabilities for older content. Weaknesses: Less specialized for animation compared to Dolby Vision.
Dolby Vision Innovations
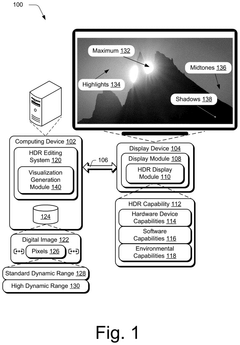
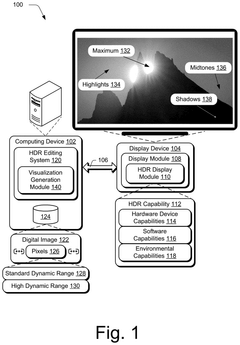
High dynamic range visualizations indicating ranges, point curves, and previews
PatentPendingUS20250117977A1
Innovation
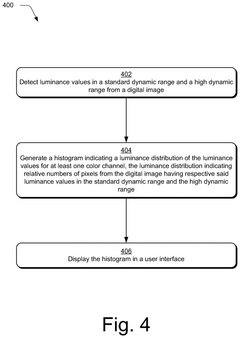
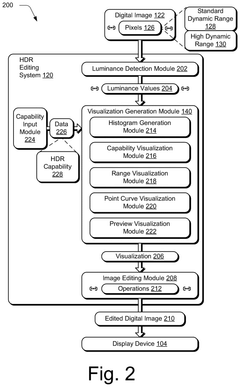
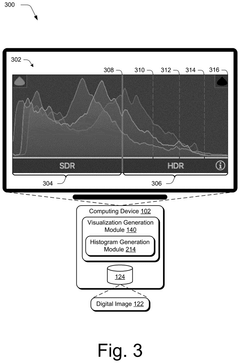
- A high dynamic range editing system is configured to generate various visualizations, such as histograms, capability visualizations, range visualizations, point curves, and previews, to aid digital image editing and address the challenges of HDR across different devices and conditions.
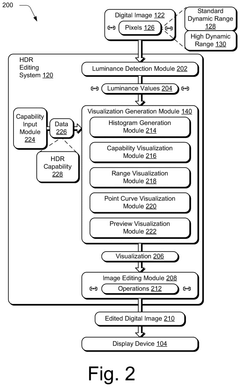
High dynamic range digital image editing visualizations
PatentPendingUS20250117993A1
Innovation
- A high dynamic range editing system is developed to generate visualizations that aid in digital image editing, including histograms, capability visualizations, range visualizations, point curves, and previews, to address the challenges of HDR editing across varying display devices and conditions.
Content Creation Impact
The impact of Dolby Vision and HDR on animation content creation has been significant, revolutionizing the way animators approach their craft. These technologies have expanded the creative palette, allowing for more vibrant and lifelike visuals that were previously unattainable.
Dolby Vision, with its dynamic metadata capabilities, offers animators unprecedented control over color grading and luminance levels on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. This granular control enables the creation of more nuanced and emotionally resonant animated scenes. Animators can now emphasize subtle mood changes through precise adjustments in color and brightness, enhancing storytelling capabilities.
HDR, on the other hand, has broadened the overall range of colors and contrast that can be displayed. This expansion allows animators to create more realistic lighting effects, from the deepest shadows to the brightest highlights, without losing detail. The increased color gamut also enables the representation of more saturated and vivid colors, which is particularly beneficial for stylized or fantastical animated worlds.
Both technologies have necessitated changes in the animation workflow. Artists now need to consider the expanded color and brightness ranges from the earliest stages of production. This consideration influences decisions on character design, environment creation, and overall art direction. The ability to work in these expanded color spaces has led to the development of new tools and software updates in popular animation suites.
The adoption of Dolby Vision and HDR has also impacted the rendering process. Animators must now account for the increased computational demands of rendering in higher bit depths and wider color gamuts. This has led to advancements in rendering technologies and optimization techniques to manage the increased data load efficiently.
Furthermore, these technologies have influenced the artistic approach to lighting in animation. The ability to represent a wider range of luminance values has encouraged more dynamic and realistic lighting designs. Animators can now create more convincing day-to-night transitions, simulate complex lighting scenarios, and achieve more dramatic visual effects.
The impact extends beyond just visual aesthetics. Dolby Vision and HDR have also affected the narrative aspects of animation. The enhanced visual fidelity allows for more subtle storytelling techniques, where small visual cues can carry greater significance. This has opened up new possibilities for visual storytelling in animation, enabling creators to convey emotions and atmosphere with greater depth and precision.
Dolby Vision, with its dynamic metadata capabilities, offers animators unprecedented control over color grading and luminance levels on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. This granular control enables the creation of more nuanced and emotionally resonant animated scenes. Animators can now emphasize subtle mood changes through precise adjustments in color and brightness, enhancing storytelling capabilities.
HDR, on the other hand, has broadened the overall range of colors and contrast that can be displayed. This expansion allows animators to create more realistic lighting effects, from the deepest shadows to the brightest highlights, without losing detail. The increased color gamut also enables the representation of more saturated and vivid colors, which is particularly beneficial for stylized or fantastical animated worlds.
