Exploring Dolby Vision Technology for Enhanced Visual Storytelling
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dolby Vision Evolution and Objectives
Dolby Vision, a cutting-edge HDR technology, has revolutionized visual storytelling since its inception in 2014. This advanced imaging format has evolved significantly, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in content creation and display technologies. The journey of Dolby Vision began with the aim to deliver a more immersive and lifelike viewing experience by enhancing contrast, color accuracy, and brightness in video content.
Initially, Dolby Vision focused on improving the dynamic range of displays, allowing for deeper blacks and brighter highlights. As the technology progressed, it expanded its capabilities to include wider color gamuts, enabling content creators to capture and display a broader spectrum of colors. This evolution has been driven by the increasing demand for more realistic and visually stunning content across various platforms, from cinema screens to home entertainment systems and mobile devices.
The objectives of Dolby Vision have consistently centered around enhancing the viewer's experience and providing content creators with powerful tools to realize their artistic vision. One key goal has been to maintain the creator's intent across different display devices, ensuring that the visual story remains consistent regardless of the viewing platform. This has led to the development of dynamic metadata, which allows for scene-by-scene and even frame-by-frame optimization of content.
Another significant objective has been to improve the efficiency of content distribution. Dolby Vision has worked towards developing compression techniques that allow for high-quality HDR content to be delivered without significantly increasing bandwidth requirements. This has been crucial in making HDR content more accessible to a wider audience through streaming services and broadcast channels.
As the technology has matured, Dolby Vision has also aimed to expand its ecosystem. This includes partnering with content creators, device manufacturers, and streaming platforms to ensure widespread adoption and compatibility. The goal has been to create a seamless end-to-end solution that covers everything from content creation to distribution and playback.
Looking towards the future, Dolby Vision continues to evolve with objectives that align with emerging trends in visual technology. These include supporting higher frame rates, increased resolution, and even more expansive color spaces. There's also a focus on integrating Dolby Vision with other technologies like 3D and virtual reality to create more immersive storytelling experiences.
In conclusion, the evolution of Dolby Vision has been marked by continuous innovation and a clear vision to enhance visual storytelling. Its objectives have consistently centered on pushing the boundaries of what's possible in image quality while ensuring practicality and accessibility for both creators and consumers. As the technology continues to advance, it promises to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of visual media.
Initially, Dolby Vision focused on improving the dynamic range of displays, allowing for deeper blacks and brighter highlights. As the technology progressed, it expanded its capabilities to include wider color gamuts, enabling content creators to capture and display a broader spectrum of colors. This evolution has been driven by the increasing demand for more realistic and visually stunning content across various platforms, from cinema screens to home entertainment systems and mobile devices.
The objectives of Dolby Vision have consistently centered around enhancing the viewer's experience and providing content creators with powerful tools to realize their artistic vision. One key goal has been to maintain the creator's intent across different display devices, ensuring that the visual story remains consistent regardless of the viewing platform. This has led to the development of dynamic metadata, which allows for scene-by-scene and even frame-by-frame optimization of content.
Another significant objective has been to improve the efficiency of content distribution. Dolby Vision has worked towards developing compression techniques that allow for high-quality HDR content to be delivered without significantly increasing bandwidth requirements. This has been crucial in making HDR content more accessible to a wider audience through streaming services and broadcast channels.
As the technology has matured, Dolby Vision has also aimed to expand its ecosystem. This includes partnering with content creators, device manufacturers, and streaming platforms to ensure widespread adoption and compatibility. The goal has been to create a seamless end-to-end solution that covers everything from content creation to distribution and playback.
Looking towards the future, Dolby Vision continues to evolve with objectives that align with emerging trends in visual technology. These include supporting higher frame rates, increased resolution, and even more expansive color spaces. There's also a focus on integrating Dolby Vision with other technologies like 3D and virtual reality to create more immersive storytelling experiences.
