How Dolby Vision Impacts Color Grading in Film Production
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dolby Vision Evolution
Dolby Vision has undergone a significant evolution since its introduction in 2014, revolutionizing the way color is handled in film production and post-production processes. Initially developed as an enhancement to High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology, Dolby Vision has continuously adapted to meet the changing needs of the film industry and consumer display technologies.
In its early stages, Dolby Vision focused primarily on expanding the dynamic range and color gamut of digital content. This allowed filmmakers to capture and display a wider range of brightness levels and colors, more closely approximating what the human eye can perceive in real-world scenarios. The technology initially required specialized hardware for both content creation and playback, limiting its widespread adoption.
As the technology matured, Dolby Vision introduced more flexible workflows for content creators. The introduction of the Dolby Vision Content Mapping Unit (CMU) in 2016 marked a significant milestone, enabling real-time color grading in Dolby Vision. This development streamlined the post-production process, allowing colorists to work more efficiently and make more precise adjustments to their content.
The evolution of Dolby Vision also saw the introduction of dynamic metadata, a key feature that sets it apart from other HDR formats. This innovation allows for scene-by-scene and even frame-by-frame optimization of brightness and color, ensuring that the creative intent is preserved across different display capabilities. This dynamic approach has become increasingly important as consumer displays have diversified in terms of peak brightness and color reproduction capabilities.
In recent years, Dolby Vision has expanded its reach beyond traditional cinema and high-end home entertainment systems. The technology has been adapted for use in a wider range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, and gaming consoles. This expansion has necessitated the development of more efficient encoding and delivery methods, as well as the creation of tools that allow for easier integration into various content creation pipelines.
The latest iterations of Dolby Vision have focused on improving interoperability with other HDR standards and workflows. This includes the development of Dolby Vision IQ, which uses ambient light sensors in displays to automatically adjust content based on viewing conditions, further enhancing the viewer experience. Additionally, Dolby has worked on integrating machine learning algorithms to improve the efficiency of content mapping and grading processes.
As the film industry continues to embrace digital technologies, Dolby Vision's evolution reflects a broader trend towards more precise and flexible color management tools. Its ongoing development aims to bridge the gap between the filmmaker's creative vision and the viewer's experience, regardless of the display technology used for playback.
In its early stages, Dolby Vision focused primarily on expanding the dynamic range and color gamut of digital content. This allowed filmmakers to capture and display a wider range of brightness levels and colors, more closely approximating what the human eye can perceive in real-world scenarios. The technology initially required specialized hardware for both content creation and playback, limiting its widespread adoption.
As the technology matured, Dolby Vision introduced more flexible workflows for content creators. The introduction of the Dolby Vision Content Mapping Unit (CMU) in 2016 marked a significant milestone, enabling real-time color grading in Dolby Vision. This development streamlined the post-production process, allowing colorists to work more efficiently and make more precise adjustments to their content.
The evolution of Dolby Vision also saw the introduction of dynamic metadata, a key feature that sets it apart from other HDR formats. This innovation allows for scene-by-scene and even frame-by-frame optimization of brightness and color, ensuring that the creative intent is preserved across different display capabilities. This dynamic approach has become increasingly important as consumer displays have diversified in terms of peak brightness and color reproduction capabilities.
In recent years, Dolby Vision has expanded its reach beyond traditional cinema and high-end home entertainment systems. The technology has been adapted for use in a wider range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, and gaming consoles. This expansion has necessitated the development of more efficient encoding and delivery methods, as well as the creation of tools that allow for easier integration into various content creation pipelines.
The latest iterations of Dolby Vision have focused on improving interoperability with other HDR standards and workflows. This includes the development of Dolby Vision IQ, which uses ambient light sensors in displays to automatically adjust content based on viewing conditions, further enhancing the viewer experience. Additionally, Dolby has worked on integrating machine learning algorithms to improve the efficiency of content mapping and grading processes.
As the film industry continues to embrace digital technologies, Dolby Vision's evolution reflects a broader trend towards more precise and flexible color management tools. Its ongoing development aims to bridge the gap between the filmmaker's creative vision and the viewer's experience, regardless of the display technology used for playback.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for Dolby Vision in film production has been steadily increasing, driven by the growing consumer appetite for high-quality visual experiences. As 4K and HDR-capable displays become more prevalent in homes, there is a corresponding rise in demand for content that can fully utilize these technologies. Dolby Vision, with its advanced HDR capabilities, has positioned itself as a premium solution for delivering superior image quality.