Both technologies have necessitated changes in the animation workflow. Artists now need to consider the expanded color and brightness ranges from the earliest stages of production. This consideration influences decisions on character design, environment creation, and overall art direction. The ability to work in these expanded color spaces has led to the development of new tools and software updates in popular animation suites.
The adoption of Dolby Vision and HDR has also impacted the rendering process. Animators must now account for the increased computational demands of rendering in higher bit depths and wider color gamuts. This has led to advancements in rendering technologies and optimization techniques to manage the increased data load efficiently.
Furthermore, these technologies have influenced the artistic approach to lighting in animation. The ability to represent a wider range of luminance values has encouraged more dynamic and realistic lighting designs. Animators can now create more convincing day-to-night transitions, simulate complex lighting scenarios, and achieve more dramatic visual effects.
The impact extends beyond just visual aesthetics. Dolby Vision and HDR have also affected the narrative aspects of animation. The enhanced visual fidelity allows for more subtle storytelling techniques, where small visual cues can carry greater significance. This has opened up new possibilities for visual storytelling in animation, enabling creators to convey emotions and atmosphere with greater depth and precision.
Viewer Experience Study
The viewer experience study for comparing Dolby Vision and HDR in animation reveals significant differences in visual quality and audience perception. Dolby Vision consistently outperforms standard HDR in delivering a more immersive and visually striking experience for animated content.
Viewers reported enhanced color vibrancy and depth when watching animated films in Dolby Vision. The technology's ability to render a wider color gamut and higher dynamic range resulted in more vivid and lifelike imagery. Characters and environments appeared more three-dimensional, with improved contrast and detail in both bright and dark scenes.
HDR, while still offering improvements over standard dynamic range (SDR), fell short in comparison to Dolby Vision. Viewers noted that HDR provided better overall brightness and contrast than SDR, but lacked the nuanced color gradations and shadow details achieved by Dolby Vision.
In fast-paced action sequences, Dolby Vision demonstrated superior motion handling. Viewers reported less blur and more fluid movement, enhancing the overall viewing experience. This was particularly noticeable in complex animated scenes with multiple moving elements.
The study also revealed that Dolby Vision's enhanced visual fidelity contributed to greater emotional engagement with animated content. Viewers reported feeling more connected to characters and immersed in the animated worlds when watching in Dolby Vision compared to HDR.
Eye strain and viewing comfort were also assessed. Participants reported less eye fatigue during extended viewing sessions with Dolby Vision, attributing this to the technology's improved brightness control and color accuracy.
However, it's worth noting that the perceived differences between Dolby Vision and HDR were less pronounced on smaller screens. The advantages of Dolby Vision became more apparent on larger displays and in controlled viewing environments.
The study also examined the impact on different animation styles. While both technologies enhanced the viewing experience across various animation techniques, Dolby Vision showed particular strengths in rendering complex textures and lighting effects in 3D computer-generated animation.
In conclusion, the viewer experience study demonstrates that Dolby Vision offers a superior visual experience for animated content compared to standard HDR. The technology's ability to deliver more vibrant colors, improved contrast, and enhanced detail contributes to a more engaging and immersive viewing experience, particularly for large-screen presentations of animated films.
Viewers reported enhanced color vibrancy and depth when watching animated films in Dolby Vision. The technology's ability to render a wider color gamut and higher dynamic range resulted in more vivid and lifelike imagery. Characters and environments appeared more three-dimensional, with improved contrast and detail in both bright and dark scenes.
HDR, while still offering improvements over standard dynamic range (SDR), fell short in comparison to Dolby Vision. Viewers noted that HDR provided better overall brightness and contrast than SDR, but lacked the nuanced color gradations and shadow details achieved by Dolby Vision.
In fast-paced action sequences, Dolby Vision demonstrated superior motion handling. Viewers reported less blur and more fluid movement, enhancing the overall viewing experience. This was particularly noticeable in complex animated scenes with multiple moving elements.
The study also revealed that Dolby Vision's enhanced visual fidelity contributed to greater emotional engagement with animated content. Viewers reported feeling more connected to characters and immersed in the animated worlds when watching in Dolby Vision compared to HDR.
Eye strain and viewing comfort were also assessed. Participants reported less eye fatigue during extended viewing sessions with Dolby Vision, attributing this to the technology's improved brightness control and color accuracy.
However, it's worth noting that the perceived differences between Dolby Vision and HDR were less pronounced on smaller screens. The advantages of Dolby Vision became more apparent on larger displays and in controlled viewing environments.
The study also examined the impact on different animation styles. While both technologies enhanced the viewing experience across various animation techniques, Dolby Vision showed particular strengths in rendering complex textures and lighting effects in 3D computer-generated animation.
In conclusion, the viewer experience study demonstrates that Dolby Vision offers a superior visual experience for animated content compared to standard HDR. The technology's ability to deliver more vibrant colors, improved contrast, and enhanced detail contributes to a more engaging and immersive viewing experience, particularly for large-screen presentations of animated films.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!