In conclusion, the evolution of Dolby Vision has been marked by continuous innovation and a clear vision to enhance visual storytelling. Its objectives have consistently centered on pushing the boundaries of what's possible in image quality while ensuring practicality and accessibility for both creators and consumers. As the technology continues to advance, it promises to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of visual media.
Market Demand for HDR Content
The demand for High Dynamic Range (HDR) content has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by advancements in display technology and a growing consumer appetite for more immersive visual experiences. As viewers become accustomed to higher quality visuals across various platforms, from cinema screens to mobile devices, the market for HDR content has expanded significantly.
In the entertainment industry, major streaming platforms have recognized the value of HDR content in attracting and retaining subscribers. Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ have all invested heavily in producing and delivering HDR content, including Dolby Vision-enabled titles. This trend is expected to continue as these platforms compete for market share and seek to differentiate their offerings.
The film and television production sector has also seen a surge in demand for HDR-capable equipment and post-production services. Cinematographers and directors are increasingly utilizing HDR technology to enhance storytelling through more vibrant and lifelike visuals. This has led to a ripple effect in the industry, with camera manufacturers, editing software developers, and visual effects companies adapting their products and services to support HDR workflows.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have responded to this market demand by introducing a wide range of HDR-compatible devices. Television sets, monitors, and mobile devices with HDR capabilities have become more prevalent and affordable, further driving consumer interest in HDR content. The adoption of HDR technology in gaming consoles has also contributed to the growing demand, as gamers seek more realistic and visually stunning experiences.
The advertising industry has begun to leverage HDR technology to create more impactful and engaging commercials. Brands are recognizing the potential of HDR to make their products stand out in a crowded media landscape, leading to increased demand for HDR-capable production and distribution channels.
As the market for HDR content expands, there is a growing need for standardization and interoperability across different HDR formats and devices. This has led to industry collaborations and the development of new standards to ensure consistent quality and compatibility across various platforms and devices.
The education and training sector has also seen an uptick in demand for HDR-related courses and workshops, as professionals in the media and entertainment industry seek to upskill and adapt to this evolving technology landscape. This trend is likely to continue as HDR becomes more prevalent across various content creation and distribution channels.
In the entertainment industry, major streaming platforms have recognized the value of HDR content in attracting and retaining subscribers. Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ have all invested heavily in producing and delivering HDR content, including Dolby Vision-enabled titles. This trend is expected to continue as these platforms compete for market share and seek to differentiate their offerings.
The film and television production sector has also seen a surge in demand for HDR-capable equipment and post-production services. Cinematographers and directors are increasingly utilizing HDR technology to enhance storytelling through more vibrant and lifelike visuals. This has led to a ripple effect in the industry, with camera manufacturers, editing software developers, and visual effects companies adapting their products and services to support HDR workflows.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have responded to this market demand by introducing a wide range of HDR-compatible devices. Television sets, monitors, and mobile devices with HDR capabilities have become more prevalent and affordable, further driving consumer interest in HDR content. The adoption of HDR technology in gaming consoles has also contributed to the growing demand, as gamers seek more realistic and visually stunning experiences.
The advertising industry has begun to leverage HDR technology to create more impactful and engaging commercials. Brands are recognizing the potential of HDR to make their products stand out in a crowded media landscape, leading to increased demand for HDR-capable production and distribution channels.
As the market for HDR content expands, there is a growing need for standardization and interoperability across different HDR formats and devices. This has led to industry collaborations and the development of new standards to ensure consistent quality and compatibility across various platforms and devices.
The education and training sector has also seen an uptick in demand for HDR-related courses and workshops, as professionals in the media and entertainment industry seek to upskill and adapt to this evolving technology landscape. This trend is likely to continue as HDR becomes more prevalent across various content creation and distribution channels.
Current Challenges in HDR Implementation
Despite the significant advancements in High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology, several challenges persist in its widespread implementation. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardization across different HDR formats and devices. This fragmentation leads to inconsistent viewing experiences and complicates content creation and distribution processes.