The film industry has recognized the potential of Dolby Vision to enhance the viewing experience, leading to increased adoption in both theatrical releases and streaming platforms. Major studios and content creators are increasingly incorporating Dolby Vision into their production workflows to future-proof their content and meet the expectations of discerning audiences.
Streaming services have become significant drivers of Dolby Vision adoption. Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Apple TV+ have all embraced Dolby Vision, offering a growing library of compatible content. This has created a ripple effect in the production industry, with more filmmakers and post-production houses investing in Dolby Vision-capable equipment and expertise to meet the demand from these platforms.
The cinema market has also shown interest in Dolby Vision, with an increasing number of theaters upgrading their projection systems to support this technology. This trend is particularly notable in premium cinema formats, where Dolby Vision is seen as a differentiator that can justify higher ticket prices and attract cinema-goers seeking the best possible visual experience.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have responded to this market demand by incorporating Dolby Vision support into a wide range of devices, from high-end televisions to mobile phones. This widespread availability of Dolby Vision-capable displays has further fueled the demand for compatible content, creating a positive feedback loop for the technology's adoption in film production.
The professional equipment market has also seen growth, with manufacturers of cameras, monitors, and color grading software integrating Dolby Vision capabilities into their products. This has made it easier for production teams to work with the technology throughout the entire filmmaking process, from capture to post-production.
While exact market size figures are challenging to pinpoint due to the integrated nature of Dolby Vision within broader film production and distribution ecosystems, industry analysts consistently report strong growth trends. The technology's impact is evident in the increasing number of Dolby Vision-enabled productions and the expanding ecosystem of compatible devices and content platforms.
The film industry has recognized the potential of Dolby Vision to enhance the viewing experience, leading to increased adoption in both theatrical releases and streaming platforms. Major studios and content creators are increasingly incorporating Dolby Vision into their production workflows to future-proof their content and meet the expectations of discerning audiences.
Streaming services have become significant drivers of Dolby Vision adoption. Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Apple TV+ have all embraced Dolby Vision, offering a growing library of compatible content. This has created a ripple effect in the production industry, with more filmmakers and post-production houses investing in Dolby Vision-capable equipment and expertise to meet the demand from these platforms.
The cinema market has also shown interest in Dolby Vision, with an increasing number of theaters upgrading their projection systems to support this technology. This trend is particularly notable in premium cinema formats, where Dolby Vision is seen as a differentiator that can justify higher ticket prices and attract cinema-goers seeking the best possible visual experience.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have responded to this market demand by incorporating Dolby Vision support into a wide range of devices, from high-end televisions to mobile phones. This widespread availability of Dolby Vision-capable displays has further fueled the demand for compatible content, creating a positive feedback loop for the technology's adoption in film production.
The professional equipment market has also seen growth, with manufacturers of cameras, monitors, and color grading software integrating Dolby Vision capabilities into their products. This has made it easier for production teams to work with the technology throughout the entire filmmaking process, from capture to post-production.
While exact market size figures are challenging to pinpoint due to the integrated nature of Dolby Vision within broader film production and distribution ecosystems, industry analysts consistently report strong growth trends. The technology's impact is evident in the increasing number of Dolby Vision-enabled productions and the expanding ecosystem of compatible devices and content platforms.
Current Challenges
Dolby Vision, as a cutting-edge HDR technology, has significantly impacted color grading in film production. However, its implementation and widespread adoption face several challenges in the current landscape of film and television production.
One of the primary challenges is the complexity of the Dolby Vision workflow. Color graders and post-production professionals need to adapt to new tools and processes, which can be time-consuming and require additional training. The learning curve associated with mastering Dolby Vision's capabilities can be steep, potentially slowing down production timelines and increasing costs.
Another significant challenge is the lack of standardization across different display technologies. While Dolby Vision aims to provide a consistent viewing experience across various devices, the reality is that not all displays are created equal. This disparity in display capabilities can lead to inconsistencies in how the final product is viewed by audiences, potentially compromising the filmmaker's creative vision.
The increased data requirements for Dolby Vision content also present challenges in terms of storage and distribution. The higher bit depth and expanded color gamut necessitate larger file sizes, which can strain existing infrastructure and increase costs for both production companies and streaming platforms.
Furthermore, there is a notable shortage of Dolby Vision-certified monitors and grading suites in many production facilities. This scarcity of equipment can create bottlenecks in the post-production process and limit the number of projects that can fully utilize Dolby Vision's capabilities.
