Dolby Vision’s Potential in Professional Video Editing Tools
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dolby Vision Evolution
Dolby Vision has undergone a remarkable evolution since its introduction in 2014, transforming the landscape of high dynamic range (HDR) video technology. Initially developed for cinema and high-end consumer displays, Dolby Vision has steadily expanded its reach into various aspects of content creation and distribution, including professional video editing tools.
The technology's journey began with a focus on enhancing the viewing experience through increased brightness, contrast, and color gamut. Early iterations of Dolby Vision were primarily hardware-dependent, requiring specialized displays and playback devices. However, as the technology matured, software-based implementations emerged, broadening its accessibility and applicability in the professional video editing sphere.
A significant milestone in Dolby Vision's evolution was the introduction of Dolby Vision IQ in 2020. This advancement incorporated ambient light sensors to dynamically adjust content based on viewing conditions, further improving the viewing experience across various environments. This development highlighted the technology's adaptability and potential for integration into diverse video production workflows.
The evolution of Dolby Vision has been closely tied to advancements in content creation tools. As the technology gained traction, major software developers began incorporating Dolby Vision support into their professional video editing suites. This integration allowed editors and colorists to work directly with Dolby Vision content, streamlining the post-production process and ensuring accurate representation of the creator's vision across different display technologies.
Another crucial development in Dolby Vision's evolution was the introduction of Dolby Vision for Content Creators in 2021. This toolset democratized access to Dolby Vision technology, enabling a broader range of professionals to create and deliver HDR content. It marked a shift towards more accessible and flexible workflows, potentially revolutionizing how smaller production houses and independent creators approach high-quality video production.
The technology's evolution has also seen improvements in metadata handling and delivery. Initially, Dolby Vision relied on static metadata, but later versions introduced dynamic metadata capabilities. This advancement allowed for frame-by-frame optimization of HDR content, providing greater creative control and enhancing the viewer's experience across a wide range of displays.
As Dolby Vision continues to evolve, its potential in professional video editing tools grows exponentially. The technology is increasingly becoming an integral part of the entire content creation pipeline, from acquisition to delivery. This evolution points towards a future where Dolby Vision could become a standard feature in professional video editing tools, offering unprecedented control over HDR content creation and ensuring consistent, high-quality viewing experiences across diverse platforms and devices.
The technology's journey began with a focus on enhancing the viewing experience through increased brightness, contrast, and color gamut. Early iterations of Dolby Vision were primarily hardware-dependent, requiring specialized displays and playback devices. However, as the technology matured, software-based implementations emerged, broadening its accessibility and applicability in the professional video editing sphere.
A significant milestone in Dolby Vision's evolution was the introduction of Dolby Vision IQ in 2020. This advancement incorporated ambient light sensors to dynamically adjust content based on viewing conditions, further improving the viewing experience across various environments. This development highlighted the technology's adaptability and potential for integration into diverse video production workflows.
The evolution of Dolby Vision has been closely tied to advancements in content creation tools. As the technology gained traction, major software developers began incorporating Dolby Vision support into their professional video editing suites. This integration allowed editors and colorists to work directly with Dolby Vision content, streamlining the post-production process and ensuring accurate representation of the creator's vision across different display technologies.
Another crucial development in Dolby Vision's evolution was the introduction of Dolby Vision for Content Creators in 2021. This toolset democratized access to Dolby Vision technology, enabling a broader range of professionals to create and deliver HDR content. It marked a shift towards more accessible and flexible workflows, potentially revolutionizing how smaller production houses and independent creators approach high-quality video production.
The technology's evolution has also seen improvements in metadata handling and delivery. Initially, Dolby Vision relied on static metadata, but later versions introduced dynamic metadata capabilities. This advancement allowed for frame-by-frame optimization of HDR content, providing greater creative control and enhancing the viewer's experience across a wide range of displays.