Hardware limitations also pose a significant challenge. Many consumer displays struggle to achieve the peak brightness levels required for optimal HDR performance, particularly in budget-friendly models. This limitation can result in compromised image quality and reduced impact of HDR content. Additionally, the increased power consumption associated with higher brightness levels presents challenges for mobile devices and energy-efficient designs.
Content creation for HDR remains a complex and resource-intensive process. Filmmakers and content producers face difficulties in accurately monitoring and grading HDR content during production, as many professional monitors and workflows are still optimized for Standard Dynamic Range (SDR). This can lead to discrepancies between the creator's intent and the final viewer experience.
The storage and transmission of HDR content present another set of challenges. HDR files are typically larger than their SDR counterparts, requiring more bandwidth for streaming and increased storage capacity. This can strain existing infrastructure and potentially limit accessibility for users with slower internet connections or limited storage devices.
Backward compatibility with SDR displays and content remains a concern. Ensuring that HDR content degrades gracefully on SDR displays while maintaining the intended artistic vision is a delicate balancing act. Conversely, upscaling SDR content to HDR can sometimes produce suboptimal results, potentially diminishing the perceived value of HDR technology.
The complexity of HDR metadata management adds another layer of difficulty. Ensuring that displays correctly interpret and apply HDR metadata throughout the content delivery chain is crucial for maintaining image quality and artistic intent. However, inconsistencies in metadata handling across different devices and platforms can lead to variations in the final viewing experience.
Lastly, consumer education and awareness present ongoing challenges. Many viewers are unfamiliar with the benefits of HDR or how to optimize their viewing setups to take full advantage of the technology. This lack of understanding can lead to underwhelming experiences and slower adoption rates, potentially hindering the growth of the HDR ecosystem.
Hardware limitations also pose a significant challenge. Many consumer displays struggle to achieve the peak brightness levels required for optimal HDR performance, particularly in budget-friendly models. This limitation can result in compromised image quality and reduced impact of HDR content. Additionally, the increased power consumption associated with higher brightness levels presents challenges for mobile devices and energy-efficient designs.
Content creation for HDR remains a complex and resource-intensive process. Filmmakers and content producers face difficulties in accurately monitoring and grading HDR content during production, as many professional monitors and workflows are still optimized for Standard Dynamic Range (SDR). This can lead to discrepancies between the creator's intent and the final viewer experience.
The storage and transmission of HDR content present another set of challenges. HDR files are typically larger than their SDR counterparts, requiring more bandwidth for streaming and increased storage capacity. This can strain existing infrastructure and potentially limit accessibility for users with slower internet connections or limited storage devices.
Backward compatibility with SDR displays and content remains a concern. Ensuring that HDR content degrades gracefully on SDR displays while maintaining the intended artistic vision is a delicate balancing act. Conversely, upscaling SDR content to HDR can sometimes produce suboptimal results, potentially diminishing the perceived value of HDR technology.
The complexity of HDR metadata management adds another layer of difficulty. Ensuring that displays correctly interpret and apply HDR metadata throughout the content delivery chain is crucial for maintaining image quality and artistic intent. However, inconsistencies in metadata handling across different devices and platforms can lead to variations in the final viewing experience.
Lastly, consumer education and awareness present ongoing challenges. Many viewers are unfamiliar with the benefits of HDR or how to optimize their viewing setups to take full advantage of the technology. This lack of understanding can lead to underwhelming experiences and slower adoption rates, potentially hindering the growth of the HDR ecosystem.