The backward compatibility of Dolby Vision content with standard dynamic range (SDR) displays is another area of concern. Ensuring that the visual experience remains high-quality across both HDR and SDR displays requires additional time and expertise in the color grading process, potentially extending post-production schedules.
There is also an ongoing debate about the perceptual benefits of Dolby Vision compared to other HDR formats like HDR10+. Some industry professionals argue that the differences may not be significant enough to justify the additional costs and complexities associated with Dolby Vision implementation.
Lastly, the licensing fees and proprietary nature of Dolby Vision technology can be a barrier for smaller production companies or independent filmmakers. The additional costs associated with implementing Dolby Vision may limit its adoption in certain segments of the industry, potentially creating a divide between high-budget and low-budget productions in terms of visual quality and technological advancement.
One of the primary challenges is the complexity of the Dolby Vision workflow. Color graders and post-production professionals need to adapt to new tools and processes, which can be time-consuming and require additional training. The learning curve associated with mastering Dolby Vision's capabilities can be steep, potentially slowing down production timelines and increasing costs.
Another significant challenge is the lack of standardization across different display technologies. While Dolby Vision aims to provide a consistent viewing experience across various devices, the reality is that not all displays are created equal. This disparity in display capabilities can lead to inconsistencies in how the final product is viewed by audiences, potentially compromising the filmmaker's creative vision.
The increased data requirements for Dolby Vision content also present challenges in terms of storage and distribution. The higher bit depth and expanded color gamut necessitate larger file sizes, which can strain existing infrastructure and increase costs for both production companies and streaming platforms.
Furthermore, there is a notable shortage of Dolby Vision-certified monitors and grading suites in many production facilities. This scarcity of equipment can create bottlenecks in the post-production process and limit the number of projects that can fully utilize Dolby Vision's capabilities.
The backward compatibility of Dolby Vision content with standard dynamic range (SDR) displays is another area of concern. Ensuring that the visual experience remains high-quality across both HDR and SDR displays requires additional time and expertise in the color grading process, potentially extending post-production schedules.
There is also an ongoing debate about the perceptual benefits of Dolby Vision compared to other HDR formats like HDR10+. Some industry professionals argue that the differences may not be significant enough to justify the additional costs and complexities associated with Dolby Vision implementation.
Lastly, the licensing fees and proprietary nature of Dolby Vision technology can be a barrier for smaller production companies or independent filmmakers. The additional costs associated with implementing Dolby Vision may limit its adoption in certain segments of the industry, potentially creating a divide between high-budget and low-budget productions in terms of visual quality and technological advancement.
Dolby Vision Workflow
01 High Dynamic Range (HDR) color grading techniques
Dolby Vision color grading involves advanced HDR techniques to enhance the visual quality of content. This includes optimizing brightness, contrast, and color range to create more vivid and lifelike images. The process allows for greater detail in both bright and dark areas of the image, resulting in a more immersive viewing experience.- HDR color grading techniques: Dolby Vision color grading involves advanced techniques for high dynamic range (HDR) content. This includes methods for adjusting brightness, contrast, and color saturation to enhance the visual experience across various display devices. The process aims to preserve the creator's intent while optimizing the content for different viewing environments.
- Metadata generation and management: A crucial aspect of Dolby Vision color grading is the generation and management of metadata. This metadata contains information about color mapping, dynamic range, and display characteristics. It allows for dynamic adjustments of the content based on the capabilities of the playback device, ensuring optimal viewing experience across different screens.
- Display device calibration: Proper calibration of display devices is essential for accurate Dolby Vision color grading. This involves adjusting various parameters such as white point, gamma, and color gamut to ensure that the graded content appears as intended across different displays. Calibration tools and methods are developed to achieve consistency in color reproduction.
- Color space conversion and mapping: Dolby Vision color grading incorporates advanced color space conversion and mapping techniques. These methods enable the transformation of content between different color spaces and gamuts, ensuring accurate color representation across various display technologies and standards. This is crucial for maintaining color fidelity in different viewing environments.
- Quality control and verification: To ensure the effectiveness of Dolby Vision color grading, robust quality control and verification processes are implemented. These include automated analysis tools, visual inspection methods, and standardized test patterns. Such processes help maintain consistency and accuracy in the color grading workflow, ensuring that the final output meets the required standards.