As Dolby Vision continues to evolve, its potential in professional video editing tools grows exponentially. The technology is increasingly becoming an integral part of the entire content creation pipeline, from acquisition to delivery. This evolution points towards a future where Dolby Vision could become a standard feature in professional video editing tools, offering unprecedented control over HDR content creation and ensuring consistent, high-quality viewing experiences across diverse platforms and devices.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for Dolby Vision integration in professional video editing tools has been steadily increasing, driven by the growing popularity of High Dynamic Range (HDR) content across various platforms. As consumers become more accustomed to superior visual experiences, content creators and post-production professionals are seeking advanced tools to meet these heightened expectations.
The rise of streaming services and the proliferation of HDR-capable devices have created a surge in demand for HDR content. This trend has led to a significant market opportunity for video editing software that can efficiently handle Dolby Vision workflows. Professional editors require tools that can seamlessly work with Dolby Vision's expanded color gamut and dynamic range, ensuring that the final product maintains its visual integrity across different display technologies.
Furthermore, the film and television industry has shown a strong inclination towards adopting Dolby Vision as a preferred HDR format. Major studios and streaming platforms are increasingly mandating Dolby Vision deliverables, creating a ripple effect in the post-production ecosystem. This industry shift has amplified the need for editing tools that can natively support Dolby Vision, streamlining the production process and reducing the time and cost associated with HDR content creation.
The professional video editing market is also witnessing a growing demand for tools that can facilitate real-time color grading and preview of Dolby Vision content. Editors and colorists require the ability to see accurate representations of their work throughout the editing process, without the need for time-consuming exports or specialized hardware. This demand is driving innovation in software solutions that can provide on-the-fly Dolby Vision processing and display.
Additionally, there is an increasing need for interoperability between different stages of the post-production workflow. Professionals are seeking editing tools that can seamlessly integrate with other Dolby Vision-enabled software and hardware, ensuring a smooth transition from editing to color grading, and finally to delivery. This interconnected ecosystem approach is becoming a key factor in the adoption of Dolby Vision-capable editing tools.
The market is also showing interest in solutions that can simplify the complex process of creating multiple versions of content for different display capabilities. Editing tools that can automatically generate and manage Dolby Vision metadata, facilitating the creation of various trim passes, are in high demand. This functionality allows content creators to efficiently produce versions optimized for both HDR and SDR displays, maximizing the reach and impact of their content across diverse viewing environments.
The rise of streaming services and the proliferation of HDR-capable devices have created a surge in demand for HDR content. This trend has led to a significant market opportunity for video editing software that can efficiently handle Dolby Vision workflows. Professional editors require tools that can seamlessly work with Dolby Vision's expanded color gamut and dynamic range, ensuring that the final product maintains its visual integrity across different display technologies.
Furthermore, the film and television industry has shown a strong inclination towards adopting Dolby Vision as a preferred HDR format. Major studios and streaming platforms are increasingly mandating Dolby Vision deliverables, creating a ripple effect in the post-production ecosystem. This industry shift has amplified the need for editing tools that can natively support Dolby Vision, streamlining the production process and reducing the time and cost associated with HDR content creation.
The professional video editing market is also witnessing a growing demand for tools that can facilitate real-time color grading and preview of Dolby Vision content. Editors and colorists require the ability to see accurate representations of their work throughout the editing process, without the need for time-consuming exports or specialized hardware. This demand is driving innovation in software solutions that can provide on-the-fly Dolby Vision processing and display.
Additionally, there is an increasing need for interoperability between different stages of the post-production workflow. Professionals are seeking editing tools that can seamlessly integrate with other Dolby Vision-enabled software and hardware, ensuring a smooth transition from editing to color grading, and finally to delivery. This interconnected ecosystem approach is becoming a key factor in the adoption of Dolby Vision-capable editing tools.
The market is also showing interest in solutions that can simplify the complex process of creating multiple versions of content for different display capabilities. Editing tools that can automatically generate and manage Dolby Vision metadata, facilitating the creation of various trim passes, are in high demand. This functionality allows content creators to efficiently produce versions optimized for both HDR and SDR displays, maximizing the reach and impact of their content across diverse viewing environments.