Dolby Vision Technical Specifications
01 Enhanced visual storytelling through HDR technology
Dolby Vision technology utilizes High Dynamic Range (HDR) to enhance visual storytelling by providing a wider range of colors, brighter highlights, and deeper blacks. This results in more lifelike and immersive images, allowing filmmakers to convey their artistic vision more accurately and create a more engaging viewing experience for the audience.- Enhanced visual storytelling through HDR technology: Dolby Vision technology enhances visual storytelling by utilizing High Dynamic Range (HDR) to provide a wider range of colors, brighter highlights, and deeper blacks. This results in more lifelike and immersive images, allowing filmmakers to convey their artistic vision more accurately and create a more engaging viewing experience for the audience.
- Adaptive content optimization: Dolby Vision incorporates adaptive content optimization techniques that analyze and adjust the visual content in real-time. This ensures that the image quality is optimized for different display capabilities and viewing environments, maintaining the creator's intent across various devices and lighting conditions.
- Integration with audio technologies: Dolby Vision technology is often integrated with advanced audio technologies to create a comprehensive audiovisual experience. This synergy between visual and audio elements enhances the overall storytelling impact, allowing for more immersive and emotionally engaging content creation and consumption.
- Content creation and post-production tools: Dolby Vision provides a suite of content creation and post-production tools that enable filmmakers and content creators to take full advantage of the technology's capabilities. These tools allow for precise color grading, dynamic range adjustment, and scene-by-scene optimization, empowering creators to achieve their desired visual storytelling goals.
- Display device optimization: Dolby Vision technology includes features for optimizing content display on various devices, from high-end cinema screens to consumer televisions and mobile devices. This ensures that the visual storytelling remains consistent and impactful across different viewing platforms, preserving the creator's intent regardless of the display technology used.
02 Dynamic metadata for scene-by-scene optimization
Dolby Vision incorporates dynamic metadata that allows for scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame optimization of the content. This enables the technology to adjust brightness, contrast, and color settings in real-time, ensuring that each scene is displayed with optimal visual quality and preserving the filmmaker's intent throughout the entire viewing experience.Expand Specific Solutions03 Content creation and post-production tools
Dolby Vision provides a suite of content creation and post-production tools that enable filmmakers, colorists, and editors to craft and fine-tune their visual stories. These tools allow for precise color grading, HDR mastering, and the creation of dynamic metadata, ensuring that the final product maintains its intended look across various display devices and viewing environments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Display device optimization and calibration
The technology includes features for optimizing and calibrating display devices to ensure accurate reproduction of Dolby Vision content. This involves adjusting various parameters such as color gamut, peak brightness, and contrast ratio to match the capabilities of each specific display, resulting in a consistent and high-quality viewing experience across different devices and platforms.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration with audio technologies for immersive storytelling
Dolby Vision technology can be integrated with advanced audio technologies like Dolby Atmos to create a more comprehensive and immersive storytelling experience. This combination of cutting-edge visual and audio technologies allows content creators to craft multi-sensory narratives that engage viewers on multiple levels, enhancing the overall impact of their visual stories.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Dolby Vision Ecosystem
The Dolby Vision technology landscape is characterized by intense competition among major players in the advanced visual storytelling sector. The market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand for high-quality visual experiences across various platforms. Key competitors include established tech giants like Apple, Google, and Microsoft, alongside specialized companies such as Magic Leap and Flawless Holdings. The technology's maturity is advancing rapidly, with companies like Sony Interactive Entertainment and Toshiba Digital Solutions contributing to its evolution. As the market expands, we're seeing a convergence of AI, AR/VR, and traditional visual technologies, driving innovation in areas like content creation, display technologies, and immersive experiences.
Google LLC
Technical Solution: Google has developed its own HDR technology called HDR+ and has also incorporated support for Dolby Vision in its Android operating system. The company's approach focuses on computational photography and machine learning to enhance image quality. Google's HDR+ technology uses burst photography and advanced algorithms to capture and process multiple exposures, resulting in improved dynamic range and detail[6]. While not directly competing with Dolby Vision, Google's technology aims to provide high-quality HDR experiences across a wide range of Android devices. Additionally, Google has worked on improving HDR video playback on YouTube, supporting various HDR formats including Dolby Vision[7].