02 Color mapping and tone mapping algorithms
Specialized algorithms are used in Dolby Vision color grading to map colors and tones accurately across different display devices. These algorithms ensure that the intended visual quality is maintained regardless of the viewing device's capabilities, adapting the content to various brightness levels and color gamuts.Expand Specific Solutions03 Metadata-driven dynamic optimization
Dolby Vision employs metadata-driven techniques to dynamically optimize the content on a scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame basis. This allows for precise control over color, brightness, and contrast throughout the content, ensuring that each scene is presented with optimal visual quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration with content creation tools
Dolby Vision color grading is integrated into various content creation tools and software used in the film and television industry. This integration allows colorists and post-production professionals to work directly with Dolby Vision capabilities, streamlining the color grading process and ensuring compatibility with the format.Expand Specific Solutions05 Display-specific calibration and optimization
The color grading process in Dolby Vision includes specific calibration and optimization techniques for different display technologies. This ensures that the content looks its best on various types of screens, from high-end professional monitors to consumer-grade televisions, maintaining consistent color accuracy and visual quality across devices.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The color grading landscape in film production is evolving rapidly with the advent of Dolby Vision technology. This market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across the film industry. The global HDR market, which includes Dolby Vision, is projected to reach significant market size in the coming years. Technologically, Dolby Vision is at a mature stage, with ongoing refinements and improvements. Key players like Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp., Adobe, Inc., and Sony Interactive Entertainment are driving innovation in this space. Other companies such as Barco NV and BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd. are also contributing to the ecosystem with complementary technologies. As the technology becomes more widespread, we can expect to see further advancements in color grading techniques and tools.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
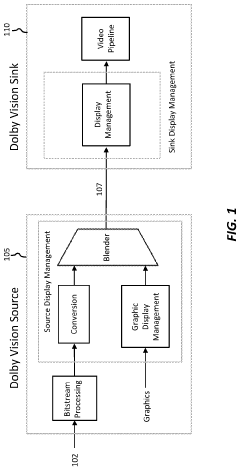
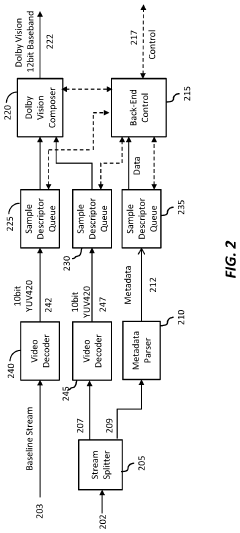
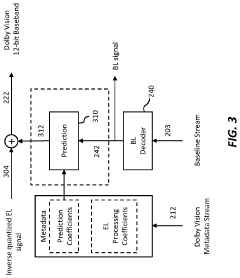
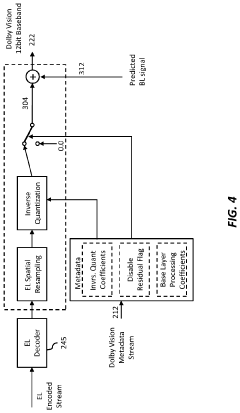
Technical Solution: Dolby Vision employs dynamic metadata to optimize HDR content on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis[1]. This technology allows for up to 12-bit color depth, enabling a palette of 68 billion colors, significantly more than standard 10-bit HDR[2]. Dolby Vision's color grading process utilizes specialized hardware and software tools that can interpret and apply this dynamic metadata, ensuring that the filmmaker's creative intent is preserved across various display devices[3]. The technology also supports both HDR and SDR workflows, allowing for efficient creation of multiple deliverables from a single master[4].
Strengths: Superior color accuracy and dynamic range; Consistent viewing experience across devices; Efficient workflow for multiple deliverables. Weaknesses: Requires specialized hardware and software; Potentially higher production costs; Limited adoption in some markets.
Adobe, Inc.
Technical Solution: Adobe has integrated Dolby Vision HDR technology into its Creative Cloud suite, particularly in Premiere Pro and After Effects[5]. This integration allows filmmakers and colorists to work directly with Dolby Vision content within familiar editing environments. Adobe's implementation includes tools for HDR color grading, tone mapping, and metadata management specific to Dolby Vision workflows[6]. The software provides real-time previews of how content will appear on various display types, from professional reference monitors to consumer devices, ensuring consistency across different viewing scenarios[7].
Strengths: Seamless integration with widely-used editing software; Accessible to a broad range of professionals. Weaknesses: Dependent on Dolby's technology; May require additional training for colorists.