Technical Challenges
The integration of Dolby Vision into professional video editing tools presents several significant technical challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of implementing High Dynamic Range (HDR) and Wide Color Gamut (WCG) capabilities within existing editing software frameworks. This requires extensive modifications to color management systems and rendering pipelines to accurately represent and manipulate the expanded color and brightness ranges offered by Dolby Vision.
Another challenge lies in the real-time processing and playback of Dolby Vision content during the editing process. The increased data volume and computational requirements for HDR content can strain hardware resources, potentially leading to performance issues on less powerful workstations. This necessitates optimized algorithms and potentially specialized hardware acceleration to maintain smooth editing experiences.
Ensuring color accuracy and consistency across different display devices poses a significant hurdle. Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata allows for optimized content display on various screens, but implementing this feature in editing tools requires sophisticated color transformation and mapping techniques. Editors need to preview how content will appear on different target devices, which demands complex simulation capabilities within the editing software.
Compatibility with existing workflows and file formats is another critical challenge. Many professional editing environments rely on established codecs and container formats that may not fully support Dolby Vision's metadata and extended color information. Developing new file formats or extending existing ones to accommodate Dolby Vision data while maintaining backward compatibility is a complex undertaking.
The challenge of managing and preserving Dolby Vision metadata throughout the post-production pipeline is also significant. This metadata is crucial for maintaining the creator's intent across different displays and viewing environments. Ensuring that this information is accurately preserved, modified when necessary, and correctly interpreted at each stage of the editing and export process requires careful implementation and robust data handling mechanisms.
Lastly, the technical challenge of providing intuitive and effective tools for manipulating Dolby Vision content cannot be understated. Editors need new interfaces and controls to work with expanded dynamic range and color spaces effectively. Developing these tools in a way that is both powerful and user-friendly, without overwhelming editors accustomed to traditional video editing paradigms, requires thoughtful design and extensive user testing.
Another challenge lies in the real-time processing and playback of Dolby Vision content during the editing process. The increased data volume and computational requirements for HDR content can strain hardware resources, potentially leading to performance issues on less powerful workstations. This necessitates optimized algorithms and potentially specialized hardware acceleration to maintain smooth editing experiences.
Ensuring color accuracy and consistency across different display devices poses a significant hurdle. Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata allows for optimized content display on various screens, but implementing this feature in editing tools requires sophisticated color transformation and mapping techniques. Editors need to preview how content will appear on different target devices, which demands complex simulation capabilities within the editing software.
Compatibility with existing workflows and file formats is another critical challenge. Many professional editing environments rely on established codecs and container formats that may not fully support Dolby Vision's metadata and extended color information. Developing new file formats or extending existing ones to accommodate Dolby Vision data while maintaining backward compatibility is a complex undertaking.
The challenge of managing and preserving Dolby Vision metadata throughout the post-production pipeline is also significant. This metadata is crucial for maintaining the creator's intent across different displays and viewing environments. Ensuring that this information is accurately preserved, modified when necessary, and correctly interpreted at each stage of the editing and export process requires careful implementation and robust data handling mechanisms.
Lastly, the technical challenge of providing intuitive and effective tools for manipulating Dolby Vision content cannot be understated. Editors need new interfaces and controls to work with expanded dynamic range and color spaces effectively. Developing these tools in a way that is both powerful and user-friendly, without overwhelming editors accustomed to traditional video editing paradigms, requires thoughtful design and extensive user testing.
Current Implementation
01 High Dynamic Range (HDR) and Wide Color Gamut
Dolby Vision technology enhances image quality by implementing HDR and wide color gamut capabilities. This allows for a broader range of colors and improved contrast, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike images with greater detail in both bright and dark areas.- High Dynamic Range (HDR) imaging technology: Dolby Vision utilizes HDR technology to enhance image quality by expanding the range of both contrast and color. This results in brighter highlights, deeper blacks, and a wider color gamut, providing a more lifelike and immersive viewing experience.
- Dynamic metadata optimization: Dolby Vision employs dynamic metadata to optimize image quality on a scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame basis. This allows for precise control over brightness, contrast, and color, ensuring that each image is displayed at its best possible quality.