Strengths: Wide device compatibility through Android, advanced computational photography techniques. Weaknesses: Less standardized approach compared to Dolby Vision, potential fragmentation across Android devices.
Apple, Inc.
Technical Solution: Apple has integrated Dolby Vision technology into its ecosystem, supporting it across various devices including iPhones, iPads, and Apple TV. The company has developed its own image signal processor (ISP) and Neural Engine to optimize Dolby Vision content capture and playback. Apple's implementation allows for real-time Dolby Vision HDR video recording on compatible devices, utilizing computational photography techniques to enhance dynamic range and color accuracy[4]. The company has also introduced ProRes with Dolby Vision support, enabling high-quality video capture and editing for professionals[5]. Apple's ecosystem approach ensures seamless integration of Dolby Vision across content creation, distribution, and consumption.
Strengths: Seamless ecosystem integration, real-time HDR video capture capabilities, and professional-grade tools. Weaknesses: Limited to Apple ecosystem, potentially higher costs for consumers.
Core Innovations in Dolby Vision
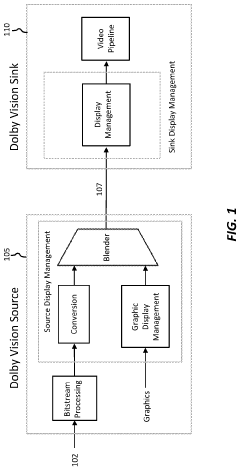
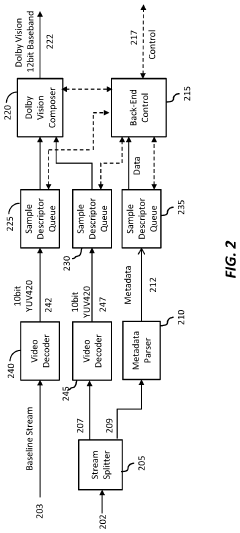
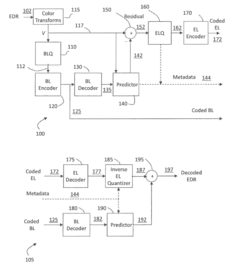
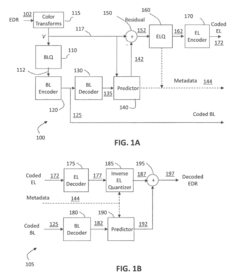
Layered representation and delivery of high dynamic range video
PatentActiveUS20190373290A1
Innovation
- The implementation of a layered representation and delivery system for HDR video, utilizing Dolby Vision technology, which includes a base layer and enhancement layer, along with metadata processing to reconstruct HDR signals, ensuring seamless playback on compatible displays.
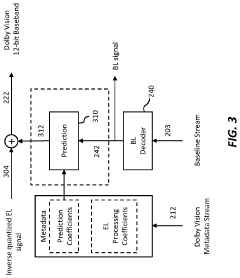
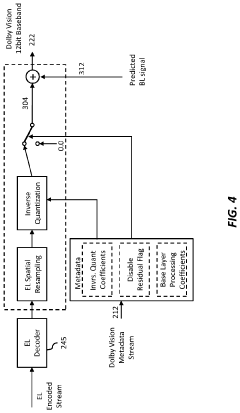
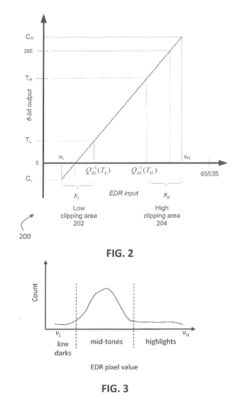
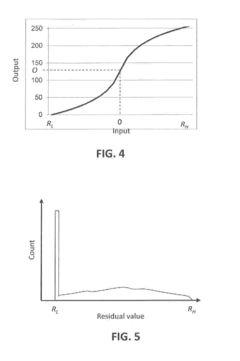
Layered Decomposition of Chroma Components in EDR Video Coding
PatentActiveUS20160065975A1
Innovation
- A dual-layer EDR video encoder employs joint adaptation of base layer and enhancement layer quantizers, optimizing parameter selection to minimize distortion and bit requirements, allowing for efficient coding and decoding of EDR video streams that can be rendered on both legacy and HDR displays.