HDR Color Science
Layered representation and delivery of high dynamic range video
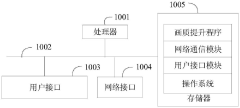
PatentActiveUS20190373290A1
Innovation
- The implementation of a layered representation and delivery system for HDR video, utilizing Dolby Vision technology, which includes a base layer and enhancement layer, along with metadata processing to reconstruct HDR signals, ensuring seamless playback on compatible displays.
Image quality enhancement method, device, playback device and computer-readable storage medium
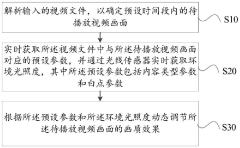
PatentActiveCN114567813B
Innovation
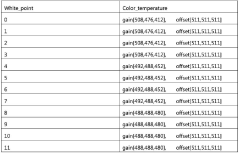
- By parsing the video file, the preset parameters and ambient illumination corresponding to the video image are obtained in real time, and the image quality effect is dynamically adjusted, including adjusting motion compensation, noise reduction, sharpness, color temperature and brightness parameters to adapt to different content types and lighting conditions.
Standardization Efforts
The standardization efforts for Dolby Vision in film production have been crucial in establishing a consistent and high-quality color grading workflow across the industry. These efforts have focused on creating uniform guidelines and specifications for implementing Dolby Vision technology in various stages of film production and post-production.
One of the key aspects of standardization has been the development of the Dolby Vision metadata format. This format allows for the precise communication of color grading information between different stages of production and across various display devices. The metadata includes critical information about color volume, brightness, and dynamic range, ensuring that the filmmaker's creative intent is preserved throughout the production and distribution process.
Dolby has also worked closely with industry bodies such as the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) to establish standards for high dynamic range (HDR) content creation and delivery. This collaboration has resulted in the development of the ST 2084 Perceptual Quantizer (PQ) EOTF standard, which forms the basis for Dolby Vision's HDR implementation.
To facilitate widespread adoption, Dolby has created standardized tools and workflows for color grading with Dolby Vision. These include the Dolby Vision Content Mapping Unit (CMU) and the Dolby Vision Professional Tools suite, which provide colorists with consistent and reliable methods for creating and quality-checking Dolby Vision content.
The company has also established certification programs for post-production facilities and consumer displays. These programs ensure that both professional and consumer equipment meet the necessary specifications to accurately reproduce Dolby Vision content, maintaining the integrity of the creative vision from production to viewing.
Standardization efforts have extended to the integration of Dolby Vision with other industry-standard formats and workflows. This includes compatibility with popular color grading software, such as DaVinci Resolve and Baselight, as well as integration with widely used camera systems and on-set monitoring solutions.
Furthermore, Dolby has worked on standardizing the delivery of Dolby Vision content across various distribution platforms. This includes establishing guidelines for streaming services, broadcast networks, and physical media formats like Ultra HD Blu-ray. These efforts have helped to ensure a consistent viewing experience across different devices and platforms.
The ongoing standardization work continues to address emerging challenges, such as the integration of Dolby Vision with virtual production techniques and real-time rendering engines. As the technology evolves, these efforts will play a crucial role in maintaining the quality and consistency of Dolby Vision implementation in film production and beyond.
One of the key aspects of standardization has been the development of the Dolby Vision metadata format. This format allows for the precise communication of color grading information between different stages of production and across various display devices. The metadata includes critical information about color volume, brightness, and dynamic range, ensuring that the filmmaker's creative intent is preserved throughout the production and distribution process.
Dolby has also worked closely with industry bodies such as the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) to establish standards for high dynamic range (HDR) content creation and delivery. This collaboration has resulted in the development of the ST 2084 Perceptual Quantizer (PQ) EOTF standard, which forms the basis for Dolby Vision's HDR implementation.
To facilitate widespread adoption, Dolby has created standardized tools and workflows for color grading with Dolby Vision. These include the Dolby Vision Content Mapping Unit (CMU) and the Dolby Vision Professional Tools suite, which provide colorists with consistent and reliable methods for creating and quality-checking Dolby Vision content.
The company has also established certification programs for post-production facilities and consumer displays. These programs ensure that both professional and consumer equipment meet the necessary specifications to accurately reproduce Dolby Vision content, maintaining the integrity of the creative vision from production to viewing.
Standardization efforts have extended to the integration of Dolby Vision with other industry-standard formats and workflows. This includes compatibility with popular color grading software, such as DaVinci Resolve and Baselight, as well as integration with widely used camera systems and on-set monitoring solutions.