- Color grading and mapping techniques: Advanced color grading and mapping techniques are used in Dolby Vision to accurately reproduce colors across different display devices. This ensures consistent image quality and color representation, regardless of the viewer's display capabilities.
- Display device calibration and optimization: Dolby Vision incorporates display device calibration and optimization to ensure that the content is displayed as intended. This includes adjusting for the specific characteristics of each display, such as peak brightness, black levels, and color gamut.
- Content creation and mastering tools: Specialized content creation and mastering tools are used in the Dolby Vision workflow to produce high-quality HDR content. These tools allow content creators to fine-tune image parameters and ensure optimal visual quality across various display devices.
02 Dynamic Metadata Processing
Dolby Vision utilizes dynamic metadata to optimize image quality on a scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame basis. This adaptive approach ensures that each image is displayed with the best possible settings for brightness, color, and contrast, resulting in a more consistent and high-quality viewing experience.Expand Specific Solutions03 Display Calibration and Optimization
Dolby Vision technology incorporates advanced display calibration and optimization techniques to ensure that images are rendered accurately across different display devices. This includes color mapping, tone mapping, and brightness adjustment to maintain image quality consistency across various screens and viewing environments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Content Creation and Mastering
Dolby Vision provides tools and workflows for content creators to master and produce high-quality HDR content. This includes color grading, encoding, and mastering processes that preserve the original creative intent and ensure optimal image quality throughout the production and distribution chain.Expand Specific Solutions05 Backward Compatibility and Scalability
Dolby Vision technology is designed to be backward compatible with standard dynamic range (SDR) displays while also being scalable for future display technologies. This ensures that content can be optimized for a wide range of devices, from legacy displays to the latest high-end screens, maintaining image quality across different viewing scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The competitive landscape for Dolby Vision in professional video editing tools is evolving rapidly, reflecting the industry's growth stage and increasing market size. The technology's maturity is advancing, with key players like Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp., Adobe, Inc., and Apple, Inc. leading the charge. These companies are leveraging their expertise in video processing and software development to integrate Dolby Vision capabilities into their professional editing suites. As the demand for high-quality HDR content grows, other major tech firms such as Microsoft, Sony, and LG are also entering the space, potentially accelerating innovation and market adoption.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Vision, developed by Dolby Laboratories, is a cutting-edge HDR technology that enhances video quality by optimizing brightness, contrast, and color on a scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame basis. In professional video editing tools, Dolby Vision offers advanced color grading capabilities, allowing editors to work with a wider color gamut and higher dynamic range. The technology supports up to 12-bit color depth, providing over 68 billion colors [1], and can reach peak brightness levels of up to 10,000 nits [2]. Dolby Vision's metadata-based approach enables content to be optimized for various display capabilities, ensuring consistent quality across different devices. The integration of Dolby Vision into professional editing suites allows for real-time HDR monitoring and more precise color adjustments, potentially streamlining the post-production workflow [3].
Strengths: Superior image quality, wide device compatibility, and future-proofing of content. Weaknesses: Requires specialized hardware for full implementation and may increase production costs.
Adobe, Inc.
Technical Solution: Adobe has integrated Dolby Vision support into its professional video editing tools, particularly in Adobe Premiere Pro. This integration allows editors to work directly with Dolby Vision content, enabling them to create, edit, and deliver HDR content more efficiently. Adobe's implementation includes features such as automatic analysis of SDR content for HDR conversion, built-in Dolby Vision mastering tools, and the ability to generate Dolby Vision metadata within the editing environment [4]. The software also provides real-time previews of how content will appear on different display types, from professional reference monitors to consumer devices. Adobe has also developed AI-powered color matching tools that can help maintain consistency across scenes and streamline the color grading process for Dolby Vision content [5].
Strengths: Seamless integration with existing workflows, powerful AI-assisted tools. Weaknesses: May require additional training for editors to fully utilize new features.