Content Creation Workflow for Dolby Vision
The content creation workflow for Dolby Vision is a comprehensive process that enables filmmakers and content creators to capture, process, and deliver high dynamic range (HDR) content with enhanced visual quality. This workflow encompasses several key stages, each designed to maximize the potential of Dolby Vision technology.
The process begins with the capture of high-quality source material. Cinematographers and camera operators use HDR-capable cameras to record footage with an expanded dynamic range, capturing more detail in both highlights and shadows. This raw footage serves as the foundation for the Dolby Vision workflow, providing a rich palette of visual information for post-production.
Once captured, the footage enters the color grading stage. Here, colorists work with specialized software and hardware to manipulate the image, adjusting color, contrast, and brightness to achieve the desired look. Dolby Vision's unique approach allows for the creation of a single master that can be used to generate both HDR and standard dynamic range (SDR) versions of the content, streamlining the post-production process.
The next crucial step is metadata creation. Dolby Vision utilizes dynamic metadata to ensure that the content is displayed optimally across various devices and viewing conditions. This metadata contains frame-by-frame instructions for how the content should be displayed, allowing for precise control over the image quality regardless of the playback device's capabilities.
Quality control and verification play a vital role in the workflow. Specialized tools and displays are used to review the Dolby Vision content, ensuring that it meets the required standards and delivers the intended visual experience. This step is critical for maintaining consistency across different viewing environments.
The final stage of the workflow involves encoding and packaging the content for distribution. Dolby Vision content can be delivered through various formats, including streaming services, broadcast, and physical media. The encoding process ensures that the HDR data and associated metadata are properly integrated into the final deliverable.
Throughout the entire workflow, collaboration between different departments is essential. Directors, cinematographers, colorists, and post-production specialists must work in harmony to fully leverage the capabilities of Dolby Vision technology. This collaborative approach ensures that the creative vision is maintained from capture to delivery, resulting in a visually stunning and immersive viewing experience for the audience.
The process begins with the capture of high-quality source material. Cinematographers and camera operators use HDR-capable cameras to record footage with an expanded dynamic range, capturing more detail in both highlights and shadows. This raw footage serves as the foundation for the Dolby Vision workflow, providing a rich palette of visual information for post-production.
Once captured, the footage enters the color grading stage. Here, colorists work with specialized software and hardware to manipulate the image, adjusting color, contrast, and brightness to achieve the desired look. Dolby Vision's unique approach allows for the creation of a single master that can be used to generate both HDR and standard dynamic range (SDR) versions of the content, streamlining the post-production process.
The next crucial step is metadata creation. Dolby Vision utilizes dynamic metadata to ensure that the content is displayed optimally across various devices and viewing conditions. This metadata contains frame-by-frame instructions for how the content should be displayed, allowing for precise control over the image quality regardless of the playback device's capabilities.
Quality control and verification play a vital role in the workflow. Specialized tools and displays are used to review the Dolby Vision content, ensuring that it meets the required standards and delivers the intended visual experience. This step is critical for maintaining consistency across different viewing environments.
The final stage of the workflow involves encoding and packaging the content for distribution. Dolby Vision content can be delivered through various formats, including streaming services, broadcast, and physical media. The encoding process ensures that the HDR data and associated metadata are properly integrated into the final deliverable.
Throughout the entire workflow, collaboration between different departments is essential. Directors, cinematographers, colorists, and post-production specialists must work in harmony to fully leverage the capabilities of Dolby Vision technology. This collaborative approach ensures that the creative vision is maintained from capture to delivery, resulting in a visually stunning and immersive viewing experience for the audience.