Furthermore, Dolby has worked on standardizing the delivery of Dolby Vision content across various distribution platforms. This includes establishing guidelines for streaming services, broadcast networks, and physical media formats like Ultra HD Blu-ray. These efforts have helped to ensure a consistent viewing experience across different devices and platforms.
The ongoing standardization work continues to address emerging challenges, such as the integration of Dolby Vision with virtual production techniques and real-time rendering engines. As the technology evolves, these efforts will play a crucial role in maintaining the quality and consistency of Dolby Vision implementation in film production and beyond.
Content Distribution
The distribution of Dolby Vision content has significantly transformed the landscape of film and television production, offering viewers an enhanced visual experience across various platforms. As streaming services and digital distribution channels continue to proliferate, Dolby Vision has become a key differentiator in the competitive content market.
Major streaming platforms such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Apple TV+ have embraced Dolby Vision, making it a standard offering for their premium content. This widespread adoption has created a ripple effect throughout the industry, influencing production workflows and consumer expectations. Content creators are now increasingly prioritizing Dolby Vision-compatible deliverables to meet the demands of these platforms and their audiences.
The integration of Dolby Vision into content distribution pipelines has necessitated changes in post-production processes. Color grading facilities have had to invest in Dolby Vision-capable equipment and software, ensuring they can deliver content that fully utilizes the technology's capabilities. This has led to a shift in the skill sets required for colorists and post-production professionals, who must now be proficient in HDR and Dolby Vision workflows.
The distribution of Dolby Vision content has also impacted consumer electronics manufacturers. Television and mobile device producers have incorporated Dolby Vision support into their products, creating a more seamless ecosystem for content consumption. This has, in turn, driven consumer demand for Dolby Vision-enabled devices, further solidifying the technology's position in the market.
However, the distribution of Dolby Vision content is not without challenges. The increased data requirements for Dolby Vision files can strain bandwidth and storage infrastructure, particularly in regions with limited internet connectivity. Additionally, the need for backwards compatibility with SDR displays has led to the development of complex distribution workflows that can handle both HDR and SDR versions of content efficiently.
As the technology continues to evolve, new distribution methods are emerging. Dynamic metadata, a key feature of Dolby Vision, allows for scene-by-scene optimization of content, ensuring the best possible viewing experience across different display capabilities. This has opened up possibilities for more adaptive content delivery, where the visual quality can be adjusted in real-time based on the viewer's device and network conditions.
The impact of Dolby Vision on content distribution extends beyond just visual quality. It has become a marketing tool for content providers, with Dolby Vision branding often prominently featured in promotional materials. This has created a perceived value proposition for consumers, associating Dolby Vision content with premium quality and a superior viewing experience.
Major streaming platforms such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Apple TV+ have embraced Dolby Vision, making it a standard offering for their premium content. This widespread adoption has created a ripple effect throughout the industry, influencing production workflows and consumer expectations. Content creators are now increasingly prioritizing Dolby Vision-compatible deliverables to meet the demands of these platforms and their audiences.
The integration of Dolby Vision into content distribution pipelines has necessitated changes in post-production processes. Color grading facilities have had to invest in Dolby Vision-capable equipment and software, ensuring they can deliver content that fully utilizes the technology's capabilities. This has led to a shift in the skill sets required for colorists and post-production professionals, who must now be proficient in HDR and Dolby Vision workflows.
The distribution of Dolby Vision content has also impacted consumer electronics manufacturers. Television and mobile device producers have incorporated Dolby Vision support into their products, creating a more seamless ecosystem for content consumption. This has, in turn, driven consumer demand for Dolby Vision-enabled devices, further solidifying the technology's position in the market.
However, the distribution of Dolby Vision content is not without challenges. The increased data requirements for Dolby Vision files can strain bandwidth and storage infrastructure, particularly in regions with limited internet connectivity. Additionally, the need for backwards compatibility with SDR displays has led to the development of complex distribution workflows that can handle both HDR and SDR versions of content efficiently.
As the technology continues to evolve, new distribution methods are emerging. Dynamic metadata, a key feature of Dolby Vision, allows for scene-by-scene optimization of content, ensuring the best possible viewing experience across different display capabilities. This has opened up possibilities for more adaptive content delivery, where the visual quality can be adjusted in real-time based on the viewer's device and network conditions.
The impact of Dolby Vision on content distribution extends beyond just visual quality. It has become a marketing tool for content providers, with Dolby Vision branding often prominently featured in promotional materials. This has created a perceived value proposition for consumers, associating Dolby Vision content with premium quality and a superior viewing experience.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!