Core Dolby Vision Tech
Chrominance high precision motion filtering for motion interpolation
PatentInactiveEP2537342A2
Innovation
- The proposed solution involves determining chrominance motion vectors with greater precision than luminance motion vectors and selecting interpolation filters based on fractional components to interpolate values at fractional pixel positions, using a set of predefined filters for specific fractional positions, thereby improving the accuracy of chrominance block processing.
Scene-creation using high-resolution video perspective manipulation and editing techniques
PatentPendingUS20250014608A1
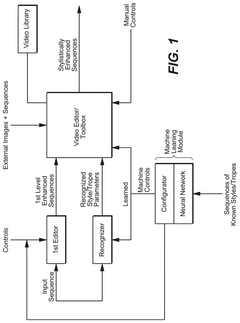
Innovation
- A machine learning-based video editing system that recognizes and conforms video sequences to signature styles of famous filmmakers, applying techniques such as image and audio processing, visual effects, and cinematographic enhancements, allowing users to enhance video quality and style, including adjustments for lighting, perspective, and audio modifications.
Workflow Integration
The integration of Dolby Vision into professional video editing tools represents a significant advancement in workflow efficiency and creative potential. This high dynamic range (HDR) imaging technology offers editors and colorists unprecedented control over the visual quality of their content, seamlessly fitting into existing post-production pipelines.
Dolby Vision's workflow integration begins with the capture of high-quality HDR footage, which can be ingested directly into compatible editing software. Leading non-linear editing (NLE) systems such as Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, and Avid Media Composer have incorporated Dolby Vision support, allowing editors to work with the full range of color and brightness information throughout the post-production process.
One of the key advantages of Dolby Vision integration is the ability to create and manipulate metadata that controls how content is displayed across various devices. This metadata-driven approach enables editors to make precise adjustments to brightness, color, and contrast that can be dynamically optimized for different viewing environments and display capabilities.
The workflow also includes tools for creating multiple versions of content, such as HDR and SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) deliverables, from a single master. This feature, known as "single-stream HDR," significantly reduces the time and complexity involved in producing content for various distribution channels and display technologies.
Dolby Vision's integration extends to color grading suites, where professional colorists can leverage the technology's expanded color palette and luminance range to achieve more nuanced and impactful visual storytelling. The ability to work in extended color spaces like BT.2020 allows for more accurate color representation and grading decisions.
Furthermore, Dolby Vision workflow integration includes quality control and mastering tools that ensure content meets technical specifications and creative intent across different viewing devices. These tools allow for real-time previewing of how content will appear on various displays, from high-end professional monitors to consumer televisions and mobile devices.
The adoption of Dolby Vision in professional editing tools also facilitates collaboration between different stages of post-production. For instance, visual effects artists can work with HDR assets and seamlessly integrate their work into the main edit, maintaining the full dynamic range throughout the process.
As the demand for HDR content continues to grow, the integration of Dolby Vision into professional video editing tools is becoming increasingly important. It not only enhances the creative possibilities for content creators but also streamlines the production of high-quality HDR content, positioning it as a valuable asset in the competitive landscape of modern video production.
Dolby Vision's workflow integration begins with the capture of high-quality HDR footage, which can be ingested directly into compatible editing software. Leading non-linear editing (NLE) systems such as Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, and Avid Media Composer have incorporated Dolby Vision support, allowing editors to work with the full range of color and brightness information throughout the post-production process.
One of the key advantages of Dolby Vision integration is the ability to create and manipulate metadata that controls how content is displayed across various devices. This metadata-driven approach enables editors to make precise adjustments to brightness, color, and contrast that can be dynamically optimized for different viewing environments and display capabilities.
The workflow also includes tools for creating multiple versions of content, such as HDR and SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) deliverables, from a single master. This feature, known as "single-stream HDR," significantly reduces the time and complexity involved in producing content for various distribution channels and display technologies.
Dolby Vision's integration extends to color grading suites, where professional colorists can leverage the technology's expanded color palette and luminance range to achieve more nuanced and impactful visual storytelling. The ability to work in extended color spaces like BT.2020 allows for more accurate color representation and grading decisions.