Dolby Vision Adoption Barriers
Despite the numerous advantages of Dolby Vision technology in enhancing visual storytelling, several barriers hinder its widespread adoption across the entertainment industry. One significant obstacle is the high implementation cost associated with Dolby Vision. The technology requires specialized hardware and software, which can be prohibitively expensive for smaller production companies and independent filmmakers. This financial barrier limits the accessibility of Dolby Vision to larger studios and high-budget productions, potentially creating a divide in visual quality between big-budget and independent films.
Another challenge is the complexity of the Dolby Vision workflow. The technology demands a specific production and post-production process that may require additional training and expertise. This learning curve can be steep for professionals accustomed to traditional color grading methods, leading to resistance in adoption and increased production time. Furthermore, the need for specialized equipment and software throughout the production pipeline can disrupt established workflows, causing reluctance among some industry professionals to embrace the technology fully.
Compatibility issues also pose a significant barrier to Dolby Vision adoption. Not all display devices support Dolby Vision, which limits the potential audience reach for content created using this technology. This fragmentation in the consumer market can discourage content creators from investing in Dolby Vision, as they may fear that their work will not be fully appreciated by a broad audience. Additionally, the lack of standardization across different platforms and devices can lead to inconsistent viewing experiences, undermining the technology's primary goal of delivering superior visual quality.
The licensing model for Dolby Vision presents another hurdle for widespread adoption. Content creators and device manufacturers must navigate complex licensing agreements and pay royalties to implement Dolby Vision. This additional cost and administrative burden can deter some companies from incorporating the technology into their products or content creation processes. The proprietary nature of Dolby Vision also raises concerns about long-term sustainability and industry-wide acceptance, as some stakeholders may prefer open standards or alternative HDR technologies.
Lastly, the perception of Dolby Vision as a premium feature rather than a standard requirement can limit its adoption in certain market segments. While high-end consumers and cinephiles may appreciate the enhanced visual experience, the average viewer may not perceive sufficient value to justify the additional cost or effort required to access Dolby Vision content. This perception challenge requires significant marketing efforts and consumer education to demonstrate the tangible benefits of Dolby Vision technology in storytelling and visual immersion.
Another challenge is the complexity of the Dolby Vision workflow. The technology demands a specific production and post-production process that may require additional training and expertise. This learning curve can be steep for professionals accustomed to traditional color grading methods, leading to resistance in adoption and increased production time. Furthermore, the need for specialized equipment and software throughout the production pipeline can disrupt established workflows, causing reluctance among some industry professionals to embrace the technology fully.
Compatibility issues also pose a significant barrier to Dolby Vision adoption. Not all display devices support Dolby Vision, which limits the potential audience reach for content created using this technology. This fragmentation in the consumer market can discourage content creators from investing in Dolby Vision, as they may fear that their work will not be fully appreciated by a broad audience. Additionally, the lack of standardization across different platforms and devices can lead to inconsistent viewing experiences, undermining the technology's primary goal of delivering superior visual quality.
The licensing model for Dolby Vision presents another hurdle for widespread adoption. Content creators and device manufacturers must navigate complex licensing agreements and pay royalties to implement Dolby Vision. This additional cost and administrative burden can deter some companies from incorporating the technology into their products or content creation processes. The proprietary nature of Dolby Vision also raises concerns about long-term sustainability and industry-wide acceptance, as some stakeholders may prefer open standards or alternative HDR technologies.
Lastly, the perception of Dolby Vision as a premium feature rather than a standard requirement can limit its adoption in certain market segments. While high-end consumers and cinephiles may appreciate the enhanced visual experience, the average viewer may not perceive sufficient value to justify the additional cost or effort required to access Dolby Vision content. This perception challenge requires significant marketing efforts and consumer education to demonstrate the tangible benefits of Dolby Vision technology in storytelling and visual immersion.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!