Furthermore, Dolby Vision workflow integration includes quality control and mastering tools that ensure content meets technical specifications and creative intent across different viewing devices. These tools allow for real-time previewing of how content will appear on various displays, from high-end professional monitors to consumer televisions and mobile devices.
The adoption of Dolby Vision in professional editing tools also facilitates collaboration between different stages of post-production. For instance, visual effects artists can work with HDR assets and seamlessly integrate their work into the main edit, maintaining the full dynamic range throughout the process.
As the demand for HDR content continues to grow, the integration of Dolby Vision into professional video editing tools is becoming increasingly important. It not only enhances the creative possibilities for content creators but also streamlines the production of high-quality HDR content, positioning it as a valuable asset in the competitive landscape of modern video production.
Color Grading Impact
Dolby Vision's integration into professional video editing tools has revolutionized color grading processes, offering unprecedented control and precision in manipulating visual aesthetics. This advanced HDR technology enables editors to work with a wider color gamut and higher dynamic range, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike images.
The impact of Dolby Vision on color grading is multifaceted. Firstly, it allows for more accurate representation of the director's creative vision. The expanded color palette and increased brightness levels provide editors with the tools to fine-tune every nuance of the image, ensuring that the final product closely aligns with the intended artistic direction.
Furthermore, Dolby Vision's implementation in editing suites has streamlined the color grading workflow. The technology's ability to simultaneously generate HDR and SDR versions of content reduces the time and effort required for multiple color passes. This efficiency gain is particularly valuable in today's fast-paced production environments, where tight deadlines are commonplace.
The technology also enhances consistency across different display devices. Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata ensures that the color-graded content maintains its intended look across various screens, from professional monitors to consumer televisions. This feature is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the creative vision throughout the distribution chain.
Additionally, Dolby Vision has raised the bar for color accuracy in post-production. Its support for 12-bit color depth allows for smoother gradients and more precise color adjustments, minimizing banding and other artifacts that can detract from the viewing experience. This level of detail is particularly beneficial in scenes with subtle color variations or challenging lighting conditions.
The technology's impact extends beyond traditional film and television production. It has found applications in emerging media formats such as virtual reality and augmented reality, where accurate color representation is vital for creating immersive experiences. As these technologies continue to evolve, Dolby Vision's role in color grading is likely to become even more significant.
However, the adoption of Dolby Vision in professional editing tools also presents challenges. It requires specialized hardware and software, which can be a significant investment for smaller production houses. Additionally, there is a learning curve associated with mastering the nuances of HDR color grading, necessitating ongoing training and skill development for colorists and editors.
The impact of Dolby Vision on color grading is multifaceted. Firstly, it allows for more accurate representation of the director's creative vision. The expanded color palette and increased brightness levels provide editors with the tools to fine-tune every nuance of the image, ensuring that the final product closely aligns with the intended artistic direction.
Furthermore, Dolby Vision's implementation in editing suites has streamlined the color grading workflow. The technology's ability to simultaneously generate HDR and SDR versions of content reduces the time and effort required for multiple color passes. This efficiency gain is particularly valuable in today's fast-paced production environments, where tight deadlines are commonplace.
The technology also enhances consistency across different display devices. Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata ensures that the color-graded content maintains its intended look across various screens, from professional monitors to consumer televisions. This feature is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the creative vision throughout the distribution chain.
Additionally, Dolby Vision has raised the bar for color accuracy in post-production. Its support for 12-bit color depth allows for smoother gradients and more precise color adjustments, minimizing banding and other artifacts that can detract from the viewing experience. This level of detail is particularly beneficial in scenes with subtle color variations or challenging lighting conditions.
The technology's impact extends beyond traditional film and television production. It has found applications in emerging media formats such as virtual reality and augmented reality, where accurate color representation is vital for creating immersive experiences. As these technologies continue to evolve, Dolby Vision's role in color grading is likely to become even more significant.
However, the adoption of Dolby Vision in professional editing tools also presents challenges. It requires specialized hardware and software, which can be a significant investment for smaller production houses. Additionally, there is a learning curve associated with mastering the nuances of HDR color grading, necessitating ongoing training and skill development for colorists and editors.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!